? ? ? ? 通過前面的學習,我們已經對C++ STL有了初步了解。然而,STL作為一個龐大復雜的體系,遠不止這些內容。接下來,我們將深入探討STL中的另外兩個重要組件——map和set。
? ? ? ? 作者的個人gitee:樓田莉子 (riko-lou-tian) - Gitee.com喜歡請點個贊謝謝
目錄
? ? ? ? 前言——序列式容器和關聯式容器
? ? ? ? set的介紹
set的接口介紹
? ? ? ? 構造函數和析構函數
? ? ? ? 構造函數
? ? ? ? 析構函數
? ? ? ? =運算符重載
? ? ? ? 迭代器
? ? ? ? 正向
? ? ? ? 反向
? ? ? ? 正向const
? ? ? ? 反向const
? ? ? ? 容量
? ? ? ? empty
? ? ? ? size
? ? ? ? max_size
? ? ? ? 相關函數
? ? ? ? insert
? ? ? ? erase
????????swap
? ? ? ? clear
????????emplace?
? ? ? ? emplace_hint
? ? ? ? 觀察者
? ? ? ? key_comp? ? ??編輯
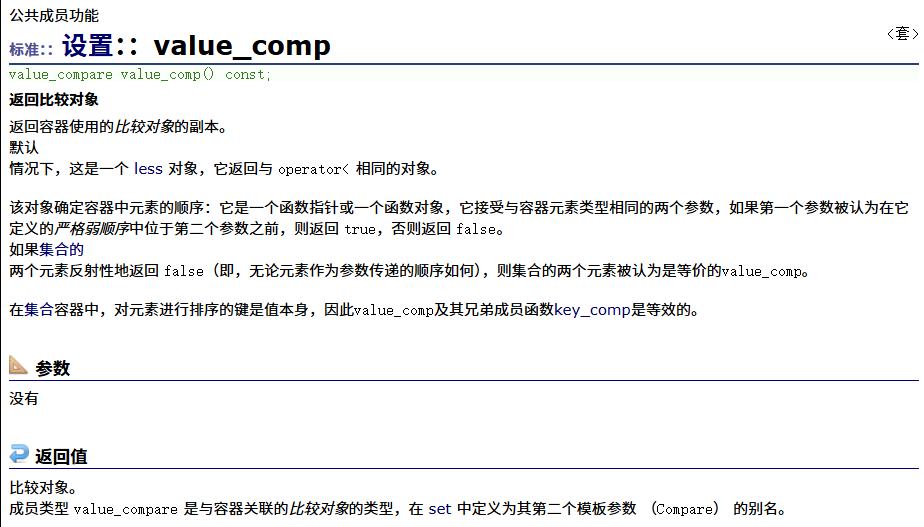
? ? ? ? value_comp
? ? ? ? 操作
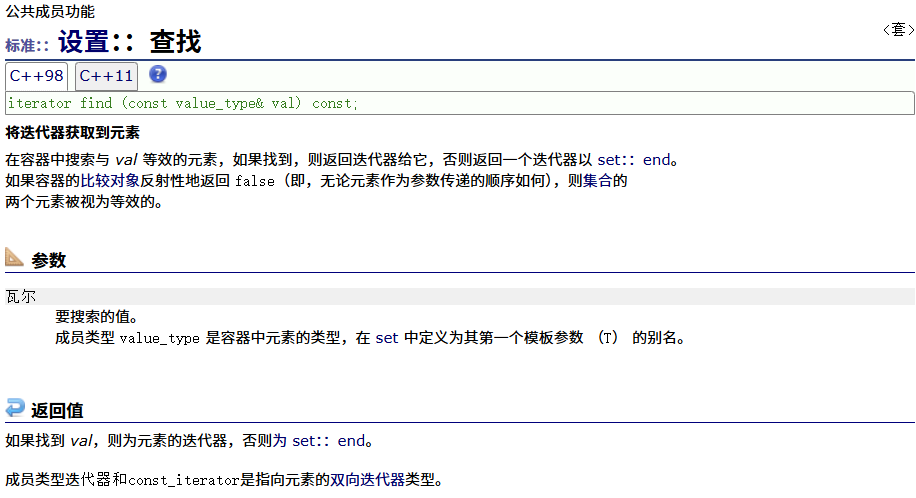
? ? ? ? find
? ? ? ? count
? ? ? ? lower_bound
? ? ? ? upper_bound
? ? ? ? equal_range
multiset和set的區別
set相關的習題
? ? ? ? 兩個數組的交集
? ? ? ? 環形鏈表
map的介紹
? ? ? ? pair結構介紹
map的接口介紹
? ? ? ? 構造和析構函數
? ? ? ? 構造函數
????????析構函數
? ? ? ? =運算符重載
? ? ? ? 迭代器
? ? ? ? 正向
? ? ? ? 反向
? ? ? ? const正向
? ? ? ? const反向
????????容量
? ? ? ? empty
? ? ? ? size
? ? ? ? max_size
????????訪問
????????[]運算符重載
????????at
????????相關函數
? ? ? ? insert
? ? ? ?erase
? ? ? ? swap
? ? ? ? clear?????????編輯
? ? ? ? emplace
? ? ? ? emplace_hint
????????觀察者
? ? ? ? key_comp
? ? ? ? value_comp
