Profile應用
- 一、何為Profile
- 二、profile配置方式
- 1.多profile文件方式
- 2.yml多文檔方式
- 三、加載順序
- 1. file:./config/: 當前項目下的/config目錄下
- 2. file:./ :當前項目的根目錄
- 3. classpath:/config/:classpath的/config目錄
- 4. classpath:/ : classpath的根目錄
- 四、profile激活方式
- 1. 配置文件
- 2. 虛擬機參數
- 3. 命令行參數
- 五、測試類編寫
- 1. 不同目錄下的編寫
- 2. 同目錄下
- 六.導入redis
一、何為Profile
在開發springboot應用時。通常一套程序會被安裝在不同環境中(比如開發,測試,生產),其中數據庫地址,服務器端口等等配置都不同,如果每次打包是,都要修改配置文件,就會非常麻煩,profile可以進行動態配置切換
二、profile配置方式
1.多profile文件方式
applicatio.yml
---server:port: 8081spring:profiles: dev
---server:port: 8082spring:profiles: test
---
server:port: 8083spring:profiles: pro
每一個框內都是一組配置
激活使用
---
spring:profiles:active: dev
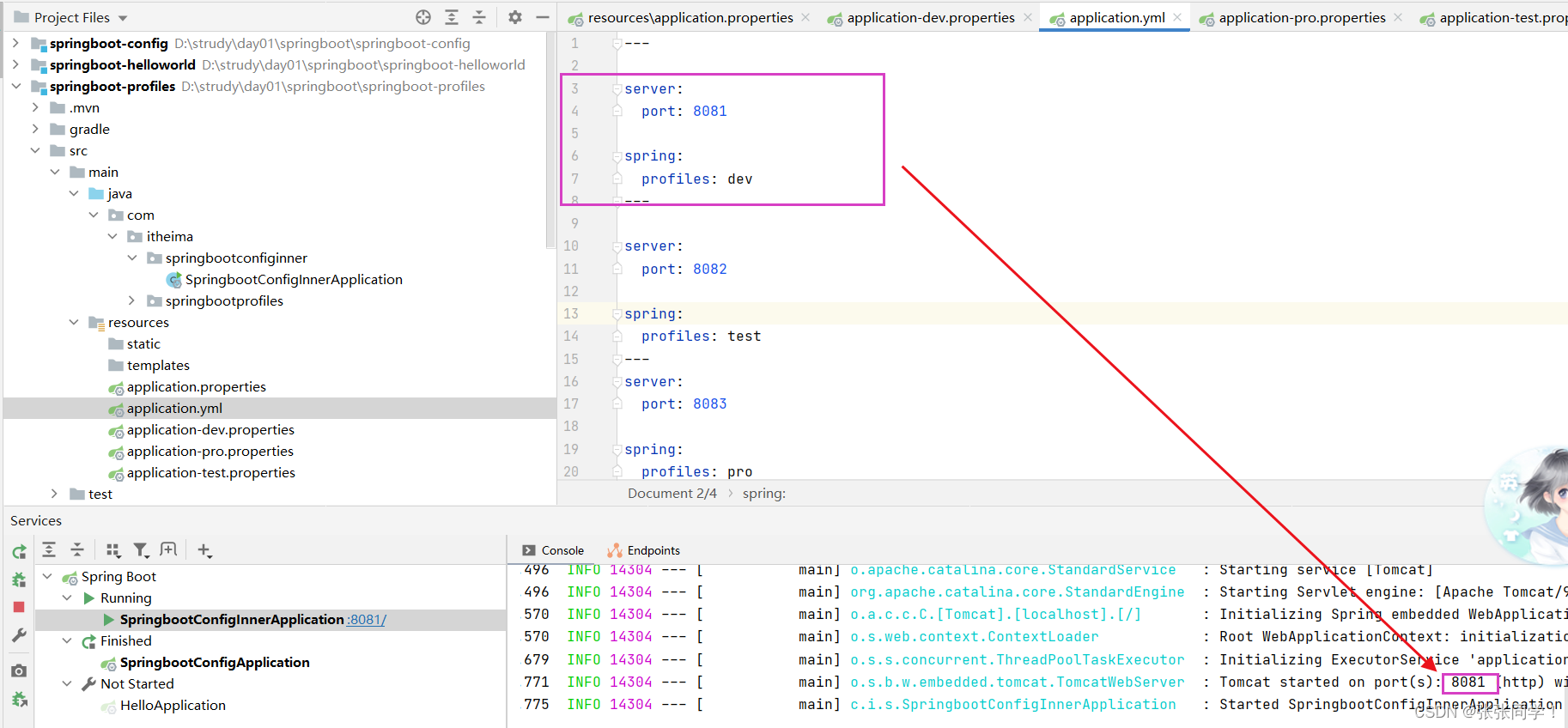
2.yml多文檔方式
三、加載順序
1. file:./config/: 當前項目下的/config目錄下
2. file:./ :當前項目的根目錄
3. classpath:/config/:classpath的/config目錄
4. classpath:/ : classpath的根目錄
高優先級屬性會生效,但是每個文件都會讀取,只是生效與否
四、profile激活方式
1. 配置文件
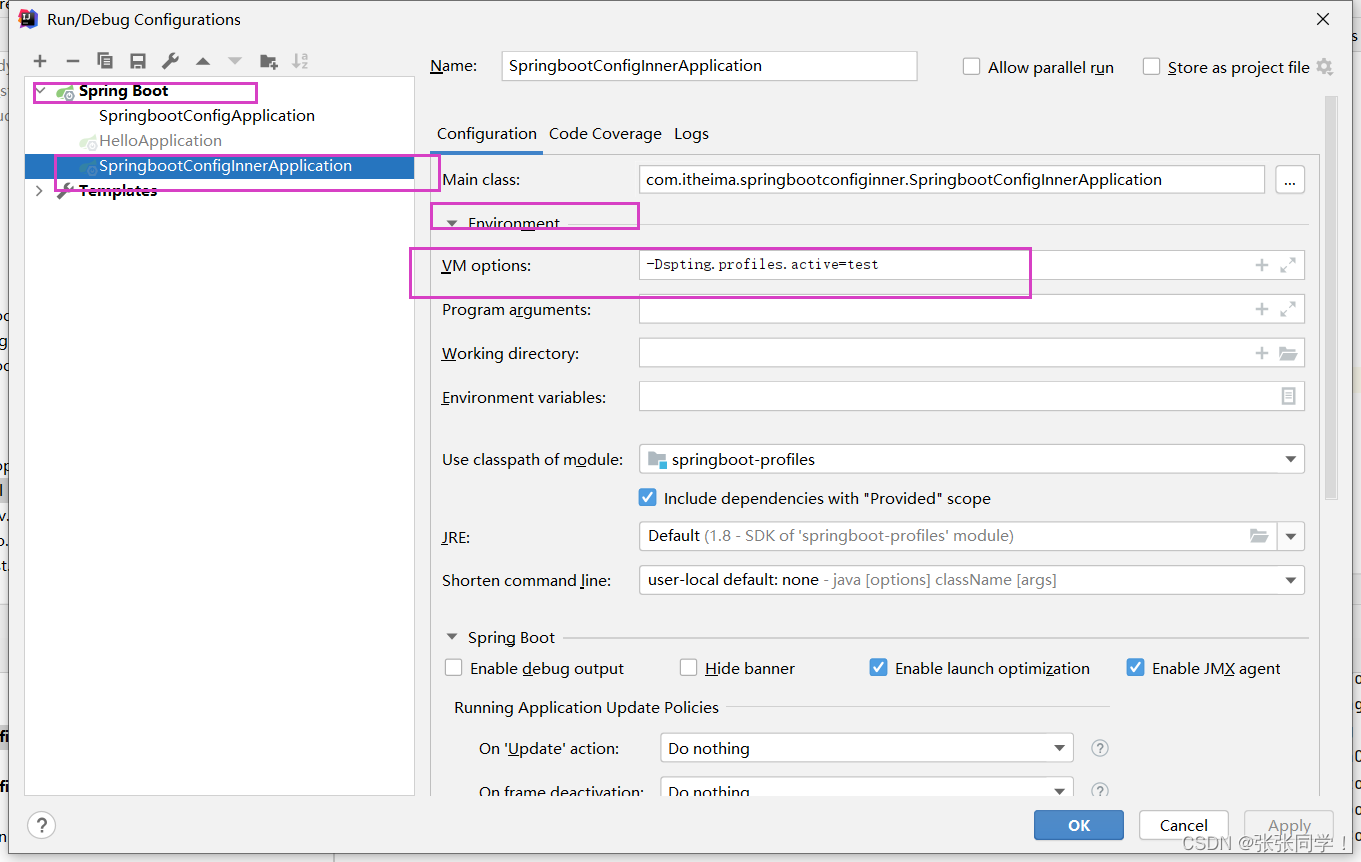
2. 虛擬機參數
部署方法
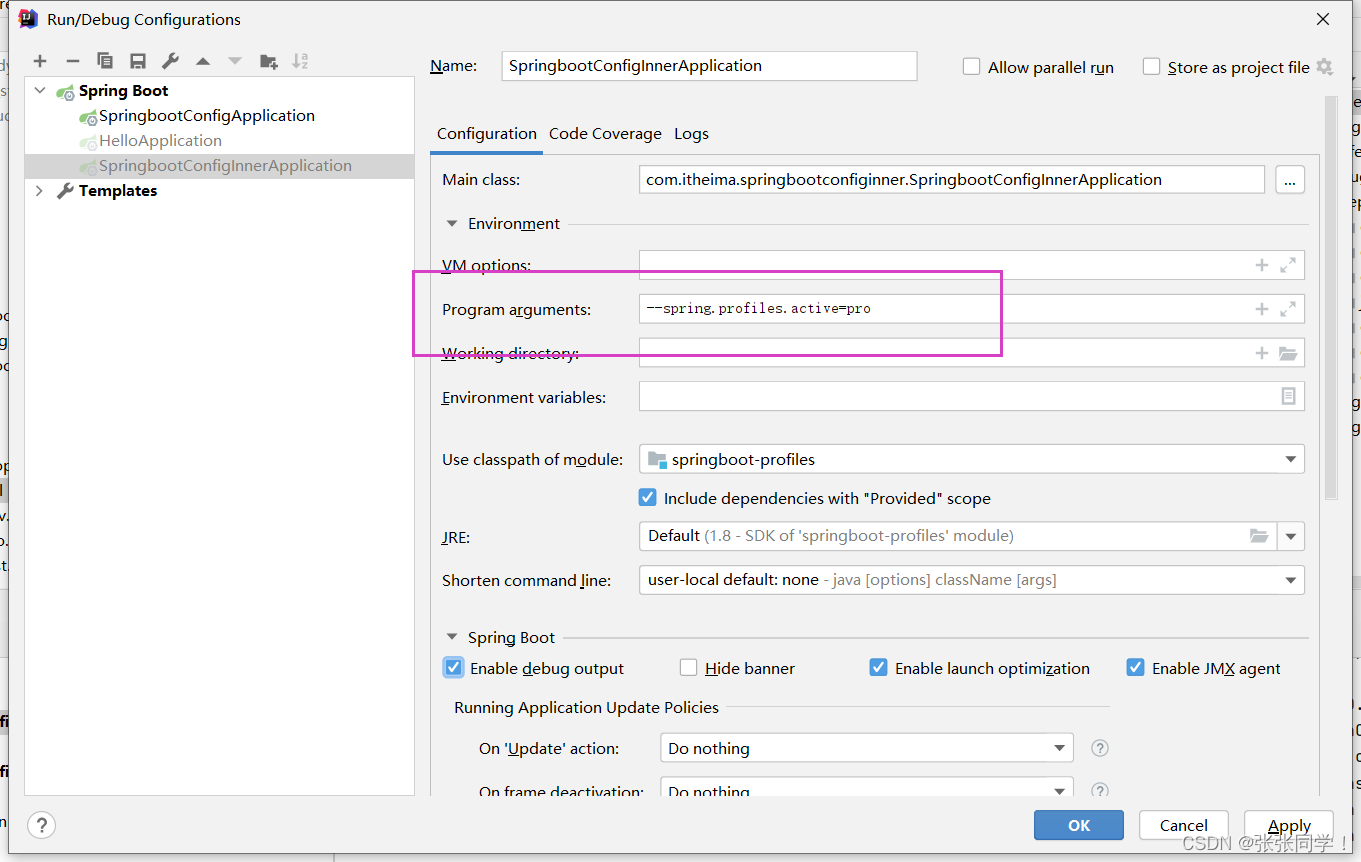
3. 命令行參數
五、測試類編寫
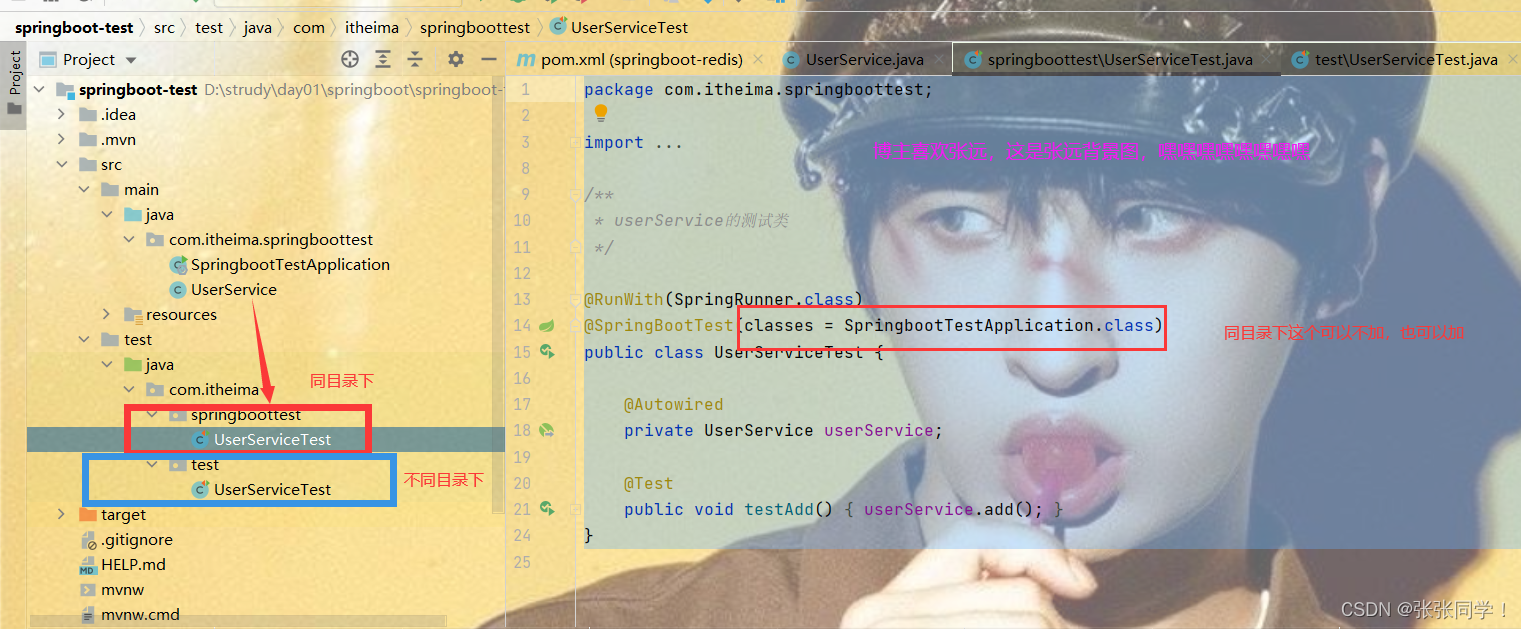
1. 不同目錄下的編寫
若目錄com.itheima.springboottest.UserService方法
package com.itheima.springboottest;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {public void add() {System.out.println("add...");}
}測試類目錄為com.itheima.test.UserServiceTest 與上面不一致,一個是applicationtest一個是test
