Title
題目
DMP-Net: Deep semantic prior compressed spectral reconstruction methodtowards intraoperative imaging of brain tissue
DMP-Net:面向腦組織術中成像的深度語義先驗壓縮光譜重建方法
01
文獻速遞介紹
腦腫瘤可分為原發性和繼發性兩類。原發性腦腫瘤多發生于腦膜、顱神經、垂體、血管及殘余胚胎組織等部位,致死率和致殘率較高(Wu等人,2018)。繼發性腦腫瘤在臨床中也較為常見,常由肺癌、乳腺癌、腎癌等部位的惡性腫瘤轉移至腦部形成。在癌癥患者中,繼發性腦腫瘤的發病率逐年上升,已成為不容忽視的重大健康問題。 ? 目前,在腦腫瘤切除手術中,臨床常采用神經導航系統(He等人,2023)、術中超聲(Carpentier等人,2024)、熒光引導技術(Mieog等人,2022)及術中磁共振成像(MRI)(Wang等人,2015a)等多種技術,以確定腫瘤的形態與位置。這些技術為神經外科醫生提供了更可靠的指導,有效提升了手術的精準度與安全性。然而,現有輔助診療技術存在一定局限性:例如,神經導航技術高度依賴術前影像數據,當數據與術中實際情況不匹配時易產生誤差,進而導致導航失誤;術中超聲分辨率較低,難以精準勾勒腫瘤邊界及術后殘余腫瘤范圍;熒光引導技術檢測精度較高,但通常適用于高級別腫瘤,且需使用熒光造影劑,該造影劑可能引發嚴重副作用,故不適用于兒童病例;術中MRI在臨床掃描時易因患者輕微移動產生偽影,降低圖像質量,此外還可能受腫瘤位置與嚴重程度影響,對微小腫瘤組織掃描時存在誤診或漏診風險(Yang等人,2024)。不僅如此,不同經驗水平的醫生對病變區域的人工標注可能存在差異,這為最終診療決策帶來了巨大挑戰(Hu等人,2020)。 ? 腦組織包含多種復雜的細胞類型與組織結構,正常腦組織與腫瘤組織在細胞代謝、組織結構等方面存在顯著差異,這些差異會體現在光譜特征上(Zhang等人,2024)。高光譜成像技術(Yoon等人,2019;Leon等人,2023)可同時捕獲腦組織不同區域在多個連續波長范圍內的空間光譜信息。通過對比腫瘤區域與正常腦組織的空間光譜信息,該技術能精準評估腫瘤占位效應及受影響體積、確定手術切除與放射治療范圍,大幅提升疾病治療的可靠性。目前,高光譜成像已廣泛應用于腫瘤組織識別(Hao等人,2021)、病變嚴重程度評估(Lee等人,2021)及腦功能研究(Li等人,2023;Cruz-Guerrero等人,2023)等領域。但傳統高光譜成像系統需較長的光譜數據采集時間,難以在手術中快速捕獲在體組織的光譜信息(Gutiérrez Navarro等人,2023)。 ? 快照式壓縮光譜成像(CSI)系統(Puustinen等人,2020)可在單次曝光時間內快速捕獲光譜細節信息,實現對腦組織區域壓縮測量圖像的實時采集。相較于傳統高光譜成像方法,該系統進一步提升了動態場景下光譜信息的采集效率(Song等人,2022;Xu等人,2023)。借助壓縮感知重建原理,可將低維測量圖像重建為高維光譜信息;通過分析腫瘤區域與正常組織的光譜特征差異,能夠更快速、精準地識別腫瘤邊界,為確定手術切除范圍提供有力支持。此外,CSI系統還可通過對比切除前后同一區域的光譜特征變化,實時監測腫瘤切除進程,及時發現殘余腫瘤組織,保障手術切除的徹底性。 ? 高質量的重建結果是確保腦組織光譜分析可靠性的關鍵。將CSI系統獲取的低維壓縮測量圖像重建為高維光譜圖像的過程,屬于欠定求解過程。傳統重建方法通常利用圖像稀疏性、平滑性等通用規律構建正則化項,以約束求解過程(Yang等人,2023;Liu等人,2021;Chen等人,2024)。但在腦腫瘤患者中,盡管不同患者的腦腫瘤形態與組織結構具有較高相似性,其個體差異與腫瘤類型仍存在區別。僅利用通用圖像屬性構建正則化項缺乏針對性,易導致較大的重建誤差。因此,需建立適配的約束項,兼顧腦腫瘤區域的空間相關性與像素表征差異,以實現更精準的信息恢復。 ? 深度神經網絡可從大規模圖像數據中有效挖掘深層特征,其應用形式主要包括端到端重建算法、深度展開及即插即用重建算法框架。然而,在腦腫瘤高光譜圖像重建任務中,現有深度網絡模型結構相對復雜,且在提取不同組織區域的空間光譜特征時,普遍存在梯度消失問題,導致重建質量較低。當前研究面臨的挑戰在于:如何更好地捕捉不同腦組織間像素信息的細微差異,同時保留不同患者間空間信息的結構共性。 ? 為解決手術中腦組織光譜信息快速采集與重建的難題,本文基于快照式壓縮光譜成像系統,提出一種基于深度語義先驗正則化的壓縮光譜重建方法,用于術中光譜成像與重建。具體方案如下:首先,為提升對不同組織類別的特征提取能力,設計金字塔結構的多尺度卷積模塊。該模塊通過不同尺度的卷積操作,更全面地捕捉組織語義信息,尤其在不同組織類型的邊界區域,展現出顯著優勢;其次,在深度卷積先驗模型的網絡結構設計中,在卷積層之間引入跳躍連接以累積先驗特征,有效適配不同疾病類型的差異,進而提高預測結果的準確性;最后,將先驗模型的預測結果作為重建過程的初始光譜估計,基于初始光譜估計與原始光譜圖像的相似性,建立CSI重建過程的正則化約束,進一步縮小可行解空間,從而提升重建結果的清晰度,為術中成像提供快速、可靠的檢測方法。
Abatract
摘要
In the diagnosis and surgical resection of brain tumors, hyperspectral imaging, as a non-invasive detectiontechnology, can effectively characterize the morphological structure and the physicochemical differences incellular metabolism of different tissues. However, live tissues typically exhibit certain motion characteristics,and traditional hyperspectral imaging systems struggle to meet the demands for real-time and rapid imaging.The snapshot compressive spectral imaging (CSI) system can quickly acquire spatial spectral informationof the lesion area in a single exposure and, combined with reconstruction algorithms, effectively restorethe high-dimensional spectral information of brain tissue. High-quality reconstruction results are crucial forensuring the reliability of spectral analysis of brain tissue. To improve the reconstruction performance ofthe CSI system, this paper proposes a compressive spectral reconstruction method based on deep semanticprior regularization. The predicted results of the deep convolutional prior model are used as the initialspectral estimate to establish a regularization term for the reconstruction