????????操作
? ? ? ? find
? ? ? ? count????????
? ? ? ? lower_bound
? ? ? ? upper_bound
? ? ? ? equal_range
multimap和map的區別
map相關的習題
? ? ? ? 隨機鏈表的復制
? ? ? ? 前k個高頻詞匯
? ? ? ? 前言——序列式容器和關聯式容器
? ? ? ?前?我們已經接觸過STL中的部分容器如:string、vector、list、deque、array、forward_list等,這些容器統稱為序列式容器,因為邏輯結構為線性序列的數據結構,兩個位置存儲的值之間?般沒有緊密的關聯關系,?如交換?下,他依舊是序列式容器。順序容器中的元素是按他們在容器中的存儲位置來順序保存和訪問的。
????????關聯式容器也是?來存儲數據的,與序列式容器不同的是,關聯式容器邏輯結構通常是?線性結構,兩個位置有緊密的關聯關系,交換?下,他的存儲結構就被破壞了。順序容器中的元素是按關鍵字來保存和訪問的。關聯式容器有map/set系列和unordered_map/unordered_set系列。
? ? ? ? 本篇中學習的map和set容器底層是紅?樹,紅?樹是?顆平衡?叉搜索樹。set是key搜索場景的結構, map是key/value搜索場景的結構。
? ? ? ? set的介紹
? ? ? ? set和multiset的文檔:<set> - C++ Reference
? ? ? ? 在使用set和multiset的時候要包含頭文件<set>和
using namespace std;? ? ? ? 進入set文檔我們會發現
? ? ? ? set不允許冗余,multiset允許冗余而不破壞結構
? ? ? ? set的官方文檔:set - C++ 參考
? ? ? ?set的介紹
? ? ? ? ? ?
????????set的聲明如下,T就是set底層關鍵字的類型
template < class T, // set::key_type/value_type
class Compare = less<T>, // set::key_compare/value_compare
class Alloc = allocator<T> // set::allocator_type
> class set;????????set默認要求T?持?于?較,如果不?持或者想按??的需求?可以??實現仿函數傳給第?個模版參數
????????set底層存儲數據的內存是從空間配置器申請的,如果需要可以??實現內存池,傳給第三個參數。
?????????般情況下,我們都不需要傳后兩個模版參數。
????????set底層是?紅?樹實現,增刪查效率是 ,迭代器遍歷是?的搜索樹的中序,所以是有序的。O(logN)
