接上文,視覺SLAM第7講:視覺里程計1(特征點法、2D-2D對極約束),本節主要學習3D-2D:PnP、3D-3D:ICP。
目錄
7.7 3D-2D:PnP
7.7.1 直接線性變換(DLT)
7.7.2 P3P?? ??
1.原理
2.小結
7.7.3 最小化重投影誤差求解PnP?
1.引言
2.原理?
7.8 實踐:求解PnP
7.8.1 使用EPnP求解位姿(調用OpenCV庫)
7.8.2 手寫位姿估計
7.8.3 使用g2o進行BA優化
7.8.4 報錯修復
1.報錯代碼
2.檢查與修復
7.9 3D-3D:ICP
7.9.1 SVD法(線性代數求解)
7.9.2 非線性優化方法
7.10 實踐:求解ICP
7.10.1 實踐:SVD方法
1.pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp
2.CmakeLists.txt
3.運行結果
7.10.2 實踐非線性優化方法
1.涉及代碼
2.運行結果
7.11 小結
7.7 3D-2D:PnP
? ? ? ?PnP(Perspective-n-Point)是求解3D到2D點對運動的方法。它描述了當知道n個3D空間點及其投影位置時,如何估計相機的位姿(外參,平移和旋轉)。2D-2D 的對極幾何方法需要8個或8個以上的點對(以八點法為例),且存在著初始化、純旋轉和尺度的問題。然而,如果兩張圖像中的一張特征點的3D位置已知,那么最少只需3個點對(以及至少一個額外點驗證結果)就可以估計相機運動。
? ? ? ?特征點的3D位置可以由三角化或者RGB-D相機的深度圖確定。因此,在雙目或RGB-D的視覺里程計中,我們可以直接使用PnP估計相機運動,3D-2D方法不需要使用對極約束,又可以在很少的匹配點中獲得較好的運動估計,是一種最重要的姿態估計方法;而在單目視覺里程計中,必須先進行初始化,才能使用PnP。
? ? ? ? PnP問題有很多種求解方法,例如,用3對點估計位姿的P3P、直接線性變換(DLT),EPnP(Efficient PnP)、UPnP等等。此外,還能用非線性優化的方式,構建最小二乘問題并迭代求解,也就是萬金油式的光束法平差(Bundle Adjustment,BA)。
7.7.1 直接線性變換(DLT)
? ? ? ?已知一組3D點的位置,以及它們在某個相機中的投影位置,求該相機的位姿。這個問題也可以用于求解給定地圖和圖像時的相機狀態問題。如果把3D點看成在另一個相機坐標系中的點的話,則也可以用來求解兩個相機的相對運動問題。
? ? ? 考慮某個空間點,它的齊次坐標為
。在圖像中
,投影到特征點
(以歸一化平面齊次坐標表示)。此時,相機的位姿
是未知的。與單應矩陣的求解類似,我們定義增廣矩陣
為一個3×4的矩陣,包含了旋轉與平移信息,展開形式為
??? ? ? ? ?
?消去
,得到兩個約束:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
?為了簡化表示,定義
的行向量:? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ??
?于是有:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?是待求的變量,每個特征點提供了兩個關于
的線性約束。假設一共有
個特征點,則可以列出如下線性方程組:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ??
一共有12維,因此最少通過6對匹配點即可實現矩陣T的線性求解,這種方法稱為DLT。當匹配點大于6對時,也可以使用SVD等方法對超定方程求最小二乘解。
? ? ? ?在DLT求解中,我們直接將T矩陣看成了12個未知數,忽略了它們之間的聯系。因為旋轉矩陣R∈ SO(3),用DLT求出的解不一定滿足該約束,它是一個一般矩陣。
? ? ? ?平移向量比較好辦,它屬于向量空間。
? ? ? ?對于旋轉矩陣R,我們必須針對DLT估計的T左邊3×3的矩陣塊,尋找一個最好的旋轉矩陣對它進行近似。這可以由QR分解完成,也可以像這樣來計算:
這相當于把結果從矩陣空間重新投影到SE(3)流形上,轉換成旋轉和平移兩部分。
? ? ? ?這里的使用歸一化平面坐標,去掉了內參矩陣K的影響——這是因為內參在SLAM中通常假設為已知。即使內參未知,也能用PnP去估計
三個量。然而由于未知量增多,效果會差一些。
7.7.2 P3P?? ??
1.原理
? ? ? ? P3P是另一種解PnP的方法,它僅使用3對匹配點,對數據要求較少。
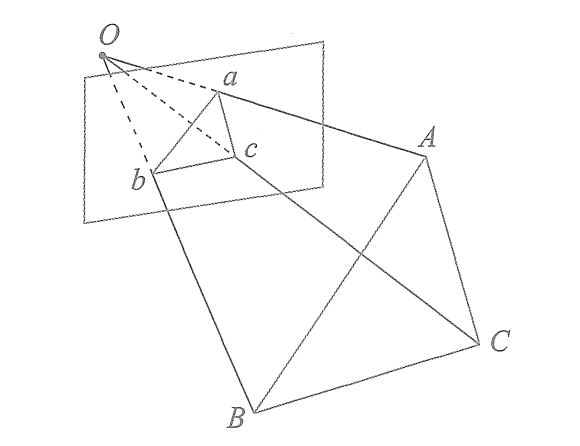
? ? ? ? P3P需要利用給定的3個點的幾何關系。它的輸入數據為3對3D-2D匹配點。記3D點為A、B、C(世界坐標系中),2D點為a、b、c,其中小寫字母代表的點為對應大寫字母代表的點在相機成像平面上的投影,如下圖。此外,P3P還需要使用一對驗證點,以從可能的解中選出正確的那一個(類似于對極幾何情形)。記驗證點對為D-d,相機光心為O。? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?一旦3D點在相機坐標系下的坐標能夠算出,我們就得到了3D-3D的對應點,把PnP問題轉換為了ICP問題。 ? ? ??