process. This is combined with theAlternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) to optimize the solution for high-dimensional spectralimages of brain tissue. The results show that using the CSI system for intraoperative brain tissue imagingcan rapidly acquire spatial spectral information of the lesion area. By optimizing the reconstruction processwith the deep convolutional prior model, this method not only better preserves the structural consistency ofspectral images from different patients but also fully considers the spectral differences of different types ofbrain tumors, achieving higher reconstruction quality. This provides strong support for the precise localizationand resection of brain tumors.
在腦腫瘤診斷與手術切除過程中,高光譜成像作為一種無創檢測技術,能夠有效表征不同組織的形態結構及細胞代謝的理化差異。然而,活體組織通常具有一定的運動特性,傳統高光譜成像系統難以滿足實時、快速成像的需求。快照式壓縮光譜成像(CSI)系統可通過單次曝光快速獲取病變區域的空間光譜信息,并結合重建算法有效恢復腦組織的高維光譜信息。而高質量的重建結果,對于保障腦組織光譜分析的可靠性至關重要。 ? 為提升CSI系統的重建性能,本文提出一種基于深度語義先驗正則化的壓縮光譜重建方法:將深度卷積先驗模型的預測結果作為初始光譜估計,為重建過程構建正則化項;并結合交替方向乘子法(ADMM),對腦組織高維光譜圖像進行優化求解。 ? 結果表明,采用CSI系統進行腦組織術中成像,可快速獲取病變區域的空間光譜信息;通過深度卷積先驗模型優化重建過程,該方法不僅能更好地保留不同患者光譜圖像的結構一致性,還充分考慮了不同類型腦腫瘤的光譜差異,實現了更高的重建質量,為腦腫瘤的精準定位與切除提供了有力支持。 ? ?### 關鍵術語補充說明: ? 1. hyperspectral imaging(高光譜成像):一種可捕獲物體在連續光譜波段上圖像信息的技術,相較于傳統成像能獲取更豐富的光譜細節,在醫療領域可用于區分不同組織(如腫瘤與正常腦組織)的生化特性。 ? 2. snapshot compressive spectral imaging(CSI,快照式壓縮光譜成像):通過單次拍攝(單次曝光)實現光譜信息采集的技術,解決了傳統高光譜成像“多次采樣、耗時久”的問題,適配術中動態組織的成像需求。 ? 3. Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers(ADMM,交替方向乘子法):一種常用的優化算法,可將復雜的高維優化問題分解為多個易求解的子問題,高效實現高維光譜圖像的重建求解。 ? 4. regularization term(正則化項):在模型優化中用于約束解的“合理性”的項,本文中通過深度語義先驗構建正則化項,可避免重建結果出現失真、噪聲等問題,提升圖像質量。
Method
方法
3.1. Deep semantic prior regularization reconstruction framework
The framework of the Deep Semantic Priors Compressed SpectralReconstruction Algorithm (DMP-Net) is shown in Fig. 2. The reconstruction model consists of three main components: the prior spectralfeature data module, the deep convolutional prior model, and theADMM optimization solving module. In the prior spectral feature datamodule, to enhance the deep convolutional neural network’s understanding and expression of different tissue structures in the image,bilinear filtering is first applied to denoise the RGB image. Then, pyramid convolution is used to capture spatial information representationsat different scales. The convolutional features are concatenated withthe RGB image along the channel dimension, thus achieving the fusionrepresentation of multi-scale information and spatial color information.Finally, the concatenated feature data is vectorized to establish a priorspectral feature database, providing data support for the training of thedeep convolutional prior model. During the training process of the deepconvolutional prior model, inter-layer skip connections are used to fuseshallow and deep features, alleviating the issue of gradient vanishingin deep features and improving the model’s ability to model complexspectral data. After the deep convolutional prior model parameters aretrained, the RGB image is used as input. The regularization term of thereconstruction process is constructed based on the prediction resultsof the deep convolutional prior model and the spatial structure andsemantic similarity of the prior spectral data. The ADMM optimization algorithm is then applied to achieve accurate reconstruction ofhigh-dimensional spectral data for the human brain.
