C語言的語句分為 5 類
- 1:表達式語句
- 2:函數調用語句
- 3:控制語句
- 4:復合語句
- 5:空語句
控制語句:用于控制程序的執行流程,以實現程序的各種結構方式,它們由特定的語句定義符組成,C語言有9種控制語句 。

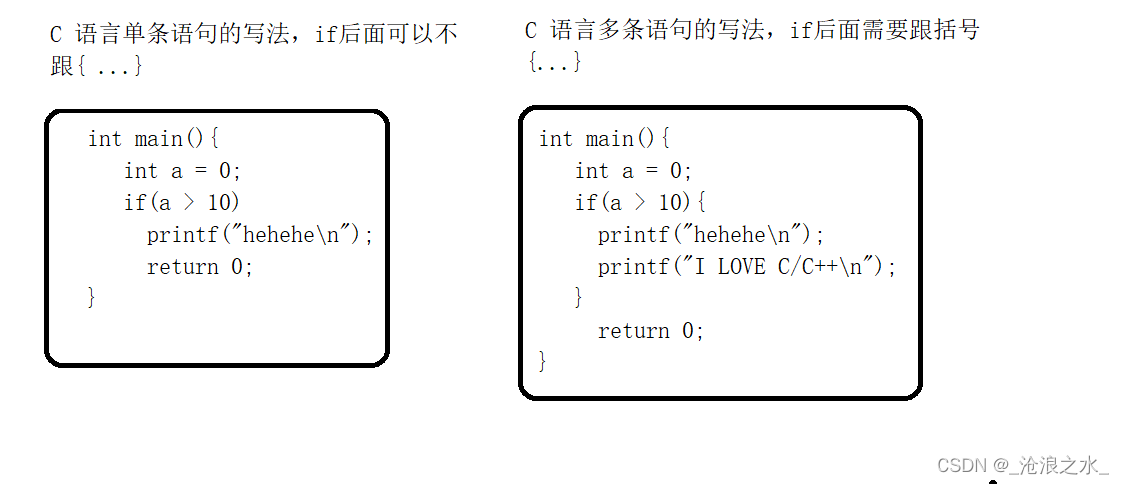
if(表達式){語句
}?if 語句
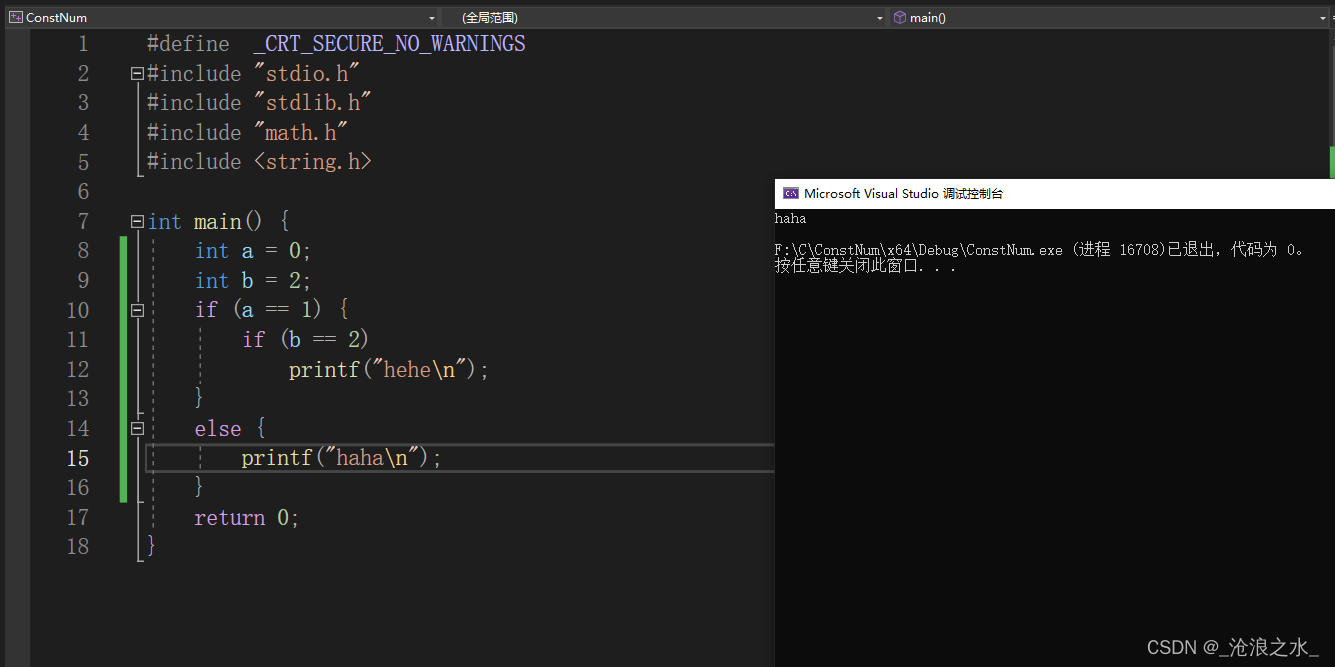
?
