目錄
1、初識Spring
1.1 Spring簡介
1.2 搭建Spring框架步驟
1.3 Spring特性
1.5 bean標簽詳解
2、SpringIOC底層實現
2.1 BeanFactory與ApplicationContexet
2.2 圖解IOC類的結構
3、Spring依賴注入數值問題【重點】
3.1 字面量數值
3.2 CDATA區
3.3 外部已聲明bean及級聯屬性賦值
3.4 內部bean
3.5 集合
4、Spring依賴注入方式【基于XML】
4.1 set注入
4.2 構造器注入
4.3 p名稱空間注入
5、Spring管理第三方bean
5.1 Spring管理druid步驟
6、Spring中FactoryBean
6.1 Spring中兩種bean
6.2 FactoryBean使用步驟
1、初識Spring
1.1 Spring簡介
Spring是一個為簡化企業級開發而生的開源框架。
Spring是一個IOC(DI)和AOP容器框架。
IOC全稱:Inversion of Control【控制反轉】
將對象【萬物皆對象】控制權交個Spring
DI全稱:(Dependency Injection):依賴注入
AOP全稱:Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面編程
官網:https://spring.io/
1.2 搭建Spring框架步驟
導入jar包
<!--導入spring-context--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.3.1</version></dependency><!--導入junit4.12--><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.12</version><scope>test</scope></dependency>編寫核心配置文件
配置文件名稱:applicationContext.xml【beans.xml或spring.xml】
配置文件路徑:src/main/resources
示例代碼
? ?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!-- 將對象裝配到IOC容器中--><bean id="stuZhenzhong" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"><property name="stuId" value="101"></property><property name="stuName" value="zhenzhong"></property></bean></beans>使用核心類庫
?
@Testpublic void testSpring(){//使用Spring之前// ? ? ? ?Student student = new Student();//使用Spring之后//創建容器對象ApplicationContext iocObj =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//通過容器對象,獲取需要對象Student stuZhenzhong = (Student)iocObj.getBean("stuZhenzhong");System.out.println("stuZhenzhong = " + stuZhenzhong);}1.3 Spring特性
非侵入式:基于Spring開發的應用中的對象可以不依賴于Spring的API。
容器:Spring是一個容器,因為它包含并且管理應用對象的生命周期。
組件化:Spring實現了使用簡單的組件配置組合成一個復雜的應用。在 Spring 中可以使用XML和Java注解組合這些對象。
一站式:在IOC和AOP的基礎上可以整合各種企業應用的開源框架和優秀的第三方類庫(實際上Spring 自身也提供了表述層的SpringMVC和持久層的JDBCTemplate)。
1.4 Spring中getBean()三種方式
getBean(String beanId):通過beanId獲取對象
不足:需要強制類型轉換,不靈活
getBean(Class clazz):通過Class方式獲取對象
不足:容器中有多個相同類型bean的時候,會報如下錯誤:
expected single matching bean but found 2: stuZhenzhong,stuZhouxu
getBean(String beanId,Clazz clazz):通過beanId和Class獲取對象
推薦使用
注意:框架默認都是通過無參構造器,幫助我們創建對象。
所以:如提供對象的構造器時,一定添加無參構造器
1.5 bean標簽詳解
屬性
id:bean的唯一標識
class:定義bean的類型【class全類名】
子標簽
property:為對象中屬性賦值【set注入】
name屬性:設置屬性名稱
value屬性:設置屬性數值
2、SpringIOC底層實現
IOC:將對象的控制器反轉給Spring
2.1 BeanFactory與ApplicationContexet
BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本實現,是Spring內部的使用接口,是面向Spring本身的,不是提供給開發人員使用的。
ApplicationContext:BeanFactory的子接口,提供了更多高級特性。面向Spring的使用者,幾乎所有場合都使用ApplicationContext而不是底層的BeanFactory。
2.2 圖解IOC類的結構
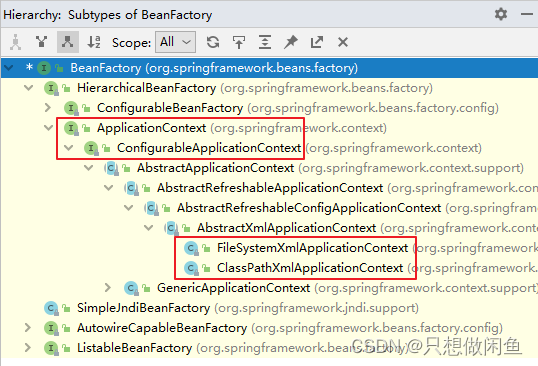
BeanFactory:Spring底層IOC實現【面向Spring框架】
ApplicationContext:面向程序員
ConfigurableApplicationContext:提供關閉或刷新容器對象方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:基于類路徑檢索xml文件
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:基于注解創建容器對象
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:基于文件系統檢索xml文件
3、Spring依賴注入數值問題【重點】
3.1 字面量數值
數據類型:基本數據類型及包裝類、String
語法:value屬性或value標簽
3.2 CDATA區
語法:\<![CDATA[]]>
作用:在xml中定義特殊字符時,使用CDATA區
3.3 外部已聲明bean及級聯屬性賦值
語法:ref
注意:級聯屬性更改數值會影響外部聲明bean【ref賦值的是引用】
示例代碼
?