3.1 深度語義先驗正則化重建框架 ? 深度語義先驗壓縮光譜重建算法(DMP-Net)的框架如圖2所示。該重建模型包含三個主要組件:先驗光譜特征數據模塊、深度卷積先驗模型以及交替方向乘子法(ADMM)優化求解模塊。 ? 在**先驗光譜特征數據模塊中,為提升深度卷積神經網絡對圖像中不同組織結構的理解與表達能力,首先對RGB圖像進行雙線性濾波去噪處理;隨后采用金字塔卷積提取不同尺度下的空間信息表征,并將卷積特征與RGB圖像沿通道維度進行拼接,從而實現多尺度信息與空間色彩信息的融合表征;最后對拼接后的特征數據進行向量化處理,構建先驗光譜特征數據庫,為深度卷積先驗模型的訓練提供數據支撐。 ? 在**深度卷積先驗模型**的訓練過程中,通過層間跳躍連接融合淺層與深層特征,緩解深層特征的梯度消失問題,提升模型對復雜光譜數據的建模能力。當深度卷積先驗模型參數訓練完成后,以RGB圖像為輸入,基于該模型的預測結果,結合先驗光譜數據的空間結構與語義相似性,構建重建過程的正則化項。 ? 最后,采用ADMM優化算法,實現對人腦高維光譜數據的精準重建。
Conclusion
結論
To achieve rapid acquisition and accurate reconstruction of intraoperative brain tissue spectral information, we propose a compressedspectral reconstruction method with deep semantic prior regularizationfor intraoperative brain imaging. This method leverages the advantagesof deep learning models by incorporating a deep semantic prior regularization mechanism, effectively enhancing the detail recovery capabilityduring the reconstruction process. Research shows that the proposedmethod can quickly acquire spatial spectral information from the lesionarea with low computational cost, while maintaining structural consistency and improving the reconstruction quality across different patientsand disease types. The multi-scale convolutional module strikes a goodbalance between pixel separation representation and continuity preservation, which helps improve the semantic representation and generalization capability of the deep prior model. By establishing a total variation regularization term based on the difference between the predictedresults of the DMP model and the reconstructed results, the methodexhibits superior constraint ability, making the solution more accurate.Currently, the proposed method has been fully validated on simulationdata, but has not yet been tested in practical applications. However, itsexcellent performance demonstrates great potential. Future work willfocus on validating and optimizing its application to clinical data toensure its reliability in surgery, further promoting the development ofprecise brain tumor localization and resection techniques.
為實現術中腦組織光譜信息的快速獲取與精準重建,本研究提出一種適用于術中腦部成像、基于深度語義先驗正則化的壓縮光譜重建方法。該方法充分利用深度學習模型的優勢,融入深度語義先驗正則化機制,有效提升了重建過程中的細節恢復能力。研究表明,所提方法能夠以較低的計算成本快速獲取病變區域的空間光譜信息,同時在不同患者與疾病類型中均能保持結構一致性并提升重建質量。其中,多尺度卷積模塊在像素分離表征與連續性保留之間取得了良好平衡,有助于增強深度先驗模型的語義表達能力與泛化能力;通過構建基于DMP(深度先驗)模型預測結果與重建結果差異的總變分正則化項,該方法展現出更優的約束能力,使求解結果更精準。 目前,所提方法已在模擬數據上完成充分驗證,但尚未在實際應用場景中開展測試。然而,其優異性能已彰顯出巨大潛力。未來研究將重點驗證并優化該方法在臨床數據上的應用,確保其在手術場景中的可靠性,進而為腦腫瘤精準定位與切除技術的發展提供助力。
Figure
圖
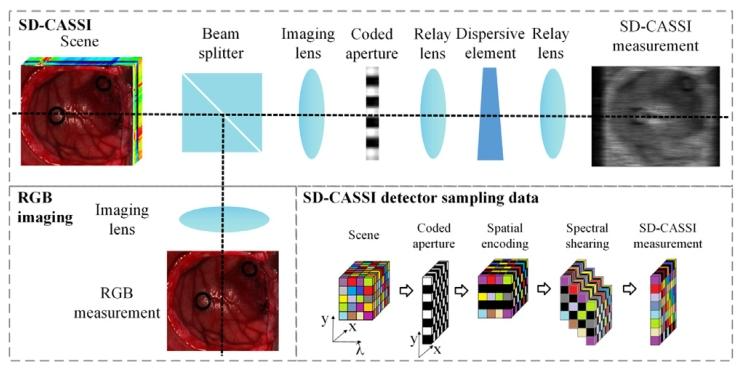
Fig. 1. The structural composition of the dual-camera CSI system and the data structureof detector sampling
圖 1 雙相機快照式壓縮光譜成像(CSI)系統的結構組成及探測器采樣的數據結構
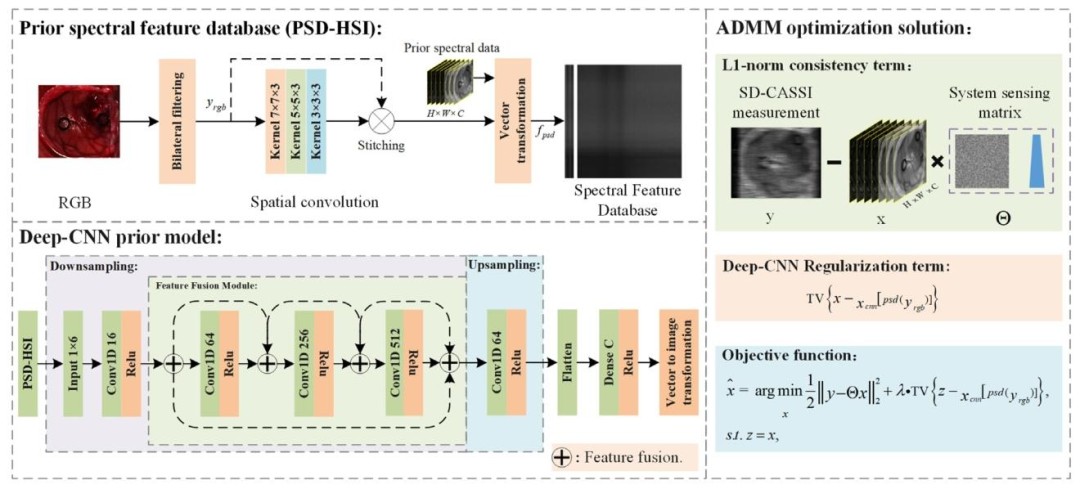
Fig. 2. The reconstruction algorithm model consists of three parts: a prior spectral feature data module (PSD-HSI), a deep convolutional prior model (DMP), and an ADMMoptimization solver module
圖 2 重建算法模型包含三部分:先驗光譜特征數據模塊(PSD-HSI)、深度卷積先驗模型(DMP)及交替方向乘子法(ADMM)優化求解器模塊
Fig. 3. RGB images of the experimental data.