三角形之間存在對應關系:
考慮Oab和OAB的關系。利用余弦定理,有??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
對于其他兩個三角形也有類似性質,于是有: ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
對以上三式全體除以
,并且記
,
得:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
記
,
有:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
化簡得:
? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?2D點的圖像位置,3個余弦角已知;
可以通過
在世界坐標系下的坐標算出,變換到相機坐標系下之后,這個比值并不改變。
未知,隨著相機移動會發生變化。
? ? ? ? 因此,該方程組是關于的一個二元二次方程(多項式方程)。求該方程組的解析解是一個復雜的過程,需要用吳消元法。類似于分解E的情況,該方程最多可能得到4個解,可以用驗證點來計算最可能的解,得到
在相機坐標系下的3D坐標。然后,根據3D-3D的點對,計算相機的運動
。
2.小結
? ? ? ?從P3P的原理可以看出,為了求解 PnP,利用三角形相似性,求解投影點
在相機坐標系下的3D坐標,最后把問題轉換成一個3D到3D的位姿估計問題。在后文中將看到,
帶有匹配信息的3D-3D位姿求解非常容易,所以這種思路是非常有效的。一些其他的方法,例如EPnP,也采用了這種思路。然而,P3P也存在著一些問題:
(1)P3P只利用3個點的信息。當給定的配對點多于3組時,難以利用更多的信息。
(2)如果3D點或2D點受噪聲影響,或者存在誤匹配,則算法失效。
? ? ? ?所以,人們還陸續提出了許多別的方法,如EPnP、UPnP等。它們利用更多的信息,而且用迭代的方式對相機位姿進行優化,以盡可能地消除噪聲的影響。在SLAM中,通常的做法是先使用P3P/EPnP等方法估計相機位姿,再構建最小二乘優化問題對估計值進行調整(即進行Bundle Adjustment )。在相機運動足夠連續時,也可以假設相機不動或勻速運動,用推測值作為初始值進行優化。接下來,我們從非線性優化的角度來看PnP問題。
7.7.3 最小化重投影誤差求解PnP?
1.引言
? ? ? ?除了使用線性方法,我們還可以把PnP問題構建成一個關于重投影誤差的非線性最小二乘問題。
? ? ? ?線性方法,是先求相機位姿,再求空間點位置;非線性優化則是把它們都看成優化變量,放在一起優化,這是一種非常通用的求解方式,可以用它對PnP或ICP給出的結果進行優化,這一類把相機和三維點放在一起進行最小化的問題,統稱為Bundle Adjustment。
? ? ? ?在PnP中構建一個Bundle Adjustment問題對相機位姿進行優化。如果相機是連續運動的(比如大多數SLAM過程),也可以直接用BA求解相機位姿。我們將在本節給出此問題在兩個視圖下的基本形式,然后在第9講討論較大規模的BA問題。
2.原理?
? ? ? ?考慮
個三維空間點
及其投影
,計算相機的位姿
,它的李群表示為
。假設某空間點坐標為
,其投影的像素坐標為
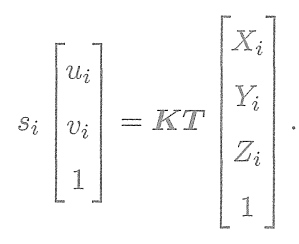
。根據第5講的內容,像素位置與空間點位置的關系為:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
矩陣形式為:
? ? ? ?這個式子隱含了一次從齊次坐標到非齊次的轉換,否則按矩陣的乘法來說,維度是不對的。現在,由于相機位姿未知及觀測點的噪聲,該等式存在一個誤差。因此,我們把誤差求和,構建最小二乘問題,然后尋找最好的相機位姿,使它最小化:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?該問題的誤差項,是將3D點的投影位置與觀測位置作差,所以稱為重投影誤差。使用齊次坐標時,這個誤差有3維。不過,由于最后一維為1,該維度的誤差一直為零,因而我們更多時候使用非齊次坐標,于是誤差就只有2維了。
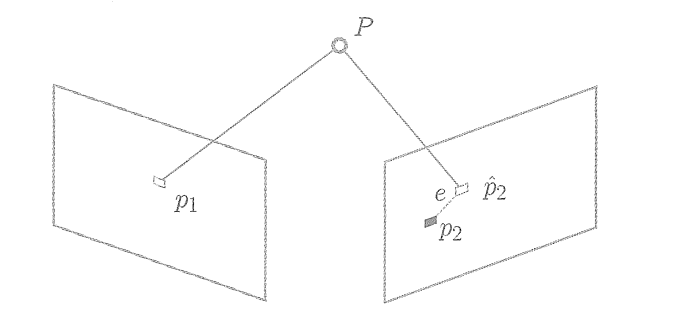
? ? ? ?如圖所示,我們通過特征匹配知道了
和
是同一個空間點
的投影,但是不知道相機的位姿。在初始值中,
的投影
與實際的
之間有一定的距離。于是我們調整相機的位姿,使得這個距離變小。不過,由于這個調整需要考慮很多個點,所以最后的效果是整體誤差的縮小,而每個點的誤差通常都不會精確為零。
? ? ? ?使用李代數,可以構建無約束的優化問題,很方便地通過高斯牛頓法、列文伯格-馬夸爾特方法等優化算法進行求解。不過,在使用高斯牛頓法和列文伯格-馬夸爾特方法之前,我們需要知道每個誤差項關于優化變量的導數,也就是線性化:? ? ? ?
的形式是關鍵所在。我們固然可以使用數值導數,但如果能夠推導出解析形式,則優先考慮解析導數。現在,當
為像素坐標誤差(2維),
為相機位姿(6維)時,
將是一個2×6的矩陣。
現推導
的形式:
? ? ? ?回憶李代數的內容,我們介紹了如何使用擾動模型來求李代數的導數。首先,記變換到相機坐標系下的空間點坐標為
,并且將其前3維取出來:
? ? ? ?那么,相機投影模型相對于
為: ?
? ? ? ?展開:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
利用第3行消去(實際上就是
的距離),得
? ? ? ?這與第5講的相機模型是一致的。當我們求誤差時,可以把這里的
與實際的測量值比較,求差。在定義了中間變量后,我們對
左乘擾動量
,然后考慮
的變化關于擾動量的導數。利用鏈式法則,可以列寫如下:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?這里的
指李代數上的左乘擾動。第一項是誤差關于投影點的導數,
易得
? ? ? ?而第二項為變換后的點關于李代數的導數,根據4.3.2節中的推導,
得
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ?
