二、numpy模塊及Pandas模型使用
numpy模塊
1.ndarray的創建
import numpy as np
a=np.array([1,2,3,4])
b=np.array([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]])
print(a) #[1 2 3 4]
print(b) #[[1 2 3 4][5 6 7 8]]1.1使用array()函數創建
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
| 名稱 | 描述 |
| object | 數組或嵌套的數列 |
| dtype | 數組元素的數據類型,可選 |
| copy | 對象是否需要復制,可選 |
| order | 創建數組的樣式,C為行方向,F為列方向,A為任意方向(默認) |
| subok | 默認返回一個與基類類型一致的數組 |
| ndmin | 指定生成數組的最小維度 |
1.2使用arange()函數
根據 start 與 stop 指定的范圍以及 step 設定的步長,生成一個 ndarray。
numpy.arange(start, stop, step, dtype)
1.3使用linespace()函數
用于創建一個一維數組,一個等差數列構成的
根據 start 與 stop 指定的范圍以及 step 設定的步長,生成一個 ndarray。
和range類似
注意:np.linspace形成的數組一定包括范圍的首位兩個元素,則步長為(end - start) / (length - 1)。而np.arange是自己指定的步長(默認為1)也就意味著形成的數組不一定包括末尾數
np.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None)
參數說明:
start: 開始值
stop: 結束值
num=50: 等差數列中默認有50個數
endpoint=True: 是否包含結束值
retstep=False: 是否返回等差值(步長)
dtype=None: 元素類型
1.4使用logspace()函數
用于創建一個一維數組,一個等比數列構成的,等間隔的一維數組
數據為對數函數log的值
參數說明:
start: 開始值
stop: 結束值
num=50: 數列中默認有50個數
endpoint=True: 是否包含結束值
base: log函數的底數,默認為10
dtype=None: 元素類型
1.5使用empty()函數創建
作用創建一個指定形狀的未初始化的數組,由于未初始化,所以輸出是隨機值
numpy.empty(shape, dtype = none, order = 'C')
1.6使用zeros(),ones(),full(),eye()函數
三個函數類似于empty(),創建指定形狀的數組,
不過zeros是以0來初始化,ones是以1來初始化,其中的1和0 默認為浮點數,
full函數()可以以自己指定的值來填充,所以會多一個參數fill_value原型,
np.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=float):對角線為1其他的位置為0的二維數組,
其中N:行數,M:列數,k=0:向右偏移0個位置
numpy.zeros(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C’)
numpy.ones(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C’)
numpy.full(shape, fill_value,dtype = float, order = 'C’)
numpy.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=float)
1.7生成隨機數:使用random.random(),random.randint(),random.rand(),random.randn(),random.choice()函數
random([size]):生成size個[0.0,1.0)的隨機數
randint(low,[high,size,dtype]):生成指定范圍的任意維度的隨機整數,數組元素的范圍[low, high)區間
rand(d0,d1,…,dn):[0,1)之間隨機數,具有均勻分布
randn(d0,d1,…,dn):返回具有標準正態分布(均值為0,方差為1)Choice(a,size=None,replace=True):從指定的一維數組中生成隨機數
1.8使用asarray()函數
從已有的數組創建數組
a1=np.zeros([3,2])
a2=np.asarray(a1)
print(a1)
print(a2)
tup=(1,2,3,4)
a3=np.asarray(tup)
print(a3)
x=((1,2,3),(4,5,6),(7,8,9))
a=np.asarray(x)
print(a)
'''
[[0. 0.][0. 0.][0. 0.]]
[[0. 0.][0. 0.][0. 0.]]
[1 2 3 4]
[[1 2 3][4 5 6][7 8 9]]
'''1.9使用frombuffer()函數
實現動態數組
numpy.frombuffer 接受 buffer 輸入參數,以流的形式讀入轉化成 ndarray 對象。
Pandas模塊
1.DataFrame對象創建
二維帶行標簽和列標簽的數組
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=index, columns=columns)
其中 index是行標簽, columns是列標簽,data可以是下面的數據
由一維 numpy數組,list, Series構成的字典
二維 numpy數組
一個 Series
另外的 DataFrame對象
| 屬性名 | 含義 |