圖 3 實驗數據的 RGB 圖像
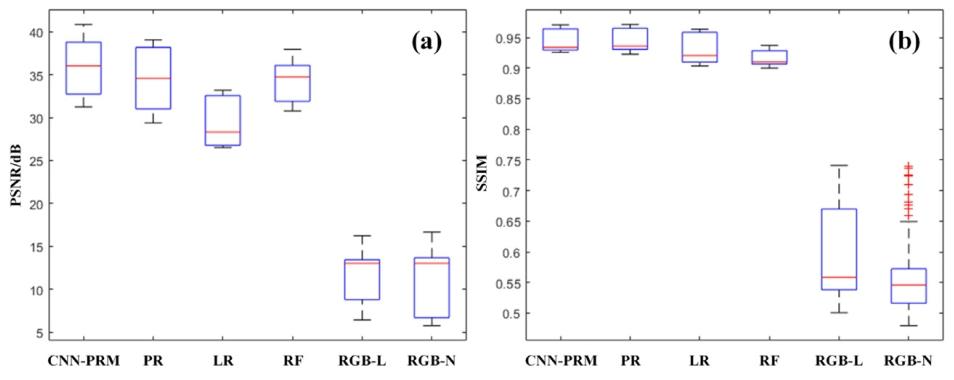
Fig. 4. A comparison of the distribution of evaluation metrics for the prediction results of Patient 4 in the spectral range from 400 nm to 700 nm using different methods. (a)shows the boxplot distribution of PSNR for each individual spectral band in the prediction results of different methods on the test dataset. (b) shows the boxplot distribution ofSSIM for each individual spectral band in the prediction results of different methods on the test dataset.
圖 4 不同方法在 400 納米(nm)至 700 納米(nm)光譜范圍內,對 4 號患者預測結果的評估指標分布對比。(a)為不同方法在測試數據集上預測結果中,各單一光譜波段峰值信噪比(PSNR)的箱線圖分布;(b)為不同方法在測試數據集上預測結果中,各單一光譜波段結構相似性指數(SSIM)的箱線圖分布。
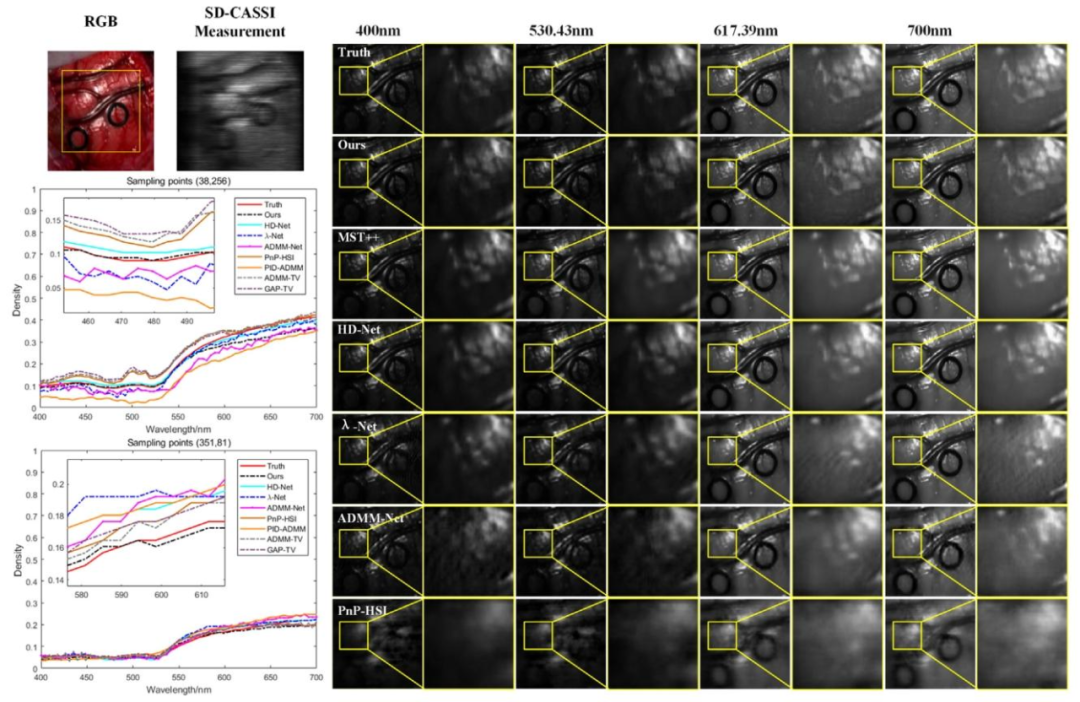
Fig. 5. Comparison of the spatial detail information of the reconstruction results using different methods for Patient 1, as well as a comparison of the spectral information at thesampling points (38, 256) and (351, 81).
