1.Mapper代理模式的特點
程序員沒有寫接口的子實現——直接獲取數據庫的數據
因為Mybatis定義了一套規則,對方法進行了實現,程序員只要遵循這套方法就可以直接使用
2.如何實現Mapper代理模式
步驟:
1.創建一個dao接口,在接口中寫增刪改查的方法
2.創建一個子清單文件,且子清單文件中的命名空間必須namespace="包名.接口名"
3.在子清單文件中:select\insert\update\delete 節點id為接口中的方法名稱
? ? ? ? 方法的參數對應parameterType,返回值對應resultType
4.在總清單文件引入子清單文件
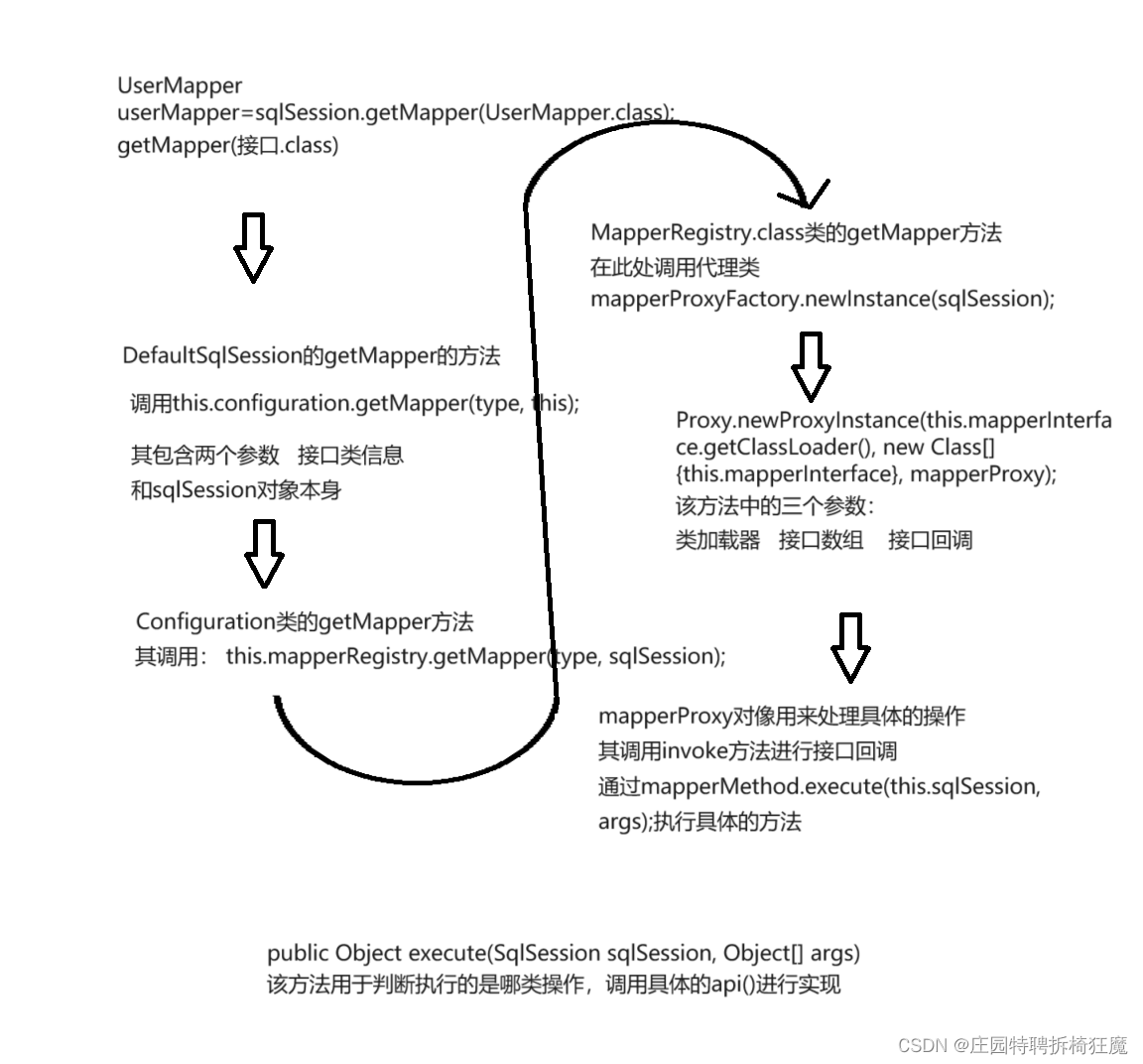
5.在需要的地方:接口類型 jdk動態代理對象=sqlSqssion.getMapper(接口類型.class)
? ? ? ?返回類型 返回類型對象?jdk動態代理對象.調用目標方法();
程序員沒有寫接口子實現,就能獲得數據庫數據
configruation.xml:
?設置類別名,方便書寫:
<typeAliases><!--設置別名--><typeAlias type="org.example.entity.User" alias="User"/></typeAliases>注意添加子清單文件?