? ? ? ?而在
的定義中,我們取出了前3維,于是得
? ? ? ?將這兩項相乘,就得到了2×6的雅可比矩陣
? ? ? ?這個雅可比矩陣描述了重投影誤差關于相機位姿李代數的一階變化關系。我們保留了前面的負號,這是因為誤差是由觀測值減預測值定義的。當然也可以反過來將它定義成“預測值減觀測值”的形式。在那種情況下,只要去掉前面的負號即可。此外,如果
的定義方式是旋轉在前,平移在后,則只要把這個矩陣的前3列與后3列對調即可。
? ? ? ?除了優化位姿,我們還希望優化特征點的空間位置。因此,需要討論關于空間點
的導數。利用鏈式法則,有
? ? ? ?第一項在前面已推導,關于第二項,按照定義
? ? ? ?我們發現
對
求導后將只剩下
。
于是
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?于是,我們推導出了觀測相機方程關于相機位姿與特征點的兩個導數矩陣。它們十分重要,能夠在優化過程中提供重要的梯度方向,指導優化的迭代。
7.8 實踐:求解PnP
7.8.1 使用EPnP求解位姿(調用OpenCV庫)
? ? ? ?首先,演示如何使用OpenCV的 EPnP求解PnP問題,然后通過非線性優化再次求解。由于PnP需要使用3D點,為了避免初始化帶來的麻煩,使用RGB-D相機中的深度圖( 1_depth.png)作為特征點的3D位置。
OpenCV提供的PnP函數如下:
int main(int argc, char **argv) {Mat r, t;solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); // 調用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可選擇EPNP,DLS等方法Mat R;cout << "R=" << endl << R << endl;cout << "t=" << endl << t << endl;? ? ? ?在例程中,得到配對特征點后,在第一個圖的深度圖中尋找它們的深度,并求出空間位置。以此空間位置為3D點,再以第二個圖像的像素位置為2D點,調用EPnP求解PnP問題。程序輸出如下:
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ ./pose_estimation_3d2d ../1.png ../2.png ../1_depth.png ../2_depth.png -- Max dist : 95.000000 -- Min dist : 4.000000 一共找到了79組匹配點 3d-2d pairs: 76 solve pnp in opencv cost time: 0.0109459 seconds. R= [0.9978662025826269, -0.05167241613316376, 0.03991244360207524;0.0505958915956335, 0.998339762771668, 0.02752769192381471;-0.04126860182960625, -0.025449547736074, 0.998823919929363] t= [-0.1272259656955879;-0.007507297652615337;0.06138584177157709]? ? ? 對比先前2D-2D情況下求解可以看到,在有3D信息時,估計的R幾乎是相同的,而t相差得較多。這是由于引入了新的深度信息所致。不過,由于Kinect采集的深度圖本身會有一些誤差,所以這里的3D點也不是準確的。在較大規模的BA中,我們會希望把位姿和所有三維特征點同時優化。
7.8.2 手寫位姿估計
? ? ? ?演示如何使用非線性優化的方式計算相機位姿。先手寫一個高斯牛頓法的PnP(高斯牛頓迭代優化),演示如何調用g2o來求解。
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose) {typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;const int iterations = 10;double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;double fx = K.at<double>(0, 0);double fy = K.at<double>(1, 1);double cx = K.at<double>(0, 2);double cy = K.at<double>(1, 2);for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero();Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();cost = 0;// compute costfor (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) {Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i];double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2];double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;Eigen::Vector2d proj(fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj;cost += e.squaredNorm();Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J;J << -fx * inv_z,0,fx * pc[0] * inv_z2,fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2,fx * pc[1] * inv_z,0,-fy * inv_z,fy * pc[1] * inv_z2,fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fy * pc[0] * inv_z;H += J.transpose() * J;b += -J.transpose() * e;}Vector6d dx;dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);if (isnan(dx[0])) {cout << "result is nan!" << endl;break;}if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {// cost increase, update is not goodcout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;break;}// update your estimationpose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose;lastCost = cost;cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << std::setprecision(12) << cost << endl;if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) {// convergebreak;}}cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl; }
7.8.3 使用g2o進行BA優化
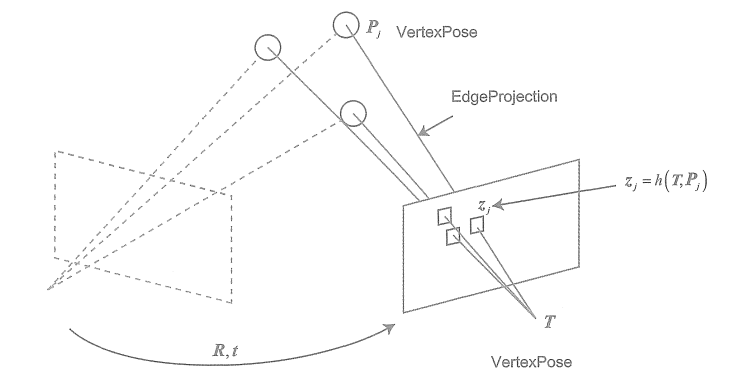
用g2o實現同樣的操作(事實上,用Ceres 也完全類似)。g2o的基本知識見第6講。在使用g2o之前,要把問題建模成一個圖優化問題,如圖。
在這個圖優化中,節點和邊的選擇如下:
①節點:第二個相機的位姿節點T∈SE(3)。
②邊:每個3D點在第二個相機中的投影,以觀測方程來描述:? ? ? ?由于第一個相機位姿固定為零,所以沒有把它寫到優化變量里,但在更多的場合里,會考慮更多相機的估計。現在根據一組3D點和第二個圖像中的2D投影,估計第二個相機的位姿。把第一個相機畫成虛線表明不希望考慮它。
? ? ? ? g2o提供了許多關于BA的節點和邊,例如g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h中提供了李代數表達的節點和邊。在本書中,我們自己實現一個 VertexPose頂點和EdgeProjection邊,代碼如下:/// vertex and edges used in g2o ba class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> { public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();}/// left multiplication on SE3virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;}virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {} };class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> { public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}virtual void computeError() override {const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();}virtual void linearizeOplus() override {const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;double fx = _K(0, 0);double fy = _K(1, 1);double cx = _K(0, 2);double cy = _K(1, 2);double X = pos_cam[0];double Y = pos_cam[1];double Z = pos_cam[2];double Z2 = Z * Z;_jacobianOplusXi<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;}virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}private:Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;Eigen::Matrix3d _K; };這里實現了頂點的更新和邊的誤差計算。下面將它們組成一個圖優化問題:
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose) {// 構建圖優化,先設定g2otypedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 3>> BlockSolverType; // pose is 6, landmark is 3typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 線性求解器類型// 梯度下降方法,可以從GN, LM, DogLeg 中選auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 圖模型optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 設置求解器optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打開調試輸出// vertexVertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_posevertex_pose->setId(0);vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);// KEigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;K_eigen <<K.at<double>(0, 0), K.at<double>(0, 1), K.at<double>(0, 2),K.at<double>(1, 0), K.at<double>(1, 1), K.at<double>(1, 2),K.at<double>(2, 0), K.at<double>(2, 1), K.at<double>(2, 2);// edgesint index = 1;for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {auto p2d = points_2d[i];auto p3d = points_3d[i];EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);edge->setId(index);edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose);edge->setMeasurement(p2d);edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity());optimizer.addEdge(edge);index++;}chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();optimizer.setVerbose(true);optimizer.initializeOptimization();optimizer.optimize(10);chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;pose = vertex_pose->estimate(); }? ? ? ?程序大體上和第6講的g2o類似。首先聲明了g2o圖優化器,并配置優化求解器和梯度下降方法。然后,根據估計到的特征點,將位姿和空間點放到圖中。最后,調用優化函數進行求解。
(1)CmakeLists.txt