| len(x) | 表示對象值的長度。 |
| size | 表示對象值的長度。 |
| index | 表示列索引數。 |
| columns | 表示行索引數。 |
| dtypes | 表示列的數據類型。 |
| shape | 表示有多少行列. |
| values | 表示對象值,即二維數組。 |
| info | 表示對象的基本信息:索引情況、各列的名稱、數據數量、數據類型等。 |
| head(num) | 從頭部開始顯示幾行,參數um表示顯示的行數,默認為5行。 |
| tail(num) | 從末尾開始顯示幾行,參數num表示顯示的行數,默認為5行。 |
數據選取
DataFrame.loc[行索引名稱或條件,列索引名稱] 【基于索引名稱】
DataFrame.iloc[行索引位置, 列索引位置] 【完全基于位置】(只接收int)
2.分組統計函數——groupby函數
DataFrame.groupby(by=None, axis=0, level=None, as_index=True, sort=True, group_keys=True, squeeze=False, **kwargs)
功能: 根據給定的條件將數據拆分成組
????????每個組否可以獨立應用函數(sum,mean,min)
????????將結果合并到一個數據結構中
3.面向列的聚合函數——agg函數
DataFrame.agg(func=None, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)
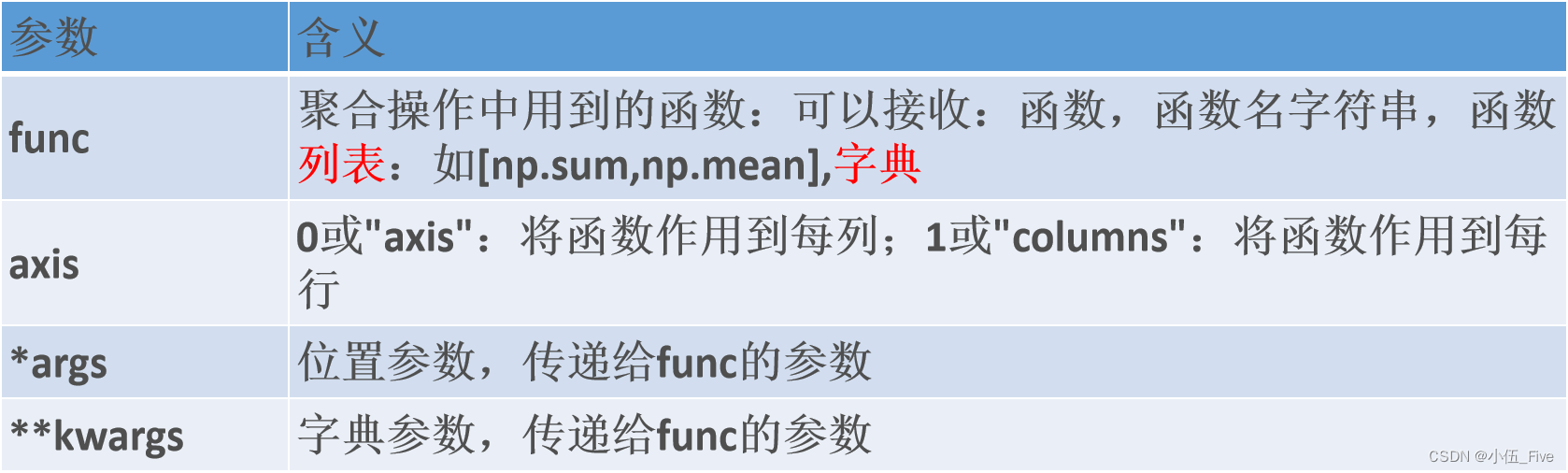
1.簡單的列或行統計
默認對列統計(axis=0)
2.對每一個列數據應用同一個函數————func參數傳入一個函數
3.對某列數據應用不同函數————func參數傳入多個函數
元組(name,function):自定義name替換function名
4.對不同列數據應用不同函數————func參數傳入字典{‘列名’:’函數名’}
4.transform() 函數:用于保持原始 DataFrame 結構的元素級轉換
總是返回一個與原始 DataFrame 或 Series 相同形狀的 DataFrame 或 Series。
即使只對一列或一行應用函數,transform() 也會返回一個完整的 DataFrame 或 Series。
DataFrame.transform(func=None, *args, **kwargs)
返回結果有兩種:1.可以廣播的標量值(np.mean) ?2.可以是與分組大小相同結果的數組。
df=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(36).reshape(6,6),columns=list('abcdef'))
df['key']=pd.Series(list('aaabbb'),name='key')
print(df)
group1=df.groupby(['key']).agg('mean')
print(group1)
group2=df.groupby(['key']).transform('mean')
print(group2)
'''a b c d e f key
0 0 1 2 3 4 5 a
1 6 7 8 9 10 11 a
2 12 13 14 15 16 17 a
3 18 19 20 21 22 23 b
4 24 25 26 27 28 29 b
5 30 31 32 33 34 35 ba b c d e f
key
a 3 4 5 6 7 8
b 24 25 26 27 28 29a b c d e f
0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0
1 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0
2 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0
3 24.0 25.0 26.0 27.0 28.0 29.0
4 24.0 25.0 26.0 27.0 28.0 29.0
5 24.0 25.0 26.0 27.0 28.0 29.0
'''5.apply() 函數:最通用的函數
DataFrame.apply(func=None, axis=0,raw=False,result_type=None,*args, **kwds)
func:要應用的函數。它可以是一個 Python 函數,也可以是一個字符串(例如 'sum'、'mean' 等)。
axis:應用函數的軸。如果 axis=0(默認值),則函數將沿著列方向應用;如果 axis=1,則函數將沿著行方向應用。
raw:是否將底層數據傳遞給函數。如果 raw=True,則傳遞底層 NumPy 數組;否則傳遞 Series 對象。
result_type:結果類型。可以是 'expand'、'reduce' 或 'broadcast'。
args:要傳遞給函數的額外參數。 *kwds:要傳遞給函數的額外關鍵字參數。
data={'A':[1,2,3],'B':[4,5,6],'C':[7,8,9]
}
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
result=df.apply(lambda x:x.mean())
result1=df.apply('mean')
print(result,result1,sep='\n')
result=df.apply(lambda x:x+1)
print(result)
'''
A 2.0
B 5.0
C 8.0
dtype: float64
A 2.0
B 5.0
C 8.0
dtype: float64A B C
0 2 5 8
1 3 6 9
2 4 7 10
'''









)

 表的內連和外連)




:進程與進程間通信設計之趣味貓咪抓老鼠游戲)

