如有問題大概率是我的理解比較片面,歡迎評論區或者私信指正。
友友們,我遇到了一個大問題,技術類的英文面(ai應用開發/java后端偏金融方向)該如何準備?本人英語就過了個六級,腦闊疼額。友友們有啥方法和資料推薦沒,可以教教我嗎?
考察以基礎概念、操作實現(主要是子串的相關操作)、存儲結構對比、模式匹配算法(尤其是 KMP)為核心,注重理論理解與代碼實現結合,需重點掌握子串相關操作、next數組計算、KMP 優化思想及樸素算法與 KMP 的復雜度對比。
一、基礎概念與術語辨析
核心定義考察?可能要求解釋串的定義及相關術語
串的定義:由零個或多個字符組成的有限序列。
子串與主串:子串是串中任意連續字符組成的子序列,主串是包含子串的串。
空串與空格串的區別:空串長度為 0,空格串由空格字符組成(每個空格占 1B,如
N=' '。
字符 / 子串的 “位置” 定義:字符位置指其在串中的序號,子串位置指其第一個字符在主串中的位置(位序從 1 開始)。
問題1:“請區分空串和空格串,并舉例說明”“子串在主串中的位置如何定義?”
問題2:“Java中,字符串本身可變嗎?”Java中,字符串本身是不可變的
存儲結構及優缺點分析
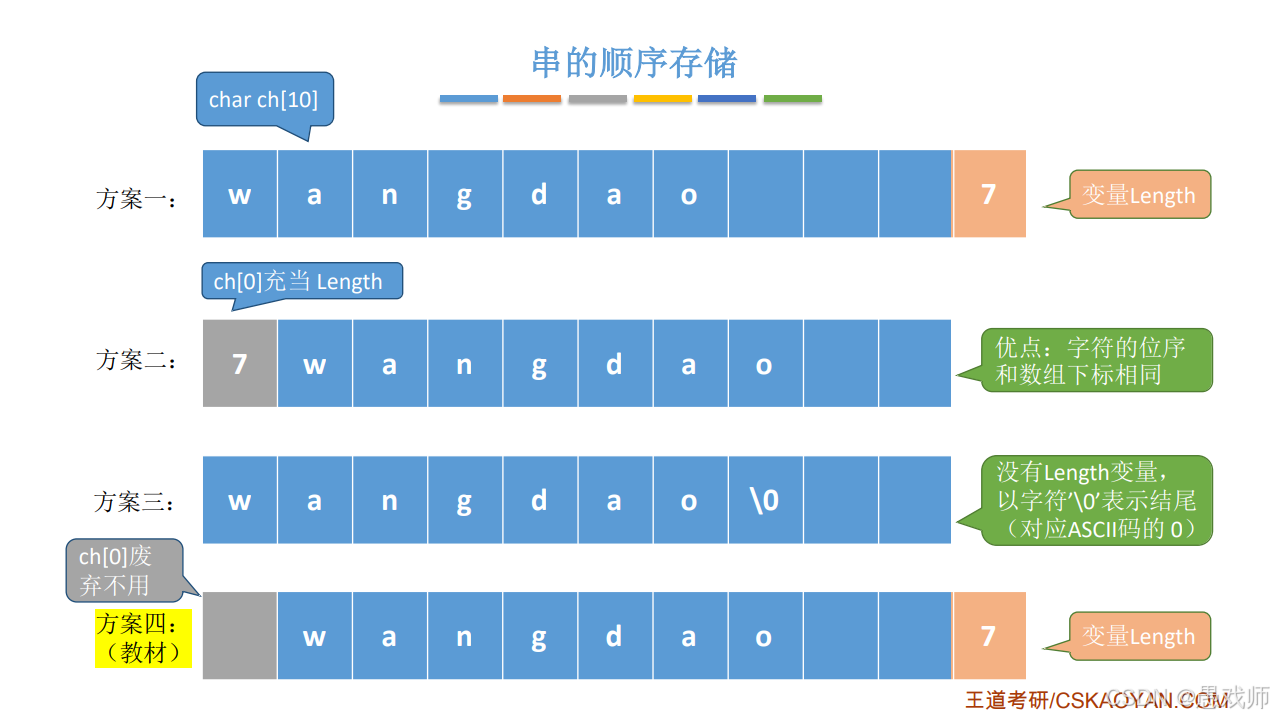
順序存儲
靜態數組(定長):用固定大小數組存儲
?優點:隨機訪問效率高;缺點:長度固定,可能浪費空間或溢出。
動態數組(堆分配):按實際長度分配空間()
優點:空間靈活;缺點:需手動管理內存。
public class StringStorageDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// ============= 靜態數組實現串 =============StaticString staticStr = new StaticString(5);staticStr.assign("Hello");System.out.println("靜態串內容: " + staticStr);System.out.println("長度: " + staticStr.length());System.out.println("索引2的字符: " + staticStr.charAt(2));// 嘗試連接字符串(會截斷)staticStr.concat(" World!");System.out.println("連接后(截斷): " + staticStr);// ============= 動態數組實現串 =============DynamicString dynamicStr = new DynamicString();dynamicStr.assign("Java");System.out.println("\n動態串初始內容: " + dynamicStr);System.out.println("長度: " + dynamicStr.length());System.out.println("容量: " + dynamicStr.capacity());// 連接字符串(自動擴容)dynamicStr.concat(" is a powerful programming language!");System.out.println("連接后: " + dynamicStr);System.out.println("新長度: " + dynamicStr.length());System.out.println("新容量: " + dynamicStr.capacity());}
}// 靜態數組實現的串(定長)
class StaticString {private final char[] data; // 固定大小數組private int length; // 實際長度public StaticString(int capacity) {data = new char[capacity];length = 0;}// 賦值操作public void assign(String str) {int copyLength = Math.min(str.length(), data.length);for (int i = 0; i < copyLength; i++) {data[i] = str.charAt(i);}length = copyLength;}// 連接操作(可能截斷)public void concat(String str) {int remaining = data.length - length;if (remaining <= 0) return;int copyLength = Math.min(str.length(), remaining);for (int i = 0; i < copyLength; i++) {data[length + i] = str.charAt(i);}length += copyLength;}// 獲取字符public char charAt(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= length) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();return data[index];}public int length() {return length;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return new String(data, 0, length);}
}// 動態數組實現的串(堆分配)