<mapper resource="mapper/userMapper.xml"/>增刪改實現?
xxMapper.java
public int addUser(User user);public int deleteUser(Integer id);public int updateUser(User user);userMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="org.example.dao.UserMapper"><!--插入用戶--><insert id="addUser"parameterType="User">insert into t_user(user_name,user_password,address)values(#{name},#{password},#{address});</insert><!--刪除用戶--><delete id="deleteUser"parameterType="java.lang.Integer">delete from t_userwhere id=#{id};</delete><!--根據id更新用戶--><update id="updateUser"parameterType="org.example.entity.User">update t_user setuser_name=#{name},user_password=#{password},address=#{address}whereid=#{id}</update>
</mapper>單元測試:
@Testpublic void addUser() {//假數據User user=new User();user.setName("add");user.setPassword("654321");user.setAddress("測試用例|mapper.addUser()");Integer rowAffect=0;SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);rowAffect= userMapper.addUser(user);sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}System.out.println(rowAffect);}@Testpublic void deleteUser() {Integer rowAffect=0;SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);rowAffect= userMapper.deleteUser(9);sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}System.out.println(rowAffect);}@Testpublic void updateUser() {//假數據User user=new User();user.setId(9);user.setName("update");user.setPassword("654321");user.setAddress("測試用例|mapper.updateUser()");Integer rowAffect=0;SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);rowAffect= userMapper.updateUser(user);sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}System.out.println(rowAffect);}
?效果展示:
addUser
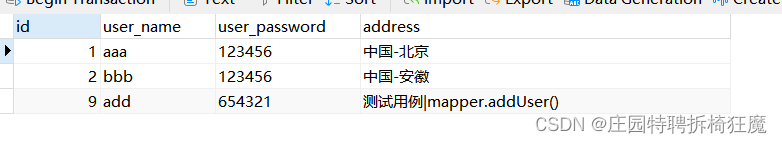 updateUser?
updateUser?
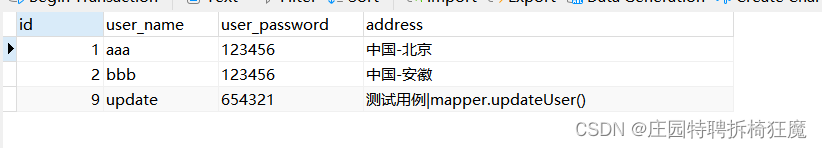 ?deleteUser
?deleteUser
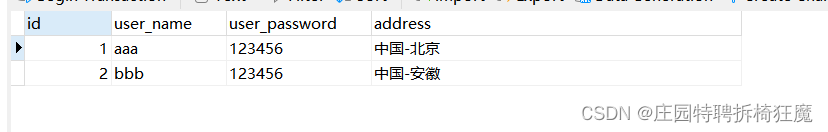