#聲明要求cmake的最低版本 cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16)#聲明一個cmake工程 project(slam_07)set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON) #啟用最高優化級別,移除調試開銷 set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release") #并行計算,加速運算 add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE") # 啟用 SSE4.2 和 POPCNT 指令 set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -msse4.2 -mpopcnt")list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake) list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH /home/caohao/g2o/cmake_modules )# OpenCV find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED) include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})# g2o find_package(G2O REQUIRED) include_directories(${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS})# Eigen find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED NO_MODULE) include_directories("/usr/local/include/eigen3") set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/usr/local" ${CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH})# 確保 Eigen3::Eigen target 存在 if(NOT TARGET Eigen3::Eigen)add_library(Eigen3::Eigen INTERFACE IMPORTED)set_target_properties(Eigen3::Eigen PROPERTIESINTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES "/usr/local/include/eigen3") endif()# Sophus set(EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR "/usr/local/include/eigen3") include_directories(${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR})find_package(Sophus REQUIRED NO_MODULE) include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})# 添加一個可執行程序,可執行文件名 cpp文件名 add_executable(orb_cv orb_cv.cpp) target_link_libraries(orb_cv ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(orb_self orb_self.cpp) target_link_libraries(orb_self ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp) target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_2d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(triangulation triangulation.cpp) target_link_libraries(triangulation ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp) target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS} g2o_core g2o_stuffSophus::Sophus )(2)程序代碼pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> #include <Eigen/Core> #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> #include <g2o/core/sparse_optimizer.h> #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> #include <g2o/core/solver.h> #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h> #include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h> #include <sophus/se3.hpp> #include <chrono>using namespace std; using namespace cv;void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches);// 像素坐標轉相機歸一化坐標 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);// BA by g2o typedef vector<Eigen::Vector2d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector2d>> VecVector2d; typedef vector<Eigen::Vector3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector3d>> VecVector3d;void bundleAdjustmentG2O(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose );// BA by gauss-newton void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose );int main(int argc, char **argv) {if (argc != 5) {cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;return 1;}//-- 讀取圖像Mat img_1 = imread("../1.png");Mat img_2 = imread("../2.png");assert(img_1.data && img_2.data && "Can not load images!");vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;vector<DMatch> matches;find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "組匹配點" << endl;// 建立3D點Mat d1 = imread(argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 深度圖為16位無符號數,單通道圖像Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);vector<Point3f> pts_3d;vector<Point2f> pts_2d;for (DMatch m:matches) {ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];if (d == 0) // bad depthcontinue;float dd = d / 5000.0;Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K);pts_3d.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd, p1.y * dd, dd));pts_2d.push_back(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt);}cout << "3d-2d pairs: " << pts_3d.size() << endl;chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();Mat r, t;solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); // 調用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可選擇EPNP,DLS等方法Mat R;cv::Rodrigues(r, R); // r為旋轉向量形式,用Rodrigues公式轉換為矩陣chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "solve pnp in opencv cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;cout << "R=" << endl << R << endl;cout << "t=" << endl << t << endl;VecVector3d pts_3d_eigen;VecVector2d pts_2d_eigen;for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_3d.size(); ++i) {pts_3d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(pts_3d[i].x, pts_3d[i].y, pts_3d[i].z));pts_2d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(pts_2d[i].x, pts_2d[i].y));}cout << "calling bundle adjustment by gauss newton" << endl;Sophus::SE3d pose_gn;t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_gn);t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "solve pnp by gauss newton cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;cout << "calling bundle adjustment by g2o" << endl;Sophus::SE3d pose_g2o;t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();bundleAdjustmentG2O(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_g2o);t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "solve pnp by g2o cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;return 0; }void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {//-- 初始化Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;// used in OpenCV3Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();// use this if you are in OpenCV2// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");//-- 第一步:檢測 Oriented FAST 角點位置detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);//-- 第二步:根據角點位置計算 BRIEF 描述子descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);//-- 第三步:對兩幅圖像中的BRIEF描述子進行匹配,使用 Hamming 距離vector<DMatch> match;// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);//-- 第四步:匹配點對篩選double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;//找出所有匹配之間的最小距離和最大距離, 即是最相似的和最不相似的兩組點之間的距離for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {double dist = match[i].distance;if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;}printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);//當描述子之間的距離大于兩倍的最小距離時,即認為匹配有誤.但有時候最小距離會非常小,設置一個經驗值30作為下限.for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {matches.push_back(match[i]);}} }Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {return Point2d((p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1)); }void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose) {typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;const int iterations = 10;double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;double fx = K.at<double>(0, 0);double fy = K.at<double>(1, 1);double cx = K.at<double>(0, 2);double cy = K.at<double>(1, 2);for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero();Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();cost = 0;// compute costfor (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) {Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i];double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2];double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;Eigen::Vector2d proj(fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj;cost += e.squaredNorm();Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J;J << -fx * inv_z,0,fx * pc[0] * inv_z2,fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2,fx * pc[1] * inv_z,0,-fy * inv_z,fy * pc[1] * inv_z2,fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,-fy * pc[0] * inv_z;H += J.transpose() * J;b += -J.transpose() * e;}Vector6d dx;dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);if (isnan(dx[0])) {cout << "result is nan!" << endl;break;}if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {// cost increase, update is not goodcout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;break;}// update your