class DynamicString {private char[] data; // 堆分配的數組private int length; // 實際長度private int capacity; // 當前容量public DynamicString() {this(16); // 默認初始容量}public DynamicString(int initialCapacity) {capacity = initialCapacity;data = new char[capacity];length = 0;}// 賦值操作public void assign(String str) {ensureCapacity(str.length());length = str.length();str.getChars(0, length, data, 0);}// 連接操作(自動擴容)public void concat(String str) {ensureCapacity(length + str.length());str.getChars(0, str.length(), data, length);length += str.length();}// 確保容量足夠(核心擴容邏輯)private void ensureCapacity(int required) {if (required <= capacity) return;// 計算新容量(通常1.5-2倍增長)int newCapacity = Math.max(required, capacity * 2);char[] newData = new char[newCapacity];// 復制數據System.arraycopy(data, 0, newData, 0, length);// 更新引用和容量data = newData;capacity = newCapacity;System.out.println("擴容至: " + newCapacity);}public char charAt(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= length) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();return data[index];}public int length() {return length;}public int capacity() {return capacity;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return new String(data, 0, length);}
}實際應用中一般用String-->靜態數組的實現,用StringBuilder-->動態數組實現
public class StringStorageDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// ============= 使用String實現(類似靜態數組特性) =============String staticString = "Hello";System.out.println("String實現:");System.out.println("原始內容: " + staticString);System.out.println("長度: " + staticString.length());System.out.println("索引2的字符: " + staticString.charAt(2));// 連接操作 - 創建新對象String newString = staticString.concat(" World!");System.out.println("連接后內容: " + newString);System.out.println("原始對象未變: " + staticString);System.out.println("新對象長度: " + newString.length());// 內存地址比較 - 證明是新對象System.out.println("原始對象地址: " + System.identityHashCode(staticString));System.out.println("新對象地址: " + System.identityHashCode(newString));// ============= 使用StringBuilder實現(類似動態數組特性) =============StringBuilder dynamicString = new StringBuilder("Java");System.out.println("\nStringBuilder實現:");System.out.println("原始內容: " + dynamicString);System.out.println("長度: " + dynamicString.length());System.out.println("容量: " + dynamicString.capacity());System.out.println("索引1的字符: " + dynamicString.charAt(1));// 連接操作 - 原地修改dynamicString.append(" is a powerful programming language!");System.out.println("連接后內容: " + dynamicString);System.out.println("新長度: " + dynamicString.length());System.out.println("新容量: " + dynamicString.capacity());// 內存地址比較 - 證明是同一個對象System.out.println("操作后對象地址: " + System.identityHashCode(dynamicString));// 插入操作展示dynamicString.insert(0, "Awesome ");System.out.println("\n插入后內容: " + dynamicString);System.out.println("最終長度: " + dynamicString.length());System.out.println("最終容量: " + dynamicString.capacity());}
}鏈式存儲(存儲密度)
單字符節點,缺點:存儲密度低(1B 字符 + 4B 指針)。
多字符節點:每個節點存多個字符(如 4 個),空閑位置用#補足。 優點:提高存儲密度。
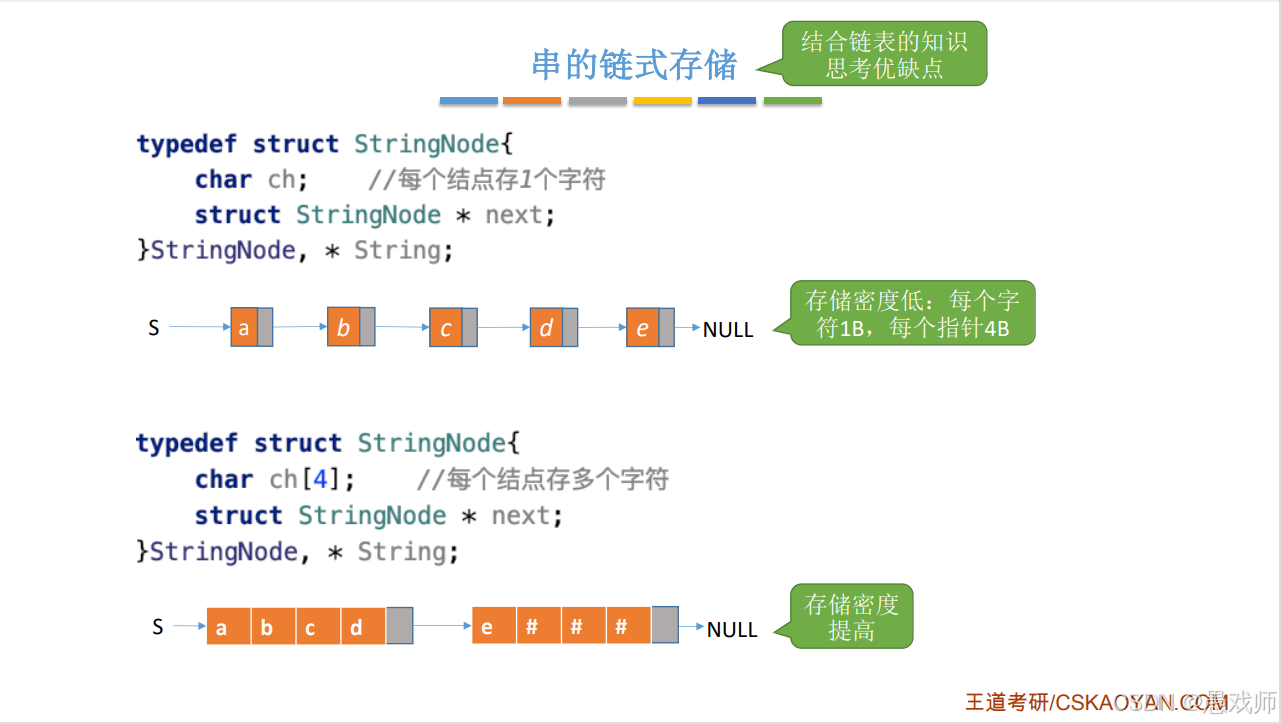
問題1:“串的順序存儲和鏈式存儲各有什么優缺點?針對頻繁拼接操作,應選擇哪種存儲結構?”