總結:
mybatis 的 mapper代理模式和原生api相比,可以不寫接口的具體實現類。
mapper模式是純接口調用,因為有接口的存在,可以使用jdk動態代理為其動態生成實現類。
jdk生成的實現類和接口之間是實現和被實現的關系,
jdk生成的實現類是實現類,也是代理類,其創建動態代理對象,通過代理對象.目標方法的方式,即invacationHandler調用invoke(),來進行實現。
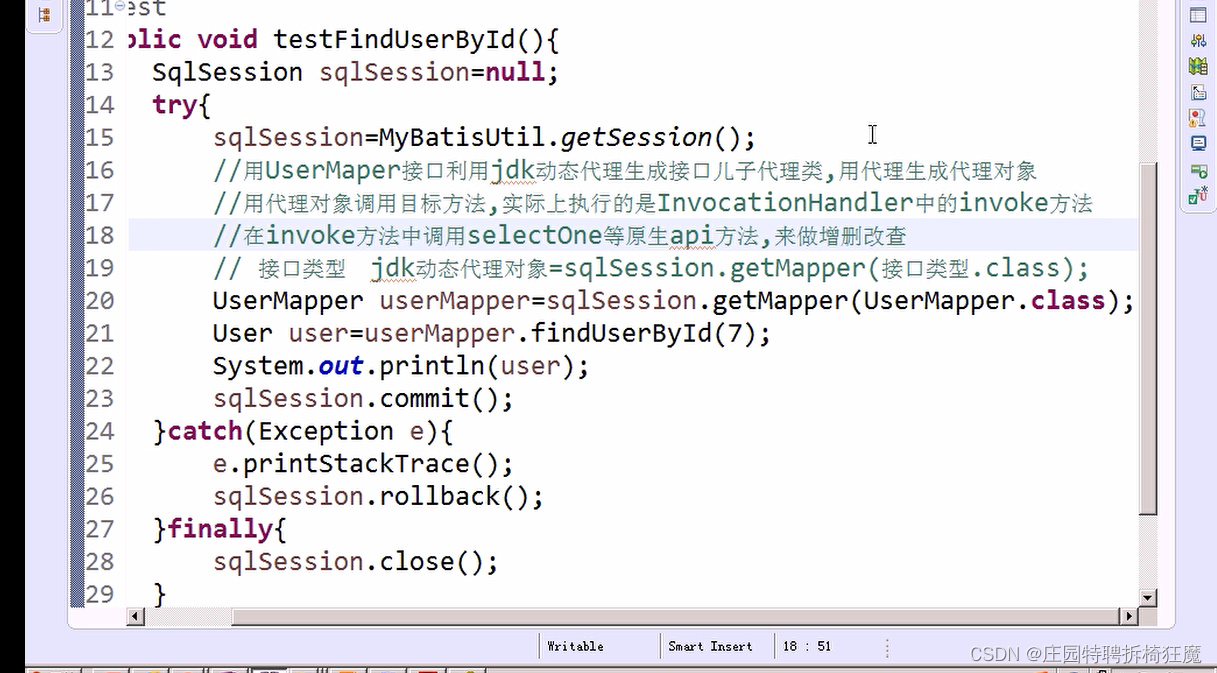
查詢:根據id獲取用戶信息
xxMapper.java
public User findUserById(Integer id);userMapper.xml
<!--根據id獲得用戶信息--><select id="findUserById"resultType="org.example.entity.User"parameterType="java.lang.Integer">selectid,user_name as name,user_password as password,addressfrom t_userwhere id = #{id}</select>單元測試:
@Testpublic void findUserById() {User user=null;SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);user= userMapper.findUserById(1);sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}System.out.println(user);}
結果展示:

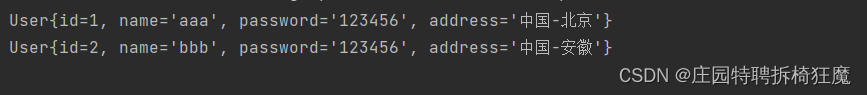
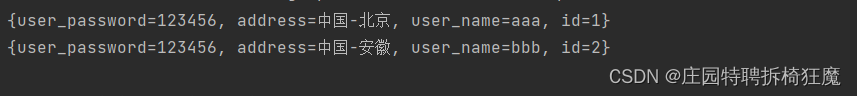
查詢:根查所有用戶List
xxMapper.java
//返回list結構public List<User> findAllUser1();public List<Map<String,Object>> findAllUser2();userMapper.xml
<!--查所有返回list<User>--><select id="findAllUser1"resultType="User">selectid,user_name as name,user_password as password,addressfrom t_user</select><!--查所有返回list<Map>--><select id="findAllUser2"resultType="java.util.Map">selectid,user_name,user_password,addressfrom t_user</select>單元測試:
@Testpublic void findAllUser1() {List<User> userList=new ArrayList<User>();SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);userList= userMapper.findAllUser1();sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}for(User user:userList){System.out.println(user);}}@Testpublic void findAllUser2() {List<Map<String,Object>> userList=new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);userList= userMapper.findAllUser2();sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}for(Map<String,Object> user:userList){System.out.println(user);}}
結果展示:
 ?
?