set的接口介紹
? ? ? ? 構造函數和析構函數
? ? ? ? 構造函數
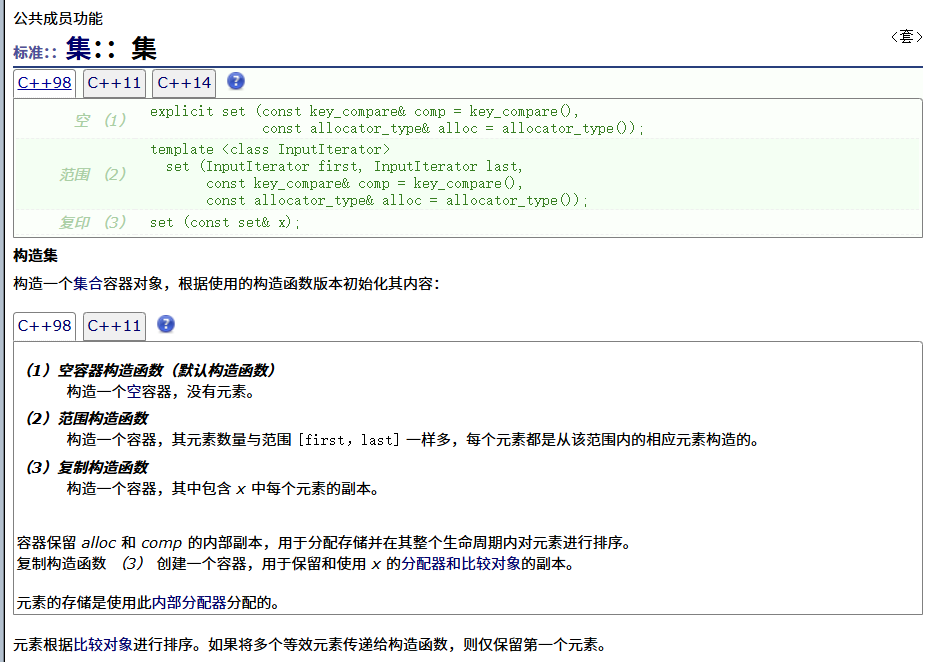
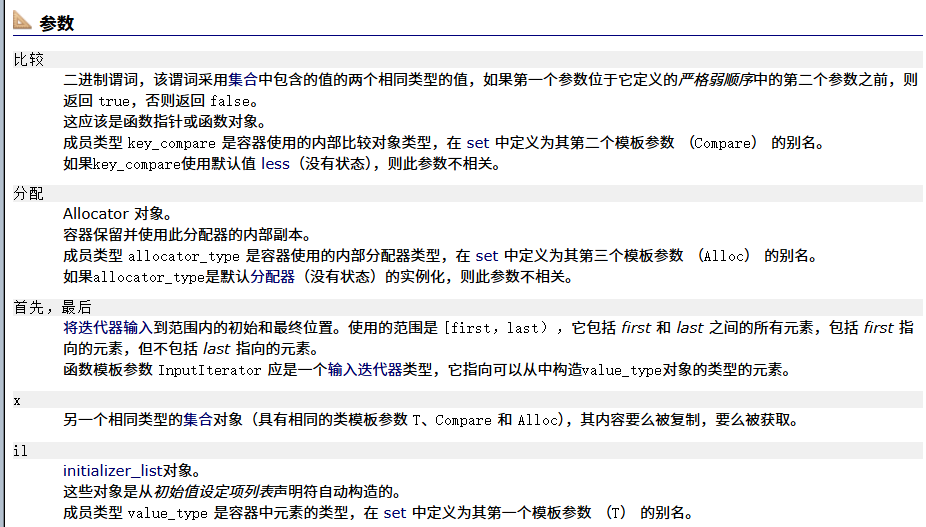
? ? ? ? 析構函數
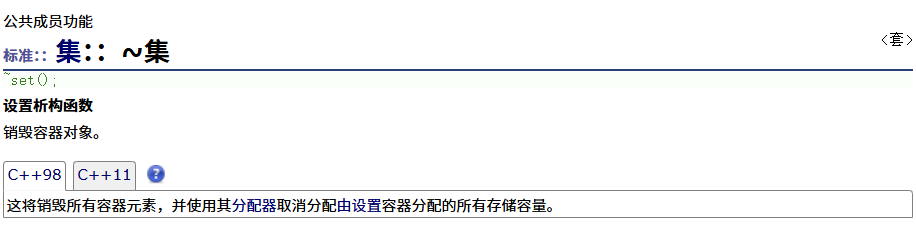
? ? ? ? =運算符重載
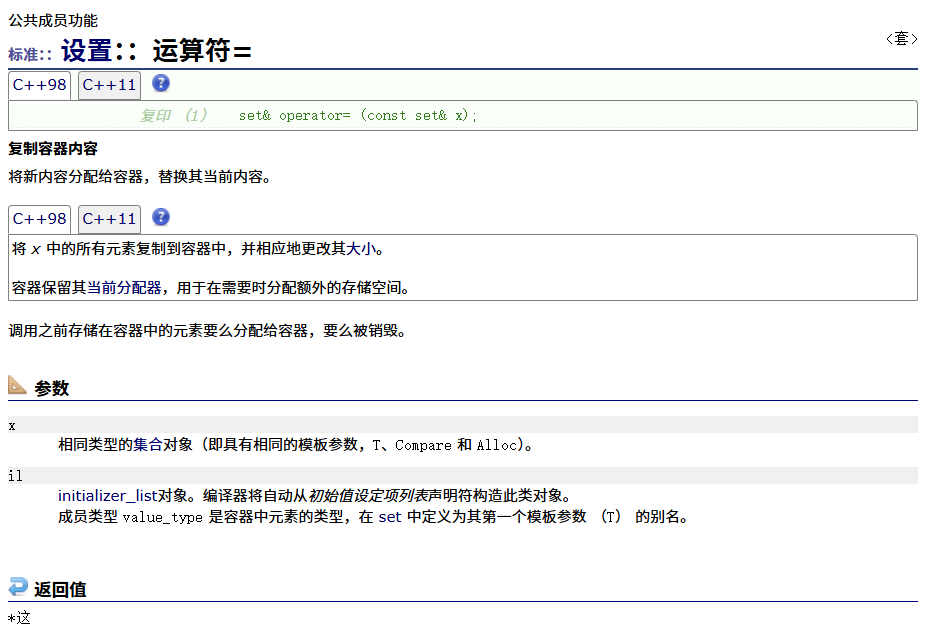
? ? ? ? 迭代器
? ? ? ? 正向
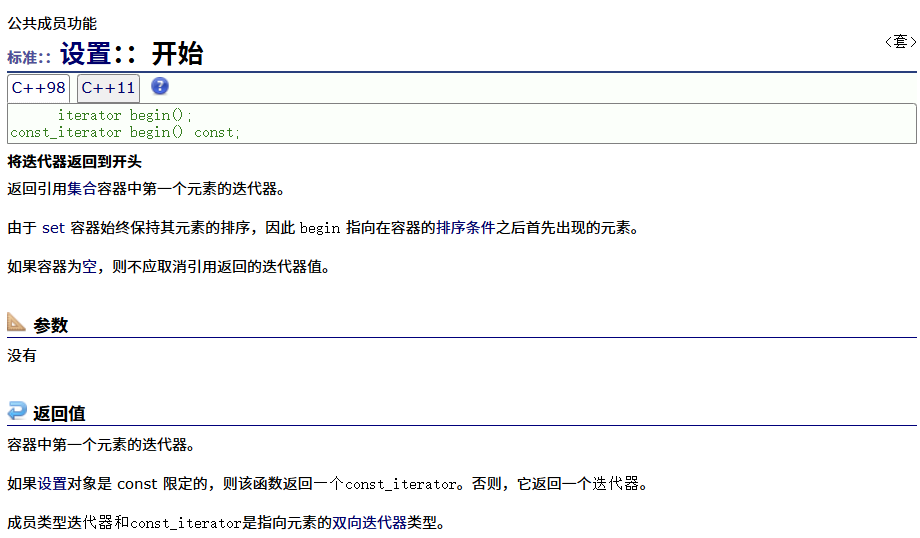
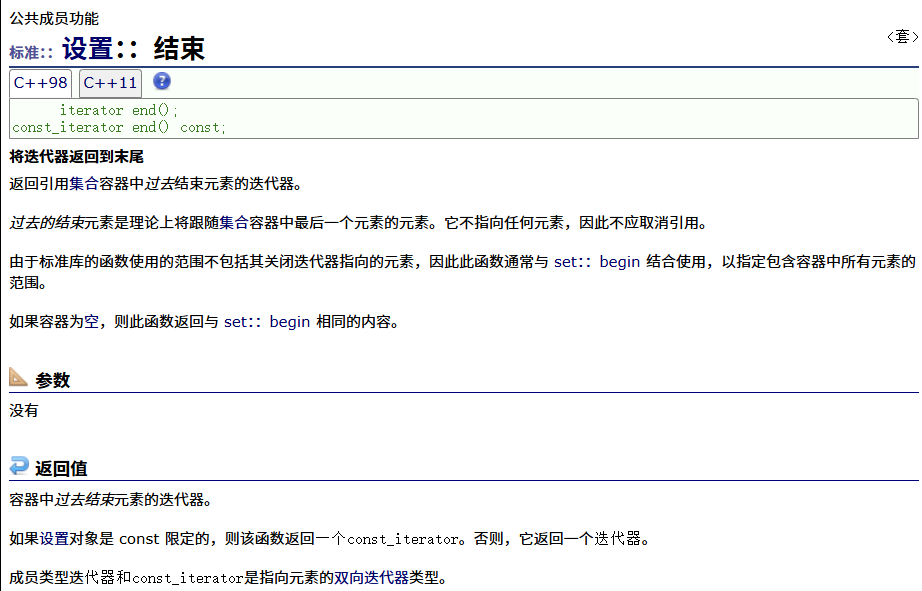
? ? ? ? 反向
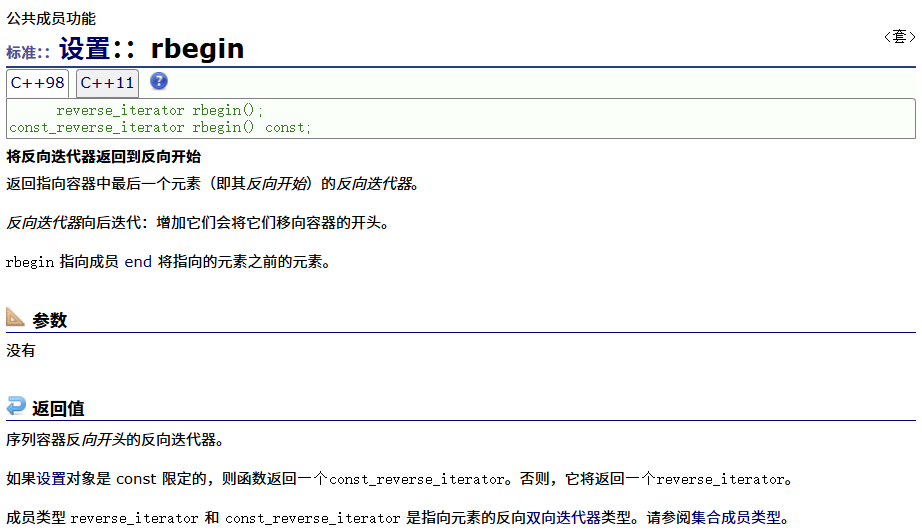

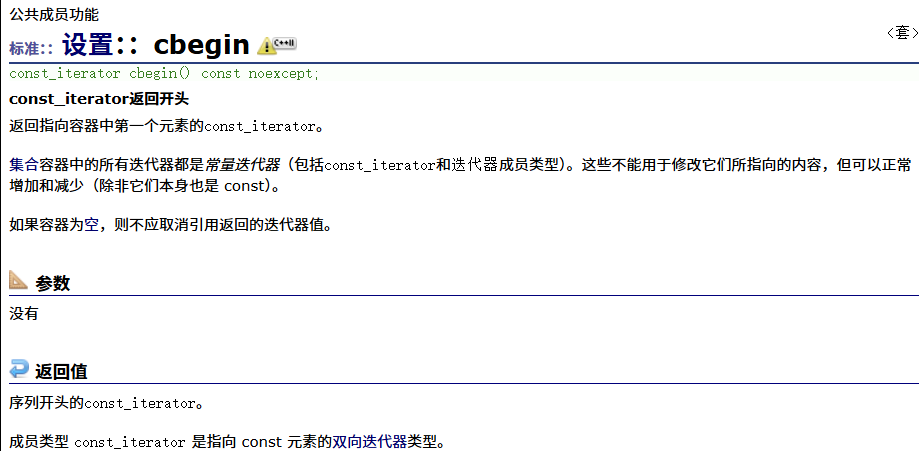
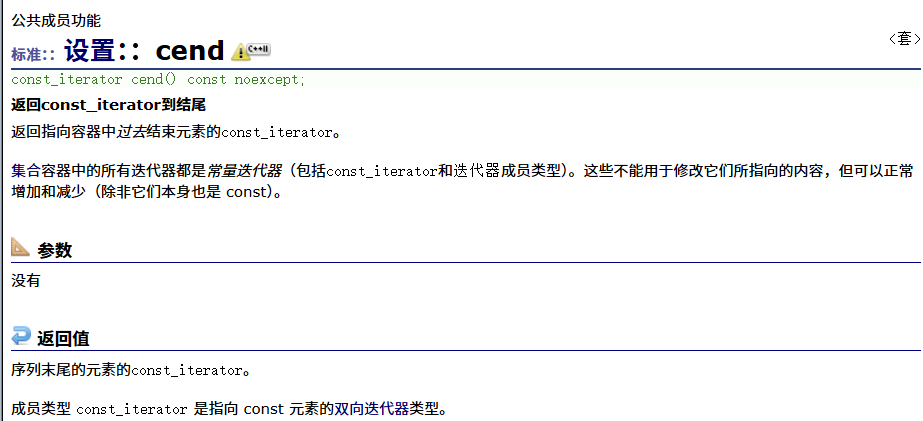
? ? ? ? 正向const
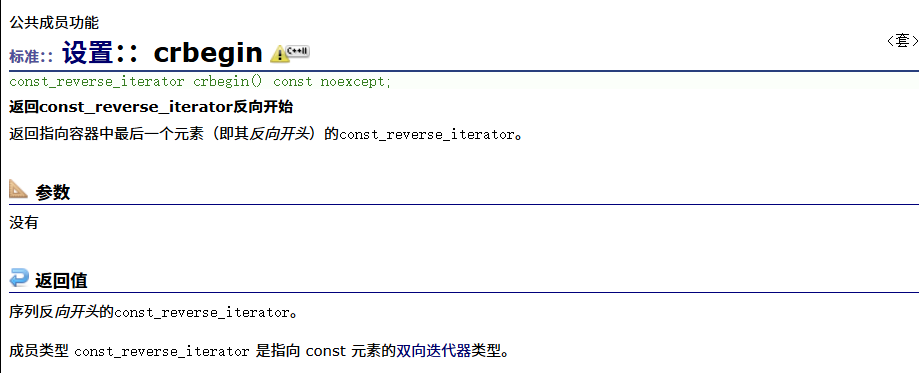
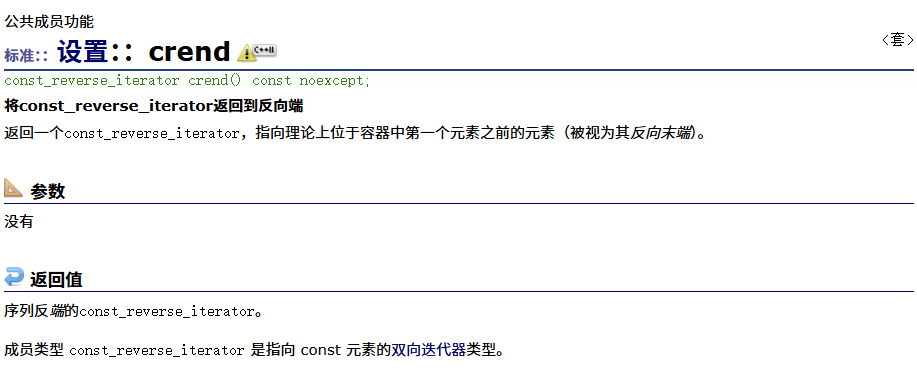
? ? ? ? 反向const
? ? ? ? 容量
? ? ? ? empty
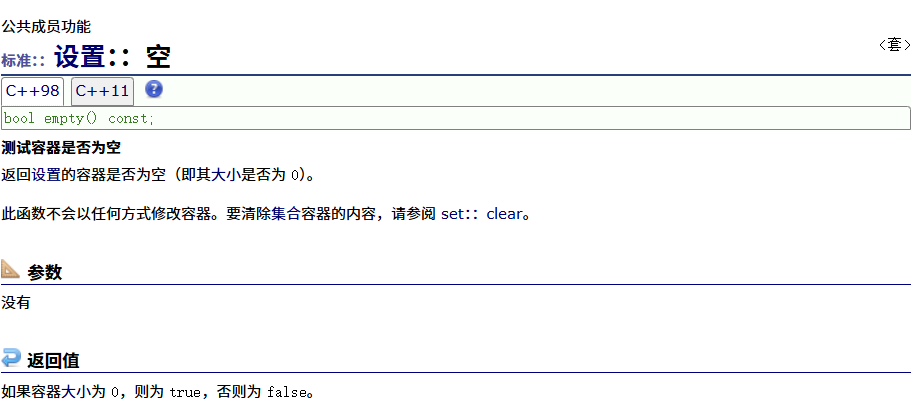
? ? ? ? size

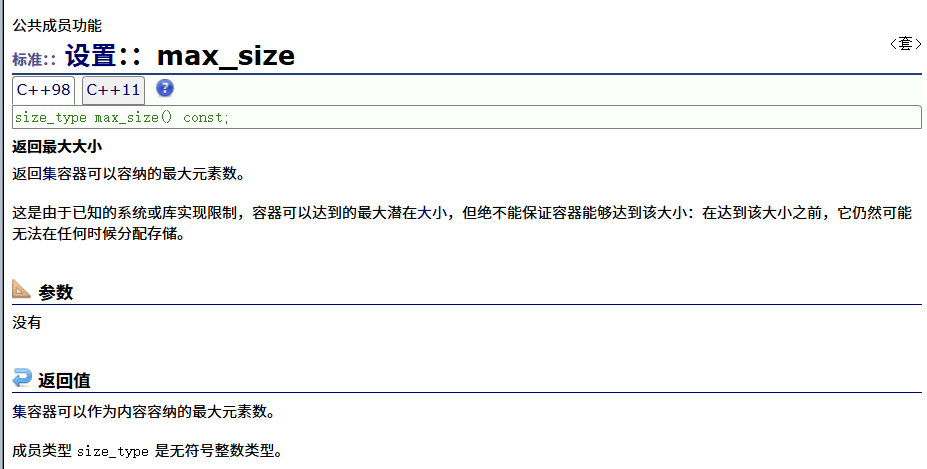
? ? ? ? max_size
? ? ? ? 相關函數
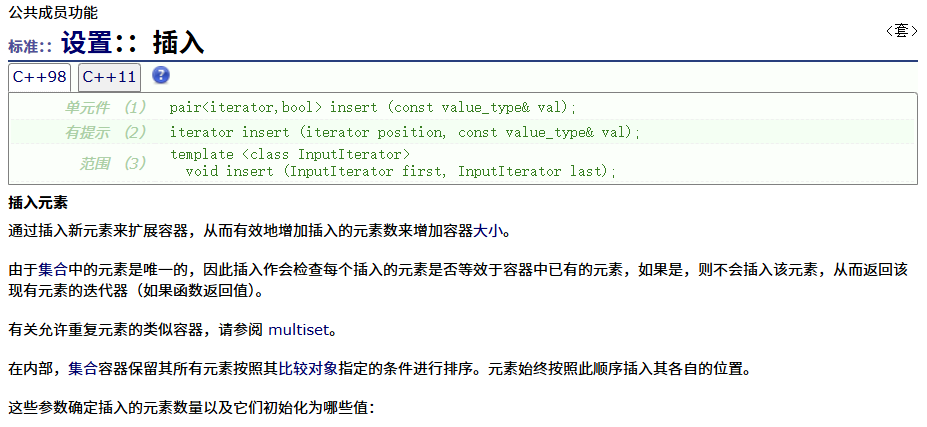
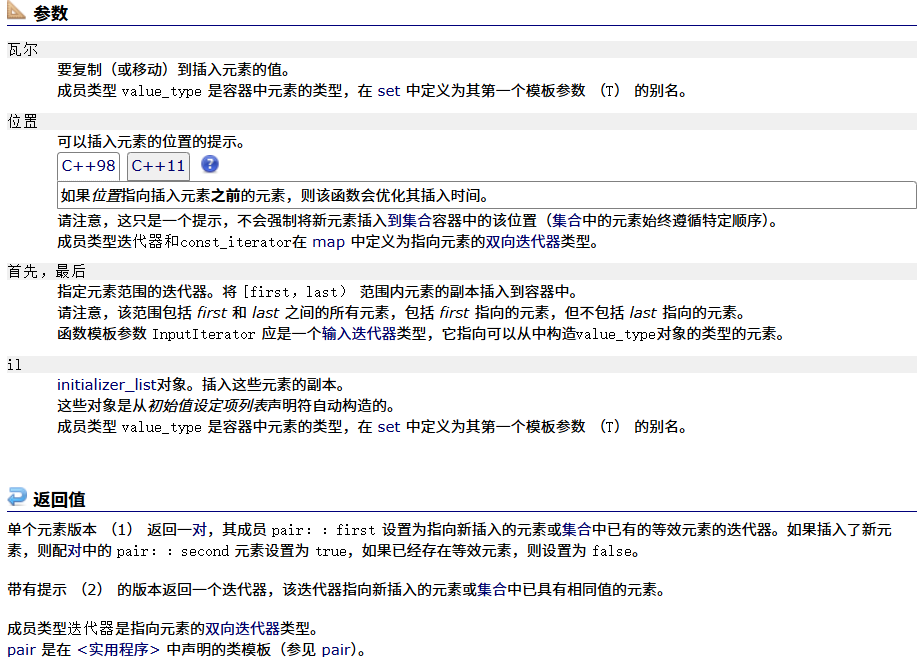
? ? ? ? insert
? ? ? ? erase
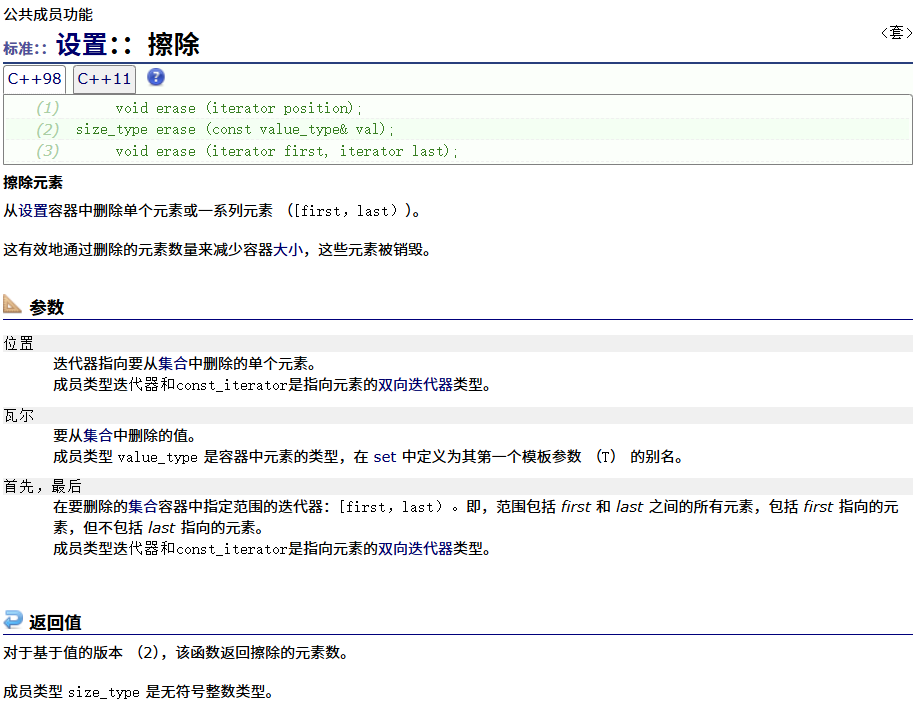
????????swap

? ? ? ? clear
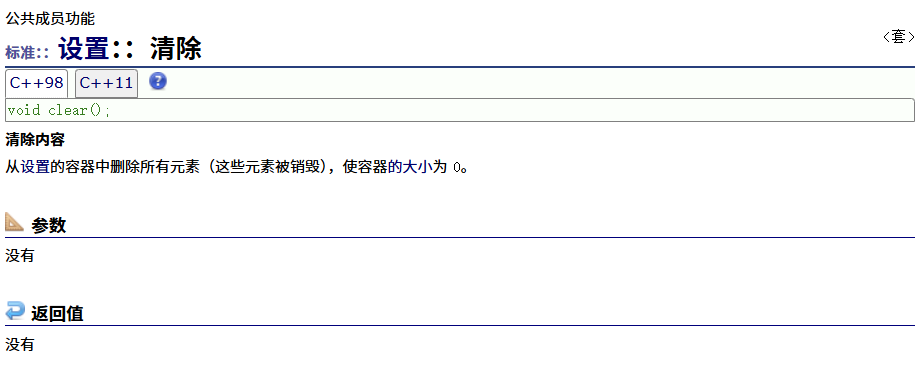
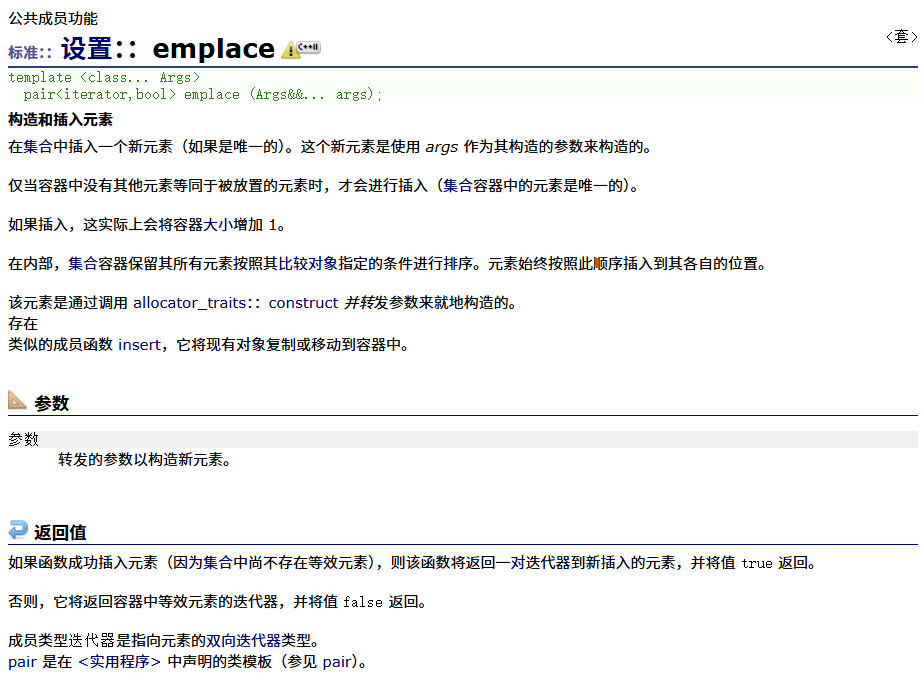
????????emplace?
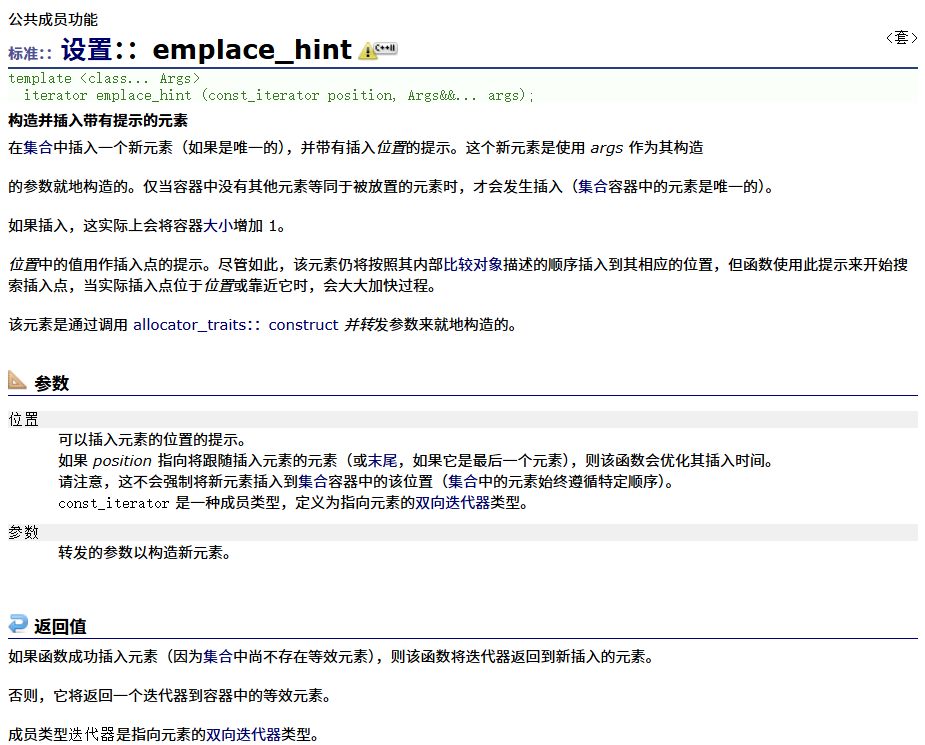
? ? ? ? emplace_hint
? ? ? ? 觀察者
? ? ? ? key_comp? ? ?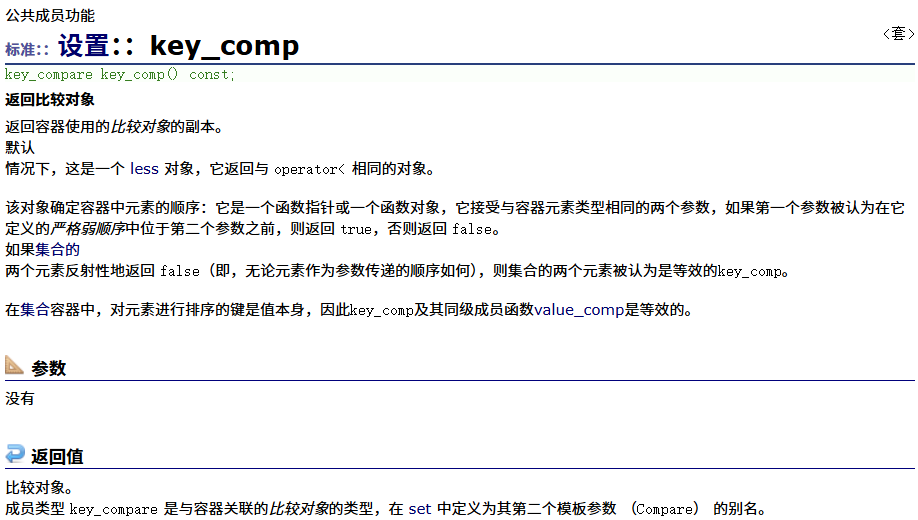
? ? ? ? value_comp
 ??
