文章目錄
- 前言
- 1.什么是棧(Stack)?
- 2. 棧的模擬實現
- 3.stack的使用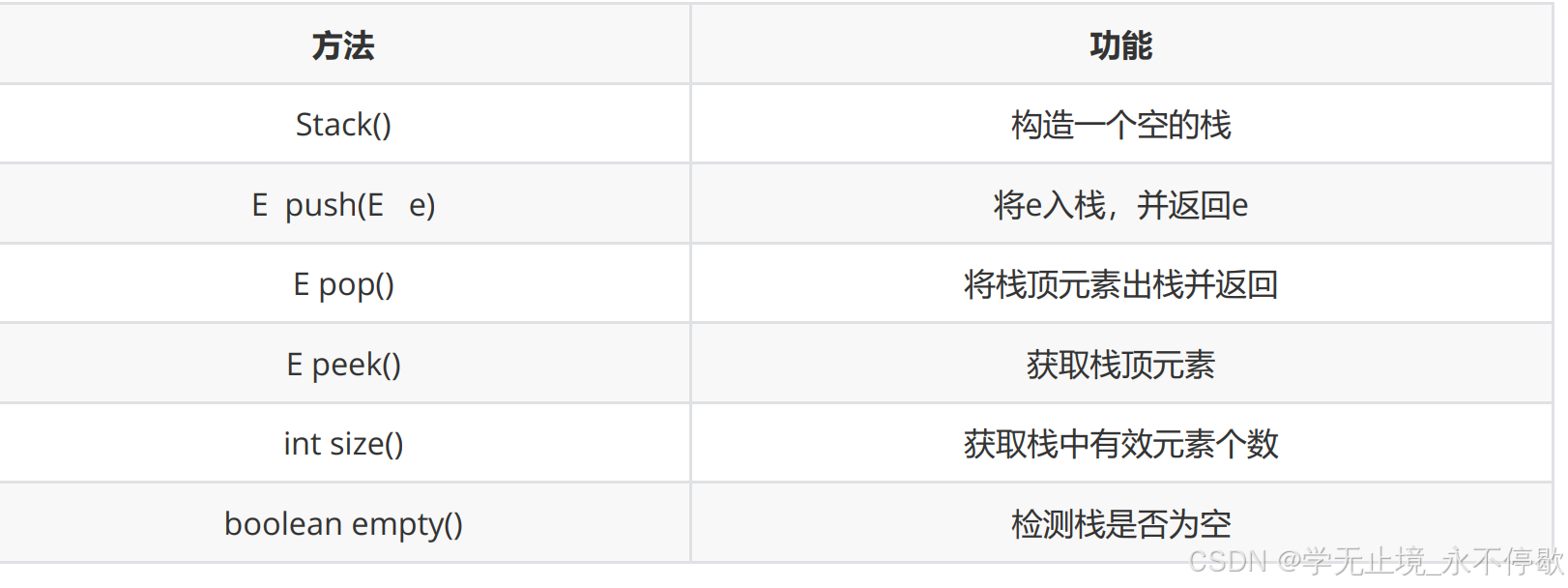
- 4.關于棧的oj題
- 4.1.有效的括號
- 4.2.逆波蘭表達式
- 4.3.棧的壓入、彈出序列
- 4.4.最小棧
前言
前面幾篇我們學習了順序表以及鏈表的模擬使用,和一些oj題,下面我們學習兩個比較特別的數據結構—棧和隊列。
由于篇幅的限制,這一次,我們先學習棧。
1.什么是棧(Stack)?
棧:一種特殊的線性表,其只允許在固定的一端進行插入和刪除元素操作。進行數據插入和刪除操作的一端稱為棧頂,另一端稱為棧底。棧中的數據元素遵守后進先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原則。
壓棧:棧的插入操作叫做進棧/壓棧/入棧,入數據在棧頂。
出棧:棧的刪除操作叫做出棧。出數據在棧頂。

棧在現實生活中的例子:

2. 棧的模擬實現
底層使用順序表進行維護,以次實現下面功能。

public class MyStack {public int[] elem;public int useSize;public MyStack(){this.elem = new int[10];}public void push(int data){if (isFull()){this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);}elem[useSize++] = data;}public boolean isFull(){return useSize == this.elem.length;}public int pop(){if (isEmpty()){throw new EmptyStackException();}int val = elem[useSize-1];useSize--;return val;}public int peek(){if (isEmpty()){throw new EmptyStackException();}return elem[useSize - 1];}public boolean isEmpty(){return useSize == 0;}
}
其主要邏輯跟順序表的一模一樣,可以先把之前順序表的重新再看一遍,再過來看上述代碼,就迎刃而解了。
3.stack的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {Stack<Integer> stack= new Stack();stack.push(1);stack.push(2);stack.push(3);stack.push(4);System.out.println(stack.size()); // 獲取棧中有效元素個數---> 4System.out.println(stack.peek()); // 獲取棧頂元素---> 4stack.pop(); // 4出棧,棧中剩余1 2 3,棧頂元素為3System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 3出棧,棧中剩余1 2 棧頂元素為3if(stack.empty()){System.out.println("棧空");}else{System.out.println(stack.size());}}
4.關于棧的oj題
4.1.有效的括號


class Solution {public boolean isValid(String s) {Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++){char ch = s.charAt(i);if (ch == '('||ch == '{'||ch == '['){stack.push(ch);}else{if (stack.isEmpty()){return false;}char chr = stack.peek();if ((chr=='['&&ch ==']')||(chr == '('&& ch == ')')||(chr == '{')&&(ch == '}')){stack.pop();}else{return false;}}}if(!stack.isEmpty()) {return false;}return true; }
}
4.2.逆波蘭表達式


首先要學習什么是逆波蘭表達式,又稱為后綴表達式,而波蘭表達式,稱為中綴表達式。
中綴表達式:有利于人們閱讀與表達。
后綴表達式,有利于機器進行運算。
咱們舉一個中綴表達式轉化為后綴表達式的一個例子。
中綴表達式:a + b * c + ( d * e + f ) * g
后綴表達式:abc* + de* f + g* +
怎么進行轉化的?

然后后綴表達式轉化為中綴表達式,并且把值算出來,就是用棧來實現。

class Solution {public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();for (String str : tokens) {if (!operation(str)) {int x = Integer.parseInt(str);stack.push(x);} else {// 要注意 val1 和 val2 的位置int val2 = stack.pop();int val1 = stack.pop();switch (str) {case "+":stack.push(val1 + val2);break;case "-":stack.push(val1 - val2);break;case "*":stack.push(val1 * val2);break;case "/":stack.push(val1 / val2);break;}}}return stack.pop();}public boolean operation(String str) {if (str.equals("+") || str.equals("-")|| str.equals("*") || str.equals("/")) {return true;}return false;}
}
4.3.棧的壓入、彈出序列


import java.util.*;public class Solution {/*** 代碼中的類名、方法名、參數名已經指定,請勿修改,直接返回方法規定的值即可** * @param pushV int整型一維數組 * @param popV int整型一維數組 * @return bool布爾型*/public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();int i = 0;int j = 0;while(i < pushV.length){stack.push(pushV[i]);while(j < popV.length&&!stack.empty()&&stack.peek() == popV[j]){stack.pop();j++;}i++;}return stack.empty();}
}
4.4.最小棧



class MinStack {public Stack<Integer> stack;public Stack<Integer> minstack;public MinStack() {stack = new Stack();minstack = new Stack();}public void push(int val) {stack.push(val);if (minstack.isEmpty()){minstack.push(val);}else{int peek = minstack.peek();if (val <= peek){minstack.push(val);}}}public void pop() {if (minstack.isEmpty()){return;}int popVal = stack.pop();if (popVal == minstack.peek()){minstack.pop();}}public int top() {if (stack.isEmpty()){return -1;}return stack.peek();}public int getMin() {if (minstack.isEmpty()){return -1;}return minstack.peek();}
}
下一篇我們學習隊列的使用,我們不見不散!
)


)


 takes 1 positional argument but 2 were given)


)

)

——字符函數和字符串函數)





(Easy-x))