文章目錄
- 前言
- ?一、二叉樹的定義
- 🚲二、創建二叉樹
- 🎡三、二叉樹的銷毀
- 🎉四、遍歷二叉樹
- 1. 前序遍歷
- 2. 中序遍歷
- 3. 后序遍歷
- 4. 層序遍歷
- 🌲五、二叉樹的計算
- 1. 計算二叉樹結點個數
- 2. 計算二叉樹葉子結點的個數
- 3. 計算二叉樹的深度
- 4. 計算二叉樹第k層的結點個數
- 5. 查找二叉樹中值為x的結點
- 6. 判斷二叉樹是否為完全二叉樹
- 🏝?六、整體代碼展示
前言
在學習二叉樹實現時,我們首先要對二叉樹基本認識有一定的了解,下面我總結了以下幾點有關二叉樹的性質以及特點:
🎈每一個節點最多有兩棵子樹,不存在度大于2的節點。
🎈左右子樹是有順序的,其次序不能顛倒。
🎈二叉樹一般有四種形態,分別為:空二叉樹,只有一個根節點,根結點只有左子樹和根節點只有右子樹。
🎈二叉樹常用的三種性質:1)二叉樹的第 i 層上最多有2 ^ (i - 1)個節點;
2)深度為K的二叉樹最多有2 ^ (k - 1)個節點。
3)度為0的節點個數比度為2的節點個數多一個。
?一、二叉樹的定義
二叉樹通常以結構體的形式定義,其結構體內容包括三部分:本節點所存儲的值、左孩子節點的指針以及右孩子節點的指針。這里需要注意,子節點必須使用指針,就像我們定義結構體鏈表一樣,下一個節點必須使用地址的方式存在在結構體當中。
typedef int BTDateType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDateType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
🚲二、創建二叉樹
當我們對二叉樹的掌握還不夠深入時,我們也可以創建一棵簡單的二叉樹,減少時間成本。
// 手搓一個二叉樹
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;
}BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;return node1;
}
而真正的二叉樹創建的過程是這樣的:首先給出一個數組,將要創建的元素放在數組里。然后通過遍歷(前 或 中 或 后序遍歷)的順序訪問并創建二叉樹每個節點,最后返回根節點的地址即創建完成。
我們假設通過前序序列的方式訪問并創建二叉樹:
// 創建樹,按前序遍歷的順序
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDateType* a, int* pi) {if (a[*pi] != '#') // '#'代表葉子結點{BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));root->data = a[*pi];(*pi)++;root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);(*pi)++;root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);return root;}else {return NULL;}
}
🎡三、二叉樹的銷毀
// 銷毀
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{if (root){BinaryTreeDestory(root->left);BinaryTreeDestory(root->right);free(root);root = NULL;}
}
🎉四、遍歷二叉樹
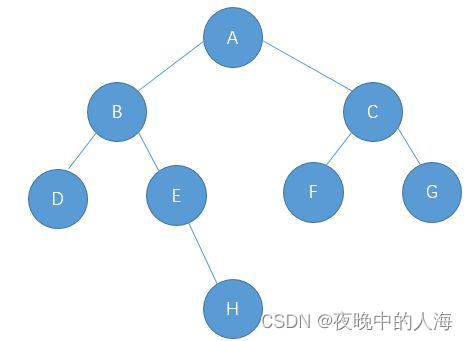
前序遍歷,中序遍歷和后序遍歷,實際上就是指根節點在子節點的先中后的順序不同。以上圖為例:
前序序列:A、B、D、E、H、C、F、G
中序遍歷:D、B、H、E、A、F、C、G
后序遍歷:D、H、E、B、F、G、C、A
這三種遍歷方式,在代碼上面還是非常相似的,只不過遞歸的順序不同。
1. 前序遍歷
先遍歷根結點,再遍歷左子樹,最后遍歷右子樹。
// 前序遍歷
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N "); //打印空節點數據return;}printf("%d ", root->data); // 輸出節點數據PrevOrder(root->left); //遞歸遍歷左子樹節點的數據PrevOrder(root->right); //遞歸遍歷右子樹節點的數據
}
2. 中序遍歷
先遍歷左子樹,再遍歷根結點,最后遍歷右子樹。
// 中序遍歷
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N "); //打印空節點數據return;}InOrder(root->left); //遞歸遍歷左子樹節點的數據printf("%d ", root->data); //輸出節點數據InOrder(root->right); //遞歸遍歷右子樹節點的數據
}
3. 后序遍歷
先遍歷左子樹,再遍歷右子樹,最后遍歷根結點。
// 后序遍歷
void EndingepilogueOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N "); //打印空節點數據return;}EndingepiloguePrevOrder(root->left); //遞歸遍歷左子樹節點的數據EndingepiloguePrevOrder(root->right); //遞歸遍歷右子樹節點的數據printf("%d ", root->data); //輸出節點數據
}
4. 層序遍歷
層序遍歷的做法和上述遍歷做法不同,不能簡單的調用遞歸來遍歷,而是要借用到隊列來輔助實現。隊列的實現我就不在敘述了,層序遍歷代碼所示:
// 層序遍歷
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Quene q;QueneInit(&q);if (root){QuenePush(&q, root); //存入根節點}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)) //隊列不為空就循環{BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q); //取出隊列中的第一個節點QuenePop(&q); //刪除第一個節點printf("%d ", front->data); //打印取出來第一個節點的數據if (front->left){QuenePush(&q, front->left); //如果左子樹不為空,就將左子樹存入隊列}if (front->right){QuenePush(&q, front->right); //如果右子樹不為空,就將右子樹存入隊列}}QueneDesTroy(&q);