??
? ? ? ? 操作
? ? ? ? find
????????
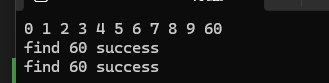
void test2()
{set<int>s = { 0,9,1,4,7,2,3,2,5,8,7,8,3,6,9 };s.insert(60);print(s);//set自己的find//時間復雜度O(log(n))auto it=s.find(60);if (it != s.end()){cout << "find 60 success" << endl;}else{cout << "find 60 failed" << endl;}//算法庫的find//時間復雜度O(N)auto ret = find(s.begin(), s.end(), 60);if (it != s.end()){cout << "find 60 success" << endl;}else{cout << "find 60 failed" << endl;}
}? ? ? ? 算法庫也有find函數,但是算法庫的find效率比set的低下。
? ? ? ? 結果為:
? ? ? ? multiset中的find中序查找
? ? ? ? count
????????
void test3()
{set<int>s = { 0,9,1,4,7,2,3,2,5,8,7,8,3,6,9 };if (s.count(2)){cout << "存在" << " ";}else{cout << "不存在" << " ";}
}結果為:
? ? ? ? count是為了和multiset區分,因為它有多個。
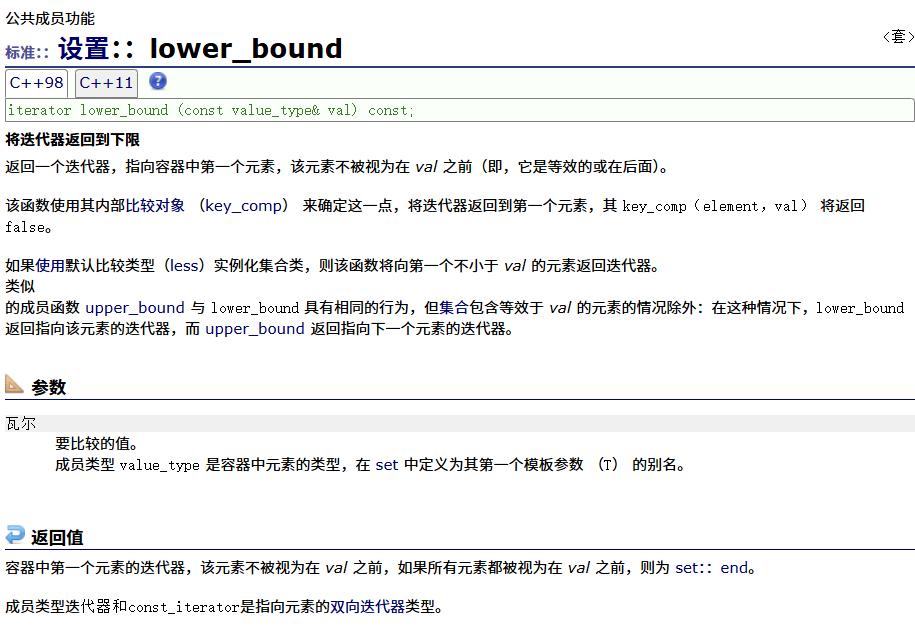
? ? ? ? lower_bound
????????
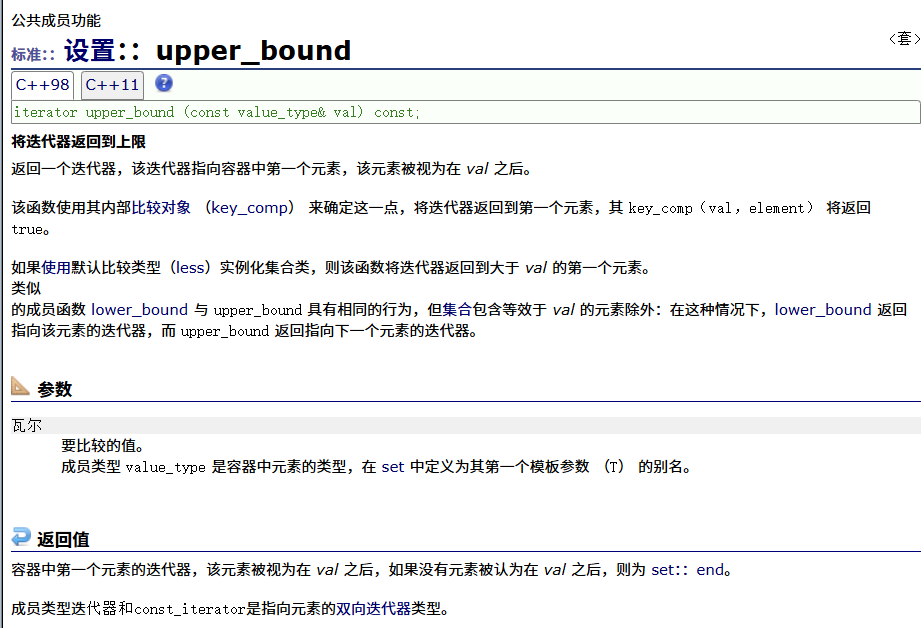
? ? ? ? upper_bound
?????? ??
??
void test4()
{set<int>s = { 0,9,1,4,7,2,3,2,5,8,7,8,3,6,9,10,21,10,11,18,19 };//找到[3,9]區間的元素刪除//>=3auto it1 = s.lower_bound(3);//>3auto it2 = s.upper_bound(9);//打印區間[it1,it2]for (auto it = it1; it != it2; ++it){cout<<*it<<" ";}cout<<endl;//刪除區間[it1,it2]s.erase(it1,it2);print(s);/*for (auto it = it1; it != it2; it++){s.erase(it);}*////print(s);
}結果為:

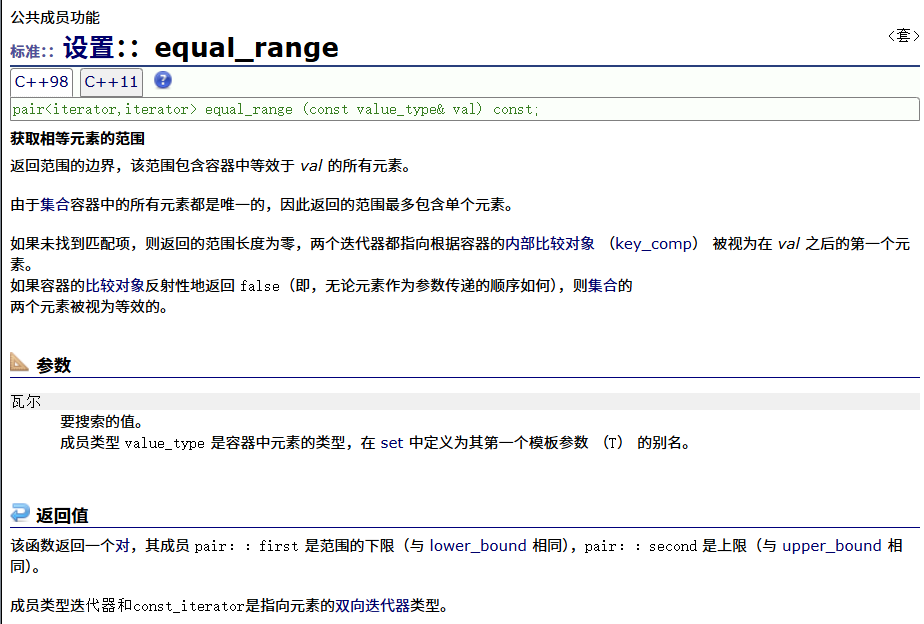
? ? ? ? equal_range
multiset和set的區別
????????multiset和set的使?基本完全類似,主要區別點在于multiset?持值冗余,那么insert/find/count/erase都圍繞著?持值冗余有所差異,具體參看下?的樣例代碼理解。
void test5()
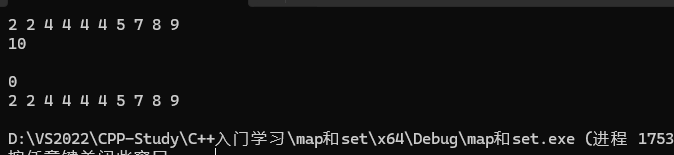
{// 相?set不同的是,multiset是排序,但是不去重multiset<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,4,8,4,5,4,9 };auto it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;// 相?set不同的是,x可能會存在多個,find查找中序的第?個int x;cin >> x;auto pos = s.find(x);while (pos != s.end() && *pos == x){cout << *pos << " ";++pos;}cout << endl;// 相?set不同的是,count會返回x的實際個數cout << s.count(x) << endl;// 相?set不同的是,erase給值時會刪除所有的xs.erase(x);for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}? ? ? ? 結果為:
set相關的習題
? ? ? ? 兩個數組的交集
????????
? ? ? ? 老方法:
? ? ? ? 先使用快慢指針判斷是否有環,隨后找到環的入口點
? ? ? ? 新方法:
????????遍歷鏈表,判斷是否在s中,不再就插入,在的第一個就是入口點,如果都不在,就插入了鏈表結束了都帶環,比較兩個set,小的++;相等就是交集,同時++。一個遍歷就結束了
class Solution {
public:vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {//老方法:太麻煩了//是否帶環(雙指針)//找環的入口點 //新方法:set<Node*>s;//遍歷鏈表,判斷是否在s中//不再就插入,在的第一個就是入口點//如果都不在,就插入了鏈表結束了都帶環set<int> s1(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());set<int> s2(nums2.begin(), nums2.end());//// 因為set遍歷是有序的,有序值,依次比較//比較//小的++;相等就是交集,同時++。一個練筆就結束了vector<int> ret;auto it1 = s1.begin();auto it2 = s2.begin();while(it1 != s1.end() && it2 != s2.end()){if(*it1 < *it2){it1++;} else if(*it1 > *it2){it2++;} else{ret.push_back(*it1);it1++;it2++;}} return ret;}
};? ? ? ? 該算法找差集也很合適
? ? ? ? 1、小的就是差集。小的++
? ? ? ? 2、相等,同時++
? ? ? ? 3、一個遍歷結束剩下的就是差集
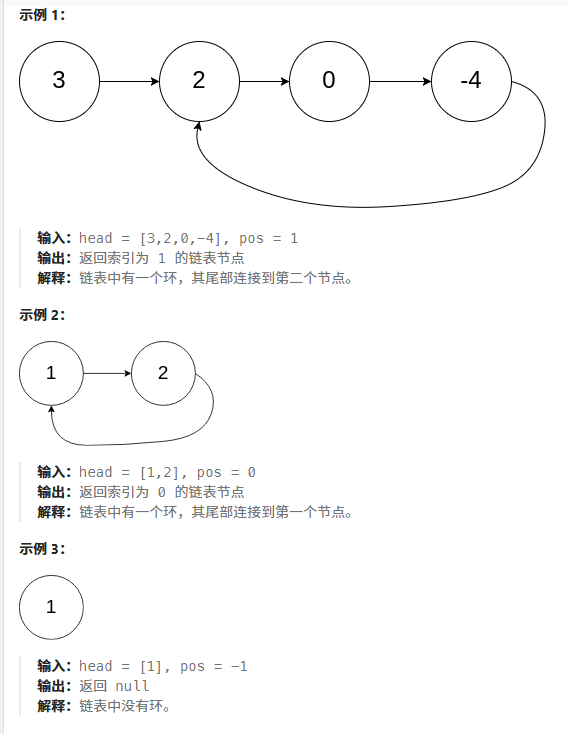
? ? ? ? 環形鏈表
???????
 ?
?
????????