優先選擇鏈式存儲??
??核心優勢??:鏈式存儲在拼接時僅需修改指針,??避免數據復制??。
??優化策略??:采用??塊鏈結構??(如每個結點存4字符),平衡存儲密度與操作效率。
單字符節點實現(塊狀存儲)
class CharLinkedList {static class CharNode {char data;CharNode next;CharNode(char c) {this.data = c;}}private CharNode head;private int length;public void append(char c) {CharNode newNode = new CharNode(c);if (head == null) {head = newNode;} else {CharNode current = head;while (current.next != null) {current = current.next;}current.next = newNode;}length++;}public char charAt(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= length) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}CharNode current = head;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {current = current.next;}return current.data;}// 其他方法:insert, delete, toString 等
}多字符節點實現(塊狀存儲)
class BlockLinkedList {static class BlockNode {static final int BLOCK_SIZE = 4;char[] data = new char[BLOCK_SIZE];int size = 0; // 當前塊中有效字符數BlockNode next;// 添加字符到塊中boolean add(char c) {if (size < BLOCK_SIZE) {data[size++] = c;return true;}return false;}// 塊中是否已滿boolean isFull() {return size == BLOCK_SIZE;}}private BlockNode head;private int totalLength;public void append(char c) {if (head == null) {head = new BlockNode();}BlockNode current = head;BlockNode prev = null;// 查找可以添加字符的塊while (current != null && current.isFull()) {prev = current;current = current.next;}if (current == null) {// 所有塊已滿,創建新塊current = new BlockNode();prev.next = current;}current.add(c);totalLength++;}public char charAt(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= totalLength) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}BlockNode current = head;int blockIndex = 0;while (current != null) {if (index < blockIndex + current.size) {return current.data[index - blockIndex];}blockIndex += current.size;current = current.next;}throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}// 其他方法:insert, delete, toString 等
}串與線性表的對比
可能通過對比考察對串特殊性的理解:
-
串是特殊的線性表,數據元素間呈線性關系,但數據對象限定為字符集(如中文字符、英文字符等)。
-
串的基本操作(如增刪改查)通常以子串為操作對象,而線性表操作多以單個元素為對象。
典型問題:“串與線性表的主要區別是什么?”
二、基本操作與實現
核心操作功能描述 需掌握串的基本操作定義:
StrAssign(賦值)、StrCopy(復制)、StrEmpty(判空)、StrLength(求長)(至)。
Concat(串聯接):將兩個串拼接為新串。
SubString(求子串):從指定位置提取長度為len的子串。
Index(定位):返回模式串在主串中首次出現的位置。
StrCompare(比較):按字符依次對比,返回正值(S>T)、0(S=T)或負值(S<T)。
public class MyString {private char[] value; // 存儲字符串的字符數組// 構造函數1:空串public MyString() {this.value = new char[0];}// 構造函數2:通過字符數組創建public MyString(char[] value) {this.value = new char[value.length];System.arraycopy(value, 0, this.value, 0, value.length);}// 構造函數3:通過Java字符串創建public MyString(String str) {this.value = str.toCharArray();}// 1. StrAssign - 賦值操作public void StrAssign(MyString str) {this.value = new char[str.value.length];System.arraycopy(str.value, 0, this.value, 0, str.value.length);}// 2. StrCopy - 復制操作public MyString StrCopy() {return new MyString(this.value);}// 3. StrEmpty - 判空操作public boolean StrEmpty() {return value.length == 0;}// 4. StrLength - 求長度public int StrLength() {return value.length;}// 5. Concat - 串聯接public MyString Concat(MyString str) {char[] result = new char[this.value.length + str.value.length];System.arraycopy(this.value, 0, result, 0, this.value.length);System.arraycopy(str.value, 0, result, this.value.length, str.value.length);return new MyString(result);}// 6. SubString - 求子串public MyString SubString(int pos, int len) {if (pos < 0 || pos >= value.length || len < 0 || pos + len > value.length) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Invalid substring parameters");}char[] sub = new char[len];System.arraycopy(value, pos, sub, 0, len);return new MyString(sub);}// 7. Index - 定位(樸素模式匹配)public int Index(MyString pattern) {if (pattern.StrEmpty()) return 0; // 空模式串總是匹配int n = this.StrLength();int m = pattern.StrLength();for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {int j;for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (value[i + j] != pattern.value[j]) {break;}}if (j == m) return i; // 匹配成功}return -1; // 未找到}// 8. StrCompare - 比較操作public int StrCompare(MyString other) {int len1 = this.StrLength();int len2 = other.StrLength();int minLen = Math.min(len1, len2);for (int i = 0; i < minLen; i++) {if (this.value[i] != other.value[i]) {return this.value[i] - other.value[i];}}// 共同部分相同,比較長度return len1 - len2;}// 輔助方法:轉換為Java字符串@Overridepublic String toString() {return new String(value);}// 測試用例public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建字符串MyString s1 = new MyString("Hello");MyString s2 = new MyString("World");MyString s3 = new MyString("HelloWorld");System.out.println("===== 基本操作測試 =====");System.out.println("s1: " + s1 + ", 長度: " + s1.StrLength());System.out.println("s2: " + s2 + ", 長度: " + s2.StrLength());System.out.println("s1是否為空: " + s1.StrEmpty());// 復制操作MyString s1Copy = s1.StrCopy();System.out.println("\n===== 復制操作 =====");System.out.println("s1的副本: " + s1Copy);// 串聯接操作MyString concatResult = s1.Concat(s2);System.out.println("\n===== 串聯接操作 =====");System.out.println(s1 + " + " + s2 + " = " + concatResult);// 求子串操作System.out.println("\n===== 求子串操作 =====");MyString sub = s3.SubString(3, 5);System.out.println(s3 + " 的子串(從位置3開始長度5): " + sub);// 定位操作System.out.println("\n===== 定位操作 =====");MyString pattern = new MyString("loW");int index = s3.Index(pattern);System.out.println("在 " + s3 + " 中查找 " + pattern + " 的位置: " + index);// 比較操作System.out.println("\n===== 比較操作 =====");MyString s4 = new MyString("Apple");MyString s5 = new MyString("Banana");System.out.println(s1 + " 與 " + s1Copy + " 比較: " + s1.StrCompare(s1Copy));System.out.println(s1 + " 與 " + s2 + " 比較: " + s1.StrCompare(s2));System.out.println(s4 + " 與 " + s5 + " 比較: " + s4.StrCompare(s5));System.out.println(s5 + " 與 " + s4 + " 比較: " + s5.StrCompare(s4));}
