文章目錄
- 1.進程替換的六個庫函數
- 2.execl
1.進程替換的六個庫函數
-
使用
man 3 execl進行查詢,3表示 Linux 中的3號手冊,即為庫函數(例如C標準庫中的庫函數,printf,malloc) -
man 1: 用戶命令(在shell中可以執行的命令,如ls, cp) -
man 2: 系統調用(由內核提供的接口,如open, read, fork)
2.execl
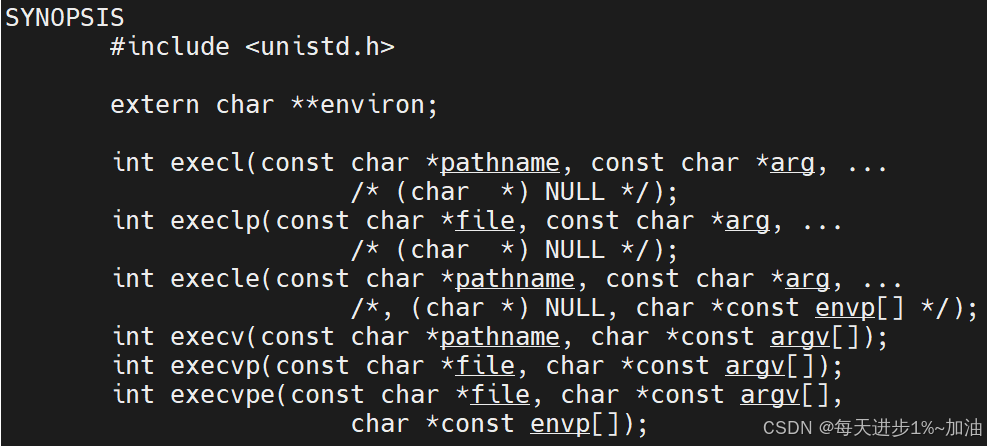
🍎參數介紹:
pathname:表示要替換程序的路徑(絕對路徑或者相對路徑都可);
arg:命令行參數的第一個參數,一般是程序名本身;
...:表示可變參數,按照要求填寫命令行參數即可;
注意:結尾一定要以 NULL,表示結束標志;
execl的返回值我們不用關心,因為只要程序替換成功,舊的代碼將不再執行,如果后續的代碼執行了,說明替換失敗。
int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, .../* (char *) NULL */);

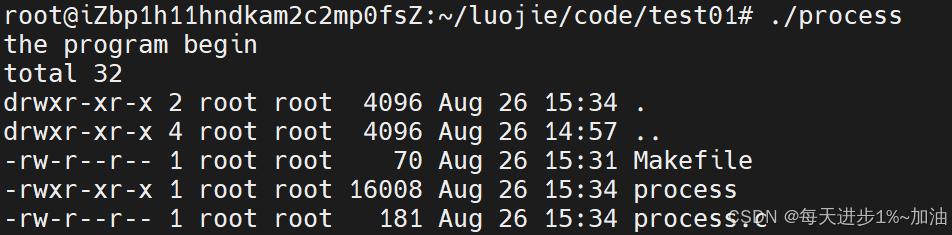
- ?小案例:使用
ls -a -l來替換程序代碼
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{printf("the program begin\n");execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-a","-l", NULL);printf("the program end\n");return 0;
}》運行結果如下:
程序替換成功,原來的程序代碼 the program end 已經被替換成為 ls -a -l
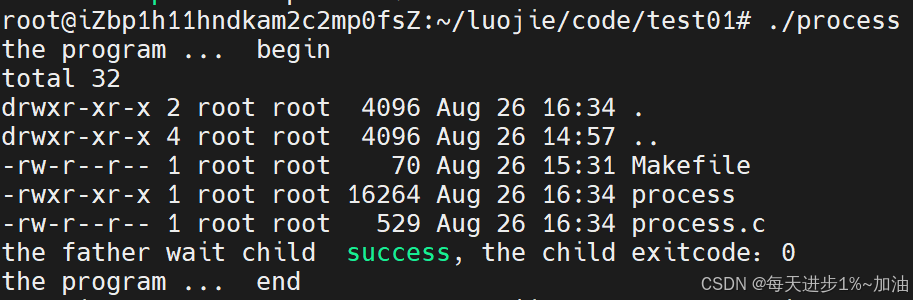
- ?多進程版本:子進程中進行程序替換,父進程正常執行
下面這個代碼案例說明,雖然剛開始父子進程是共享同一塊代碼的內存區域的,但是當子進程發生程序替換要對代碼進行修改時,此時OS會發生寫時拷貝,在物理內存上新建一塊內存區域,首先把父進程的代碼進行復制,然后再把子進程要替換的代碼加載進來。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{printf("the program ... begin\n");pid_t id =fork();// child processif (id == 0){sleep(2);execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", "-a", NULL);exit(123);}// father processint status = 0;pid_t wid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);if (wid > 0){printf("the father wait child success, the child exitcode:%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));}printf("the program ... end\n");return 0;
}》運行結果如下:





全景解析)





)




![ICBC_TDR_UShield2_Install.exe [ICBC UKEY]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/ICBC_TDR_UShield2_Install.exe [ICBC UKEY])

--下)
)