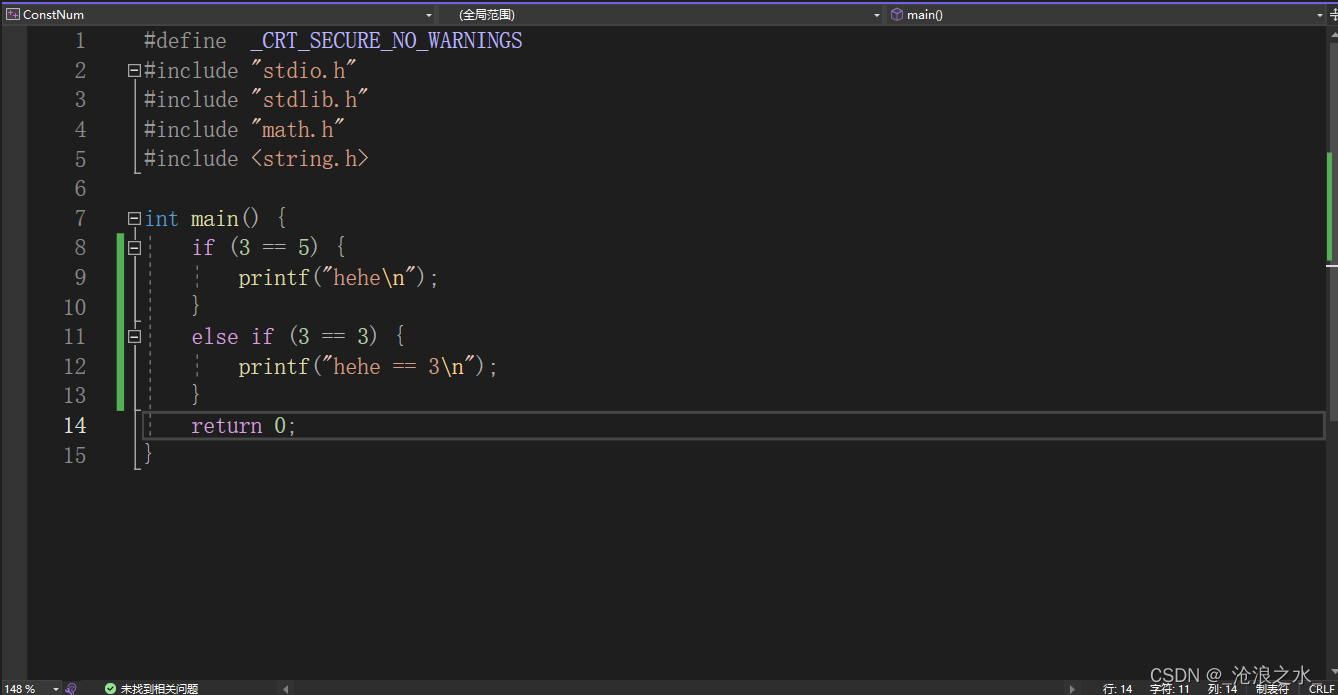
if ------------else 語句
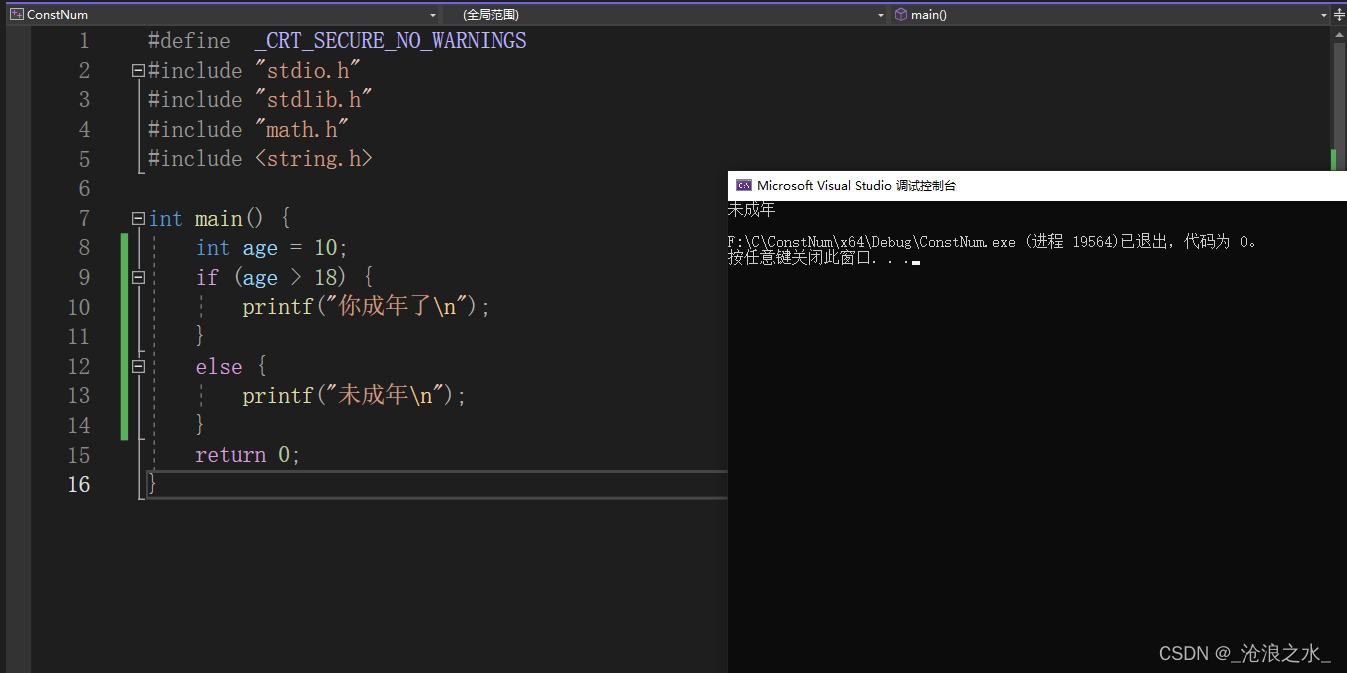
if 實現多分支語句
?