}題目一字符串反轉
344. 反轉字符串
考察點:字符串的遍歷與元素交換,基礎操作實現。
class Solution {public void reverseString(char[] s) {int head=0,tail=s.length-1;while(head<=tail){char temp=s[head];s[head]=s[tail];s[tail]=temp;head++;tail--;}}
}題目二字符串拼接與分割
151. 反轉字符串中的單詞
考察點:字符串的分割(按空格)、反轉后拼接,處理首尾空格等邊界情況。
import java.util.*;class Solution {public String reverseWords(String s) {// 去除字符串首尾空格String trimmed = s.trim();// 如果去除空格后為空,直接返回空字符串if (trimmed.isEmpty()) {return "";}// 按一個或多個空格分割字符串String[] words = trimmed.split("\\s+");// 將數組轉換為列表并反轉List<String> wordList = Arrays.asList(words);Collections.reverse(wordList);// 用單個空格連接反轉后的單詞列表return String.join(" ", wordList);}
}三、模式匹配算法(重點)
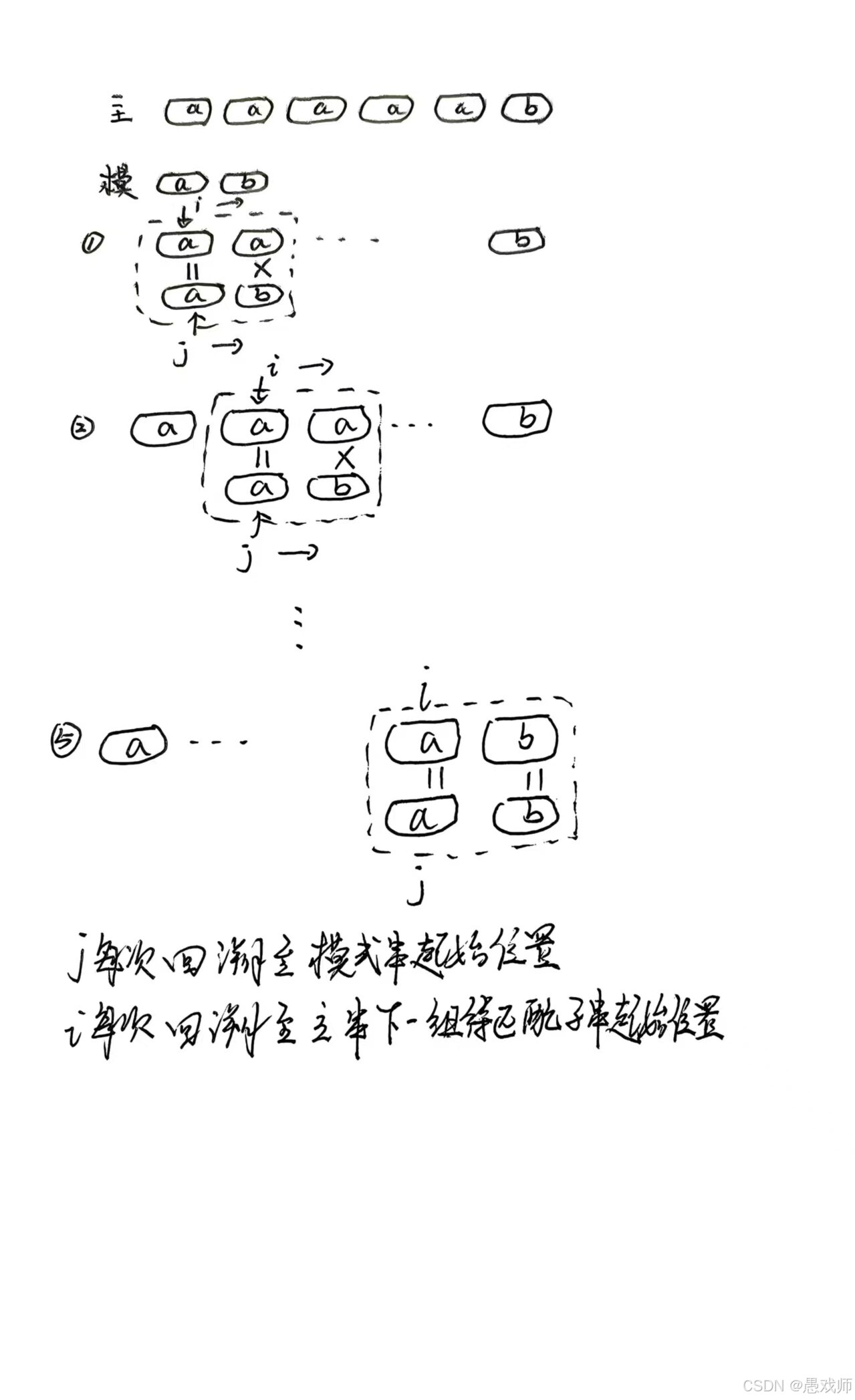
樸素模式匹配算法
思想:將主串中所有長度為模式串長度的子串依次與模式串對比。
時間復雜度:最壞情況(n為主串長度,m為模式串長度),如主串為
aaaaab、模式串為ab時。
考察點:手動模擬匹配過程,分析最壞情況成因。
KMP 算法
核心目標:?更快地在主串(文本)S?中找到模式串(關鍵詞)T?出現的位置。
1. 樸素匹配算法的痛點:低效的回溯
想象一下,你想在一本很厚的書(S)里找一個特定的單詞(T),比如?"abaabc"。
-
樸素方法:?你從書的第一頁第一行第一個字母開始,一個字母一個字母地對比?
"abaabc"。-
如果第一個字母就不同(比如書上是?
b,單詞是?a),你立刻把書往后翻一點點(移動一格),重新從單詞開頭對比。 -
如果前面幾個字母都相同,但到第 5 個字母不同了(比如書上第 5 個是?
x,單詞第 5 個是?b),你會把書往后翻一點點(移動一格),然后完全從頭開始對比單詞?"abaabc",即使你知道剛剛書上的?"abaa"?和單詞開頭的?"abaa"?是匹配的!這就是低效的來源——主串指針?i?經常回溯。
-
2. KMP 的聰明想法:利用已知信息,避免回溯主串
KMP 算法觀察到一個關鍵點:當匹配失敗時(比如在?T[j]?處失敗了),模式串?T[1..j-1]?這一段是和主串?S[i-j+1..i-1]?完全匹配的!?這個信息非常寶貴,因為這段信息將對未知主串的處理映射轉化成對已知的模式串的處理上來,從而有效避免主串指針回溯問題。
KMP 的核心問題是:既然?T[1..j-1]?已經匹配成功了,那么當?T[j]?匹配失敗時,我們能不能直接把模式串?T?“滑動”到一個新的位置,讓這個新位置之前的某個前綴,剛好對上主串?S?中剛匹配成功的那段后綴?并且保持主串指針?i?不動(不回溯)!
-
目標:?找到一個新的位置?
k(k < j),使得?T[1..k]?=?T[j-k..j-1]。-
T[1..k]?是模式串開頭的前?k?個字符(前綴)。 -
T[j-k..j-1]?是模式串匹配失敗位置?j?前面?k?個字符(后綴)。 -
要求這兩段相等。
-
-
為什么這樣滑動有效?
-
因為主串?
S[i-j+1..i-1]?=?T[1..j-1](已匹配)。 -
滑動后,我們希望?
T[1..k]?去對齊?S?中?[i-k..i-1]?這段。 -
根據要求?
T[1..k]?=?T[j-k..j-1],而?T[j-k..j-1]?又等于?S[i-k..i-1](因為?T[1..j-1]?=?S[i-j+1..i-1],取最后?k?個)。 -
所以?
T[1..k]?=?S[i-k..i-1],滑動后,T[1..k]?這段不用重新比較就已經知道匹配了!我們可以直接從?T[k+1]?和?S[i]?開始繼續比較(主串?i?沒動,模式串指針?j?更新為?k+1)。
-

3. next 數組:存儲“滑動位置”信息
-
定義:?
next[j]?表示當模式串?T?的第?j?個字符?T[j]?與主串失配時,模式串指針?j?應該回退到的位置(k)加 1。或者說,next[j]?指示了下一次應該用?T?的第?next[j]?個字符去和主串當前失配字符?S[i]?進行比較。-
更直觀的公式:
j?回退到?next[j]?(j = next[j])
-
-
核心任務:?
next[j]?的值等于?T[1..j-1]?這個子串的最長相等真前綴和真后綴的長度 + 1。-
真前綴:?去掉最后一個字符的前綴(如?
"aba"?的真前綴有?"a",?"ab")。 -
真后綴:?去掉第一個字符的后綴(如?
"aba"?的真后綴有?"ba",?"a")。 -
最長相等真前后綴:?找一個最長的字符串,它既是?