}
🌲五、二叉樹的計算
1. 計算二叉樹結點個數
計算二叉樹的結點個數,只需要將左子樹的結點個數加上右子樹的結點個數,最后再加上根結點就完成了。
int TreeSide(BTNode* root)
{return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSide(root->left) + TreeSide(root->right) + 1; //運用條件表達式,如果根結點為空就返回0,否則就遞歸調用遍歷左子樹和右子樹的結點個數,兩者相加,最后再加一個最上面的根結點。
}
2. 計算二叉樹葉子結點的個數
首先要明白什么是葉子結點,實際上就是度為0的結點即孩子結點。
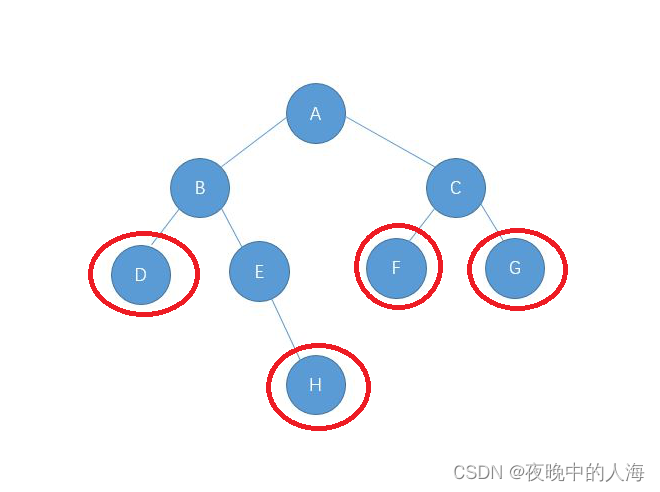
如上圖,D、H、F、G都為葉子結點。代碼展示:
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0; //空樹返回0}else if (TreeLeafSize(root->left)== NULL && TreeLeafSize(root->right) == NULL){return 1; //只含有根節點就返回1}return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right); ///遞歸調用遍歷左子樹和右子樹的葉子數,兩者相加
}
3. 計算二叉樹的深度
什么是二叉樹的深度呢?簡單的來說就是左子樹或者右子樹的深度+1。
// 求樹的深度
int TreeHight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int highleft = TreeHight(root->left); //獲取左子樹的深度int highright = TreeHight(root->right); //獲得右子樹的深度return highleft > highright ? highleft + 1 : highright + 1; //運用條件表達式,返回左子樹和右子樹中較大的深度+1
}
4. 計算二叉樹第k層的結點個數
實現這一操作的核心思路,就是要知道:求當前樹的第k層結點個數 = 左子樹的第k - 1層的結點個數 + 右子樹的第k-1層的結點個數。
// 二叉樹第k層節點個數
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0; // 空樹返回0}if (k == 1){return 1; //第一層為根節點返回1}return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
5. 查找二叉樹中值為x的結點
這里需要注意的是,我們要記錄查找到的結點,否則當我們想要返回所找到的結點數據,卻發現又要重新遞歸去找,時間會消耗好幾倍,因此需要記錄找到的結點數據
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDateType x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->data == x){return root;}BTNode* left = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);if (left != NULL)return left;BTNode* right = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);if (right != NULL)return right;// 左右子樹都沒有return NULL;
}
6. 判斷二叉樹是否為完全二叉樹
按照層序遍歷的方式遍歷完全二叉樹,當我們遍歷到空結點時,就開始判斷。如果隊列中還有空,就不是完全二叉樹
// 判斷二叉樹是否為完全二叉樹
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Quene q;QueneInit(&q);if (root){QuenePush(&q, root);}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q);QuenePop(&q);// 遇到第一個空就開始判斷,如果隊列中還有空,就不是完全二叉樹if (front == NULL){break;}QuenePush(&q, front->left);QuenePush(&q, front->right);}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q);QuenePop(&q);// 如果有非空,就不是完全二叉樹if (front){QueneDesTroy(&q);return false;}}QueneDesTroy(&q);return true;
}
🏝?六、整體代碼展示
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include "Quene.h"typedef int BTDateType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDateType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;// 手搓一個二叉樹BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;
}BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;return node1;
}// 銷毀
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{if (root){BinaryTreeDestory(root->left);BinaryTreeDestory(root->right);free(root);root = NULL;}
}// 層序遍歷