<bean id="dept1" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="1"></property><property name="deptName" value="研發部門"></property></bean><bean id="empChai" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee"><property name="id" value="101"></property><property name="lastName" value="chai"></property><property name="email" value="chai@163.com"></property><property name="salary" value="50.5"></property><property name="dept" ref="dept1"></property><property name="dept.deptName" value="財務部門"></property></bean>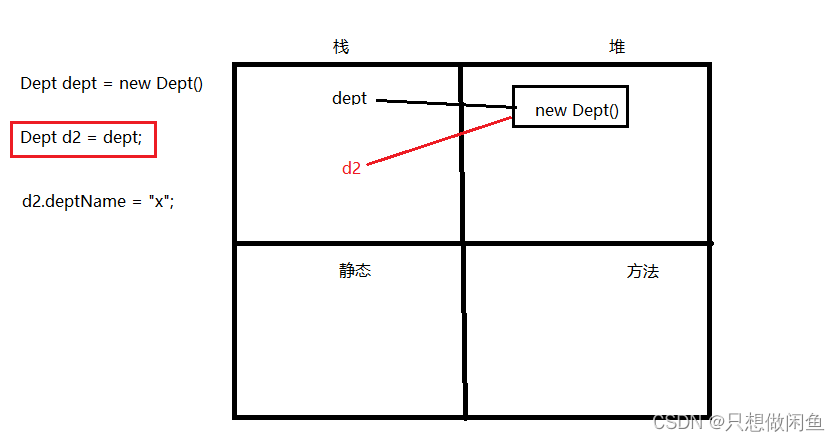
3.4 內部bean
概述
內部類:在一個類中完整定義另一個類,當前類稱之為內部類
內部bean:在一個bean中完整定義另一個bean,當前bean稱之為內部bean
注意:內部bean不會直接裝配到IOC容器中
示例代碼
? <!-- ? ?測試內部bean--><bean id="empXin" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee"><property name="id" value="102"></property><property name="lastName" value="xx"></property><property name="email" value="xx@163.com"></property><property name="salary" value="51.5"></property><property name="dept"><bean class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="2"></property><property name="deptName" value="人事部門"></property></bean></property></bean>3.5 集合
List
<!-- ? ?測試集合--><bean id="dept3" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="3"></property><property name="deptName" value="程序員鼓勵師"></property><property name="empList"><list><ref bean="empChai"></ref><ref bean="empXin"></ref><!-- ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?<bean></bean>--></list></property></bean><!-- ? ?測試提取List--><util:list id="empList"><ref bean="empChai"></ref><ref bean="empXin"></ref></util:list><bean id="dept4" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="4"></property><property name="deptName" value="運營部門"></property><property name="empList" ref="empList"></property></bean>Map
?