T[1..j-1]?的真前綴,又是?T[1..j-1]?的真后綴。 -
next[j]?= 這個最長長度 + 1
-
-
為什么是“最長”??為了保證滑動的幅度盡可能大(跳過盡可能多的無效比較),同時不會漏掉可能的匹配起點。
-
約定:
-
next[1] = 0:如果模式串第一個字符就失配,主串指針?i?后移一位 (i++),模式串指針?j?保持為 1 (或者?j?回退到 0 后緊接著?j++?回到 1,效果一樣) 去匹配下一個子串。這對應樸素匹配中“移動一格從頭開始”。 -
next[2] = 1:如果模式串第二個字符失配,說明第一個字符是匹配的。此時?T[1..1]?的真前綴和真后綴都是空集(長度 0),next[2] = 0 + 1 = 1。意思是?j?回退到 1,用?T[1]?去和當前?S[i]?比較(雖然?T[1]?之前匹配過,但主串?i?沒動,當前?S[i]?是導致?T[2]?失配的那個字符,所以需要重新比較?T[1]?和它是否匹配)。
-
4. 手算 next 數組(核心:找最長相等真前后綴)
以模式串?T = "abaabc"?為例:
j | T[1..j] | T[1..j-1] | T[1..j-1]?的最長相等真前后綴長度?L | next[j]?=?L + 1 | 解釋 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | - | - (約定) | 0 | 第一個字符失配,i++,?j?重置 |
| 2 | ab | a | 真前綴:[]真后綴:[]L = 0 | 1 | 第二個字符失配,回退到第一個字符?T[1]?比較 |
| 3 | aba | ab | 真前綴:["a"]真后綴:["b"]不相等L = 0 | 1 | 第三個字符失配,回退到第一個字符?T[1]?比較 |
| 4 | abaa | aba | 真前綴:["a", "ab"]真后綴:["ba", "a"]相等部分:"a" (長度1)L = 1 | 2 | 第四個字符失配,回退到第二個字符?T[2]?比較 |
| 5 | abaab | abaa | 真前綴:["a", "ab", "aba"]真后綴:["baa", "aa", "a"]相等部分:"a" (長度1)L = 1 | 2 | 第五個字符失配,回退到第二個字符?T[2]?比較 |
| 6 | abaabc | abaab | 真前綴:["a", "ab", "aba", "abaa"]真后綴:["baab", "aab", "ab", "b"]相等部分:"ab" (長度2)L = 2 | 3 | 第六個字符失配,回退到第三個字符?T[3]?比較 |
最終 next 數組:next[] = [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3]?(通常?next[0]?不用,下標從 1 開始對應?j)
5.代碼實現(Java中一般用0-base)
public class KMPMatcher {// 構建next數組(部分匹配表)public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {if (ms.length == 1) {return new int[]{-1};}int[] next = new int[ms.length];next[0] = -1;next[1] = 0;int i = 2; // next數組填充位置int cn = 0; // 當前比較位置while (i < ms.length) {if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) {//next[i]=cn+1;//cn++;//i++;next[i++] = ++cn;} else if (cn > 0) {cn = next[cn];} else {next[i++] = 0;}}return next;}// KMP字符串匹配算法public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) {// 參數合法性校驗if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) {return -1;}char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();int i1 = 0; // 主串指針int i2 = 0; // 模式串指針int[] next = getNextArray(str2); // 獲取部分匹配表while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) {if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) {i1++;i2++; // 字符匹配成功,雙指針后移} else if (next[i2] == -1) {i1++; // 模式串首位不匹配,主串后移} else {i2 = next[i2]; // 利用next數組跳過已匹配前綴}}// 返回匹配起始位置或-1return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1;}// 使用示例public static void main(String[] args) {String text = "ababaabaabc";String pattern = "abaabc";int index = getIndexOf(text, pattern);System.out.println("匹配位置: " + index); // 輸出: 5}
}求next數組的的關鍵在于cn,(1、cn指的是p[1..i-1]的最長前后綴長度;2、cn指的是與i-1元素進行比較的元素的下標位置),next[0]=-1作為回退邊界
kmp的關鍵在于next數組的回退過程,回退邊界判斷和返回值。我的理解可能比較片面,可以參考以下大佬的講解,建議從1:28:00開始看。
基礎提升:2 有序表、并查集等_嗶哩嗶哩_bilibili![]() https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ef4y1T7Qi?spm_id_from=333.788.player.switch&vd_source=4b89f462036a892baf8931104a1f36b1&p=35
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ef4y1T7Qi?spm_id_from=333.788.player.switch&vd_source=4b89f462036a892baf8931104a1f36b1&p=35
-
next?數組的意義:?它告訴我們在模式串?T?的?j?位置匹配失敗時,應該把?j?回退到哪個位置(next[j])去繼續和主串當前的?S[i]?比較。主串指針?i?永不回溯! -
next[j]?的計算本質:?就是求?T[1..j-1]?這個子串的最長相等真前綴和真后綴的長度 + 1。這個值完全由模式串?T?自身決定。 -
效率提升:?通過?
next?數組,KMP 避免了主串指針?i?的無效回溯(這是樸素算法慢的主要原因),在失配時能跳過一大段肯定不匹配的位置。預處理?next?數組的時間是?O(m),匹配過程是?O(n),整體?O(m+n),遠優于樸素算法的?O(m*n)(尤其在主串和模式串有很多部分匹配時)。
簡單來說:?KMP 利用匹配失敗時已經匹配成功的那部分模式串的信息(體現在?next?數組中),聰明地“滑動”模式串,跳過一些肯定不匹配的位置,讓匹配過程加速。next?數組就是這個聰明滑動的導航圖。
進一步優化:
nextval數組,解決next數組的冗余跳轉(如模式串aaaab的nextval為[0,0,0,0,4]),本質就是利用當前匹配信息,如當前模式串與文本串的當前字符不匹配則文本串的當前字符一定和跳轉后相同的模式串字符(如有)不匹配,所以可以在next的基礎上寫出nextval數組。?
nextval[0] = -1;
nextval[1] = 0;
for (int j = 2; j <= T.length; j++) {if (T.ch[next[j]] == T.ch[j])nextval[j] = nextval[next[j]];elsenextval[j] = next[j];
}問題1:“KMP 算法相比樸素算法有什么優化?next數組的含義是什么?”