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Quene q;QueneInit(&q);if (root){QuenePush(&q, root);}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q);QuenePop(&q);printf("%d ", front->data);if (front->left){QuenePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right){QuenePush(&q, front->right);}}QueneDesTroy(&q);
}// 前序遍歷
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N ");return;}printf("%d ", root->data);PrevOrder(root->left);PrevOrder(root->right);
}// 中序遍歷
void InPrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N ");return;}InPrevOrder(root->left);printf("%d ", root->data);InPrevOrder(root->right);
}// 后序遍歷
void EndingepiloguePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("N ");return;}EndingepiloguePrevOrder(root->left);EndingepiloguePrevOrder(root->right);printf("%d ", root->data);
}int TreeSide(BTNode* root)
{return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSide(root->left) + TreeSide(root->right) + 1;
}// 求葉子結點的個數
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}else if (TreeLeafSize(root->left)== NULL && TreeLeafSize(root->right) == NULL){return 1;}return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}// 求樹的深度
int TreeHight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int highleft = TreeHight(root->left);int highright = TreeHight(root->right);return highleft > highright ? highleft + 1 : highright + 1;
}// 二叉樹第k層節點個數
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}// 二叉樹查找值為x的節點
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDateType x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->data == x){return root;}BTNode* left = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);if (left != NULL)return left;BTNode* right = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);if (right != NULL)return right;// 左右子樹都沒有return NULL;
}// 判斷二叉樹是否為完全二叉樹
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Quene q;QueneInit(&q);if (root){QuenePush(&q, root);}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q);QuenePop(&q);// 遇到第一個空就開始判斷,如果隊列中還有空,就不是完全二叉樹if (front == NULL){break;}QuenePush(&q, front->left);QuenePush(&q, front->right);}while (!QueneEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueneFront(&q);QuenePop(&q);// 如果有非空,就不是完全二叉樹if (front){QueneDesTroy(&q);return false;}}QueneDesTroy(&q);return true;
}int main()
{BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();PrevOrder(root);printf("\n");InPrevOrder(root);printf("\n");EndingepiloguePrevOrder(root);printf("\n");printf("TreeSide:%d\n", TreeSide(root));printf("TreeLeafSize:%d\n", TreeLeafSize(root));printf("TreeHight:%d\n", TreeHight(root));printf("BinaryTreeFind:%p\n", BinaryTreeFind(root,3));printf("BinaryTreeLevelKSize:%d\n", BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root, 3));printf("\n");BinaryTreeLevelOrder(root);return 0;
}
今天的分享就到這里啦,如果感覺內容不錯,記得一鍵三連噢。創作不易,感謝大家的支持,我們下次再見!ヾ( ̄▽ ̄)ByeBye


)
















