文章目錄
- 一、賦值運算符重載
- 1.1定義
- 1.2基本規則
- 1.3為什么需要運算符重載?
- 1.4示例:
- 二、前置++和后置++區別
- 2.1前置++的實現與特點
- 2.2后置++的實現與特點
- 2.3核心區別
- 三、const
- 四、取地址及const取地址操作符重載
- 4.1定義
- 4.2語法
- 4.3注意事項
一、賦值運算符重載
1.1定義
運算符重載是C++的一項特性,允許我們為自定義類型(類或結構體)重新定義運算符的行為(如+, -, =, ==等),使其像內置類型一樣直觀操作。如果用戶沒有顯式實現時,編譯器會生成一個默認賦值運算符重載,以值的方式逐字節拷貝。
1.2基本規則
1. 函數命名
運算符重載函數的名稱必須是 operator 后接運算符符號。
返回值類型 operator運算符(參數列表)
示例:
ClassName& operator=(const ClassName& other) {if (this != &other) { // 關鍵點1:自賦值檢查// 釋放舊資源 + 深拷貝新資源}return *this; // 關鍵點2:返回引用支持鏈式賦值
}
2. 關鍵限制
? 不能創建新運算符(如 operator@ 是非法的)。
? 不能修改內置類型的運算符含義(例如 int 的 + 必須保持加法語義)。
? 以下運算符不可重載:
.* :: sizeof ?: .
3. 參數規則
-
如果重載為成員函數,第一個操作數是隱式的 this,參數比操作數少1。
例如 a + b 會調用 a.operator+(b)。 -
如果重載為全局函數,參數數量必須與操作數一致。
例如 operator+(a, b)。
1.3為什么需要運算符重載?
-
提升代碼可讀性:date1 < date2 比 date1.isEarlierThan(date2) 更直觀。
-
保持一致性:讓自定義類型像內置類型一樣工作。
-
支持標準庫算法:如 std::sort 依賴 < 運算符。
1.4示例:
h文件:
#pragma once
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}bool operator<(const Date& x);bool operator==(const Date& x);bool operator<=(const Date& x);bool operator>(const Date& x);bool operator>=(const Date& x);bool operator!=(const Date& x);int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//+xx天的情況Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);Date& operator++();Date operator++(int);
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
cpp文件
#include "20250722A.h"Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& x)
{if (_year < x._year){return true;}else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month){return true;}else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day){return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& x)
{return _year == x._year&& _month == x._month&& _day == x._day;
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x)
{return *this < x || *this == x;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& x)
{return !(*this <= x);
}bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x)
{return !(*this < x);
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x)
{return !(*this == x);
}int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{static int daysArr[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))//先判斷month是否等于2可以提高效率{return 29;}else{return daysArr[month];}
}Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;}
int main()
{Date d1(2025, 7, 24);d1 = d1 + 100;d1.Print();return 0;
}
二、前置++和后置++區別
2.1前置++的實現與特點
Date& Date::operator++() {*this += 1; // 調用已重載的+=return *this; // 返回當前對象的引用
}
使用示例:
Date d(2023, 1, 1);
++d; // 等價于 d.operator++()
2.2后置++的實現與特點
Date Date::operator++(int) {Date tmp = *this; // 保存舊值*this += 1; // 修改當前對象return tmp; // 返回舊值副本
}
使用示例:
Date d1(2023, 1, 1);
Date d2 = d1++; // d2獲得舊值,d1自增
2.3核心區別
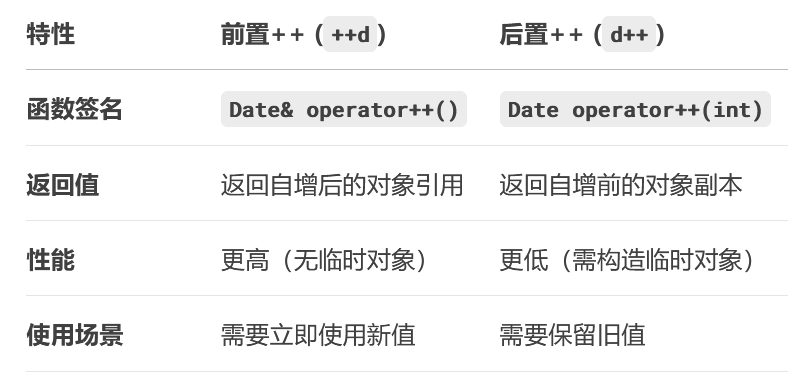
// 前置++(推薦)
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) // 無臨時對象生成// 后置++
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 每次循環構造臨時int
故我們更推薦使用前置++。
三、const
const 是 C++ 中的關鍵字,用于定義"常量"或"不可修改"的變量、函數參數、成員函數等。它的核心作用是增強程序的安全性和可讀性,幫助編譯器在編譯階段發現潛在的錯誤。
- const對象只能調用const成員函數
- const成員函數對任何對象都是安全的
- const成員函數內不可以調用其它的非const成員函數
- 非const成員函數內可以調用其它的const成員函數
四、取地址及const取地址操作符重載
4.1定義
在 C++ 中,取地址操作符 & 可以被重載,包括普通版本和 const 版本。這種重載允許你控制當用戶獲取類對象地址時的行為。
4.2語法
class MyClass {
public:// 普通取地址操作符重載MyClass* operator&() {return this; // 通常返回 this,但可以自定義}// const 取地址操作符重載const MyClass* operator&() const {return this; // 通常返回 this,但可以自定義}
};
4.3注意事項
-
通常不建議重載取地址以及const取地址操作符,除非有充分理由,因為這可能違反用戶預期
-
如果重載了取地址操作符,確保行為合理且文檔化
)





)


)