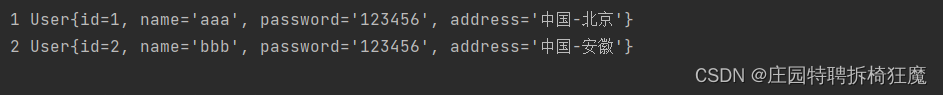
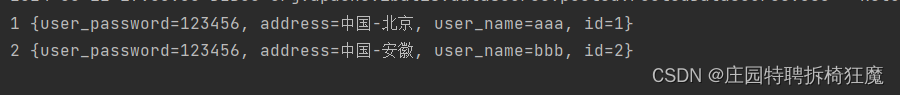
查詢:根查所有用戶Map
xxMapper.java
//返回map結構@MapKey("id")public Map<Integer,User> findAllUser3();@MapKey("id")public Map<Integer,Map<String,Object>> findAllUser4();userMapper.xml
<!--查所有返回Map<User>--><select id="findAllUser3"resultType="User">selectid,user_name as name,user_password as password,addressfrom t_user</select><!--查所有返回Map<Map>--><select id="findAllUser4"resultType="java.util.Map">selectid,user_name,user_password,addressfrom t_user</select>
單元測試:
@Testpublic void findAllUser3() {Map<Integer,User> userMap= new HashMap<Integer, User>();SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);userMap= userMapper.findAllUser3();sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}for(Integer key:userMap.keySet()){System.out.println(key+" "+userMap.get(key));}}@Testpublic void findAllUser4() {Map<Integer,Map<String,Object>> userMap= new HashMap<Integer, Map<String,Object>>();SqlSession sqlSession=null;try{sqlSession= MybatisUtil.getSession();//接口類型, jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper();UserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);userMap= userMapper.findAllUser4();sqlSession.commit();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();sqlSession.rollback();}finally {if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}for(Integer key:userMap.keySet()){System.out.println(key+" "+userMap.get(key));}}結果展示:
3.JDKProxy模擬Mapper代理實現
Mybatis的Mapper代理模式,可以通過接口使用jdk的代理機制實現自動代理。(jdk的動態代理是基于接口的,而此處的xxMapper接口即為被代理的對象接口)
? ? ? ? 本質上xxMapper并沒有實現類,jdk的動態代理也沒有對所謂的老方法進行代理。
程序員不需要寫接口的具體實現,只要根據規則定義好接口,即可使用相關功能。
我們使用JDKProxy類模擬Mybatis實現getMapper()的方法,理解其中的內部實現。
package org.example.proxy;import org.example.proxy.handler.MapperHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class JDKProxy {/*** 根據接口獲取代理對象* @param clazz* @return*/public static Object getMapper(Class clazz){Object proxyObject=null;/*** 參數一: 類加載器* 參數二: 接口數組* 參數三: InvocationHandler 接口的回調*/proxyObject= Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{clazz},new MapperHandler());return proxyObject;}}
這里雖然使用了動態代理,但是并不是動態代理的常規用法,這里只有代理對象的接口,且該接口沒有任何實現。動態代理在這里的目的并不是調用老方法做切面設計,而是獲取方法信息:參數列表、返回值等,進行判斷,根據方法選擇調用mybatis的原生api。所以Mapper代理模式底層調用的還是Mybatis的原生api,??其只是通過動態代理實現了一個默認實現版本,來較少程序員的代碼量。
關于JDK的第三個參數?InvocationHandler 接口的回調,我們構建實現類MapperHandler,其實現InvocationHandler接口。具體來說就是:
package org.example.proxy.handler;import org.example.entity.User;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class MapperHandler implements InvocationHandler {@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object returnValue=null;System.out.println("由Mybatis根據若干信息選擇執行對應的api");/*** mybatis 根據method能得到目標方法的返回值,方法名,參數類型* if判斷返回的數據為一個值,則調用mybatis的原生api selectOne方法* if判斷返回的數據為多個值時,看返回類型是否為List,則調用mybatis的原生 selectList()方法* if判斷返回的數據為多個值時,看返回類型是否為Map,則調用mybatis的原生 selectMap()方法* if判斷為insert/delete/update時,調用原生api insert() delete() update()*///eg:執行selectOne()User user=new User();user.setId(1);user.setName("aaa");user.setPassword("123456");user.setAddress("諾亞方舟");returnValue=user;return returnValue;}
}
?使用單元測試來對方法進行測試:
package org.example.proxy;import org.example.dao.UserMapper;
import org.example.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;import static org.junit.Assert.*;public class JDKProxyTest {@Testpublic void getMapper() {//接口類型 jdk動態代理對象=sqlSession.getMapper(接口類型.class);UserMapper userMapper=(UserMapper) JDKProxy.getMapper(UserMapper.class);User user=userMapper.findUserById(1);System.out.println(user);}
}值得注意的是,getMapper中我們并沒有寫具體的實現邏輯,因為測試的是findUserById()方法,我們在getMapper()中返回了一個假數據,用來做測試。而Mybatis則根據邏輯寫了具體的實現。?
