一、背景
在當今的軟件開發中,服務接口通常需要對應多個實現類,以滿足不同的需求和場景。舉例來說,假設我們是一家2B公司,公司的產品具備對象存儲服務的能力。然而,在不同的合作機構部署時,發現每家公司底層的對象存儲服務都不相同,比如機構A使用阿里云,機構B使用AWS S3等。針對這種情況,公司應用底層需要支持多種云存儲平臺,如阿里云、AWS S3等。
又由于每種云存儲平臺都擁有獨特的API和特性,因此在設計軟件時必須考慮到系統的可擴展性。通常情況下,我們會編寫一個對外開放的openAPI接口,而應用底層需要根據不同的需求選擇合適的實現類。
在這種情況下,如何避免硬編碼并以一種優雅的方式實現上述需求成為了本篇博客要討論的問題。
以下示例均可在 gitHub#inject-condition 倉庫上找到。
二、解決方案
由于應用需要對外提供服務,我們以業內常見的Spring Boot服務應用為前提進行討論。
在這種情況下,常見的解決方案可分為兩類:SPI 和 Spring條件注解。
- SPI(Service Provider Interface):
- SPI 是一種標準的Java擴展機制,允許第三方實現提供服務的接口,并由應用程序在運行時動態加載。
- 在Spring Boot應用中,我們可以定義一個服務接口,然后多個實現類分別實現這個接口。使用SPI機制,我們可以在配置文件中指定想要使用的實現類。
- 優點:靈活性高,支持動態加載和配置。
- 缺點:需要手動管理配置文件,并且在服務實現類數量較多時,容易出現配置混亂的問題。
- Spring條件注解:
- Spring提供了一系列的條件注解,如
@ConditionalOnProperty、@ConditionalOnClass等,用于根據應用程序的配置或環境條件來動態地選擇加載或配置Bean。 - 我們可以使用條件注解來根據應用程序的配置來選擇合適的實現類。比如,可以根據配置文件中的屬性來決定使用哪個實現類。
- 優點:無需手動管理配置文件,能夠根據配置自動選擇合適的實現類。
- 缺點:相比SPI,條件注解的動態加載能力稍遜,使用上稍顯復雜,需要了解和掌握Spring的條件注解機制。
- Spring提供了一系列的條件注解,如
綜上所述,針對Spring Boot服務應用中服務接口對應多個實現類的需求,我們可以選擇SPI或Spring條件注解作為解決方案。
由于SPI已在另一篇博客中有詳細講解,本文將重點講解Spring條件注解。更多關于SPI的內容可參考筆者的另一篇博客:Java SPI解讀:揭秘服務提供接口的設計與應用
三、示例
3.1、場景模擬
- 在應用中新建一個
ObjectStorageService存儲接口,代碼如下:
import java.io.File;public interface ObjectStorageService {/*** 上傳文件到對象存儲* @param file 文件* @param bucketName 存儲桶名稱* @param objectKey 對象鍵(文件名)* @return 文件在對象存儲中的URL*/String uploadObject(File file, String bucketName, String objectKey);/*** 從對象存儲下載文件* @param bucketName 存儲桶名稱* @param objectKey 對象鍵(文件名)* @return 文件*/File downloadObject(String bucketName, String objectKey);
}
- 接下來,我們創建了三個通過
@Service注入的實現類。首先是默認實現類DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl,其次是阿里云存儲服務的實現類AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl,最后是S3存儲服務的實現類S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl。具體的代碼實現:
@Slf4j
@Service
public class DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Overridepublic String uploadObject(File file, String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 默認實現上傳邏輯return "Default implementation: Upload successful";}@Overridepublic File downloadObject(String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 默認實現下載邏輯return new File("default-file.txt");}
}
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Overridepublic String uploadObject(File file, String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 阿里云實現上傳邏輯return "Aliyun implementation: Upload successful";}@Overridepublic File downloadObject(String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 阿里云實現下載邏輯return new File("aliyun-file.txt");}
}
@Slf4j
@Service
public class S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Overridepublic String uploadObject(File file, String bucketName, String objectKey) {// S3實現上傳邏輯return "S3 implementation: Upload successful";}@Overridepublic File downloadObject(String bucketName, String objectKey) {// S3實現下載邏輯return new File("s3-file.txt");}
}
- 最后再創建一個Controller類通過
@Autowired注解注入ObjectStorageService,并對外開放接口,代碼如下:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
- 此時運行應用報錯信息如下:
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************Description:Field objectStorageService in org.example.inject.web.controller.StorageController required a single bean, but 3 were found:- aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl: defined in file [D:\IdeaProjects\inject-examples\inject-condition\target\classes\org\example\inject\web\service\impl\AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl.class]- defaultObjectStorageServiceImpl: defined in file [D:\IdeaProjects\inject-examples\inject-condition\target\classes\org\example\inject\web\service\impl\DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl.class]- s3ObjectStorageServiceImpl: defined in file [D:\IdeaProjects\inject-examples\inject-condition\target\classes\org\example\inject\web\service\impl\S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl.class]Action:Consider marking one of the beans as @Primary, updating the consumer to accept multiple beans, or using @Qualifier to identify the bean that should be consumed
錯誤提示StorageController需要一個objectStorageService bean,但是卻找到了3個可用的bean:aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl、defaultObjectStorageServiceImpl和s3ObjectStorageServiceImpl。spring也提示了解決方案:
- 在其中一個實現類上添加
@Primary注解,指示Spring優先選擇這個bean。 - 修改
StorageController以接受多個objectStorageService,或者使用@Qualifier注解指定要注入的特定bean。
3.2、@Qualifier解決方案
@Autowired是Spring2.5 引入的注解,@Autowired注解只根據類型進行注入,不會根據名稱匹配。當類型無法辨別注入對象時,可以使用@Qualifier或@Primary注解來修飾,修改后代碼如下:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {@Autowired@Qualifier("aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl")private ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
@Qualifier注解中的參數是BeanID,即@Service注解所注入的實現類的名稱。
- 運行應用后一切正常,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:注入成功
objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl@6f2aa58b
- 遺憾的是,
@Qualifier注解并不支持變量賦值,只能通過硬編碼的方式指定具體的實現類。下面是一個錯誤示例:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {@Value("${storage.provider}")private String storageProvider;@Autowired@Qualifier("${storageProvider}")private ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
雖然我們希望通過配置變量的方式來指定具體的實現類,但是由于@Qualifier注解的限制,這種方案并不可行,因此不推薦使用。
3.3、@Resource解決方案
- 在Spring Boot應用中,除了
@Autowired,還可以使用@Resource來進行依賴注入,代碼如下:
import javax.annotation.Resource;@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {// @Autowired@Resourceprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
-
@Resource與@Autowired區別在于:-
@Resource是 JDK 原生的注解,而@Autowired是 Spring 2.5 引入的注解。 -
@Resource注解有兩個屬性:name和type。Spring 將@Resource注解的name屬性解析為 bean 的名稱,而type屬性則解析為 bean 的類型。因此,如果使用name屬性,則采用 byName 的自動注入策略;如果使用type屬性,則采用 byType 的自動注入策略。如果既不指定name也不指定type屬性,則將通過反射機制使用 byName 自動注入策略。 -
@Autowired注解只根據類型進行注入,不會根據名稱匹配。當類型無法辨別注入對象時,可以使用@Qualifier或@Primary注解來修飾。
-
-
所以我們可以通過
@Resource注解指定name屬性從而實現指定實現類注入,代碼如下:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {// @Autowired@Resource(name = "aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl")private ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
- 運行應用后一切正常,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:注入成功
objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl@6f2aa58b
- 遺憾的是,
@Resource注解也不支持變量賦值,只能通過硬編碼的方式指定具體的實現類,因此不推薦使用。
3.4、@Primary解決方案
-