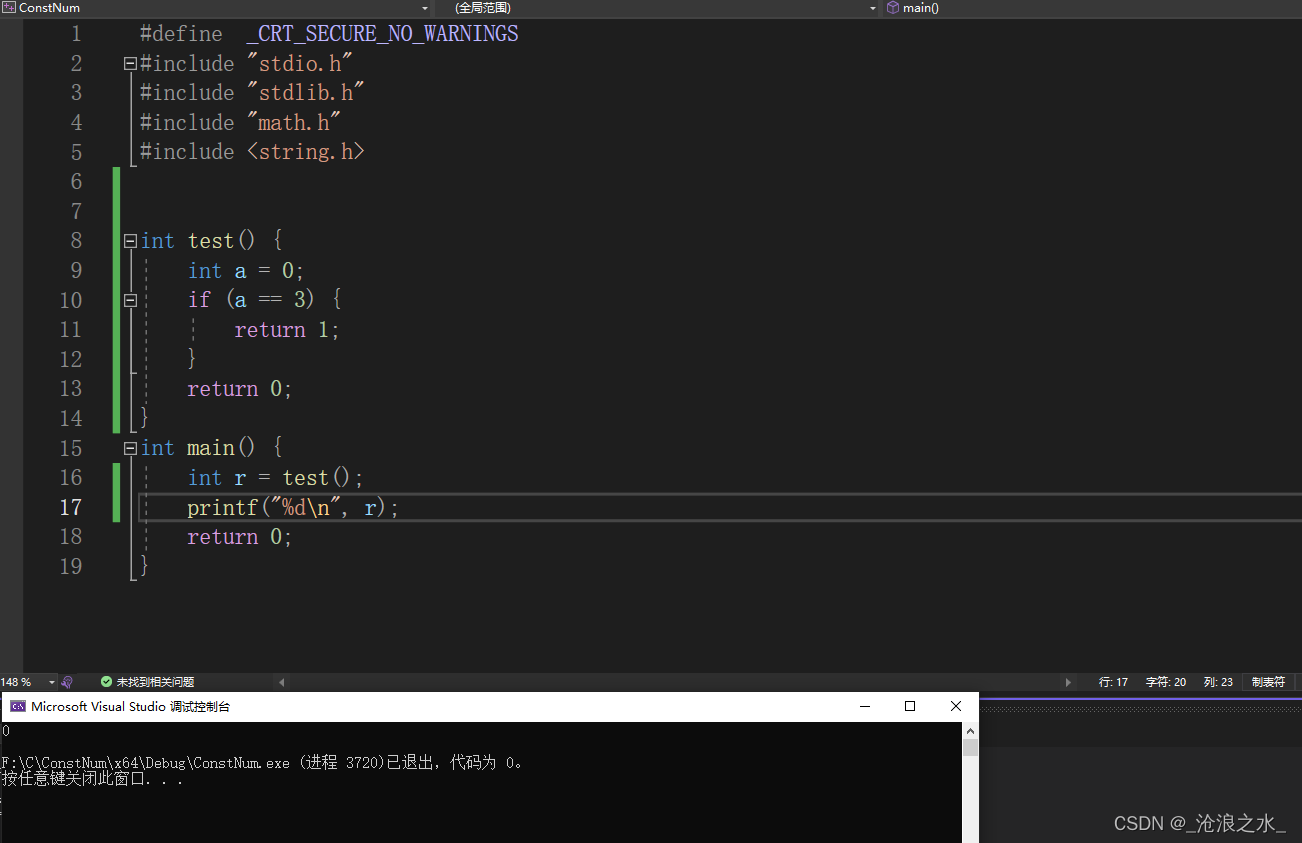
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
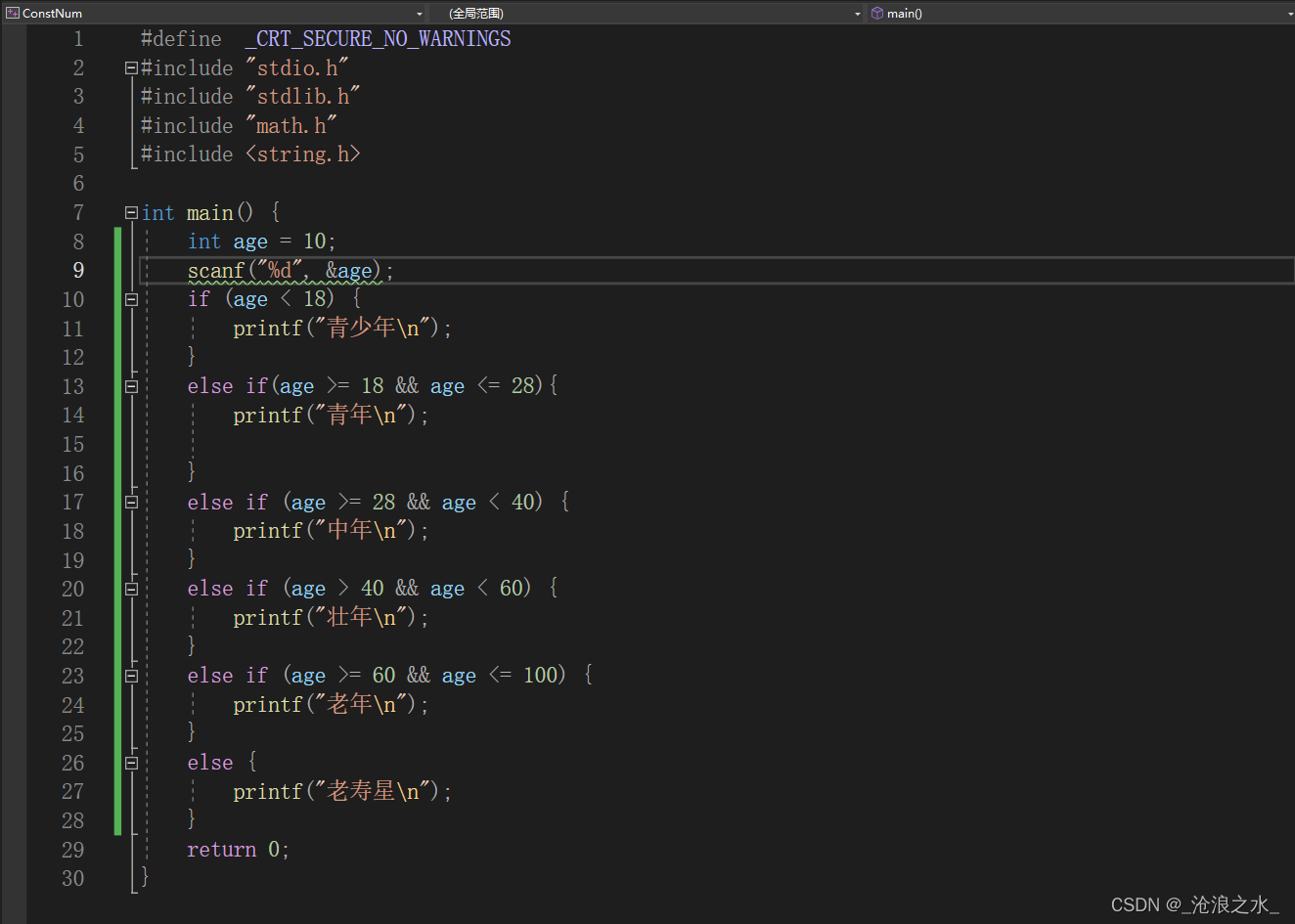
#include <string.h>int main() {int age = 10;scanf("%d", &age);if (age < 18) {printf("青少年\n");}else if(age >= 18 && age <= 28){printf("青年\n");}else if (age >= 28 && age < 40) {printf("中年\n");}else