
?
3.無頭單向非循環鏈表實現:
這里可以把方法先寫在一個接口中,再通過MyLinkList實現接口,這樣寫可能更好,代碼好復用。
public class MyLinkList {public int data;public MyLinkList.Node next;//靜態內部類public static class Node {public int data;//0public Node next;//引用類型默認值為NULLpublic Node(int data) {this.data = data;}}
}public void addFirst(int data) {//第一次插入節點(鏈表為空)if (this.head == null) {Node node = new Node(data);//鏈表頭為空時(head == null),整了鏈表的頭引用為 nodethis.head = node;return;}//鏈表不為空,單鏈表插入要先綁后面Node node = new Node(data);node.next = this.head;head = node;//把node的引用給head,然head變成新的頭}(2)尾插法:
public void addList(int data) {//第一次插入時if (this.head == null) {Node node = new Node(data);head = node;return;}Node node = new Node(data);Node cur = this.head;//cur從頭開始/*這里注意cur不可以先走到空,如果cur走到null,那么cur的next就是cull*/while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}//出來時cur==null,就尾插cur.next = node;}(3)打印單鏈表:這里我們可以寫一個,重載方法display2,可以讓鏈表從返回的某個節點開始打印;
//打印單鏈表public void display2(Node nodeH) {Node cur = this.head;//cur從頭開始cur = nodeH;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.data + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}public void display() {Node cur = this.head;//cur從頭開始while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.data + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}
(4)查找鏈表中是否包含某一數據節點:
//查找是否包含關鍵字Key,是否在鏈表中public boolean contains(int key) {Node cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.data == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}?
public void clear() {Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {//注意定義一個,變量記住置為空的,后驅節點Node curN = cur.next;cur.next =null;//引用類型必須制空cur = curN;}//最后把頭節點手動置為nullhead = null;}(6).返回鏈表的長度:
public int size() {Node cur = this.head;int count = 0;//count不能為1,如果是空鏈表,count=1返回就,寄了while (cur != null) {cur = cur.next;count++;}return count;}(7)任意位置插入:這里我畫了個圖來理解:

//任意位置插入(第一個數據節點為0號下標)public void addIndex(int index, int data) {//相當于頭插if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}//相當于尾插if (index == this.size()) {addList(data);return;}//正常插入方法:/*** 1. 先找到index前一個節點的地址->定義一個cur走index-1步* 2.畫圖插入*///先找到index前一個節點的地址Node cur = searchIndex(index);//插入Node node = new Node(data);/*** 這里注意,先綁后面(node = cur.next;),因為單鏈表前一個節點負責,單獨的維護后一個節點,前一個節點的引用被覆蓋(cur節點)* 那么原本和cur節點連接的節點就找不到了*/node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}//找到index前一個節點的地址的方法private Node searchIndex(int index) {//index下標位置檢驗if (index < 0 || index > this.size()) {throw new RuntimeException("下標位置不合法");}Node cur = this.head;while (index-1 != 0/*走index-1步*/) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;//返回走index-1步后的,cur類型地址} //找key節點的前驅private Node searchPrev(int key) {Node prev = this.head;while(prev.next != null) {if (prev.next.data == key) {return prev;}else {prev = prev.next;//繼續往后走}}return null;}//刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點public void remove(int key) {/** 1. 找到,要刪除節點del的前驅* 2. 找到要刪除的節點del* 3. 刪除節點*///空節點直接返回if (this.head == null) {return;}//頭節點直接刪除if (this.head.data == key) {head = head.next;return;//這里注意別忘記了}//1. 找到,要刪除節點del的前驅Node prev = searchPrev(key);if (prev == null) {throw new RuntimeException("沒有你要刪除的節點,請考量要刪除的節點");}//2. 找到要刪除的節點delNode del = prev.next;//3. 刪除節點prev.next = del.next;}(9)只遍歷一遍鏈表,刪除所有指定的節點:這里我畫了一個圖可以幫助理解:定義一個一直往后走的快指針,和一個,不需要時往后走,判斷是否要刪除的慢指針