@Primary是一個 Spring 框架中的注解,用于解決多個 Bean 實例同一類型的自動裝配問題。當一個接口或者類有多個實現時,Spring 在自動裝配時可能會出現歧義,不知道選擇哪個 Bean 注入。這時候,可以使用@Primary注解來指定首選的 Bean,這樣在自動裝配時就會選擇這個首選的 Bean。 -
將
DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl設置為首選實現類,代碼如下:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;@Slf4j
@Service
@Primary
public class DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Overridepublic String uploadObject(File file, String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 默認實現上傳邏輯return "Default implementation: Upload successful";}@Overridepublic File downloadObject(String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 默認實現下載邏輯return new File("default-file.txt");}
}
StorageController控制層恢復為最初形態,代碼如下:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class StorageController {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@GetMapping("/example")public void example() {log.info("objectStorageService: {}", objectStorageService);}
}
-
運行應用,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:默認實現類注入成功objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl@633df06 -
遺憾的是,
@Primary注解也是只能通過硬編碼的方式指定具體的實現類,因此不推薦使用。
3.5、@Conditional解決方案[推薦]
-
@Conditional注解是 Spring 框架提供的一種條件化裝配的機制,它可以根據特定的條件來決定是否創建一個 Bean 實例。通過@Conditional注解,可以在 Spring 容器啟動時根據一些條件來動態地確定是否創建某個 Bean,從而實現更靈活的 Bean 裝配。 -
在 Spring 中,有一系列內置的條件注解,例如:
@ConditionalOnClass:當類路徑中存在指定的類時,才創建該 Bean。@ConditionalOnMissingClass:當類路徑中不存在指定的類時,才創建該 Bean。@ConditionalOnBean:當容器中存在指定的 Bean 時,才創建該 Bean。@ConditionalOnMissingBean:當容器中不存在指定的 Bean 時,才創建該 Bean。@ConditionalOnProperty:當指定的配置屬性滿足一定條件時,才創建該 Bean。@ConditionalOnExpression:當指定的 SpEL 表達式為 true 時,才創建該 Bean。
-
我們希望達到的效果是通過
application.properties或application.yml配置文件的一個配置項就可以指定具體實現類,而非通過硬編碼的形式來實現,所以我們將使用@ConditionalOnProperty配置屬性條件注解實現。其余注解可參考:官網介紹 -
先看下
@ConditionalOnProperty注解的幾個入參介紹:@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Documented @Conditional({OnPropertyCondition.class}) public @interface ConditionalOnProperty {/*** 配置文件中 key 的前綴,可與 value 或 name 組合使用。*/String prefix() default "";/*** 與 value 作用相同,但不能與 value 同時使用。*/String[] name() default {};/*** 與 value 或 name 組合使用,只有當 value 或 name 對應的值與 havingValue 的值相同時,注入生效。*/String havingValue() default "";/*** 當該屬性為 true 時,配置文件中缺少對應的 value 或 name 的屬性值,也會注入成功。*/boolean matchIfMissing() default false; } -
接下來定義配置key,在
application.properties或application.yml配置文件新增如下內容:storage.provider=aliyun -
在各個實現類中新增
@ConditionalOnProperty注解,代碼如下:import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;@Slf4j @Service //@Primary @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "default", matchIfMissing = true) public class DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 }@Slf4j @Service @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "aliyun") public class AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 }@Slf4j @Service @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "s3") public class S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 } -
運行應用,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl@3b46e282 -
如果在