4.Mybatis 中getMapper的實現
重點:模擬getMapper的實現
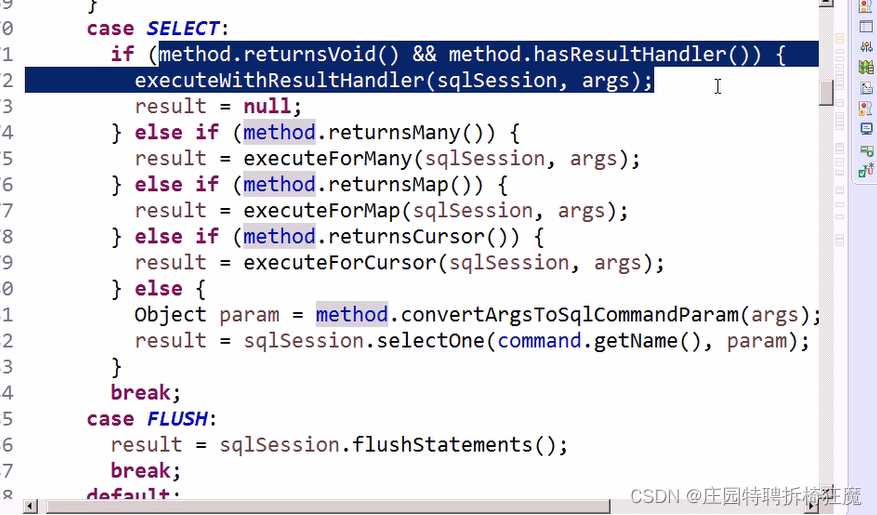
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object param;Object result;switch (this.command.getType()) {case INSERT:param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));break;case UPDATE:param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));break;case DELETE:param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));break;case SELECT:if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) {result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());}if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");} else {return result;}}
基本流程:getMapper()接口——>創建Proxy對象——>execute()實現具體實現???
特別的關于select()方法
其中method.hasResultHandler()來實現自定義的方法處理
還可以匹配不同的返回類型,其中游標模式Cursor不怎么用了
5.總結
接口定義:userDao 和UserMapper一樣的寫法不同,用來定義方法接口
? ? ? ? 其可以自己寫實現類也可以通過mapper() 方式來操作數據
總清單文件:
????????數據庫配置
????????子清單文件
????????????????模板統一
????????????????原生寫法的子清單文件 namespace和增刪改查節點信息任意配置
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? mapper寫法的子清單 namespace="包名.接口"
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 接口方法名和節點id一致
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 接口方法參數和節點parameterType一樣
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 接口的返回值跟節點resultType一樣
mybatis自己的api解析xml來構建sqlSessionFactory,用于生產SqlSession
使用sqlSession來做增刪改查
mapper接口方法底層還是原生api? api結合jdk動態代理
原生api
- insert() delete() update()
- selectOne()? selectList() selectMap()
- select() 自定義返回的數據結構(策略+回調)
- 返回結果類型豐富
6.設計模式:
代理模式:MapperProxy實現jdk動態代理
7.補充
什么是面向接口編程?
如select面向接口、jdbc面向接口和spring面向接口都有相關的面向對象接口編程,其目的是實現解耦操作
- 面向接口編程是一種編程范式,它強調的是在設計軟件應用時,應該先定義接口,然后再實現接口。這種方式有很多優點,包括提高代碼的可讀性、可維護性和可擴展性,以及降低代碼之間的耦合度。
- 接口是一種契約,它定義了一組方法,這些方法應該在實現接口的類中實現。接口本身并不包含任何實現細節,它只是定義了一種規范,規定了實現接口的類應該做什么,而不是怎么做。
摘自:《17.Spring 面向接口編程 - 知乎》
select()也是面向接口編程提供select接口但沒有實現,其具體的實現在handler中去處理。實現了接口和實現的分離。
?
)



—— 希爾排序(思路演進版))




)


——客戶端)



)