if (age > 40 && age < 60) {printf("壯年\n");}else if (age >= 60 && age <= 100) {printf("老年\n");}else {printf("老壽星\n");}return 0;
}
注:C語言的概念 0 表示假,1表示真,if else 語句在輸出多條語句時需要添加{ }

規范編碼:防止出現一些低級的錯誤
【變量的命名規則】
1:變量的命名要規范,命名見名知義,不能是C語言中的關鍵字,有一點理解障礙 。
好的代碼風格,更容易讓閱讀者理解
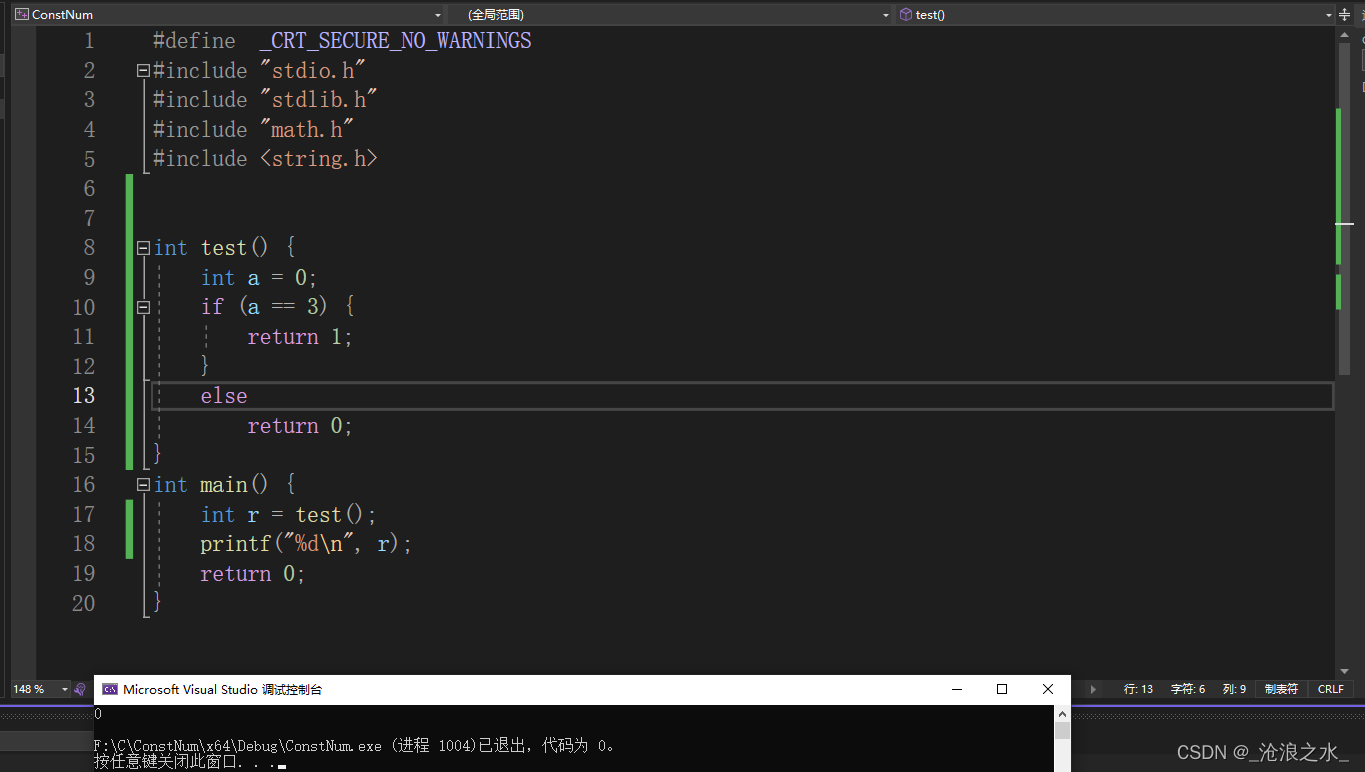