圖 5 不同方法對 1 號患者的重建結果空間細節信息對比,以及采樣點(38, 256)和(351, 81)處的光譜信息對比
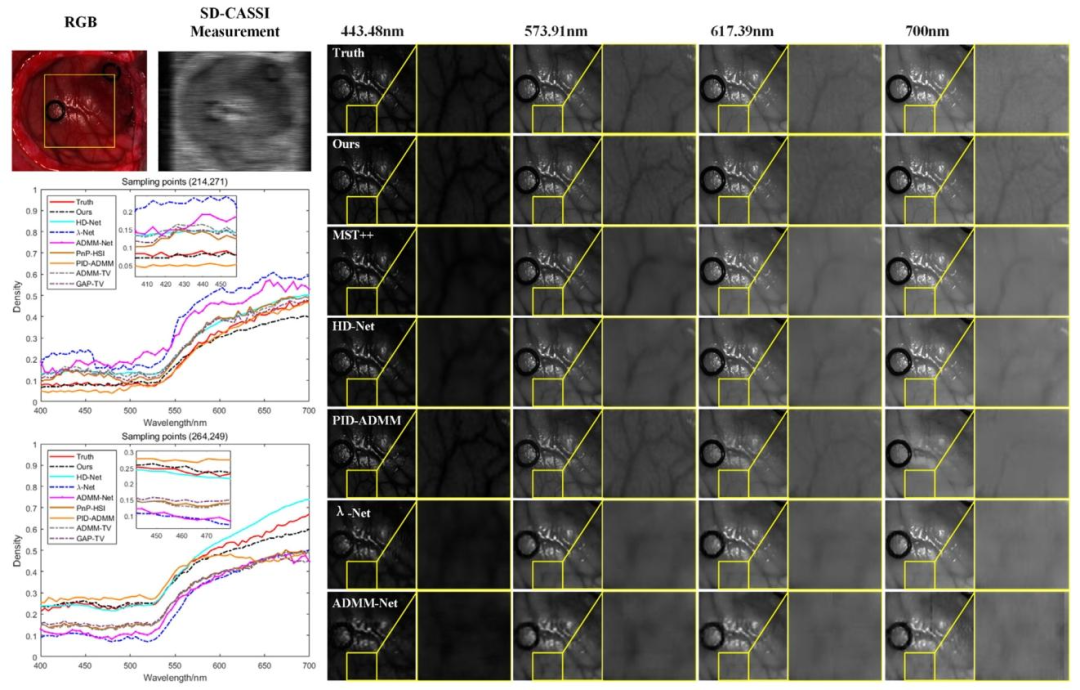
Fig. 6. Comparison of the spatial detail information of the reconstruction results using different methods for Patient 3, as well as a comparison of the spectral information at thesampling points (214, 271) and (264, 249)
圖6 不同方法對3號患者的重建結果空間細節信息對比,以及采樣點(214, 271)和(264, 249)處的光譜信息對比
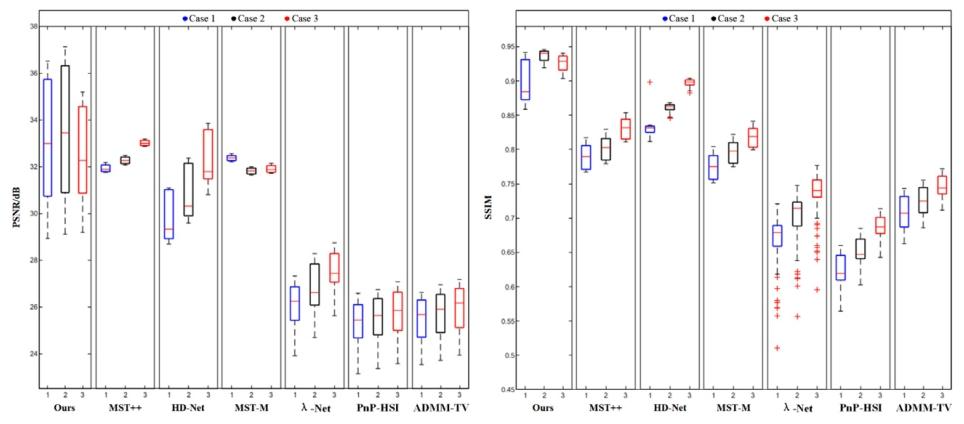
Fig. 7. Box plot distributions of PSNR and SSIM parameters for reconstruction results under three different noise environments.