application.properties或application.yml配置文件中沒有配置storage.provider屬性,則會注入DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl實現類。這是因為DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl實現類的matchIfMissing = true屬性已經指定了。 -
上述注解的實現方式是配置在每個實現類中,這種方式過于分散。為了讓開發人員更清晰地了解應用的注入關系,我們應該通過
@Configuration整合所有實現類的配置。以下是新增的WebConfiguration配置類的代碼:import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 自動裝配類*/ @Configuration public class WebConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "default", matchIfMissing = true)public ObjectStorageService defaultObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl();}@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "aliyun")public ObjectStorageService aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl();}@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "storage", name = "provider", havingValue = "s3")public ObjectStorageService s3ObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl();} }再將各個實現類中的
@Service,@ConditionalOnProperty注解去掉,更改后代碼如下:import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;@Slf4j public class DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 }@Slf4j public class AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 }@Slf4j public class S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {// 省略 }運行應用,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl@3b46e282 -
通過
@ConditionalOnProperty注解和WebConfiguration統一裝配類,我們基本實現了可配置化注入實現類的方案,初步實現了我們的目標。
3.6、自定義@Conditional解決方案[強烈推薦]
在上面的示例中,我們是通過在配置文件中定義屬性來決定實現類,這需要在配置文件中定義一份屬性,并在各個 @ConditionalOnProperty 注解中配置 prefix 和 name 屬性。以前面的示例為例,就需要進行4次配置。然而,這種方式容易出錯,特別是當服務有多個接口需要配置多個實現類時,需要配置更多的屬性,增加了配置的復雜性和出錯的可能性,如下圖所示:
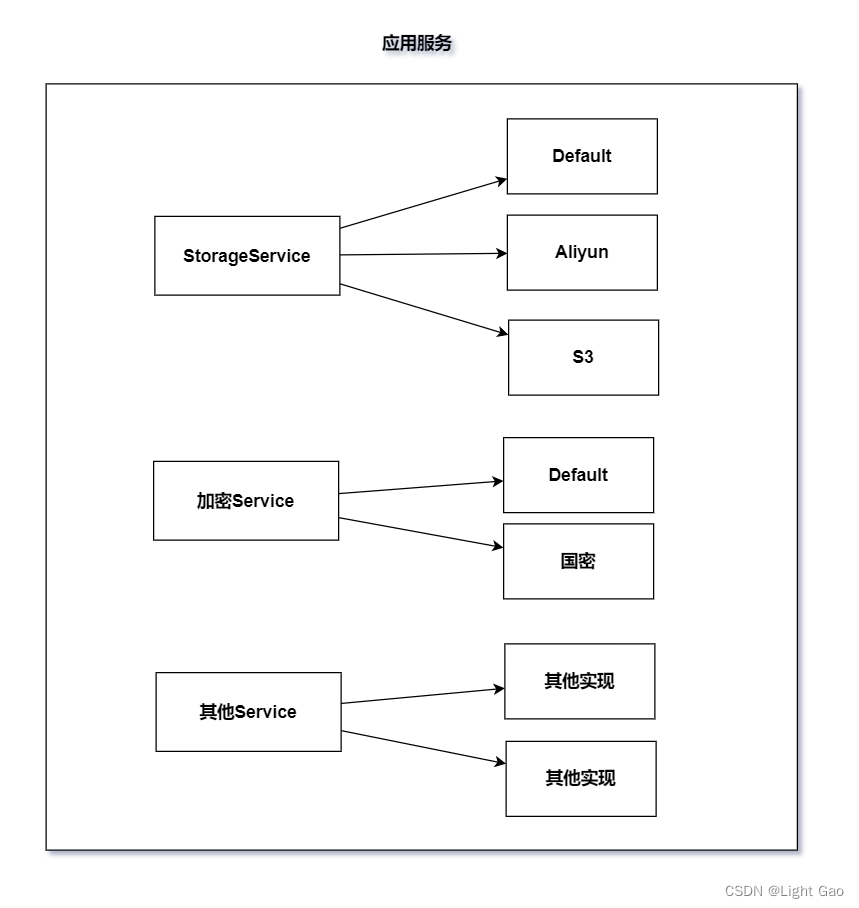
根據上圖中的三個接口,需要配置三個配置項以及7次 @ConditionalOnProperty 注解;因此,我們需要采用一種簡化的方式來減少配置,只需要在配置文件中配置一次即可,而無需更改@ConditionalOnProperty 注解。
-
要滿足上述需求,首先需要重點關注配置文件中的屬性。以上面的對象存儲的情景舉例,一個重要的配置項是
storage.provider=aliyun。為了更通用地解決所有接口的配置需求,建議統一將配置項命名為接口的全限定名。這種做法不僅能夠確保配置項的唯一性,同時也讓人一目了然,清晰明了。以上面對象存儲場景為例,修改后的配置如下所示:org.example.inject.condition.service.ObjectStorageService=aliyun -
其次希望簡化
@ConditionalOnProperty注解的編寫,不再需要指定prefix = "storage", name = "provider"等屬性。而是根據注解所在位置自動分析當前返回值類的全限定名稱,然后直接從配置文件中讀取相應的配置項。示例如下:@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(name = ObjectStorageService.class, matchIfMissing = true) public ObjectStorageService defaultObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl(); }@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(name = ObjectStorageService.class, havingValue = "aliyun") public ObjectStorageService aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl(); }@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(name = ObjectStorageService.class, havingValue = "s3") public ObjectStorageService s3ObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl(); }可以觀察到,除了需要配置
havingValue屬性外,其他配置項無需手動設置,使得配置變得十分簡潔。 -
注意,目前Spring并未提供類似的能力來實現我們需要的條件判斷,因此我們需要自定義條件注解。幸運的是,Spring 提供了條件接口,讓我們可以自行創建自定義的條件類來實現所需的條件判斷邏輯。首先,我們創建一個自定義條件類,它繼承
