- 實驗目的:
- 熟練掌握Shell程序的建立與執行;
- 掌握Shell變量的兩種類型(Shell環境變量和用戶自定義變量)及其用法;
- 掌握Shell中的特殊字符、算術與邏輯運算;
- 掌握Shell中輸入輸出命令;
- 掌握Shell程序控制結構語句。
實驗內容:
在VMware中啟動CentOS7虛擬機后,打開putty或者MobaXterm,遠程登錄root賬號,完成以下任務,截圖并粘貼于以下空行中。
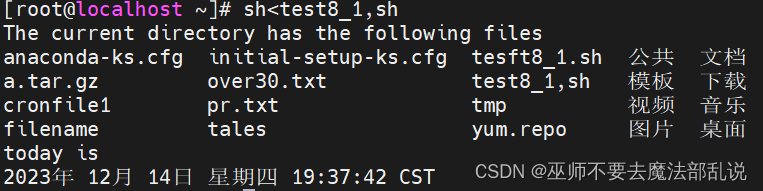
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_1.sh的Shell程序,該程序查看當前目錄和日期(腳本代碼如下),并用給定的三種方式執行。
#!/bin/bash
echo "The current directory has the following files"
ls
echo "today is"
date
sh<程序名
sh?程序名
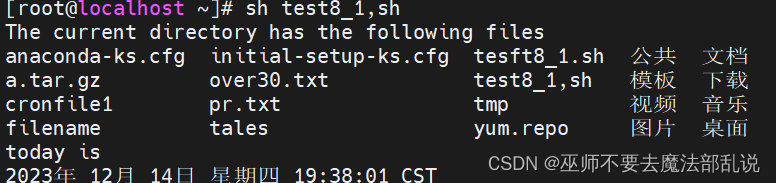
用chmod?a+x 程序名,使該程序成為可執行文件,然后進入該程序文件所在目錄,執行./程序名

說明:在這三種運行Shell程序的方法中,最好按下面的方式選擇:當剛創建一個Shell程序,對它的正確性還沒有把握時,最好使用第一或第二種方式進行調試。當一個Shell程序已經調試好時,應使用第三種方式把它固定下來,以后只要鍵入相應的文件名即可,并可被另一個程序所調用。另外,注意這三種運行方法都是創建一個新的Shell子進程來執行腳本內容。
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_2.sh的Shell程序,該程序在用戶輸入年、月之后,自動打印數出該年該月的日歷。任選一種方法執行該程序。
#!/bin/bash
echo "Please input the month : "
read month
echo "Please input the year : "
read year
cal ??① ???②

Shell編程中,單引號和雙引號是有區別的:單引號里所有字符或字符串都視為一般字符,而雙引號仍然可以保留$、倒引號、反斜線\等特殊功能。比較以下兩個命令的結果。
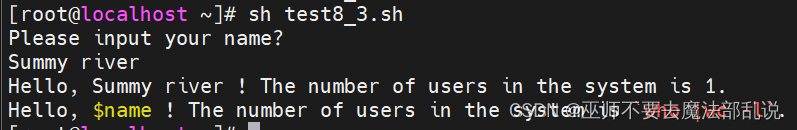
#!/bin/bash
echo "Please input your name?"
read name
echo "Hello, $name ! The number of users in the system is `who |wc -l`."
echo 'Hello, $name ! The number of users in the system is `who |wc -l`.'
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_4.sh的Shell程序,該程序根據用戶輸入的分數判斷成績是否通過考試。
#法1:使用if語句
#!/bin/bash
echo??$score??"please?input?a?score:\c"
read?score
echo?"Your score?is?$score"
if???????[?$score -ge 60 ]; then?????? #變量score的值大于等于60
then?echo?"Congratulation!?You?Pass?the?Examination."
else?echo?"Sorry!?You?Fail?the?Examination!"
?if?

#法2:使用case語句。注意理解由通配符和“|”隔開的多個模式組成的表達式。
#!/bin/bash
echo ?$score??"please input a score:\c"
read score
echo "Your score is $score"
case ?$scorr???in?
?[0-9]|[1-5][0-9]) echo "Sorry! You Fail the Examination!" ;; ?#0-9或者10-59
?[6-9][0-9]|100) echo "Congratulation! You Pass the Examination." ;; ?#60-99或者100
?esac?