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {set<ListNode*> s;ListNode* cur = head;while(cur){auto ret = s.insert(cur);if(ret.second == false)return cur;cur = cur->next;} return nullptr;}
};map的介紹
? ? ? ? map和multimap的官方文檔:<地圖> - C++參考
? ? ? ? map的介紹

????????map的聲明如下,Key就是map底層關鍵字的類型,T是map底層value的類型,set默認要求Key?持?于?較,如果不?持或者需要的話可以??實現仿函數傳給第?個模版參數,map底層存儲數據的內存是從空間配置器申請的。?般情況下,我們都不需要傳后兩個模版參數。map底層是?紅?樹實現,增刪查改效率是 O(logN) ,迭代器遍歷是?的中序,所以是按key有序順序遍歷的
template < class Key, // map::key_type
class T, // map::mapped_type
class Compare = less<Key>, // map::key_compare
class Alloc = allocator<pair<const Key,T> >//map::allocator_type
> class map;? ? ? ? pair結構介紹
????????map底層的紅?樹節點中的數據,使?pair<Key, T>存儲鍵值對數據。
? ? ? ? pair的官方文檔:pair - C++ 參考
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{typedef T1 first_type;typedef T2 second_type;T1 first;T2 second;pair() : first(T1()), second(T2()){}pair(const T1& a, const T2& b) : first(a), second(b){}template<class U, class V>pair(const pair<U, V>& pr) : first(pr.first), second(pr.second){}
};
template <class T1, class T2>
inline pair<T1, T2> make_pair(T1 x, T2 y)
{return (pair<T1, T2>(x, y));
}map的接口介紹
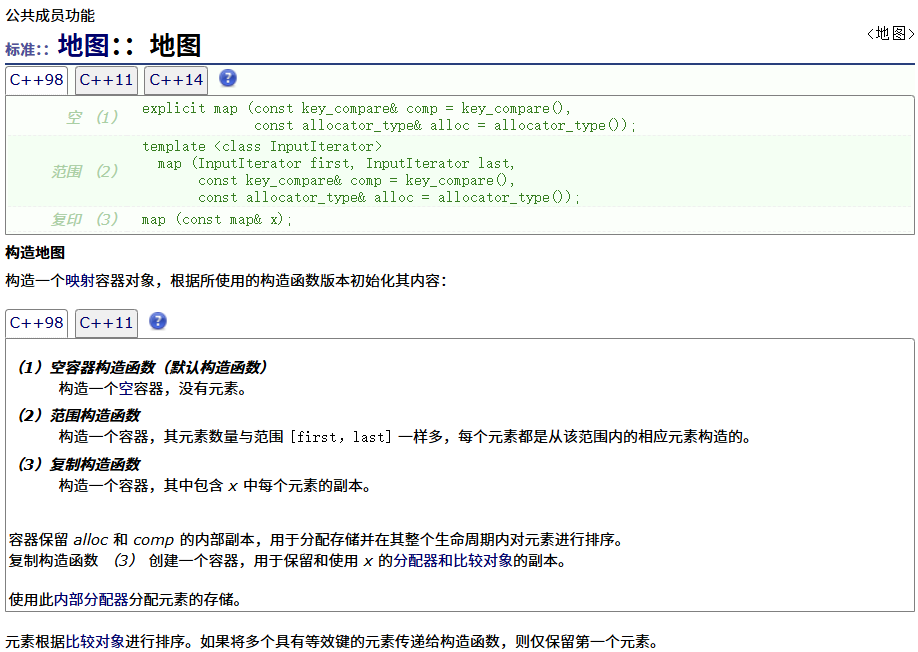
? ? ? ? 構造和析構函數
? ? ? ? 構造函數
????????

????????析構函數

? ? ? ? =運算符重載
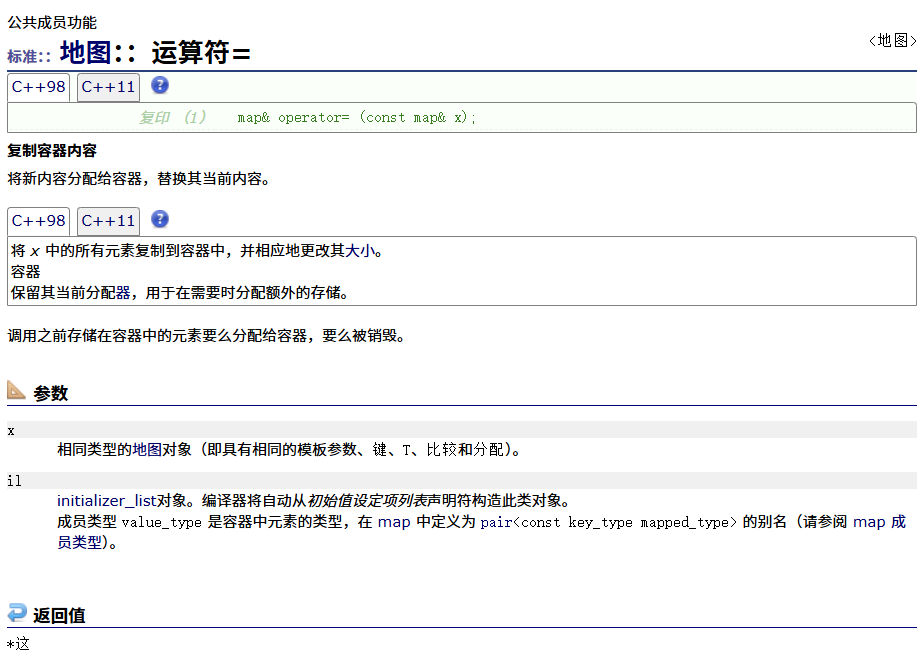
? ? ? ? 迭代器
? ? ? ? 正向
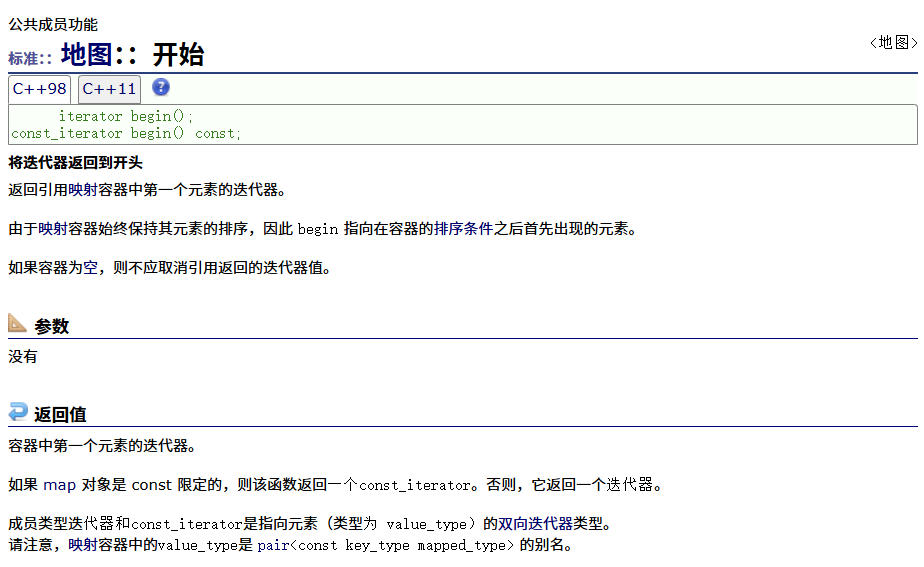
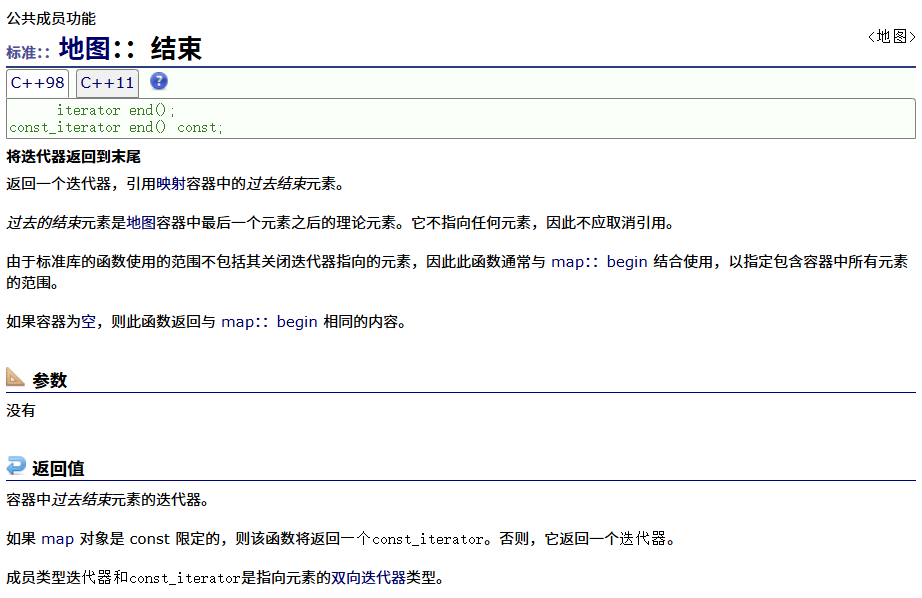
? ? ? ? 反向
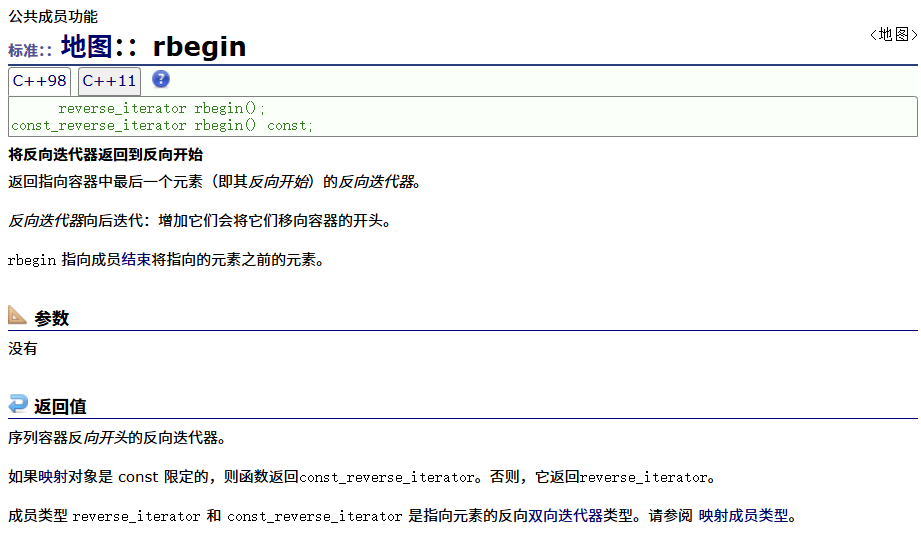

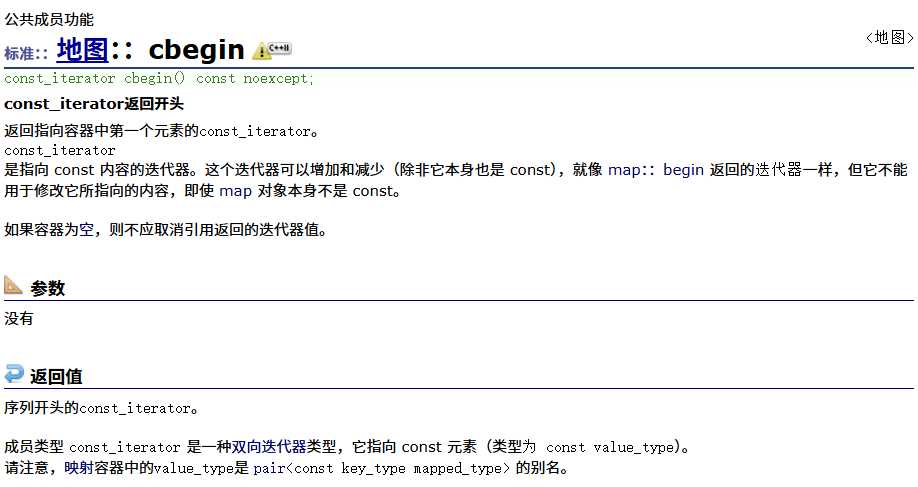
? ? ? ? const正向
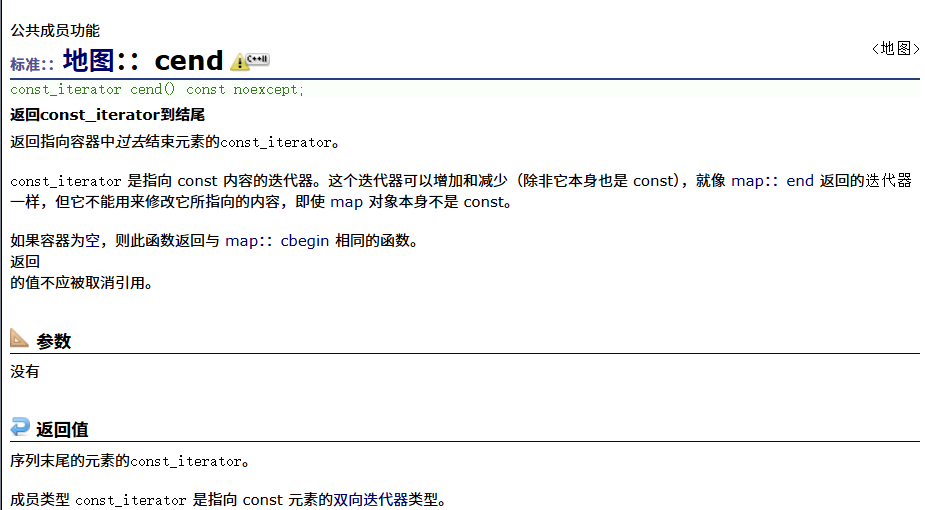
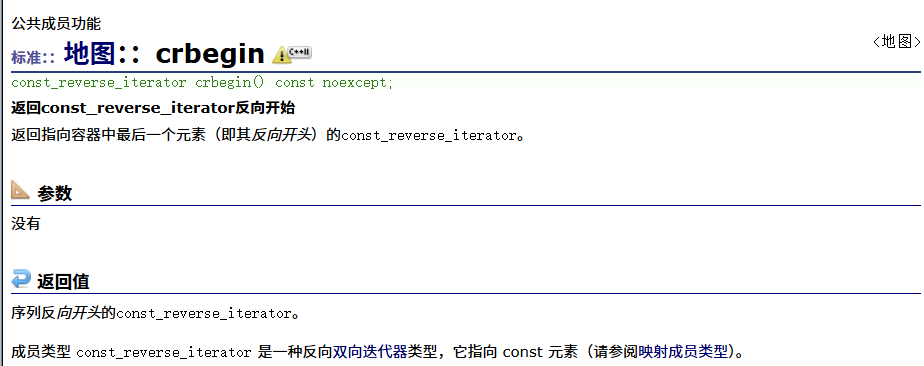
? ? ? ? const反向
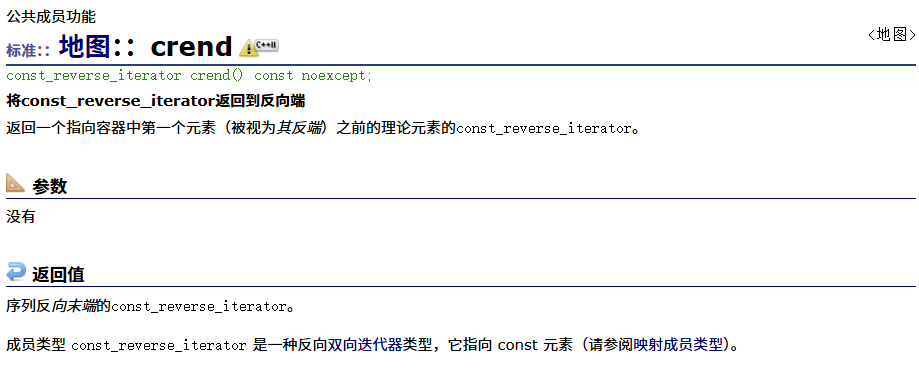
????????容量
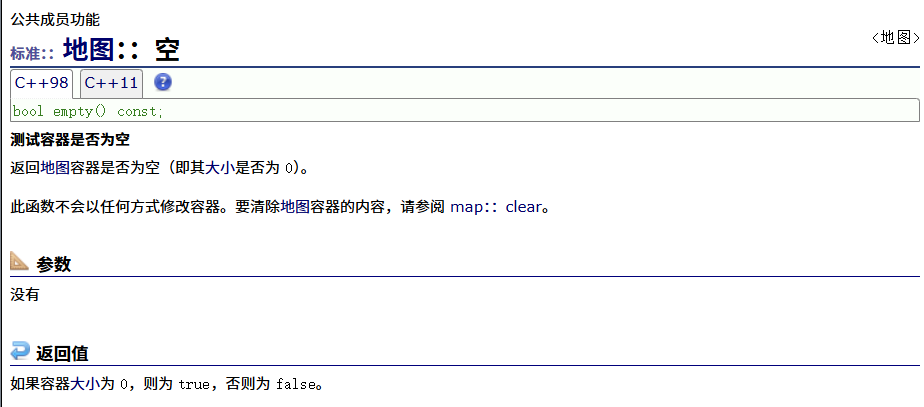
? ? ? ? empty
????????