問題2:字符匹配
28. 找出字符串中第一個匹配項的下標 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/description/
class Solution {public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {return getIndexOf(haystack,needle);}// 構建next數組(部分匹配表)public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {if (ms.length == 1) {return new int[]{-1};}int[] next = new int[ms.length];next[0] = -1;next[1] = 0;int i = 2; // next數組填充位置int cn = 0; // 當前比較位置while (i < ms.length) {if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) {//next[i]=cn+1;//cn++;//i++;next[i++] = ++cn;} else if (cn > 0) {cn = next[cn];} else {next[i++] = 0;}}return next;}// KMP字符串匹配算法public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) {// 參數合法性校驗if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) {return -1;}char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();int i1 = 0; // 主串指針int i2 = 0; // 模式串指針int[] next = getNextArray(str2); // 獲取部分匹配表while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) {if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) {i1++;i2++; // 字符匹配成功,雙指針后移} else if (next[i2] == -1) {i1++; // 模式串首位不匹配,主串后移} else {i2 = next[i2]; // 利用next數組跳過已匹配前綴}}// 返回匹配起始位置或-1return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1;}}問題3:“請計算模式串ababaa的next數組和nextval數組”。
class Solution {public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {return getIndexOf(haystack, needle);}// 構建next數組public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {if (ms.length == 1) {return new int[]{-1};}int[] next = new int[ms.length];next[0] = -1;next[1] = 0;int i = 2;int cn = 0;while (i < ms.length) {if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) {next[i++] = ++cn;} else if (cn > 0) {cn = next[cn];} else {next[i++] = 0;}}return next;}public static int[] getNextvalArray(char[] ms, int[] next) {if (ms.length == 1) {return new int[]{-1};}int[] nextval = new int[ms.length];nextval[0] = -1; // 固定值for (int i = 1; i < ms.length; i++) {//保證next[i]有效才優化if (next[i] > 0 && ms[i] == ms[next[i]]){nextval[i] = nextval[next[i]]; } else {nextval[i] = next[i]; }}return nextval;}// KMP匹配算法public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) {if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) {return -1;}char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();int i1 = 0;int i2 = 0;int[] next = getNextArray(str2);next = getNextvalArray(str2, next); while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) {if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) {i1++;i2++;} else if (next[i2] == -1) {i1++;} else {i2 = next[i2];}}return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1;}
}四、算法綜合設計與實現
滑動窗口與串結合
3. 無重復字符的最長子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
滑動窗口 + 哈希集合
??核心思想??:
使用左右指針(left和?right)表示當前子串的窗口,并用哈希集合存儲窗口內的字符。右指針不斷向右擴展,遇到重復字符時,左指針向右移動直至移除重復字符,同時更新最大子串長度。
??算法步驟??:
-
??初始化??:
-
左右指針?
left = right = 0 -
哈希集合?
char_set存儲窗口字符 -
最大長度?
max_len = 0
-
-
??滑動窗口??:
-
??擴展右指針??:若?
s[right]不在集合中,將其加入集合并更新最大長度。 -
??收縮左指針??:若?
s[right]已在集合中,移除?s[left]并將左指針右移,直到重復字符被移除。
-
-
??終止條件??:右指針到達字符串末尾。
??時間復雜度??:O(N)(每個字符最多被遍歷兩次)
??空間復雜度??:O(∣Σ∣)(字符集大小,如 ASCII 為 128)
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {// 使用哈希集合存儲當前窗口中的字符Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();int maxLen = 0; // 最大子串長度int left = 0; // 滑動窗口左指針// 右指針遍歷字符串for (int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++) {char current = s.charAt(right);// 當字符已存在集合中時,移動左指針直到移除重復字符while (set.contains(current)) {set.remove(s.charAt(left));left++;}// 添加當前字符到集合,并更新最大長度set.add(current);maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left + 1);}return maxLen;}
}438. 找到字符串中所有字母異位詞 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
??核心思路??
-
使用長度為 26 的數組統計字符頻次
-
在?
s上滑動長度為?p_len的窗口 -
比較窗口頻次與?
p的頻次是否完全一致
??算法步驟??
1. 若 len(s) < len(p): 返回空列表
2. 初始化兩個數組 s_count 和 p_count(長度26)
3. 遍歷前 p_len 個字符,填充兩個數組
4. 檢查第一個窗口:若兩數組相同,記錄索引0
5. 滑動窗口: - 移除窗口左端字符(s_count索引減1) - 加入窗口右端新字符(s_count索引加1) - 檢查并記錄新窗口是否匹配
??復雜度分析??