C 語言練習判斷一個數是否為奇數
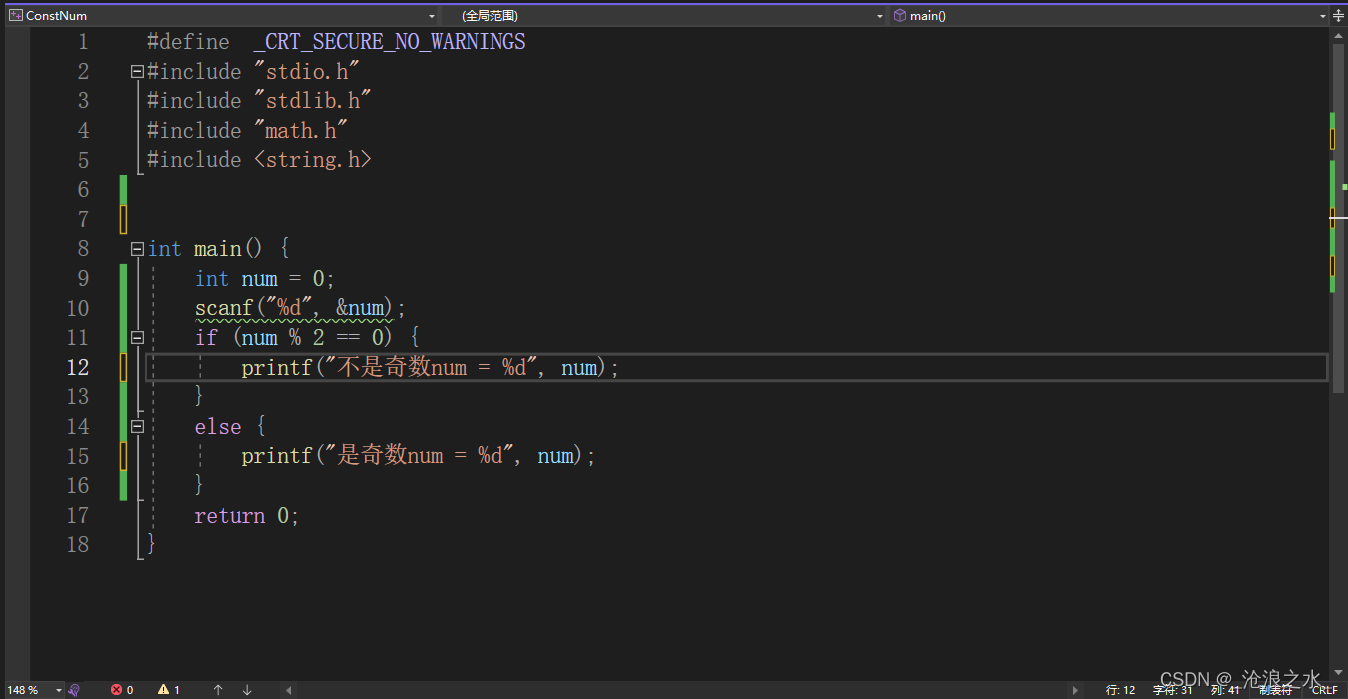
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <string.h>int main() {int num = 0;scanf("%d", &num);if (num % 2 == 0) {printf("不是奇數num = %d", num);}else {printf("是奇數num = %d", num);}return 0;
}【輸出1-100之間的奇數】
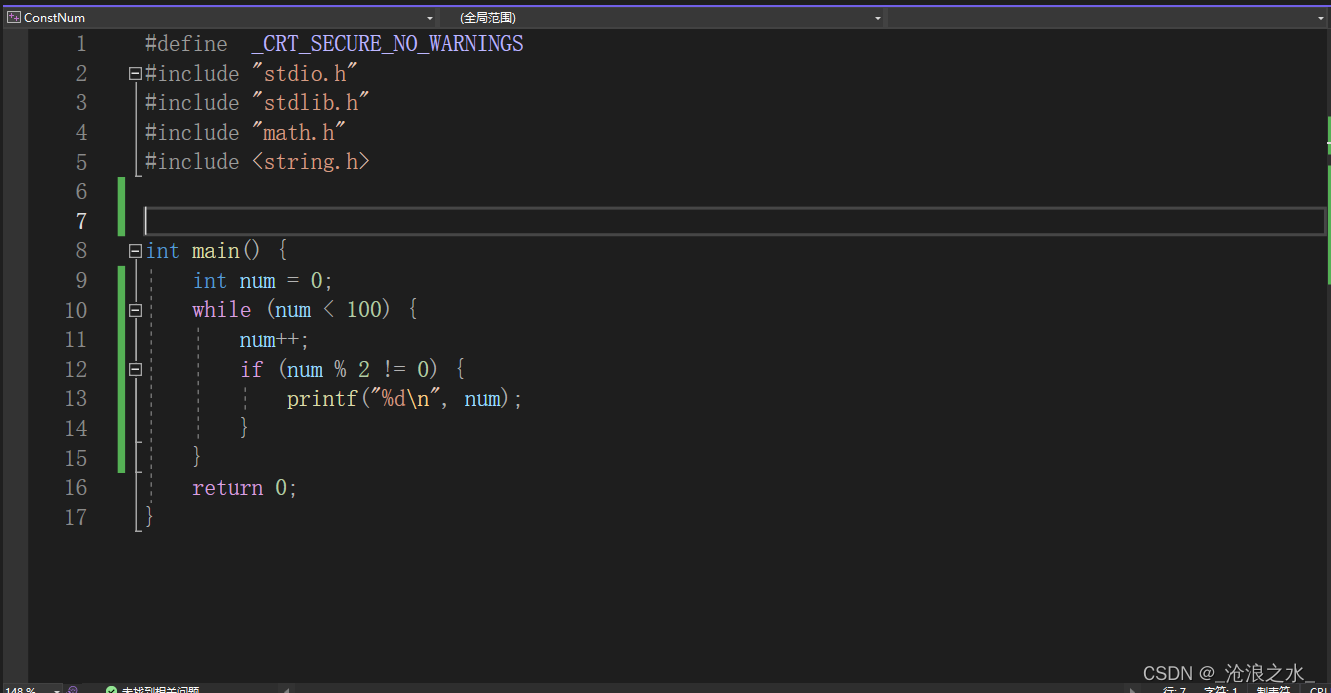
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <string.h>int main() {int num = 0;while (num < 100) {num++;if (num % 2 != 0) {printf("%d\n", num);}}return 0;
}C語言學習方法總結
1:多練才是解藥
2:練習在熟悉語法,語法熟悉才能無障礙的編寫代碼
3:練習就是在鍛煉編程的思維,把實際問題轉換為編寫代碼的能力
4:學會畫圖,理解內存,理解指針
畫圖可以理清思路
畫圖可以輔助理解強化理解
學會調試:調試可以讓我們更好的理解和感知代碼
借助調試:可以讓我們找出代碼中的bug
...............