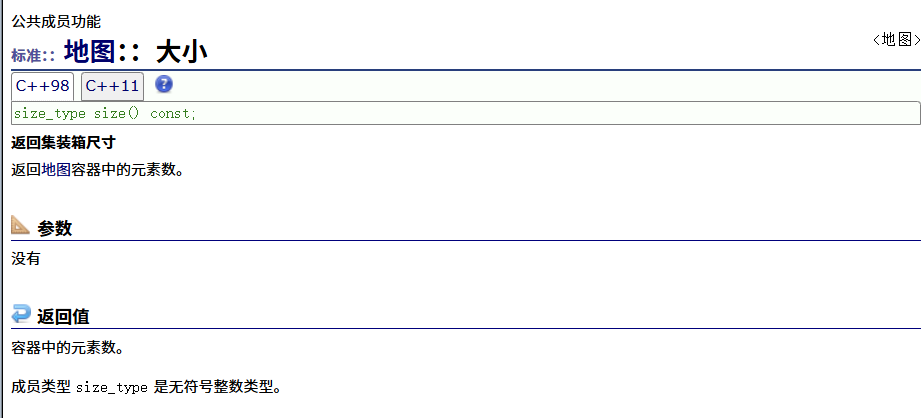
? ? ? ? size
????????
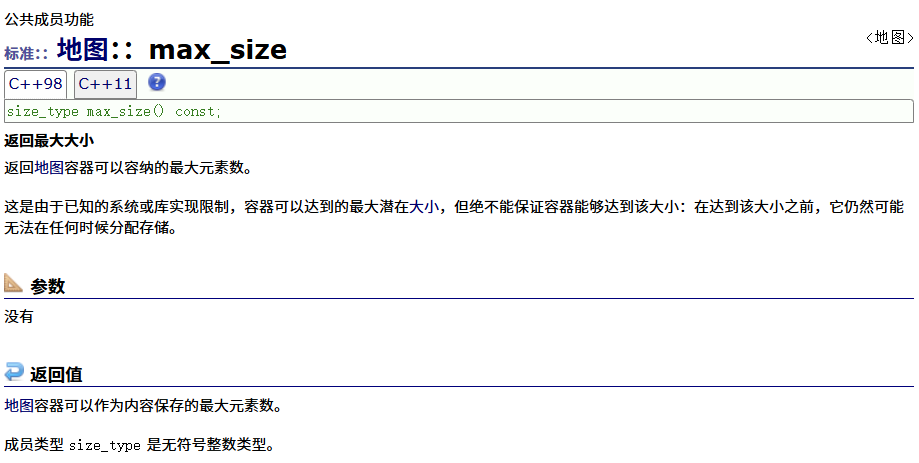
? ? ? ? max_size
????????
????????訪問
????????[]運算符重載
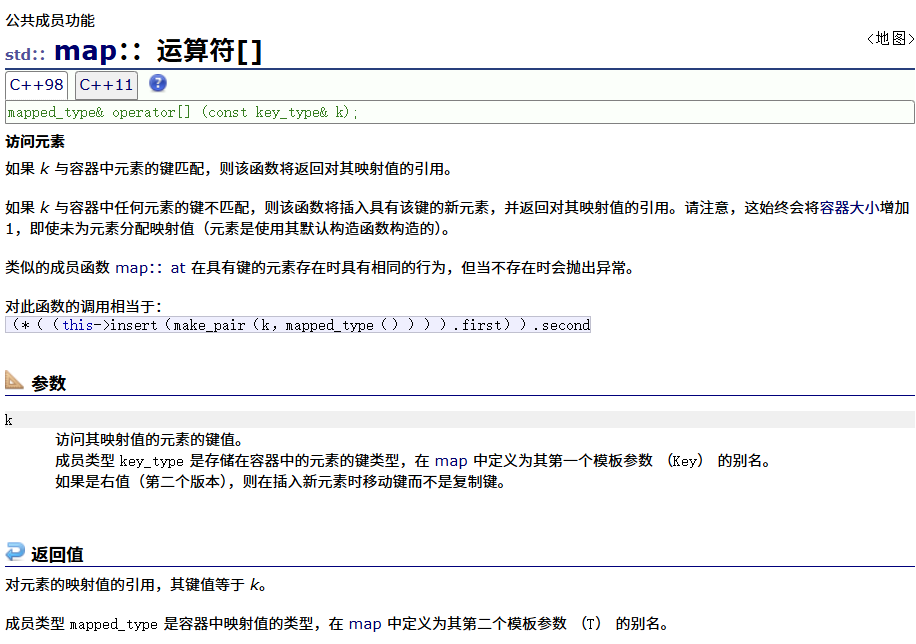
? ? ? ? key在map中就插入;如果不在就查找并修改
????????at
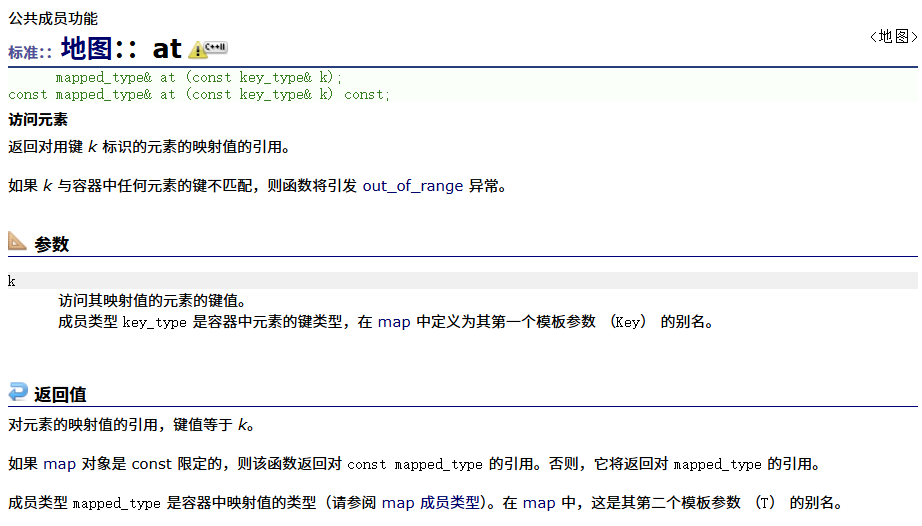
????????相關函數
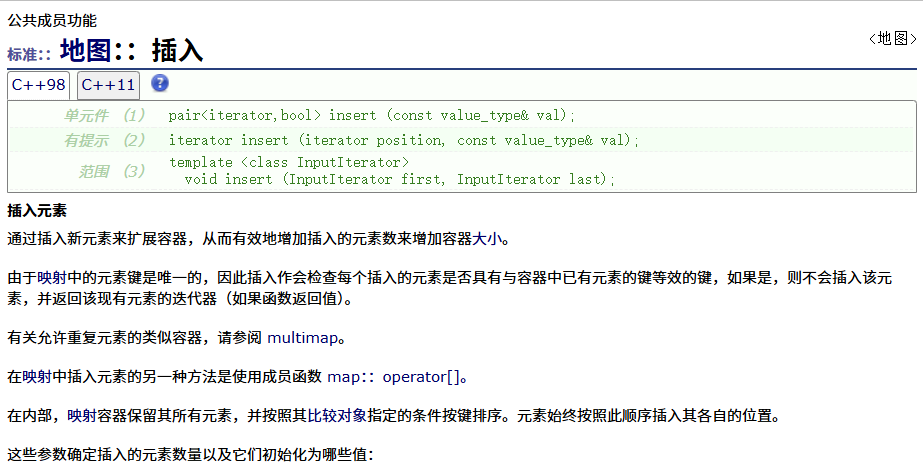
? ? ? ? insert
????????