<!-- ? ?測試Map--><bean id="dept5" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="5"></property><property name="deptName" value="采購部門"></property><property name="empMap"><map><entry key="101" value-ref="empChai"></entry><entry><key><value>103</value></key><ref bean="empChai"></ref></entry><entry><key><value>102</value></key><ref bean="empXin"></ref></entry></map></property></bean><util:map id="empMap"><entry key="101" value-ref="empChai"></entry><entry><key><value>103</value></key><ref bean="empChai"></ref></entry><entry><key><value>102</value></key><ref bean="empXin"></ref></entry></util:map><bean id="dept6" class="com.atguigu.pojo.Dept"><property name="deptId" value="106"></property><property name="deptName" value="后勤部門"></property><property name="empMap" ref="empMap"></property></bean>4、Spring依賴注入方式【基于XML】
為屬性賦值方式:
-
通過xxxset()方法:這是一種常見的方式,在類中提供了一系列的set方法,用于設置類的屬性值。例如,如果有一個屬性名為
name,那么可能會有一個名為setName()的方法用于設置name屬性的值。 -
通過構造器:另一種常見的方式是通過類的構造器來傳遞屬性值。在構造對象時,通過構造器的參數列表將屬性值傳遞給對象。這種方式可以在對象被創建時一次性地設置屬性值,使得對象的狀態在創建后就被確定下來。
-
反射:反射是一種高級的Java特性,允許在運行時檢查類、獲取類的信息以及動態調用類的方法和操作類的屬性。通過反射,可以通過類的
Field對象來設置對象的屬性值,無論這些屬性的可見性如何。
4.1 set注入
通過在XML配置文件中使用<property>標簽來進行屬性注入。在這種方式中,你可以指定屬性的名稱,并通過value屬性或ref屬性為屬性賦值。如果是基本數據類型或字符串等簡單類型,可以使用value屬性直接賦值;如果是引用其他bean,可以使用ref屬性指定引用的bean的id。
語法:\<property>
4.2 構造器注入
通過在XML配置文件中使用<constructor-arg>標簽來進行構造器注入。與set注入類似,你可以在構造對象時指定構造器的參數,并通過value屬性或ref屬性為構造器參數賦值。這種方式適用于在創建對象時將屬性值通過構造器傳遞給對象。
語法:\<constructor-arg>
4.3 p名稱空間注入
導入名稱空間:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
語法:<bean p:xxx>
示例代碼
? <bean id="stuZhouxu" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"><property name="stuId" value="102"></property><property name="stuName"><value><![CDATA[<<zhouxu>>]]></value></property></bean><bean id="stuZhiFeng" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"><constructor-arg name="stuId" value="103"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg name="stuName" value="zhifeng"></constructor-arg></bean><bean id="stuXiaoxi"class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"p:stuId="104"p:stuName="xiaoxi"></bean>5、Spring管理第三方bean
5.1 Spring管理druid步驟
導入jar包
<!--導入druid的jar包--><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.1.10</version></dependency><!--導入mysql的jar包--><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.37</version><!-- ? ? ? ? ? ?<version>8.0.26</version>--></dependency>編寫db.properties配置文件
properties
? #key=valuedb.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverdb.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db220106db.username=rootdb.password=root編寫applicationContext.xml相關代碼
? <!-- ? ?加載外部屬性文件db.properties--><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder><!-- ? ?裝配數據源--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverClassName}"></property><property name="url" value="${db.url}"></property><property name="username" value="${db.username}"></property><property name="password" value="${db.password}"></property></bean>測試
@Testpublic void testDruidDataSource() throws Exception{//獲取容器對象ApplicationContext ioc =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_druid.xml");DruidDataSource dataSource = ioc.getBean("dataSource", DruidDataSource.class);System.out.println("dataSource = " + dataSource);DruidPooledConnection connection = dataSource.getConnection();System.out.println("connection = " + connection);}6、Spring中FactoryBean
6.1 Spring中兩種bean
一種是普通bean:
普通bean是指在Spring容器中以普通的方式配置和管理的bean。這些bean通常是通過在XML配置文件或Java配置類中定義并注冊的,它們的創建和初始化由Spring容器負責。
另一種是工廠bean【FactoryBean】:
工廠bean是一種特殊的bean,它實現了org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean接口。與普通bean不同,工廠bean負責創建其他bean實例,允許程序員在bean的創建過程中進行參數化或自定義。使用工廠bean可以更靈活地控制bean的創建邏輯和初始化過程。
作用:如需我們程序員參數到bean的創建時,使用FactoryBean
6.2 FactoryBean使用步驟
實現FactoryBean接口:創建一個類并實現FactoryBean接口,該接口要求實現getObject()方法來返回所創建的bean實例,并可選擇實現getObjectType()方法來指定工廠bean所創建的對象類型。
重寫方法【三個】:在實現FactoryBean接口的類中,需要重寫getObject()方法來指定如何創建所需的bean實例。可選地,也可以重寫getObjectType()方法來提供所創建的bean的類型。
裝配工廠bean:將實現了FactoryBean接口的類配置到Spring容器中,可以通過XML配置文件或Java配置類進行裝配。
測試
示例代碼:
示例代碼:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;// 實現FactoryBean接口
public class MyBeanFactory implements FactoryBean<MyBean> {// 重寫getObject()方法,指定創建bean的邏輯@Overridepublic MyBean getObject() throws Exception {// 這里可以根據需要進行一些自定義的邏輯,然后創建并返回所需的bean實例return new MyBean();}// 可選地重寫getObjectType()方法,指定所創建的bean的類型@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {return MyBean.class;}
}
在Spring配置文件中裝配工廠bean:
<bean id="myBeanFactory" class="com.example.MyBeanFactory"/>
在測試代碼中獲取并使用工廠bean:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 加載Spring配置文件ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");// 獲取工廠bean實例MyBean myBean = context.getBean("myBeanFactory", MyBean.class);// 使用工廠創建的bean實例myBean.doSomething();}
}

)






)










)