圖7 三種不同噪聲環境下重建結果的峰值信噪比(PSNR)與結構相似性指數(SSIM)參數箱線圖分布
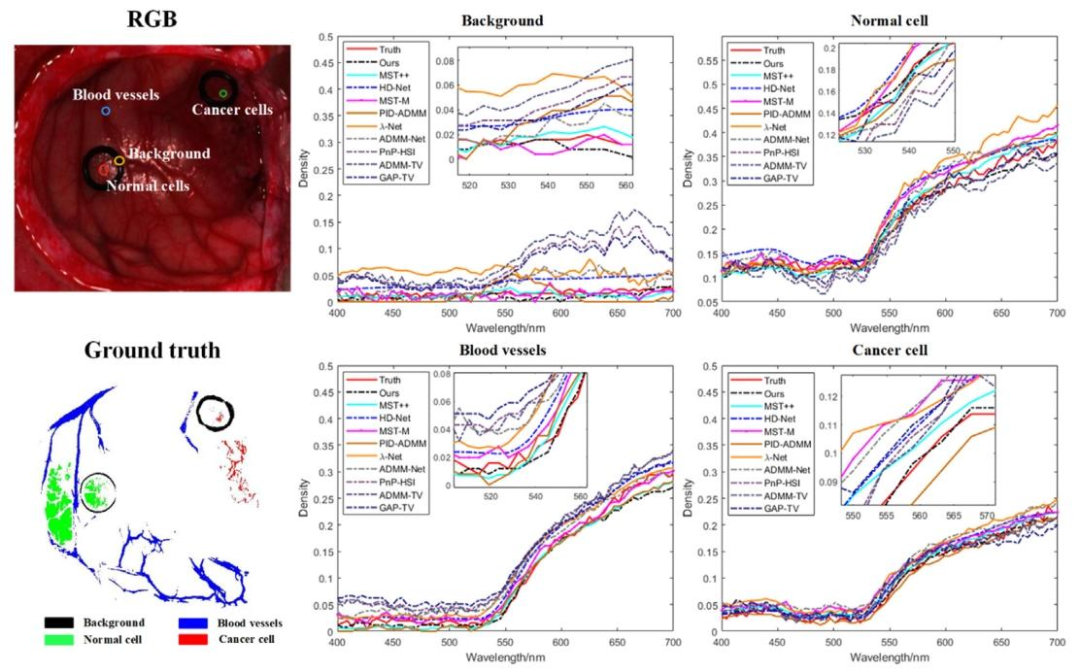
Fig. 8. Comparison of Spectral Reconstruction Results for Background, Normal Cell, Blood Vessels, and Cancer Cell
圖 8 背景、正常細胞、血管及癌細胞的光譜重建結果對比

Fig. 9. Visual Comparison of Reconstruction Results with Depth Prior Regularizationusing Multi-scale Convolutional Modules for Patient 4. PSNR and SSIM are theevaluation metric calculation results for the selected band full image.
圖9 采用多尺度卷積模塊的深度先驗正則化方法對4號患者的重建結果可視化對比。其中,峰值信噪比(PSNR)與結構相似性指數(SSIM)為所選波段全圖像的評估指標計算結果
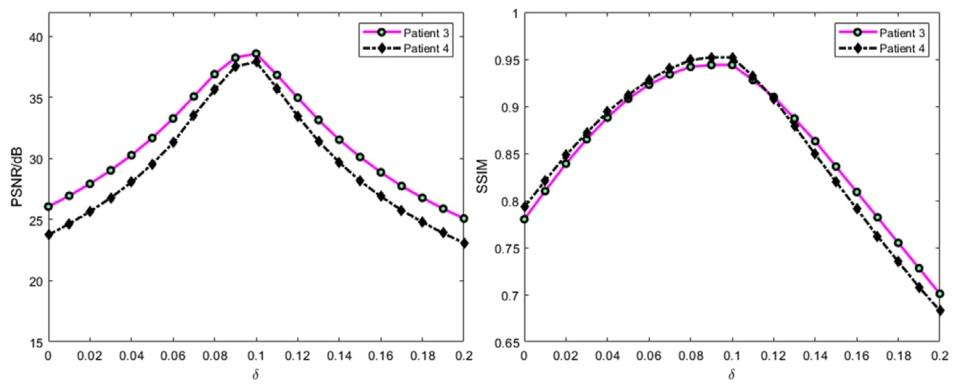
Fig. 10. The variation of PSNR and SSIM evaluation metrics with the change in the value of 𝛿.
圖10 峰值信噪比(PSNR)與結構相似性指數(SSIM)評估指標隨參數𝛿取值變化的變化趨勢
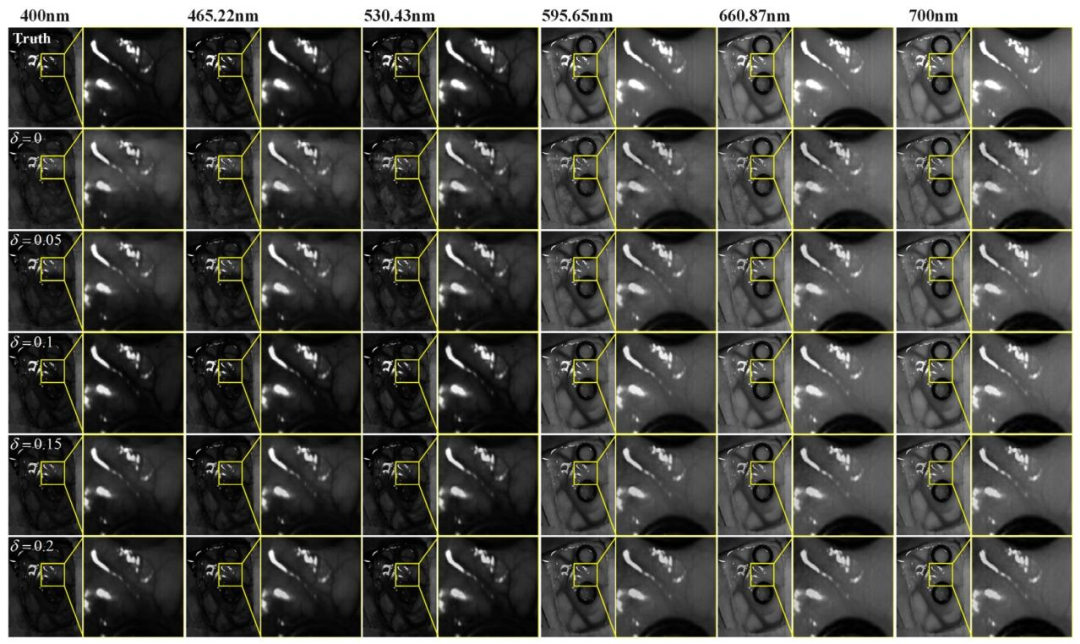
Fig. 11. Comparison of spatial detail information in the reconstruction results at different wavelengths for patient 4 under different 𝛿 values.