C語言的 Switch語句
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <string.h>int main() {int day = 5;scanf("%d", &day);if (1 == day) {printf("星期一");}else if (2 == day) {printf("星期二");}else if (3 == day) {printf("星期三");}else if (4 == day) {printf("星期四");}else if (5 == day) {printf("星期五");}else if (6 == day) {printf("星期六");}else if (7 == day) {printf("星期日");}return 0;
}
Switch 語句實現控制輸出:switch語句后面的表達是必須是整型的不能是其他類型,case后面也必須是整型常量表達式 。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <string.h>int main() {int day = 5;scanf("%d", &day);switch (day) {case 1:printf("星期一");break;case 2:printf("星期二");break;case 3:printf("星期三");break;case 4:printf("星期四");break;case 5:printf("星期五");break;case 6:printf("星期六");break;case 7:printf("星期日");break;}return 0;
}
【一種不同的寫法】

C語言的編程習慣
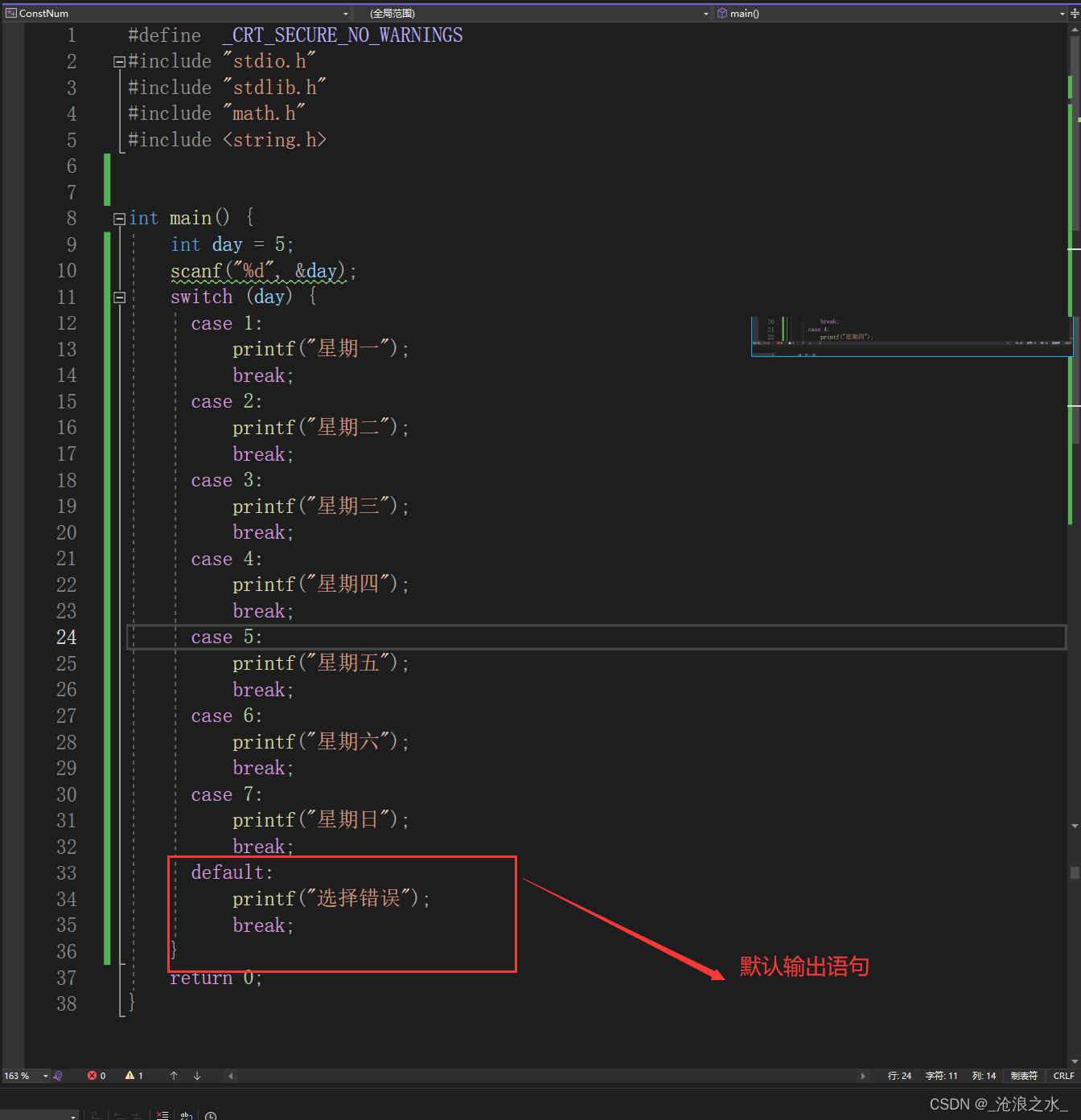
注:case 后面是可以加字符的,因為字符后面是ASCII值,相當于也是一個整型的數
注:switch 語句是可以嵌套使用的,switch語句中的break只能跳出自己所在的switch語句
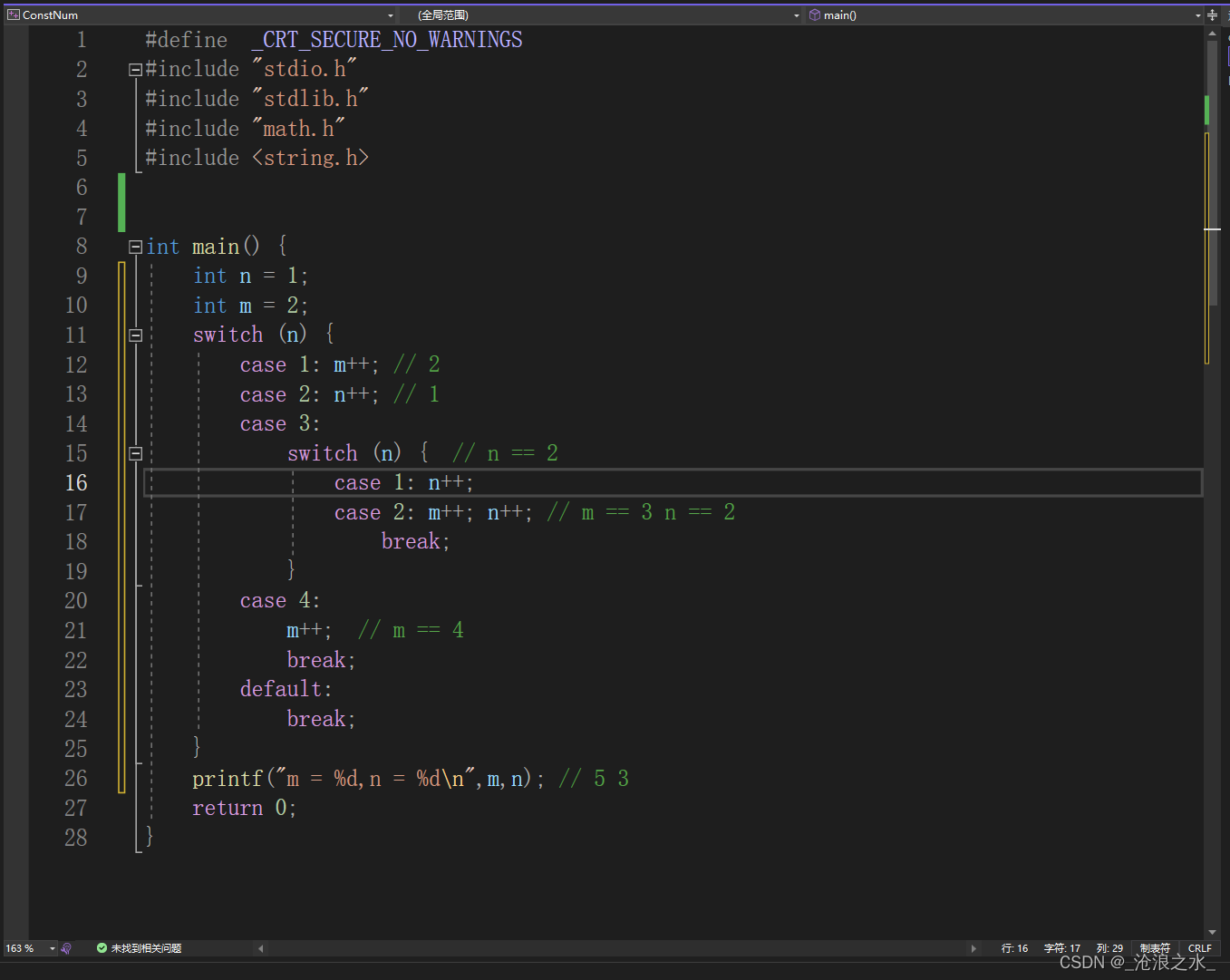
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <string.h>int main() {int n = 1;int m = 2;switch (n) {case 1: m++; // 2case 2: n++; // 1case 3:switch (n) { // n == 2case 1: n++;case 2: m++; n++; // m == 3 n == 2break;}case 4:m++; // m == 4break;default:break;}printf("m = %d,n = %d\n",m,n); // 5 3 return 0;
}


)












)

![[NOVATEK] NT96580行車記錄儀功能學習筆記(持續更新~](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[NOVATEK] NT96580行車記錄儀功能學習筆記(持續更新~)
?JWT的用途和優勢是什么?)