estimationpose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose;lastCost = cost;cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << std::setprecision(12) << cost << endl;if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) {// convergebreak;}}cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl; }/// vertex and edges used in g2o ba class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> { public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();}/// left multiplication on SE3virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;}virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {} };class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> { public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}virtual void computeError() override {const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();}virtual void linearizeOplus() override {const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;double fx = _K(0, 0);double fy = _K(1, 1);double cx = _K(0, 2);double cy = _K(1, 2);double X = pos_cam[0];double Y = pos_cam[1];double Z = pos_cam[2];double Z2 = Z * Z;_jacobianOplusXi<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;}virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}private:Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;Eigen::Matrix3d _K; };void bundleAdjustmentG2O(const VecVector3d &points_3d,const VecVector2d &points_2d,const Mat &K,Sophus::SE3d &pose) {// 構建圖優化,先設定g2otypedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 3>> BlockSolverType; // pose is 6, landmark is 3typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 線性求解器類型// 梯度下降方法,可以從GN, LM, DogLeg 中選auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 圖模型optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 設置求解器optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打開調試輸出// vertexVertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_posevertex_pose->setId(0);vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);// KEigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;K_eigen <<K.at<double>(0, 0), K.at<double>(0, 1), K.at<double>(0, 2),K.at<double>(1, 0), K.at<double>(1, 1), K.at<double>(1, 2),K.at<double>(2, 0), K.at<double>(2, 1), K.at<double>(2, 2);// edgesint index = 1;for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {auto p2d = points_2d[i];auto p3d = points_3d[i];EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);edge->setId(index);edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose);edge->setMeasurement(p2d);edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity());optimizer.addEdge(edge);index++;}chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();optimizer.setVerbose(true);optimizer.initializeOptimization();optimizer.optimize(10);chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;pose = vertex_pose->estimate(); }(3)運行的輸出如下:
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ ./pose_estimation_3d2d ../1.png ../2.png ../1_depth.png ../2_depth.png -- Max dist : 95.000000 -- Min dist : 4.000000 一共找到了79組匹配點 3d-2d pairs: 76 solve pnp in opencv cost time: 0.0109459 seconds. R= [0.9978662025826269, -0.05167241613316376, 0.03991244360207524;0.0505958915956335, 0.998339762771668, 0.02752769192381471;-0.04126860182960625, -0.025449547736074, 0.998823919929363] t= [-0.1272259656955879;-0.007507297652615337;0.06138584177157709] calling bundle adjustment by gauss newton iteration 0 cost=45538.1857253 iteration 1 cost=413.221881688 iteration 2 cost=301.36705717 iteration 3 cost=301.365779441 pose by g-n: 0.99786620258 -0.0516724160901 0.0399124437155 -0.1272259658860.050595891549 0.998339762774 0.02752769194 -0.00750729768072-0.0412686019426 -0.0254495477483 0.998823919924 0.06138584181510 0 0 1 solve pnp by gauss newton cost time: 0.000261044 seconds. calling bundle adjustment by g2o iteration= 0 chi2= 413.221882 time= 3.1152e-05 cumTime= 3.1152e-05 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 1 chi2= 301.367057 time= 1.45281e-05 cumTime= 4.56801e-05 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 2 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.8e-05 cumTime= 6.36801e-05 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 3 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.61299e-05 cumTime= 7.981e-05 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 4 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.42941e-05 cumTime= 9.41041e-05 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 5 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.4359e-05 cumTime= 0.000108463 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 6 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.48481e-05 cumTime= 0.000123311 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 7 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.3574e-05 cumTime= 0.000136885 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 8 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.7683e-05 cumTime= 0.000154568 edges= 76 schur= 0 iteration= 9 chi2= 301.365779 time= 1.4461e-05 cumTime= 0.000169029 edges= 76 schur= 0 optimization costs time: 0.000962538 seconds. pose estimated by g2o =0.997866202583 -0.0516724161336 0.0399124436024 -0.1272259656960.050595891596 0.998339762772 0.0275276919261 -0.00750729765631-0.04126860183 -0.0254495477384 0.998823919929 0.06138584177110 0 0 1 solve pnp by g2o cost time: 0.003256208 seconds.? ? ? ?從估計結果上看,三者基本一致。從優化時間來看,實現的高斯牛頓法排在第一,其次是OpenCV的PnP,最后是g2o的實現。盡管如此,三者的用時都在1毫秒以內,這說明位姿估計算法并不耗費計算量。
? ? ? ? BA是一種通用的做法。它可以不限于兩幅圖像。完全可以放入多幅圖像匹配到的位姿和空間點進行迭代優化,甚至可以把整個SLAM過程放進來。那種做法規模較大,主要在后端使用,第10講會再次遇到這個問題。在前端,通常考慮局部相機位姿和特征點的小型BA問題,希望對它進行實時求解和優化。
7.8.4 報錯修復
1.報錯代碼
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ ./pose_estimation_3d2d ../1.png ../2.png ../1_depth.png ../2_depth.png
-- Max dist : 0.000000
-- Min dist : 10000.000000
一共找到了0組匹配點
3d-2d pairs: 0
OpenCV Error: Assertion failed (npoints >= 0 && npoints == std::max(ipoints.checkVector(2, CV_32F), ipoints.checkVector(2, CV_64F))) in solvePnP, file /build/opencv-L2vuMj/opencv-3.2.0+dfsg/modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp, line 63
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'cv::Exception'what(): /build/opencv-L2vuMj/opencv-3.2.0+dfsg/modules/calib3d/src/solvepnp.cpp:63: error: (-215) npoints >= 0 && npoints == std::max(ipoints.checkVector(2, CV_32F), ipoints.checkVector(2, CV_64F)) in function solvePnP已放棄 (核心已轉儲)2.檢查與修復
(1)檢查Eigen3是否安裝,筆者版本3.4
(2)確認Eigen3.4安裝位置,筆者/usr/local/include/eigen3/Eigen
(3)確認是否有SophusConfig.cmake,查找路徑/usr/local/share/sophus/cmake/SophusConfig.cmake
(4)如上述都有修改CmakeLists.txt(如上),編譯是運行如下指令
cd ~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build rm -rf * cmake .. -DEigen3_INCLUDE_DIR=/usr/local/include/eigen3 make -j4
7.9 3D-3D:ICP
? ? ? ?假設有一組配對好的3D點(例如我們對兩幅RGB-D圖像進行了匹配):? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?現在,想要找一個歐氏變換,使得
? ? ? ?這個問題可以用迭代最近點(Iterative Closest Point,ICP)求解。
? ? ? ?3D-3D位姿估計問題中并沒有出現相機模型,僅考慮兩組3D點之間的變換時和相機無關。因此,在激光SLAM中也會碰到ICP,不過由于激光數據特征不夠豐富,無從知道兩個點集之間的匹配關系,只能認為距離最近的兩個點為同一個。
? ? ? ? 所以這個方法稱為迭代最近點。而在視覺中,特征點為我們提供了較好的匹配關系,所以整個問題就變得更簡單了。在RGB-D SLAM中,可以用這種方式估計相機位姿。下文我們用ICP指代匹配好的兩組點間的運動估計問題。
? ? ? ? 和 PnP類似,ICP的求解也分為兩種方式:利用線性代數的求解(主要是SVD),以及利用非線性優化方式的求解(類似于BA)。
7.9.1 SVD法(線性代數求解)
定義第i對點的誤差項:
構建最小二乘問題,求使誤差平方和達到極小的R、t(公式推導略):? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?