圖11 不同𝛿值下,4號患者在不同波長處重建結果的空間細節信息對比
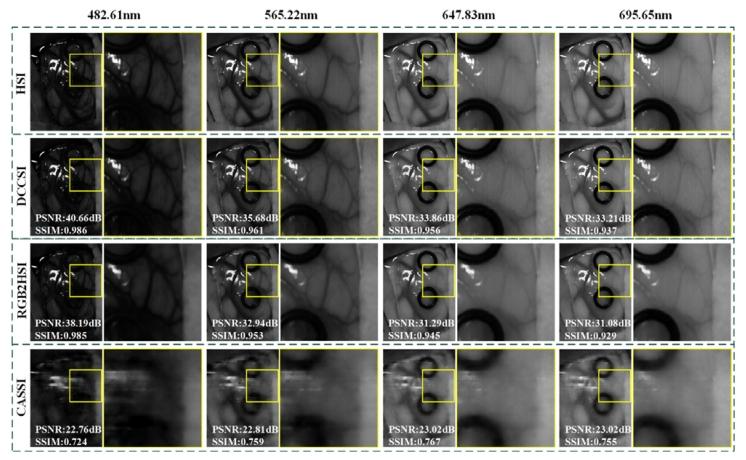
Fig. 12. Comparison of reconstruction results for Patient 4 across different imagingsystems. PSNR and SSIM are the evaluation metric calculation results for the selectedband full image.
圖12 不同成像系統對4號患者的重建結果對比。其中,峰值信噪比(PSNR)與結構相似性指數(SSIM)為所選波段全圖像的評估指標計算結果
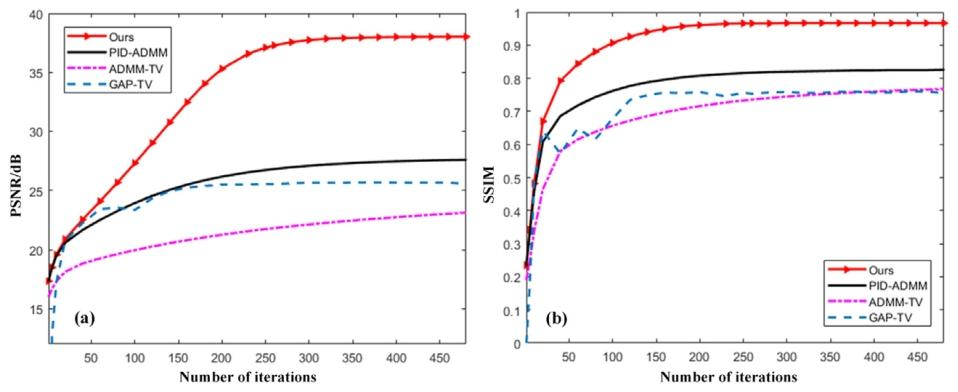
Fig. 13. The variation of PSNR and SSIM with the number of iterations for the reconstruction results of patient 1.