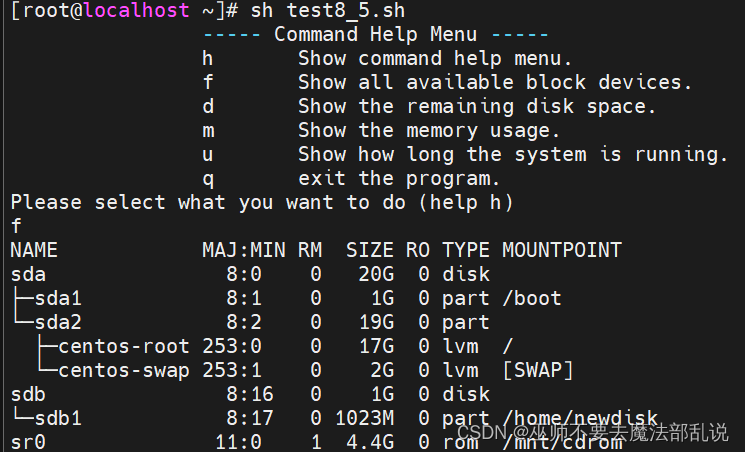
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_5.sh的Shell程序,該程序模擬一個多任務維護界面,當執行程序先顯示菜單,然后進行選擇后做相應的維護監控操作。顯示菜單使用自定義函數實現。
#!/bin/bash
display()
{
echo " -----?Command Help Menu?-----"
echo " h Show command help?menu. "
echo " f Show all available block devices.?"
echo " d Show the remaining disk space. "
echo " m Show the memory usage. "
echo " u Show how long the system is running. "
echo " q exit the program. "
}
display
while true
do
echo "Please select what you want to do?(help h)"
read action
case ?$action???in?
h) display;;???
f) lsblk;;
d) df -h;;
m) free -m;;
u) uptime;;
q) exit;;
??esac??
??done??
已知變量a=3,b=2,完成以下算術運算,并截圖。
expr方法。注意運算符前后都有空格。
代碼:expr $a - $b,用于計算a與b的差。仿此計算:
a與b的乘積。
a除以b的商。
a除以b的余數。
#!/bin/bash
a=3
b=2
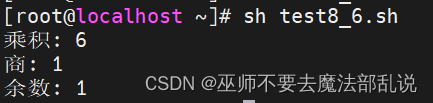
# 計算 a 與 b 的乘積
product=$(expr $a \* $b)
echo "乘積: $product"
# 計算 a 除以 b 的商
quotient=$(expr $a / $b)
echo "商: $quotient"
# 計算 a 除以 b 的余數
remainder=$(expr $a % $b)
echo "余數: $remainder"
let方法。運算符前后不需要有空格,需要結合echo命令輸出結果。
代碼:let c=$a-$b; echo $c,用于計算變量a與b差。仿此計算:
a與b的乘積
a的b次方。符號“**”對兩個變量做冪運算。
#!/bin/bash
a=3
b=2
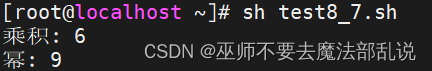
# 計算 a 與 b 的乘積
let c=$a*$b
echo "乘積: $c"
# 計算 a 的 b 次方
let d=$a**$b
echo "冪: $d"
$((表達式))方法。運算符前后不需要有空格,且表達式中的變量前面不需要加上$符號,需要結合echo命令輸出結果。
運行代碼:c=$((a-b)); echo $c,用于計算變量a與b差。仿此計算:
a與b的乘積
a的b次方。符號“**”對兩個變量做冪運算。
#!/bin/bash
a=3
b=2
# 計算 a 與 b 的乘積
c=$((a*b))
echo "乘積: $c"
# 計算 a 的 b 次方
d=$((a**b))
echo "冪: $d"

$[表達式]方法。與$((表達式))方法類似。
運行代碼::c=$[a-b]; echo $c,用于計算變量a與b差。仿此計算:
a與b的乘積
a的b次方。符號“**”對兩個變量做冪運算。
#!/bin/bash
a=3
b=2
# 計算 a 與 b 的乘積
c=$((a*b))
echo "Product: $c"
# 計算 a 的 b 次方
d=$((a**b))
echo "Power: $d"

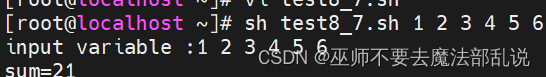
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_7.sh的Shell程序,該程序實現計算用戶輸入命令后的若干個數字參數的和。例如運行sh test8_7.sh 1 2 3,結果是1、2、3的和6。
#法一:用for循環
#!/bin/bash
sum=0
for i #這里for i?完整的寫法應該是????① ???
do
let ????②??????
done
echo sum=??③??
#法二:用while循環和shift命令(注意理解shift命令的用法。供參考)
#!/bin/bash
sum=0
while [ $# -ne 0 ] #這里的$#表示命令后所有參數$1、$2…的總個數
do
let sum=$sum+$1 #想想這里為什么是$1
shift
done
echo sum=$sum