Condition接口,并編寫自定義的條件判斷邏輯。代碼如下:import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;/*** 自定義的條件判斷類,用于根據指定類名的配置值判斷是否應用某個配置。*/ public class ConditionalOnClassNameCustom implements Condition {/*** 判斷是否滿足條件。** @param context 條件上下文* @param metadata 注解元數據* @return 如果滿足條件,則返回true;否則返回false*/@Overridepublic boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {// 獲取ConditionalOnClassName注解的屬性值Class<?>[] annotationValues = (Class<?>[]) metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnClassName.class.getName()).get("name");String annotationClassName = annotationValues[0].getName(); // 獲取類的全限定名String havingValue = (String) metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnClassName.class.getName()).get("havingValue");boolean matchIfMissing = (boolean) metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnClassName.class.getName()).get("matchIfMissing");// 獲取配置項對應的配置值String propertyValue = context.getEnvironment().getProperty(annotationClassName);// 檢查配置值是否符合預期if (StringUtils.hasText(propertyValue)) {return havingValue.equals(propertyValue);} else {return matchIfMissing;}} } -
借助這個條件判斷邏輯,我們接下來設計一個全新的條件配置注解:
ConditionalOnClassName,它將使用前述的ConditionalOnClassNameCustom實現類。具體代碼如下:import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;import java.lang.annotation.*;/*** 定義一個自定義條件注解,用于根據指定類名的配置值判斷是否應用某個配置。*/ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) // 注解可以應用于類和方法 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解會在運行時保留 @Documented // 注解會被包含在javadoc中 @Conditional(ConditionalOnClassNameCustom.class) // 該注解條件受到 ConditionalOnClassNameCustom 類的限制 public @interface ConditionalOnClassName {Class<?>[] value() default {}; // 作為 value 屬性的別名,用于更簡潔地指定需要檢查的類Class<?>[] name(); // 需要檢查的類的全限定名數組String havingValue() default "default"; // 期望的配置值,默認為 "default"boolean matchIfMissing() default false; // 如果配置值缺失是否匹配,默認為 false } -
完成了上述準備工作后,接下來是驗證新創建的注解。我們需要修改
WebConfiguration配置類。代碼如下:/*** 自動裝配類*/ @Configuration public class WebConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnClassName(name = ObjectStorageService.class, matchIfMissing = true)public ObjectStorageService defaultObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new DefaultObjectStorageServiceImpl();}@Bean@ConditionalOnClassName(name = ObjectStorageService.class, havingValue = "aliyun")public ObjectStorageService aliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl();}@Bean@ConditionalOnClassName(name = ObjectStorageService.class, havingValue = "s3")public ObjectStorageService s3ObjectStorageServiceImpl() {return new S3ObjectStorageServiceImpl();} } -
接下來定義配置key,在
application.properties或application.yml配置文件新增如下內容:org.example.inject.condition.service.ObjectStorageService=aliyun -
運行應用,命令行輸入:
curl http://localhost:8080/example,日志打印:objectStorageService: org.example.inject.condition.service.impl.AliyunObjectStorageServiceImpl@4cf4e0a
在這個示例中,我們利用自定義條件注解簡化了@ConditionalOnProperty注解的配置,同時統一了配置文件屬性命名,實現了一次配置多處使用。這種優化提高了配置的簡潔性和可維護性,同時減少了配置的復雜度和錯誤可能性。
四、總結
本文通過自定義條件注解,簡化了@ConditionalOnProperty注解的配置,同時統一了配置文件屬性命名。這一優化方案提高了系統的可維護性和穩定性。以往的配置模式需要在不同的類或方法上重復配置屬性的前綴和名稱,容易出錯且繁瑣。通過優化后的方案,只需在配置文件中一次性配置,即可在多處重復使用,簡化了配置過程。這種優化提高了開發效率,降低了配置錯誤的風險,尤其適用于大型項目。
總的來說,通過自定義條件注解來簡化配置,統一配置文件屬性命名,是一種非常實用的優化方案。它不僅提高了系統的可維護性和穩定性,還能夠提升開發效率,減少配置錯誤的可能性,是服務開發中值得推廣的實踐之一。
五、相關資料
- Java SPI解讀:揭秘服務提供接口的設計與應用
- Spring條件注解官網介紹
- 產品SDK化轉型:標準化與機構個性化定制解決方案















)

-MVCC多版本管理)