//遍歷單鏈表一遍,刪除所有值為key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key) {/** 1.定義一個快指針 cur : cur指針一直往后走;* 2.定義一個慢指針 prev: prev指針,只有cur遇到要刪除的數據時,prev指針才往后走,不然保持不動* 3.注意最后不要漏了,head頭節點*/// 1.定義一個 cur指針 : cur指針一直往后走// 2.定義一個 prev指針: prev指針,只有cur遇到要刪除的數據時,prev指針才往后走,不然保持不動Node cur = this.head.next;//Node prev = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.data == key) {//cur.data == key,時只有cur指針都在走,因為要遍歷刪除數據prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {//cur.data != key,兩個指針都在動,prev指針,指向cur指針prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}// 3.注意最后不要漏了,head頭節點if (this.head.data == key) {this.head = this.head.next;}}反轉一個鏈表
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode cur = head;if(head == null) {return null;}head = null;while(cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = curN;}return head;}
}
2.給定一個帶有頭結點 head 的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間結點。如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點:
理解視頻:找到鏈表中間節點-CSDN直播
找到鏈表中間節點
class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return null;}ListNode fast = head;//快指針一次走2步ListNode slow = head;//慢指針一次走一步
//條件不可以交換:(fast != null && slow.next != null),fast可能開始就為nullwhile (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
}3.將兩個有序鏈表合并為一個新的有序鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的:
理解視頻:合并兩個有序鏈表-CSDN直播
合并兩個有序鏈表
?
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode headH = new ListNode(-1);ListNode tmp = headH;//tmp用來遍歷兩個鏈表while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {//哪個節點數據小,就接在tmp后面if(list1.val < list2.val) {tmp.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;tmp = tmp.next;}else {tmp.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;tmp = tmp.next;}}//當其中一個鏈表遍歷完,就直接接上另一個鏈表的后半部分if(list1 != null) {tmp.next = list1;}if(list2 != null) {tmp.next = list2;}return headH.next;}
}4.鏈表的回文結構:
這里有兩個點要注意:1.從后往前用slow走,因為偶數節點,fast指針會走到null,無法往前走。
?2.回文時偶數情況下,A的下一個節點是slow節點,并且兩個節點的val相等。這個時候就要直接返回ture
理解視頻:鏈表的回文結構-CSDN直播
鏈表的回文結構
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {// write code hereif (A == null) {return true;}// write code hereListNode fast = A;ListNode slow = A;//1.找到中間節點while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//2.翻轉鏈表ListNode cur = slow.next;while (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur = curN;}//3.判斷回文//讓A往后走,slow往前走直到;A.val==slow.val//注意:回文時會有偶數情況下,A的下一個節點是slow節點,并且兩個節點的val相等。這個時候就要直接返回turewhile (A != slow) {if (A.val != slow.val) {return false;}//到這里A.val == slow.val//A.val == slow.val前提下,偶數情況下,A的下一個節點是slow節點,并且兩個節點的val相等。這個時候就要直接返回tureif (A.next == slow) {return true;}A = A.next;slow = slow.next;}return true;}
}
?
5.編寫代碼,以給定值x為基準將鏈表分割成兩部分,所有小于x的結點排在大于或等于x的結點之前:
注意:這里我的方法是,改完后,鏈表數據從小到大的,而做題在牛客網是,要求反過來(但是方法都一樣)
理解視頻:鏈表分割-CSDN直播
鏈表分割
//鏈表的分割public Node partition(Node pHead, int x) {Node as = null;Node ae = null;Node bs = null;Node be = null;Node cur = pHead;while (cur != null) {if (cur.data > x) {//第一次插入if (as == null) {as = ae = cur;}else {//第N次插入ae.next = cur;ae = ae.next;}} else {//第一次插入if (bs == null) {bs = be = cur;}else{//第N次插入be.next = cur;be = be.next;}}cur = cur.next;}//當一個鏈表為空時,返回if(as == null) {return bs;}//如果到這里as!= null//連接兩部分ae.next = bs;//注意,第二部分結尾不為空時,要手動把第二部分最后一個節點,手動制空if(bs != null) {be.next = null;}//最后返回asreturn bs;}
6.給定一個鏈表,返回鏈表開始入環的第一個節點。 如果鏈表無環返回空 :
方法是:第一次相遇點,到入口點的距離,等于起始點到入口點的距離
這里我畫了這個圖的推到:

public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;// 方法:第一次相遇點,到入口點的距離,等于起始點到入口點的距離while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {break;}}/**1.走到這里,要么不滿足{(fast != null && fast.next != null)}就是沒有環;2. 要么就是有環*///沒有環if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {return null;}/**有環:讓slow以和fast以相同的速度,從起始點到入口點,fast從第一次相遇的成環點走到入口點*/slow = head;//把slow返回起始點while(slow != fast) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow;}
}
7.輸入兩個鏈表,找出它們的第一個公共結點:
方法:先找到哪個鏈表長,再讓長的鏈表先走,他們的差值步,最后兩個鏈表一起走,直到他們第一次相遇。
public class Solution {public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {//1.先分別求出兩個鏈表的長度ListNode pl = pHead1;ListNode ps = pHead2;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while (pl != null) {lenA++;pl = pl.next;}while (ps != null) {lenB++;ps = ps.next;}//注意pl和ps,指向了null,要賦值回來pl = pHead1;ps = pHead2;//2.求差值int len = lenA - lenB;if (len < 0) {pl = pHead2;ps = pHead1;len = lenB - lenA;//len變為為正數}//現在知道pl指向長的鏈表,ps指向短的鏈表//3.操作兩個鏈表pl和ps,長的鏈表(pl)先走鏈表的差值,然后再一起走直到相交while (len != 0) {pl = pl.next;len--;}//兩個鏈表分別都走,直到他們相遇while (pl != ps) {pl = pl.next;ps = ps.next;}if (pl == null) {//pl,ps為空,也不可能相交return null;}return pl;}
}
?
?
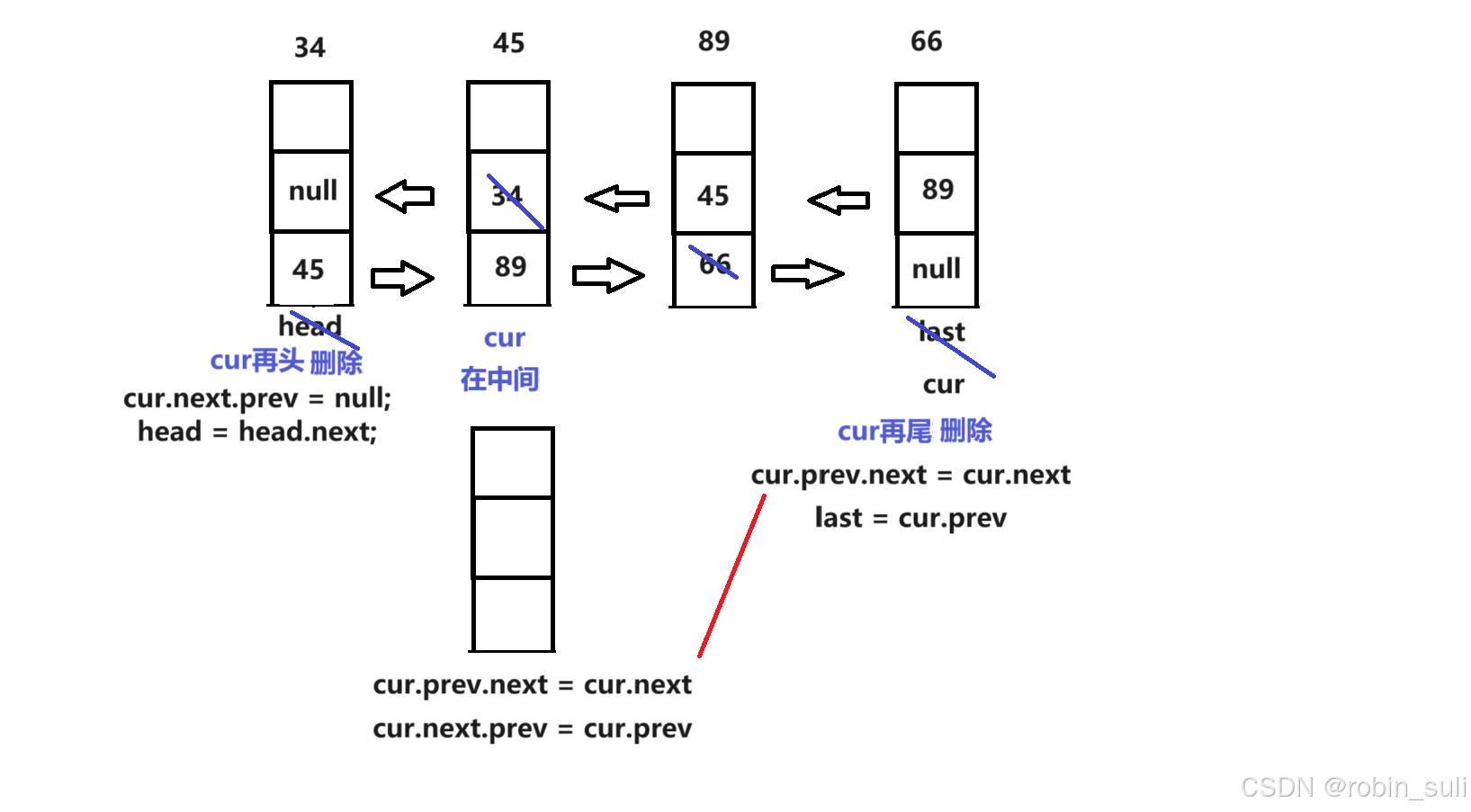
public class MyLinkList implements IList{static class ListNode{public int val;public ListNode prev;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//頭節點public ListNode last;//尾節點@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if (head == null) {head = last = node;}else {//所有的插入優先綁定后面node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}}@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if (head == null) {head = last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = last.next;}}@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {int len = size();if (index > len || index < 0) {return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);}ListNode cur = findIndex(index);ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = cur;cur.prev.next = node;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = node;}private ListNode findIndex(int index) {ListNode cur = head;while (index != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == head) {//當只有一個節點要刪除時if (head == null) {cur.next.prev = null;}head = head.next;//刪除就走人return;}else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;//優化后,刪除中間和尾巴的代碼if (cur == last) {last = cur.prev;}else {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}//刪除就走人return;}}cur = cur.next;}}@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == head) {//當只有一個節點要刪除時,cur.next.prev = null會為空,所以加上if判斷if (head == null) {cur.next.prev = null;}head = head.next;//刪除不能走人,接著刪除后面。}else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;//優化后,刪除中間和尾巴的代碼if (cur == last) {last = cur.prev;}else {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}//刪除不能走人,接著刪除后面。}}cur = cur.next;}}@Overridepublic int size() {ListNode cur = head;int len = 0;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur.prev = null;cur = curN;}//注意head和last節點在鏈表中還被引用著head = last = null;}
}
總結:
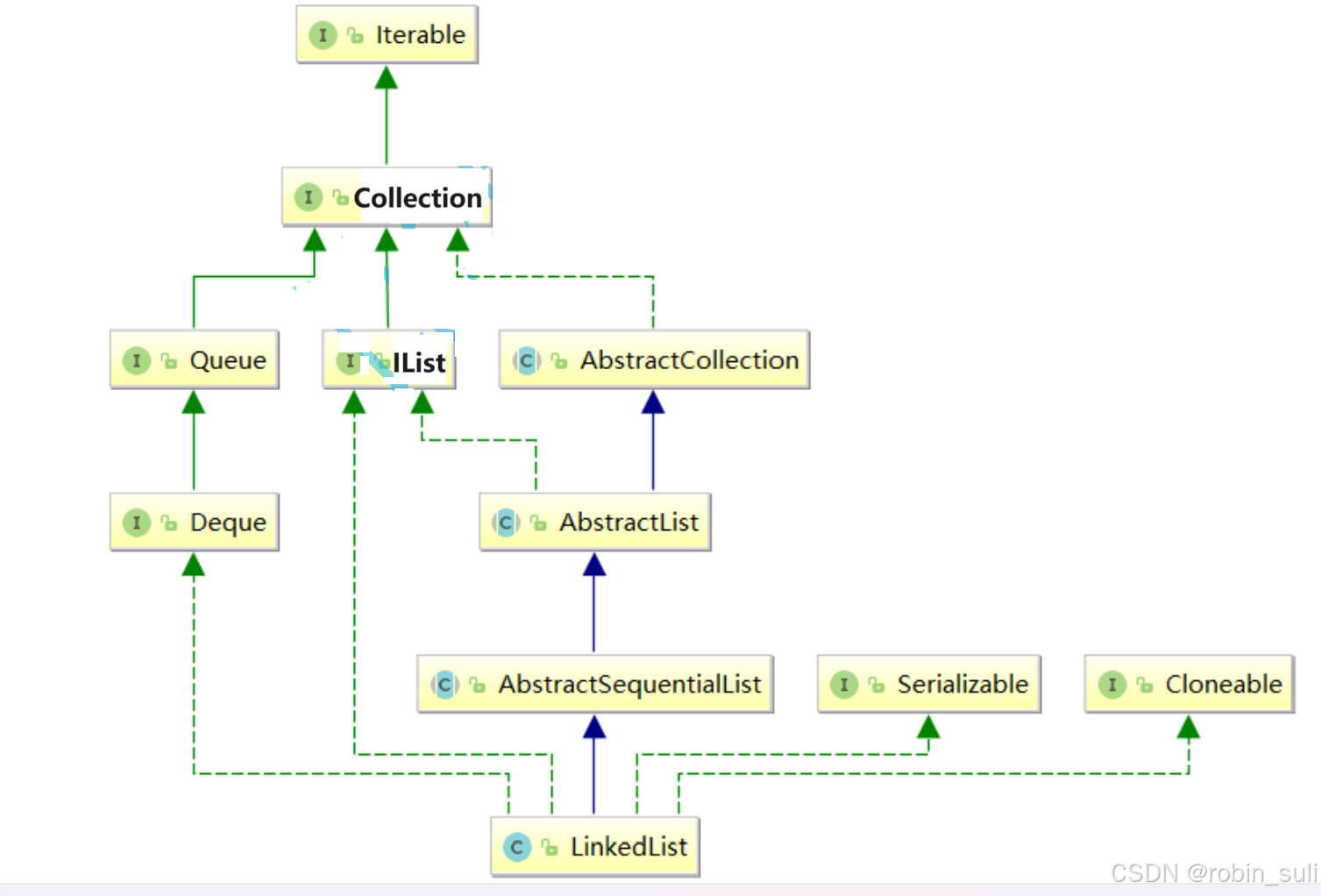
2. LinkedList的底層使用了雙向鏈表
3. LinkedList沒有實現RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持隨機訪問
5. LinkedList比較適合任意位置插入的場景
?

public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);System.out.println(list);ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();list1.add(11);list1.add(12);list1.add(13);System.out.println("==============");list.addAll(list1);System.out.println(list);}
}輸出:

5.LinkedList的遍歷:ListIterator是Iterator的一個子類,可以專門用來打印鏈表
代碼如下:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);System.out.println(list);ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();list1.add(11);list1.add(12);list1.add(13);System.out.println("foreach遍歷");for (Integer x:list) {System.out.print(x + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("迭代器遍歷歷");Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}/*** ListIterator是Iterator的一個子類,可以專門用來打印鏈表*/System.out.println();System.out.println("使用迭代器遍歷---正向遍歷");ListIterator<Integer> it1 = list.listIterator();while (it1.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it1.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("使用反向迭代器---反向遍歷");ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator(/*這里要傳鏈表的長度*/ list.size());while (it2.hasPrevious()) {System.out.print(it2.previous() + " ");}}
}
?
?六.ArrayList和LinkedList的區別:

? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?



![BUUCTF逆向wp [HDCTF2019]Maze](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BUUCTF逆向wp [HDCTF2019]Maze)








--容器概述和序列概述)



)