package com.itheima.test;import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;/*** userService的測試類*/@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootTestApplication.class)
# 不同目錄,這里的classes不可以省略
public class UserServiceTest {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Testpublic void testAdd() {userService.add();}
}-
RunWith通常是一個用于測試的編程概念,特別是在框架如JUnit(Java Unit Testing Framework)或.NET的Moq、NUnit等中。RunWith的作用是用來標記或裝飾測試方法,告訴測試運行器如何執行這個特定的測試。例如,在JUnit中,@RunWith(Suite.class)表明該測試類應該作為一組測試用例的集合(suite)來運行,而不是獨立的測試。
-
在Java中,@ RunWith注解通常放在測試類的定義上方,這樣測試框架就能識別并按照指定的方式運行測試方法。如果你看到RunWith并且是編程相關的上下文,那可能是在討論單元測試或行為驅動開發(BDD)中的測試組織方式。
-
@Autowired 是Spring框架中的一個注解,用于依賴注入(Dependency Injection, DI)機制。它是一個懶加載注解,用于自動裝配bean到其他bean中,簡化了組件之間的依賴管理。當你在一個字段、方法參數或構造器上使用 @Autowired,Spring容器會嘗試找到并注入合適的bean實例,滿足該字段或方法的需求。
-
@Autowired 具體使用時,例如在控制器、服務類或DAO接口等地方,你不再需要顯式地創建和管理這些對象,Spring會在運行時自動完成這個過程。這有助于降低代碼的耦合度,使得組件更加松耦合,提高代碼的可測試性和可用性
2. 同目錄下
package com.itheima.springboottest;import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;/*** userService的測試類*/@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootTestApplication.class)
public class UserServiceTest {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Testpublic void testAdd() {userService.add();}
}











)






:了解Python語言基礎以及數據類型轉換、基礎輸入輸出)