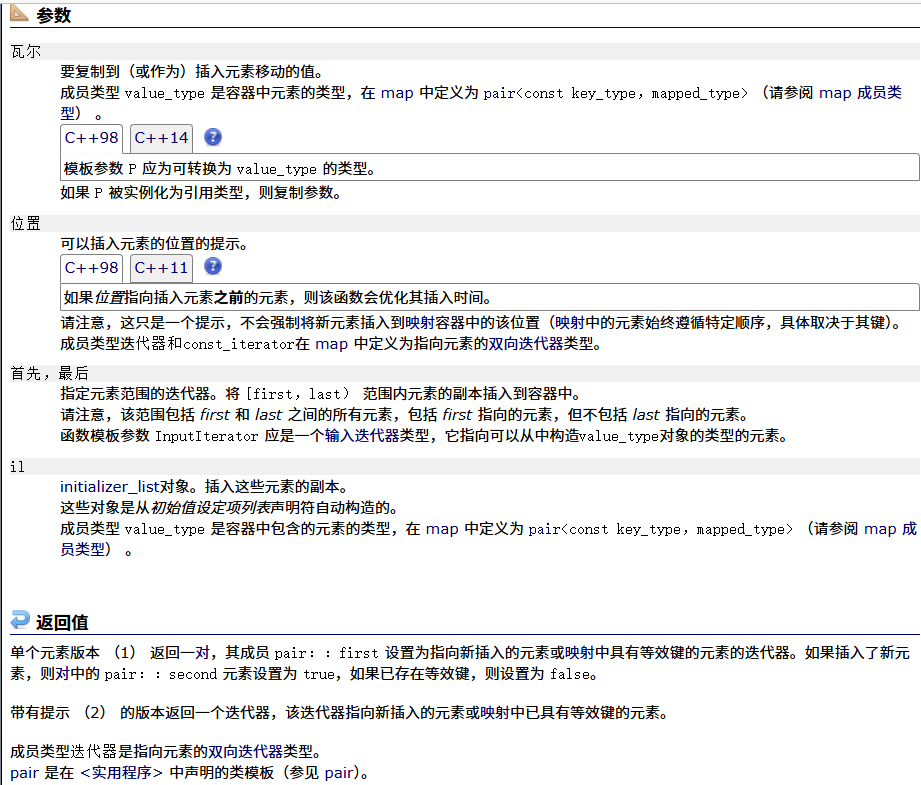
? ? ? ?erase
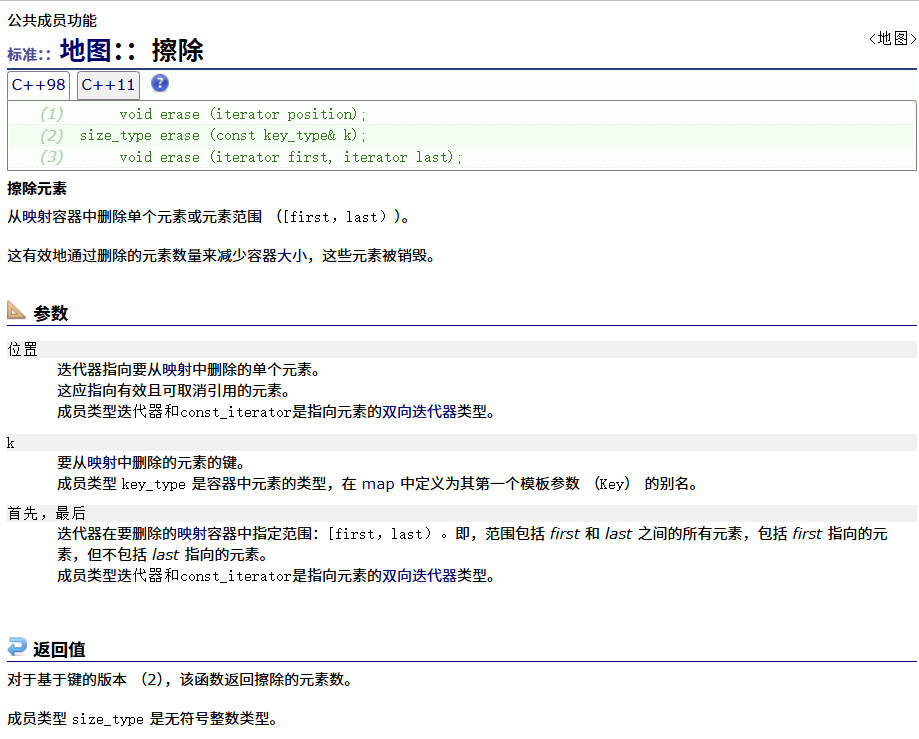
? ? ? ? swap
????????
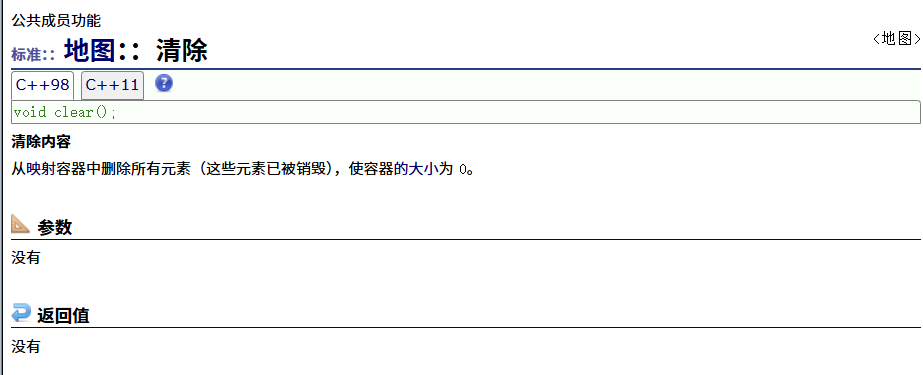
? ? ? ? clear
????????
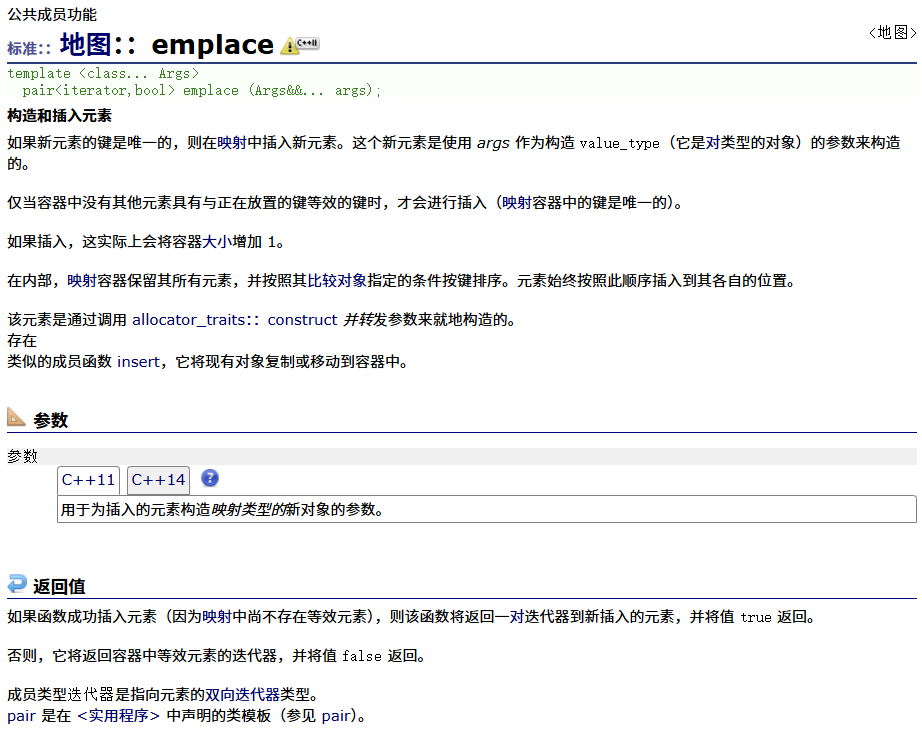
? ? ? ? emplace
????????
? ? ? ? emplace_hint
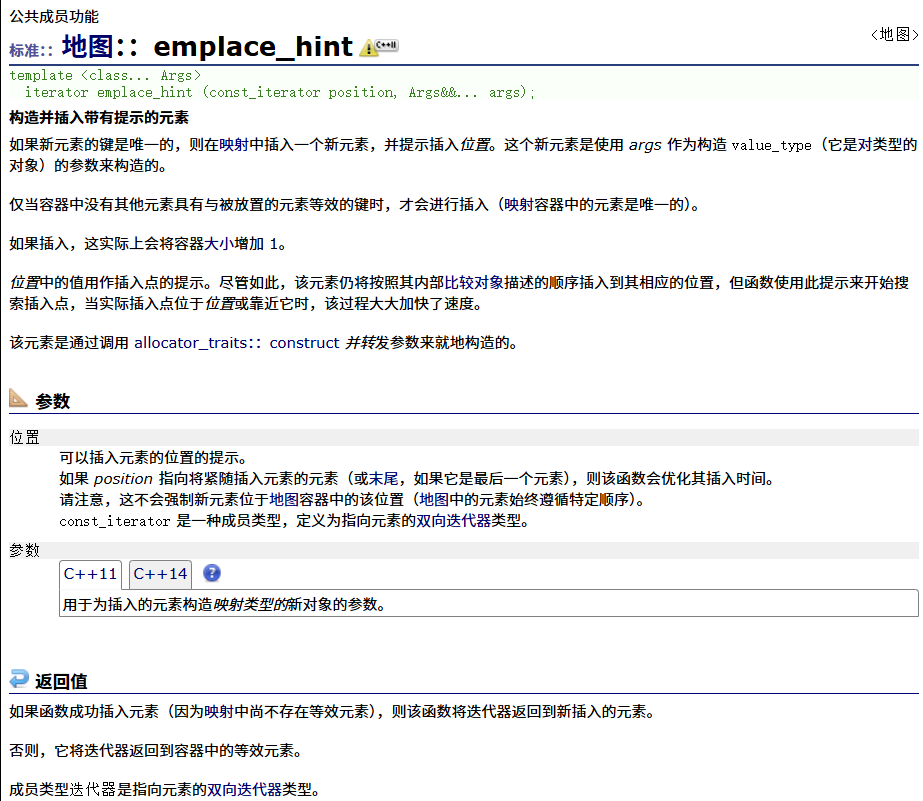
? ? ? ? 測試:?
void test1()
{//比較麻煩的構造方式/*pair<string, string>kv1 = {"sort","排序"};pair<string, string>kv2 = { "left","左" };pair<string, string>kv3 = { "right","右" };pair<string, string>kv4 = { "up","上" };pair<string, string>kv5 = { "down","下" };map<string, string> dirt = {kv1, kv2, kv3, kv4, kv5};*///簡化的構造方式map<string, string> dirt = { {"sort","排序"}, {"left","左"}, {"right","右"}, {"up","上"}, {"down","下"} };pair<string, string>kv1 = { "sort","排序" };//dirt.insert(kv1);//make_pair()函數來源于pair文檔//make_pair()可以自動推導參數類型,不用模板參數dirt.insert(pair<string, string>{ "sort", "排序" });dirt.insert(make_pair("const","常量屬性"));//insert()函數可以自動推導參數類型,不用模板參數//隱式類型轉換//推薦這種寫法dirt.insert({ "volatile","易變性" });//遍歷dirt//map<string,string>::iterator it=dirt.begin();auto it = dirt.begin();while (it!= dirt.end()){//pair沒有流重載所以不能寫*it//可以這樣寫cout<<(*it).first<<" : "<<(*it).second<<endl;//更推薦這種寫法cout << it->first << " : " << it->second << " ";//相當于//cout << it.operator->()->first << " : " << it.operator->()->second << " ";it++;}cout << endl;//范圍forfor (auto& kv : dirt){cout << kv.first << " : " << kv.second << endl;}//使用auto&的原因//避免拷貝開銷:/*dirt的元素類型是pair<const string, string>每個pair包含兩個string對象,每個string可能包含動態分配的堆內存使用引用auto& 直接訪問容器內元素,不創建任何副本*/// 內存布局對比:// 容器內元素: [pair1] -> [key_str_data][val_str_data]// [pair2] -> [key_str_data][val_str_data]// 使用auto&: kv 直接指向容器內元素的內存// 使用auto: kv 是完整的拷貝(包括所有字符串數據)/* 特性 auto& kv auto kv拷貝開銷 無拷貝(零開銷) 每個元素兩次深拷貝內存占用 僅指針大小(約8字節) 每個元素兩份完整字符串動態內存 不分配新內存 每次迭代分配新內存修改原容器 可修改value 修改無效(副本)循環速度 ?? 極快 🐢 極慢(尤其大字符串)推薦指數 ★★★★★ ★☆☆☆☆(禁止使用)*///更推薦C++17的結構化綁定//auto& [x, y] = kv1;for (auto& [x, y] : dirt){cout<<"x="<<x<<" y="<<y<<" ";}cout<<endl;
}????????觀察者
? ? ? ? key_comp
????????