ICP可以分為以下三個步驟求解:
①計算兩組點的質心位置
,然后計算每個點的去質心坐標:
②根據以下優化問題計算旋轉矩陣:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
③根據第2步的R計算t:
? ? ? 我們看到,只要求出了兩組點之間的旋轉,平移量是非常容易得到的。所以重點關注R的計算。展開關于R的誤差項,得
? ? ? ?注意到第一項和R無關,第二項由于
,亦與R無關。因此,實際上優化目標函
數變為
? ? ? ?接下來通過SVD解出上述問題中最優的R。為了解R,先定義矩陣
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?W是一個3×3的矩陣,對W進行SVD分解,得
? ? ? ?其中,
為奇異值組成的對角矩陣,對角線元素從大到小排列,U,V為對角矩陣。當W滿秩時,R為?
? ? ? ? 解得R后,求解t即可。如果此時R的行列式為負,則取-R作為最優值。
7.9.2 非線性優化方法
? ? ? 非線性優化方法是以迭代的方式去找最優值。該方法和 PnP非常相似。以李代數表達位姿時,目標函數寫成
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? 單個誤差項關于位姿的導數在前面已推導,使用李代數擾動模型
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? 于是,在非線性優化中只需不斷迭代,就能找到極小值。而且,可以證明,ICP問題存在
唯一解或無窮多解的情況。在唯一解的情況下,只要能找到極小值解,這個極小值就是全局最優值——因此不會遇到局部極小而非全局最小的情況。這也意味著ICP求解可以任意選定初始值。這是已匹配點時求解ICP的一大好處。
? ? ? ? 這里講的ICP是指已由圖像特征給定了匹配的情況下進行位姿估計的問題。在匹配已知的情況下,這個最小二乘問題實際上具有解析解,所以并沒有必要進行迭代優化。ICP的研究者們往往更加關心匹配未知的情況。那么,為什么我們要介紹基于優化的ICP呢?這是因為,某些場合下,例如在RGB-D SLAM中,一個像素的深度數據可能有,也可能測量不到,所以我們可以混合著使用PnP和ICP優化:對于深度已知的特征點,建模它們的3D-3D誤差;對于深度未知的特征點,則建模3D-2D的重投影誤差。于是,可以將所有的誤差放在同一個問題中考慮,使得求解更加方便。
7.10 實踐:求解ICP
7.10.1 實踐:SVD方法
使用SVD及非線性優化來求解ICP。本節使用兩幅RGB-D圖像,通過特征匹配獲取兩組3D點,最后用ICP計算它們的位姿變換。由于OpenCV目前還沒有計算兩組帶匹配點的ICP的方法,而且它的原理也并不復雜,所以我們自己來實現一個ICP。
1.pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <Eigen/SVD>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace cv;void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches);// 像素坐標轉相機歸一化坐標
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1,const vector<Point3f> &pts2,Mat &R, Mat &t
);void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> &points_3d,const vector<Point3f> &points_2d,Mat &R, Mat &t
);/// vertex and edges used in g2o ba
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();}/// left multiplication on SE3virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;}virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
};/// g2o edge
class EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<3, Eigen::Vector3d, VertexPose> {
public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly(const Eigen::Vector3d &point) : _point(point) {}virtual void computeError() override {const VertexPose *pose = static_cast<const VertexPose *> ( _vertices[0] );_error = _measurement - pose->estimate() * _point;}virtual void linearizeOplus() override {VertexPose *pose = static_cast<VertexPose *>(_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = pose->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d xyz_trans = T * _point;_jacobianOplusXi.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = -Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();_jacobianOplusXi.block<3, 3>(0, 3) = Sophus::SO3d::hat(xyz_trans);}bool read(istream &in) {}bool write(ostream &out) const {}protected:Eigen::Vector3d _point;
};int main(int argc, char **argv) {if (argc != 5) {cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;return 1;}//-- 讀取圖像Mat img_1 = imread("../1.png");Mat img_2 = imread("../2.png");vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;vector<DMatch> matches;find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "組匹配點" << endl;// 建立3D點Mat depth1 = imread(argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 深度圖為16位無符號數,單通道圖像Mat depth2 = imread(argv[4], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 深度圖為16位無符號數,單通道圖像Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);vector<Point3f> pts1, pts2;for (DMatch m:matches) {ushort d1 = depth1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];ushort d2 = depth2.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x)];if (d1 == 0 || d2 == 0) // bad depthcontinue;Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K);Point2d p2 = pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K);float dd1 = float(d1) / 5000.0;float dd2 = float(d2) / 5000.0;pts1.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd1, p1.y * dd1, dd1));pts2.push_back(Point3f(p2.x * dd2, p2.y * dd2, dd2));}cout << "3d-3d pairs: " << pts1.size() << endl;Mat R, t;pose_estimation_3d3d(pts1, pts2, R, t);cout << "ICP via SVD results: " << endl;cout << "R = " << R << endl;cout << "t = " << t << endl;cout << "R_inv = " << R.t() << endl;cout << "t_inv = " << -R.t() * t << endl;cout << "calling bundle adjustment" << endl;bundleAdjustment(pts1, pts2, R, t);// verify p1 = R * p2 + tfor (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {cout << "p1 = " << pts1[i] << endl;cout << "p2 = " << pts2[i] << endl;cout << "(R*p2+t) = " <<R * (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y, pts2[i].z) + t<< endl;cout << endl;}
}void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {//-- 初始化Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;// used in OpenCV3Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();// use this if you are in OpenCV2// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");//-- 第一步:檢測 Oriented FAST 角點位置detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);//-- 第二步:根據角點位置計算 BRIEF 描述子descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);//-- 第三步:對兩幅圖像中的BRIEF描述子進行匹配,使用 Hamming 距離vector<DMatch> match;// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);//-- 第四步:匹配點對篩選double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;//找出所有匹配之間的最小距離和最大距離, 即是最相似的和最不相似的兩組點之間的距離for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {double dist = match[i].distance;if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;}printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);//當描述子之間的距離大于兩倍的最小距離時,即認為匹配有誤.但有時候最小距離會非常小,設置一個經驗值30作為下限.for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {matches.push_back(match[i]);}}
}Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {return Point2d((p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1));