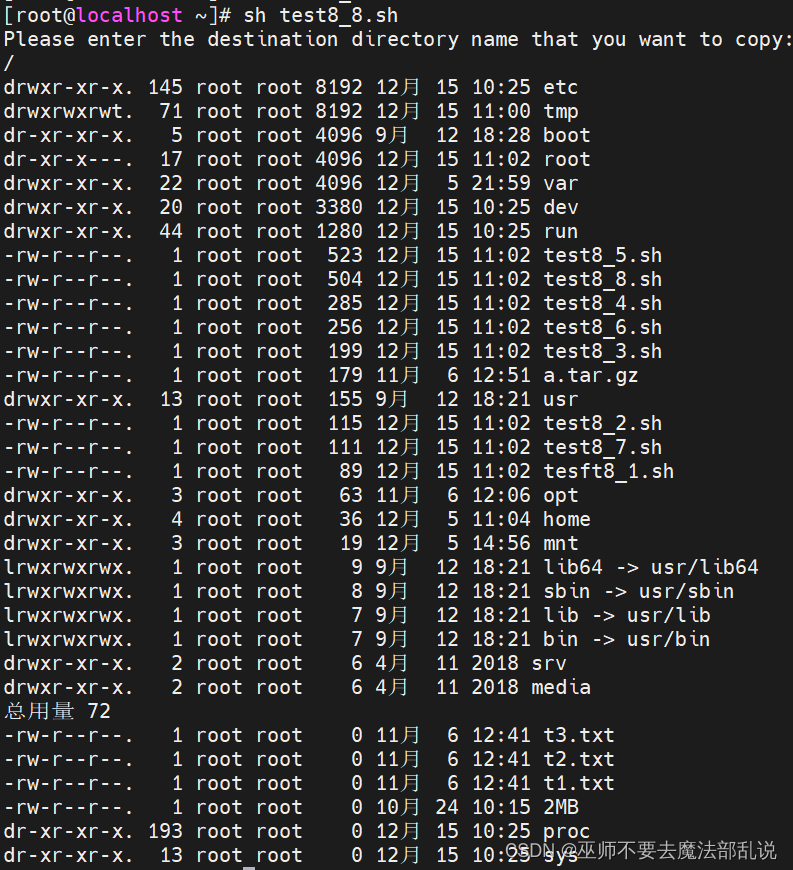
利用vi在宿主目錄中編寫一個名為test8_8.sh的Shell程序,該程序把當前目錄下的所有*.sh文件到指定的目錄(如home目錄下某個普通用戶的家目錄下)中,并顯示復制后該目錄內按文件大小排序的目錄文件清單。
echo "Please enter the destination directory name that you want to copy:"
read dir
if ????①????? #文件測試。若變量dir代表的文件存在且是目錄文件
then
for filename in ??②??? #所有*.sh文件,使用通配符
do
cp $filename ??③?? #將所有*.sh文件復制到目標目錄
done
ls -l $dir | sort -n -r -k 5 #-n數值排序,-r逆序,-k?5按第5個字段。教材P83
else
echo "$dir is a bad directory name."
fi

思考:
Shell變量兩種類型,即Shell環境變量和____局部變量_________。Shell環境變量又分成可寫和只讀兩大類。
在使用用戶自定義變量時,要在變量名前面加上符號__$___。
Shell標準輸入命令是__<stdin>_____,輸出命令是___<stdout>_____。
Shell順序結構中的操作符有4種:順序分隔符(;)、__邏輯否(!)_______、邏輯與(&&)和邏輯或(||)。
通過使用Linux/Unix中文件重定向命令,可以將命令的輸入、輸出以及錯誤消息重定向到其他文件中,重定向方式有以下幾種:輸入重定向命令、輸出重定向命令、輸出附加定向命令和標準錯誤重定向命令,它們使用的符號分別是什么?
輸入重定向命令:<
輸出重定向命令:>
輸出附加定向命令:>>
標準錯誤重定向命令:2>
Shell選擇分支結構主要有2類:if語句和____case___語句。
Shell循環結構有3類語句:for語句、__while____語句和until語句。
Shell循環結構中的循環體需要放在___do__和___done___兩個關鍵字之間。
Shell腳本中,退出腳本程序命令是____exit____。





)










)