圖13 1號患者重建結果的峰值信噪比(PSNR)與結構相似性指數(SSIM)隨迭代次數變化的趨勢
Table
表
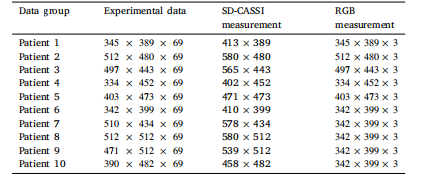
Table 1Specifications of the dataset used in the experiment
表 1 實驗所用數據集的規格說明
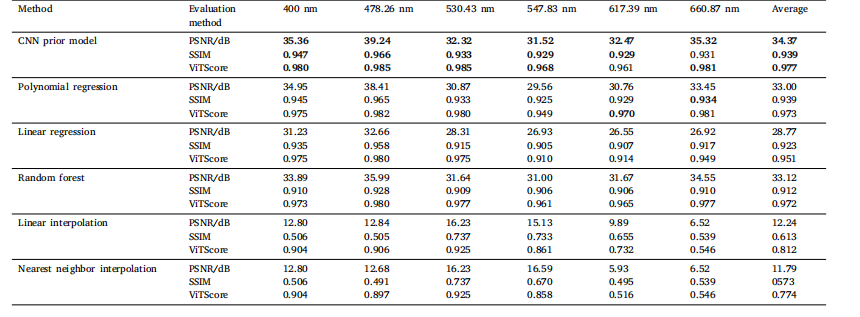
Table 2Comparison of spatial structure and semantic similarity across different prior regularization methods
表 2 不同先驗正則化方法的空間結構與語義相似性對比
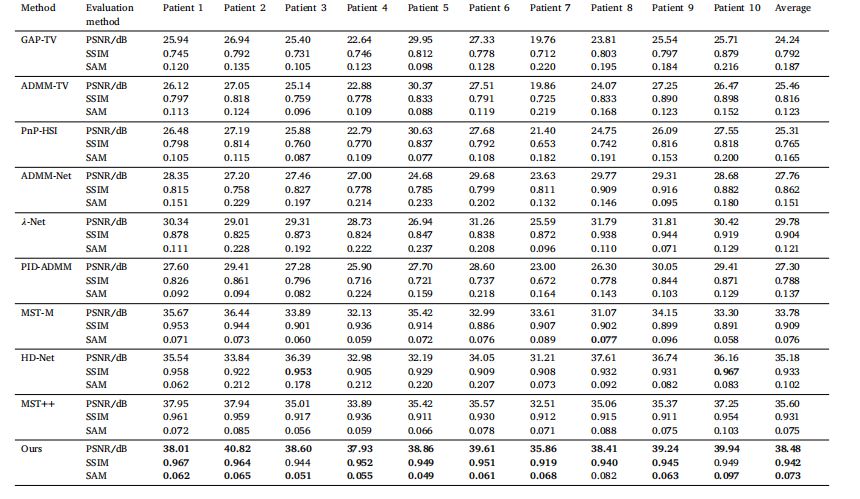
Table 3Comparison of reconstruction results from different algorithms.
表 3 不同算法的重建結果對比
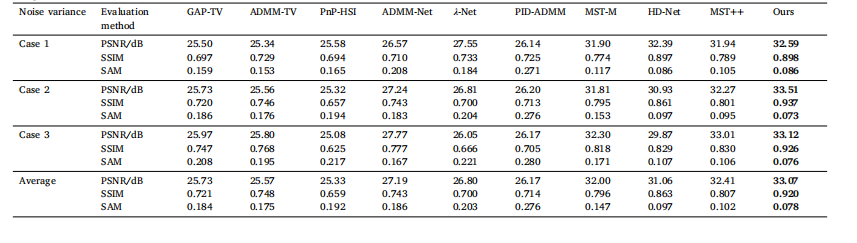
Table 4Comparison of reconstruction results under different noise environments
表4 不同噪聲環境下的重建結果對比
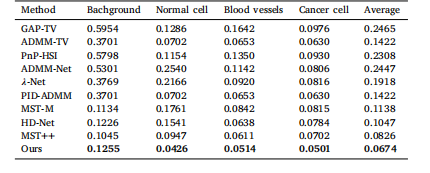
Table 5SAM calculation results for spectral reconstruction of background, Normal cell, Bloodvessels, and Cancer cell.
表 5 背景、正常細胞、血管及癌細胞光譜重建的光譜角匹配度(SAM)計算結果
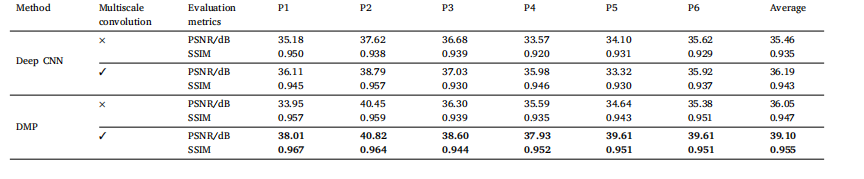
Table 6Impact of the multi-scale convolutional module on the reconstruction results.
表 6 多尺度卷積模塊對重建結果的影響
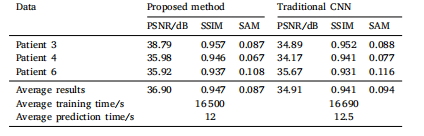
Table 7The influence of the network structure of the deep convolutional prior model on thereconstruction results.
表 7 深度卷積先驗模型的網絡結構對重建結果的影響
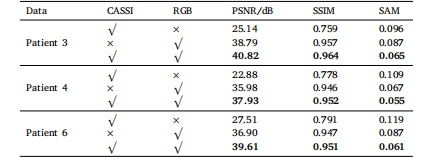
Table 8Ablation study of spectral reconstruction for brain tumors in different patients using adual-camera system.
表 8 基于雙相機系統的腦腫瘤光譜重建消融實驗結果
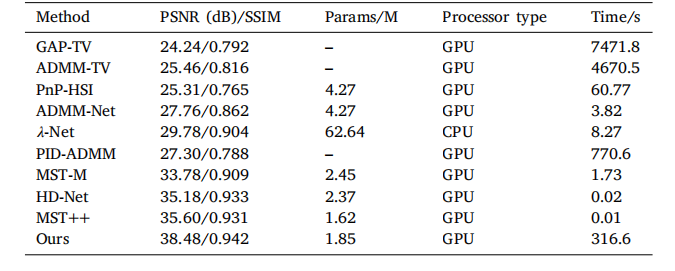
Table 9Comparison of reconstruction performance among different algorithms.
表 9不同算法的重建性能對比

Table 10Comparison of reconstruction results from different imaging systems.
表 10 不同成像系統的重建結果對比










)


)




)