}void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1,const vector<Point3f> &pts2,Mat &R, Mat &t) {Point3f p1, p2; // center of massint N = pts1.size();for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {p1 += pts1[i];p2 += pts2[i];}p1 = Point3f(Vec3f(p1) / N);p2 = Point3f(Vec3f(p2) / N);vector<Point3f> q1(N), q2(N); // remove the centerfor (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {q1[i] = pts1[i] - p1;q2[i] = pts2[i] - p2;}// compute q1*q2^TEigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {W += Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x, q1[i].y, q1[i].z) * Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x, q2[i].y, q2[i].z).transpose();}cout << "W=" << W << endl;// SVD on WEigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);Eigen::Matrix3d U = svd.matrixU();Eigen::Matrix3d V = svd.matrixV();cout << "U=" << U << endl;cout << "V=" << V << endl;Eigen::Matrix3d R_ = U * (V.transpose());if (R_.determinant() < 0) {R_ = -R_;}Eigen::Vector3d t_ = Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x, p1.y, p1.z) - R_ * Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x, p2.y, p2.z);// convert to cv::MatR = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) <<R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0, 2),R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1, 2),R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2, 2));t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> &pts1,const vector<Point3f> &pts2,Mat &R, Mat &t) {// 構建圖優化,先設定g2otypedef g2o::BlockSolverX BlockSolverType;typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 線性求解器類型// 梯度下降方法,可以從GN, LM, DogLeg 中選auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 圖模型optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 設置求解器optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打開調試輸出// vertexVertexPose *pose = new VertexPose(); // camera posepose->setId(0);pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());optimizer.addVertex(pose);// edgesfor (size_t i = 0; i < pts1.size(); i++) {EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly *edge = new EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly(Eigen::Vector3d(pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y, pts2[i].z));edge->setVertex(0, pose);edge->setMeasurement(Eigen::Vector3d(pts1[i].x, pts1[i].y, pts1[i].z));edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity());optimizer.addEdge(edge);}chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();optimizer.initializeOptimization();optimizer.optimize(10);chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;cout << endl << "after optimization:" << endl;cout << "T=\n" << pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;// convert to cv::MatEigen::Matrix3d R_ = pose->estimate().rotationMatrix();Eigen::Vector3d t_ = pose->estimate().translation();R = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) <<R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0, 2),R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1, 2),R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2, 2));t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}2.CmakeLists.txt
#include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
include_directories("/usr/local/include/eigen3")
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/usr/local" ${CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH})# 確保 Eigen3::Eigen target 存在
if(NOT TARGET Eigen3::Eigen)add_library(Eigen3::Eigen INTERFACE IMPORTED)set_target_properties(Eigen3::Eigen PROPERTIESINTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES "/usr/local/include/eigen3")
endif()# Sophus
set(EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR "/usr/local/include/eigen3")
include_directories(${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR})find_package(Sophus REQUIRED NO_MODULE)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
#find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
##include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
#target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d Sophus::Sophus)# 添加一個可執行程序,可執行文件名 cpp文件名
add_executable(orb_cv orb_cv.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_cv ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(orb_self orb_self.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_self ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_2d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(triangulation triangulation.cpp)
target_link_libraries(triangulation ${OpenCV_LIBS})add_executable(pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS} g2o_core g2o_stuffSophus::Sophus
)add_executable(pose_estimation_3d3d pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d3d ${OpenCV_LIBS} g2o_core g2o_stuffSophus::Sophus
)
3.運行結果
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ cmake ..
-- Configuring done
-- Generating done
-- Build files have been written to: /home/caohao/桌面/slam/slam_07/build
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ make
Consolidate compiler generated dependencies of target orb_cv
[ 16%] Built target orb_cv
Consolidate compiler generated dependencies of target orb_self
[ 33%] Built target orb_self
Consolidate compiler generated dependencies of target pose_estimation_2d2d
[ 50%] Built target pose_estimation_2d2d
Consolidate compiler generated dependencies of target triangulation
[ 66%] Built target triangulation
Consolidate compiler generated dependencies of target pose_estimation_3d2d
[ 83%] Built target pose_estimation_3d2d
[ 91%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/pose_estimation_3d3d.dir/pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp.o
[100%] Linking CXX executable pose_estimation_3d3d
[100%] Built target pose_estimation_3d3d
caohao@ubuntu:~/桌面/slam/slam_07/build$ ./pose_estimation_3d3d ../1.png ../2.png ../1_depth.png ../2_depth.png
-- Max dist : 95.000000
-- Min dist : 4.000000
一共找到了79組匹配點
3d-3d pairs: 74
W= 11.9404 -0.567258 1.64182-1.79283 4.31299 -6.576153.12791 -6.55815 10.8576