? ? ? ? value_comp
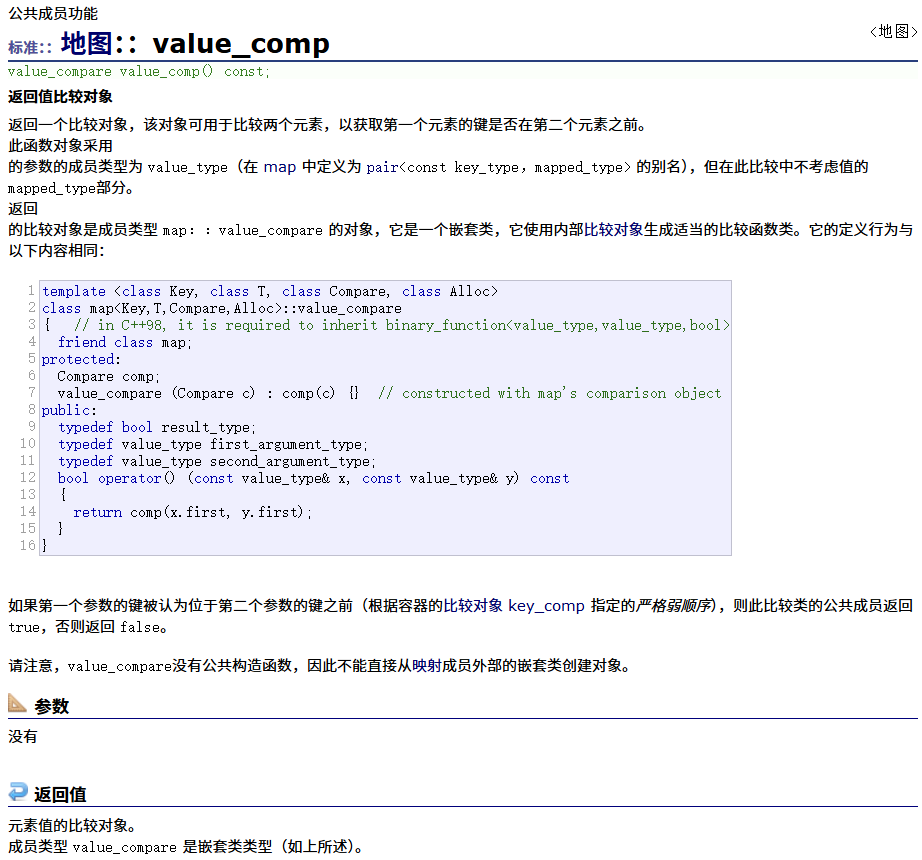
????????操作
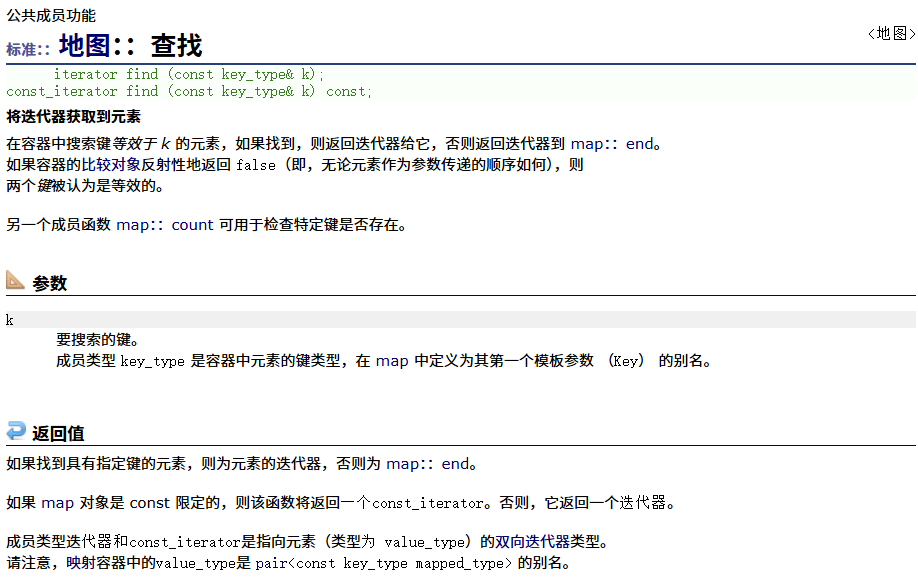
? ? ? ? find
????????
? ? ? ? count????????
???????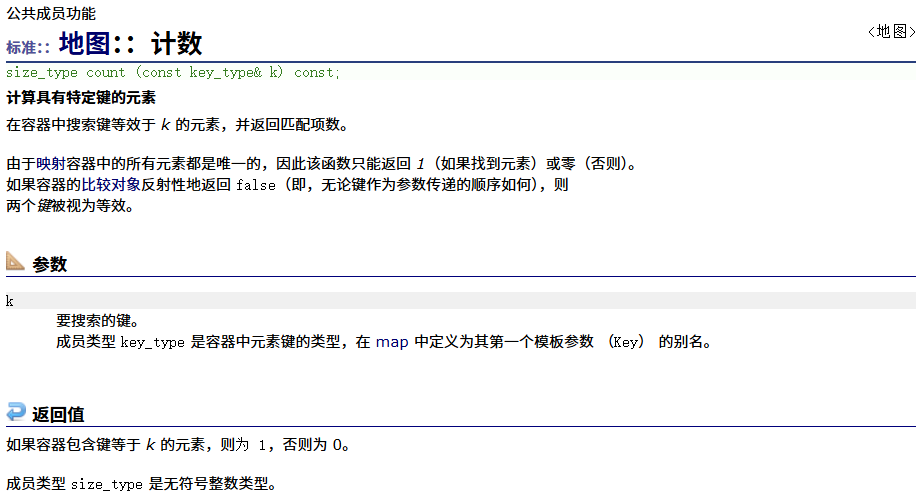 ?
?
? ? ? ? lower_bound
????????
? ? ? ? upper_bound
????????
? ? ? ? equal_range
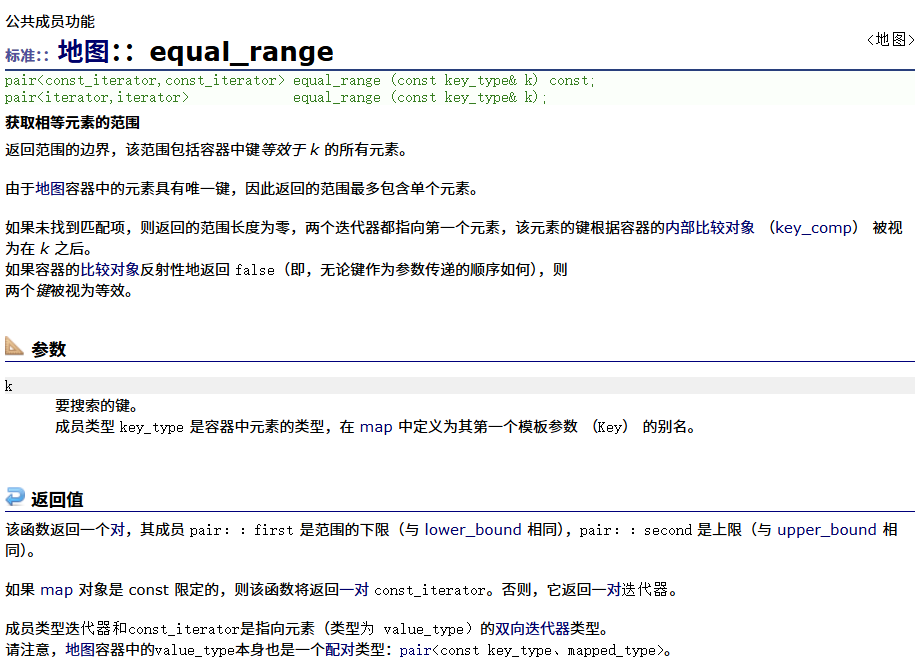
? ? ? ? 找與key相等的區間[x,y)。
? ? ? ? 主要適合于multimap
multimap和map的區別
????????multimap和map的使?基本完全類似,主要區別點在于multimap?持關鍵值key冗余,那么insert/find/count/erase都圍繞著?持關鍵值key冗余有所差異,這?跟set和multiset完全?樣,?如find時,有多個key,返回中序第?個。其次就是multimap不?持[],因為?持key冗余,[]就只能?持插?了,不能?持修改。
map相關的習題
? ? ? ? 隨機鏈表的復制
????????
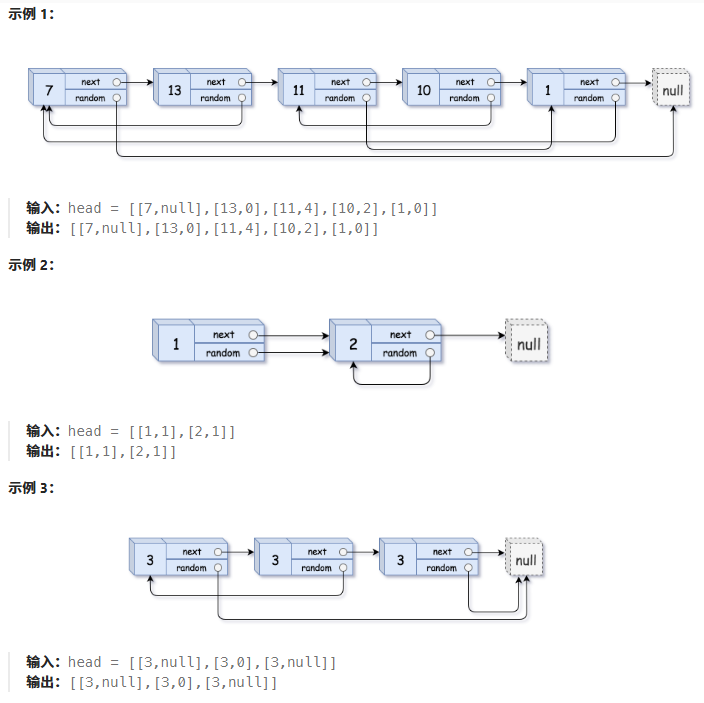
思路:拷貝節點在原節點后面
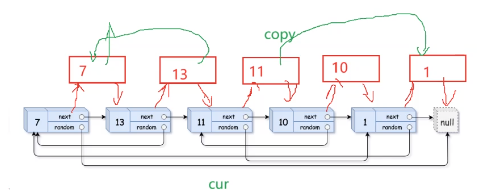
? ? ? ? 關鍵的地方在于:copy->random=cur->random->next
? ? ? ? 步驟:? ? ? ?
????????1、拷貝節點插在原節點后面
? ? ? ? 2、原節點random控制新節點的random
? ? ? ? 3、將新節點解下來鏈接到上面
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:int val;Node* next;Node* random;Node(int _val) {val = _val;next = NULL;random = NULL;}
};
*/class Solution
{
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {map<Node*, Node*> nodeMap;Node* copyhead = nullptr,*copytail = nullptr;Node* cur = head;while(cur){if(copytail == nullptr){copyhead = copytail = new Node(cur->val);} else{copytail->next = new Node(cur->val);copytail = copytail->next;} // 原節點和拷?節點map kv存儲nodeMap[cur] = copytail;cur = cur->next;} // 處理randomcur = head;Node* copy = copyhead;while(cur){if(cur->random == nullptr){copy->random = nullptr;} else{copy->random = nodeMap[cur->random];} cur = cur->next;copy = copy->next;} return copyhead;}
};? ? ? ? 前k個高頻詞匯
????????
????????
class Solution
{
public://老方法:stable_sort函數(穩定排序)// 仿函數// struct compare// {// bool operator()(const pair<string ,int>&kv1,const pair<string ,int>&kv2)// {// return kv1.second>kv2.second;// }// };// vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) // {// map<string ,int>countMap;// for(auto& str:words)// {// //統計次數// countMap[str]++;// }// //數據量很大的時候要建小堆// //數據量不大用大堆// //但是這里要按頻率所以不建議用小堆// //用排序和大堆都差不多// //不可以用sort直接去排序// //sort要求是隨機迭代器,只用string、vector、deque支持// vector<pair<string,int>>v(countMap.begin(),countMap.end());// //sort(v.begin(),v.end(),compare());// //sort不是一個穩定的排序// stable_sort(v.begin(),v.end(),compare());//穩定的排序算法// vector<string>ret;// //取出k個// for(int i=0;i<k;i++)// {// ret.push_back(v[i].first);// }// return ret;//方法二:仿函數//仿函數// struct compare// {// bool operator()(const pair<string ,int>&kv1,const pair<string ,int>&kv2)// {// return kv1.second>kv2.second||(kv1.second==kv2.second&&kv1.first<kv2.first);// }// };// vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) // {// map<string ,int>countMap;// for(auto& str:words)// {// //統計次數// countMap[str]++;// }// //數據量很大的時候要建小堆// //數據量不大用大堆// //但是這里要按頻率所以不建議用小堆// //用排序和大堆都差不多// //不可以用sort直接去排序// //sort要求是隨機迭代器,只用string、vector、deque支持// vector<pair<string,int>>v(countMap.begin(),countMap.end());// //仿函數可以控制比較邏輯// sort(v.begin(),v.end(),compare());//穩定的排序算法// vector<string>ret;// //取出k個// for(int i=0;i<k;i++)// {// ret.push_back(v[i].first);// }// return ret;//方法三:優先級隊列struct compare{bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& kv1, const pair<string, int>& kv2) const{// 比較邏輯:頻率高優先,頻率相同則字典序小優先return kv1.second < kv2.second ||(kv1.second == kv2.second && kv1.first > kv2.first);}};vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k){map<string, int> countMap;for (auto& str : words){countMap[str]++;}//數據量很大的時候要建小堆//數據量不大用大堆//但是這里要按頻率所以不建議用小堆//用排序和大堆都差不多//不可以用sort直接去排序//sort要求是隨機迭代器,只用string、vector、deque支持//建立大堆//priority_queue默認為大堆//不寫仿函數的時候priority_queue按pair比,pair默認按小于比priority_queue<pair<string, int>, // - 元素類型: pair<string, int>vector<pair<string, int>>, // - 容器類型: vector<pair<string, int>>compare> // - 比較器類型: compare (去掉括號)pq(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());vector<string> ret;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){ret.push_back(pq.top().first);pq.pop();}return ret;}
};? ? ? ? 本期內容就到這里了,喜歡請點個贊謝謝。
封面圖自取:
 ? ? ?
? ? ?
![[學習] CORDIC算法詳解:從數學原理到反正切計算實戰](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[學習] CORDIC算法詳解:從數學原理到反正切計算實戰)








的定義與使用)

)