?? 時間復雜度:O(26*(n-m))
n-m次窗口滑動 × 26 次數組比較
💾 空間復雜度:O(1)(固定長度26的數組)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;class Solution {public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();int sLen = s.length(), pLen = p.length();if (sLen < pLen) return result;// 創建兩個計數數組int[] sCount = new int[26];int[] pCount = new int[26];// 初始化第一個窗口和p的計數for (int i = 0; i < pLen; i++) {pCount[p.charAt(i) - 'a']++;sCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;}// 檢查第一個窗口if (arraysEqual(sCount, pCount)) {result.add(0);}// 滑動窗口for (int i = 0; i < sLen - pLen; i++) {// 移除窗口左側字符sCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a']--;// 添加窗口右側新字符sCount[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a']++;// 檢查當前窗口if (arraysEqual(sCount, pCount)) {result.add(i + 1);}}return result;}// 輔助方法:比較兩個數組是否相等private boolean arraysEqual(int[] a, int[] b) {for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {if (a[i] != b[i]) return false;}return true;}
}前綴和與串
560. 和為 K 的子數組 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
問題定義??
統計數組中??和為 k 的連續子數組的個數??。
??核心思想??
-
??前綴和轉換??
-
定義?
pre[i]= 數組前?i項和(nums[0]到?nums[i]) -
子數組?
[j, i]的和轉化為:??
pre[i] - pre[j-1] = k??? ??
pre[j-1] = pre[i] - k?這一步很關鍵,因為把尋找求和為k的子數組轉化為查詢是否存在pre[j-1],即pre[i] - k,問題轉化為:??找有多少個?j滿足?pre[j] = pre[i] - k??,其中?j < i?
-
-
??哈希表優化??
-
建立哈希表?
map<前綴和, 出現次數> -
遍歷時動態記錄所有前綴和的出現次數
-
對于每個?
pre[i],查找 ??pre[i] - k?? 在歷史中出現的次數
-
在這我用個比喻解釋前綴和轉化和哈希表優化
想象你在一家商店連續幾天記賬:
每次記賬,你記錄的是??從開店至今的總營業額??
你想知道??連續幾天的營業額加起來正好是K元??的日子有多少次
1. 前綴和是什么?
就像記賬本里的??累計營業額??
示例:每日收入 [1元, 2元, 3元]
第一天結束:累計1元
第二天結束:累計3元 (1+2)
第三天結束:累計6元 (1+2+3)
2. 如何找連續幾天和為K?
假設你想找和為2的連續收入
如果你發現:
第三天結束時累計6元
第一天結束時累計4元
那么第二天到第三天:6 - 4 = 2元!
這就是核心思想:??累計營業額差等于K時,中間時段的營業額和就是K??
3. 如何用哈希表優化?
我們拿個本子記錄所有出現過的累計營業額
記錄形式:{累計營業額: 出現次數}
初始:記下開店前0元(出現1次)
邊記賬邊檢查:
當前累計營業額 = 之前累計 + 今天收入
看看本子上是否記過:[當前累計 - K]的數值?
如果記過,說明這中間有段時間收入正好是K元!
class Solution {public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {if(nums.length<1)return 0;HashMap<Integer,Integer> m=new HashMap<>();m.put(0,1);int count=0,pre_sum=0;for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){pre_sum+=nums[i];int target=pre_sum-k;if(m.containsKey(target)){count+=m.get(target);}m.put(pre_sum,m.getOrDefault(pre_sum,0)+1);}return count;}
}用前綴和快速計算區間和,用哈希表記住歷史值,把兩重循環優化成一重遍歷。
數組、隊列、滑動窗口與串*
239. 滑動窗口最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
關鍵思路
-
用一個雙端隊列維護當前窗口內 ??可能成為最大值的元素下標??。隊列中的元素保持從大到小的順序(單調遞減),隊首始終是當前窗口的最大值。
操作步驟
-
??初始化??:處理第一個窗口(前k個元素)
-
??維護隊列??(兩個關鍵操作):
-
??隊尾維護??:當新元素≥隊尾元素時,彈出隊尾(因為舊的較小值不再可能成為最大值)
-
??隊首維護??:當隊首元素超出窗口范圍時,彈出隊首
-
-
??記錄結果??:每次窗口移動后,隊首就是當前窗口的最大值
-
class Solution {public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {if(nums.length<1)return new int[]{0};int nlen=nums.length;Deque<Integer> deque=new LinkedList<>();int[] ans=new int[nlen-k+1];//初始化隊列for(int i=0;i<k;i++){while(!deque.isEmpty() &&nums[i]>=nums[deque.peekLast()]){deque.pollLast();}deque.offerLast(i);}ans[0]=nums[deque.peekFirst()];//移動隊列for(int i=k;i<nlen;i++){//向右移動,維持單調while(!deque.isEmpty() &&nums[i]>=nums[deque.peekLast()]){deque.pollLast();}deque.offerLast(i);//判斷隊首是否在窗口內while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst()<=i-k){deque.pollFirst();}ans[i-k+1]=nums[deque.peekFirst()];}return ans;}
}動態規劃與串*
題目:回文判斷(動態規劃、中心擴展)
5. 最長回文子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/description/
class Solution {public String longestPalindrome(String s) {if (s == null || s.length() < 1) return "";int start = 0, end = 0; // 記錄最長回文的起止位置for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {// 奇數長度擴展 (中心點為i)int len1 = expand(s, i, i);// 偶數長度擴展 (中心點為i和i+1之間)int len2 = expand(s, i, i + 1);int len = Math.max(len1, len2); // 取兩種擴展的最大值// 發現更長回文時更新起止位置if (len > end - start) {start = i - (len - 1) / 2;end = i + len / 2;}}return s.substring(start, end + 1);}// 中心擴展函數private int expand(String s, int left, int right) {while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {left--;right++;}return right - left - 1; // 計算實際回文長度}
})










)

學習算法例題及詳解)

)