U= 0.474144 -0.880373 -0.0114952-0.460275 -0.258979 0.8491630.750556 0.397334 0.528006
V= 0.535211 -0.844064 -0.0332488-0.434767 -0.309001 0.845870.724242 0.438263 0.532352
ICP via SVD results:
R = [0.9972395977366735, 0.05617039856770108, -0.04855997354553421;-0.05598345194682008, 0.9984181427731503, 0.005202431117422968;0.04877538122983249, -0.002469515369266706, 0.9988067198811419]
t = [0.1417248739257467;-0.05551033302525168;-0.03119093188273836]
R_inv = [0.9972395977366735, -0.05598345194682008, 0.04877538122983249;0.05617039856770108, 0.9984181427731503, -0.002469515369266706;-0.04855997354553421, 0.005202431117422968, 0.9988067198811419]
t_inv = [-0.1429199667309692;0.04738475446275831;0.03832465717628154]
calling bundle adjustment
iteration= 0 chi2= 1.811537 time= 3.054e-05 cumTime= 3.054e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000795 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 1 chi2= 1.811051 time= 1.7044e-05 cumTime= 4.7584e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000530 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 2 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.4962e-05 cumTime= 6.2546e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000353 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 3 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5674e-05 cumTime= 7.822e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000236 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 4 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5218e-05 cumTime= 9.3438e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000157 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 5 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5405e-05 cumTime= 0.000108843 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000105 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 6 chi2= 1.811050 time= 2.1392e-05 cumTime= 0.000130235 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.006703 levenbergIter= 3
optimization costs time: 0.000536153 seconds.after optimization:
T=0.99724 0.0561704 -0.04856 0.141725
-0.0559834 0.998418 0.00520242 -0.05551030.0487754 -0.0024695 0.998807 -0.03119130 0 0 1
p1 = [-0.0374123, -0.830816, 2.7448]
p2 = [-0.0111479, -0.746763, 2.7652]
(R*p2+t) = [-0.0456162060096475;-0.7860824176937432;2.732009294040371]p1 = [-0.243698, -0.117719, 1.5848]
p2 = [-0.299118, -0.0975683, 1.6558]
(R*p2+t) = [-0.2424538642667685;-0.127564412420742;1.608284141645051]p1 = [-0.627753, 0.160186, 1.3396]
p2 = [-0.709645, 0.159033, 1.4212]
(R*p2+t) = [-0.6260418020833747;0.1503926994308992;1.353306864239974]p1 = [-0.323443, 0.104873, 1.4266]
p2 = [-0.399079, 0.12047, 1.4838]
(R*p2+t) = [-0.3215392021872832;0.09483002837549004;1.43107537937968]p1 = [-0.627221, 0.101454, 1.3116]
p2 = [-0.709709, 0.100216, 1.3998]
(R*p2+t) = [-0.6283696073388314;0.09156140480846489;1.33207446092358]
7.10.2 實踐非線性優化方法
1.涉及代碼
/// g2o edge
class EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<3, Eigen::Vector3d, VertexPose> {
public:EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly(const Eigen::Vector3d &point) : _point(point) {}virtual void computeError() override {const VertexPose *pose = static_cast<const VertexPose *> ( _vertices[0] );_error = _measurement - pose->estimate() * _point;}virtual void linearizeOplus() override {VertexPose *pose = static_cast<VertexPose *>(_vertices[0]);Sophus::SE3d T = pose->estimate();Eigen::Vector3d xyz_trans = T * _point;_jacobianOplusXi.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = -Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();_jacobianOplusXi.block<3, 3>(0, 3) = Sophus::SO3d::hat(xyz_trans);}bool read(istream &in) {}bool write(ostream &out) const {}protected:Eigen::Vector3d _point;
};
2.運行結果
iteration= 0 chi2= 1.811537 time= 3.054e-05 cumTime= 3.054e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000795 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 1 chi2= 1.811051 time= 1.7044e-05 cumTime= 4.7584e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000530 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 2 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.4962e-05 cumTime= 6.2546e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000353 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 3 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5674e-05 cumTime= 7.822e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000236 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 4 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5218e-05 cumTime= 9.3438e-05 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000157 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 5 chi2= 1.811050 time= 1.5405e-05 cumTime= 0.000108843 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.000105 levenbergIter= 1
iteration= 6 chi2= 1.811050 time= 2.1392e-05 cumTime= 0.000130235 edges= 74 schur= 0 lambda= 0.006703 levenbergIter= 3
optimization costs time: 0.000536153 seconds.after optimization:
T=0.99724 0.0561704 -0.04856 0.141725
-0.0559834 0.998418 0.00520242 -0.05551030.0487754 -0.0024695 0.998807 -0.03119130 0 0 1
7.11 小結
本講介紹了基于特征點的視覺里程計中的幾個重要的問題。
1.特征點是如何提取并匹配的
2.如何通過2D-2D的特征點估計相機運動
3.如何從2D-2D的匹配估計一個點的空間位置
4.3D-2D的 PnP問題,其線性解法和BA解法
5.3D-3D的ICP問題,其線性解法和 BA解法
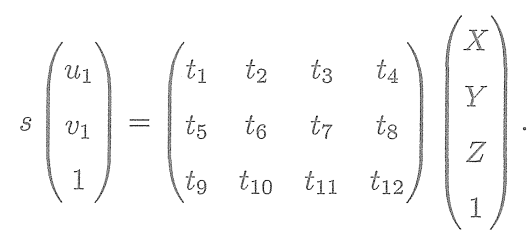
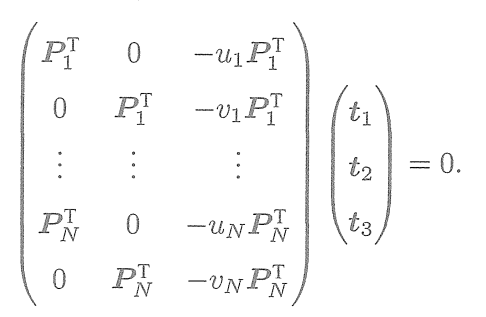
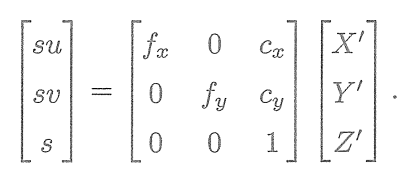
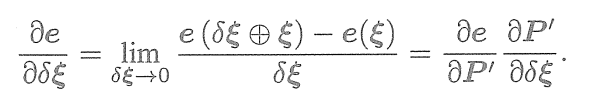
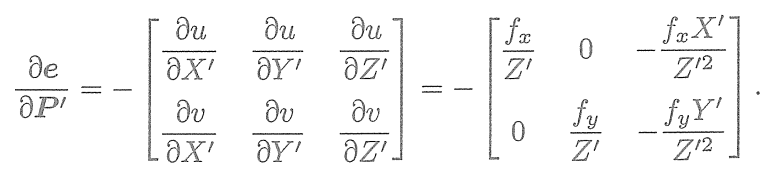
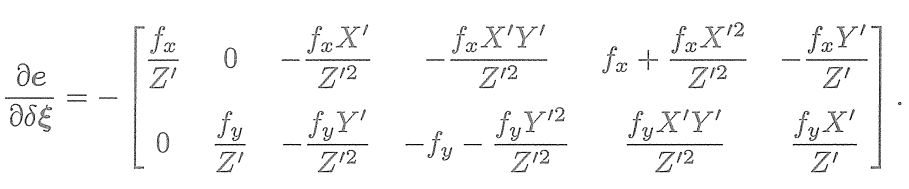
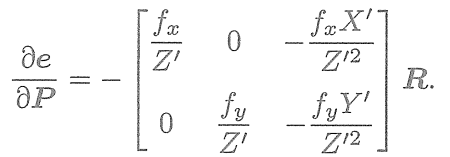
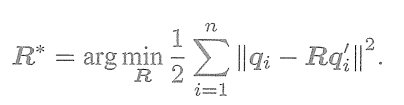
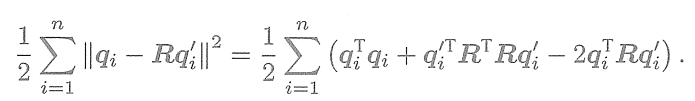
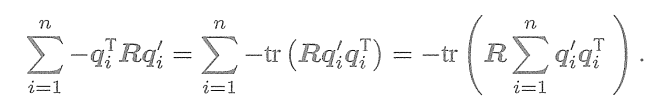
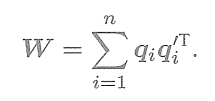
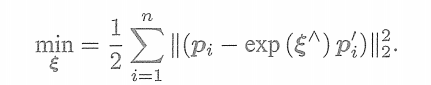
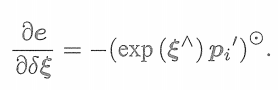




)

 的前端示例)












(90))