文章目錄
- 1.使用flink的原因:
- 2. Flink支持兩種模式:
- 3. flink table api工作原理:
- 4. Flink table api 使用
- 5. select語句&flink table api:
- 6. 使用flink table api 創建table
- 7. 使用flink table api 寫流式數據輸出到表或sink
- 8. flink auto-scaling(自動伸縮)
- 9. watermarks(水印)
- 10. 聚合數據(Aggregating Data)
- 11. 使用窗口聚合數據(using windows to aggregate data)
- 12.flink 多表連接(joining flink tables)
- 13.flink table api 代碼
1.使用flink的原因:
- real-time
- scalable
- reliable
- Fully-managed
2. Flink支持兩種模式:
- Batch processing
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.ExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.AggregateOperator;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.DataSource;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.FlatMapOperator;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.UnsortedGrouping;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;/*** DataSet api實現(不推薦),官方推薦直接使用DataStream api* 批處理:字符分割*/
public class WordCountBatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//1.創建執行環境ExecutionEnvironment env=ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();//2.讀取數據:從文件中讀取DataSource<String> lineDS = env.readTextFile("D:\\ideawork\\javaBasics\\input\\word.txt");//3.切分、轉換(word,1)FlatMapOperator<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lineDS.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() {@Overridepublic void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) throws Exception {//3.1 按照空格進行切分單詞String[] words = value.split(" ");for (String word : words) {//3.2 將單詞,轉換二元組(word,1)Tuple2<String, Integer> wordTuple2 = Tuple2.of(word, 1);//3.3 使用collector向下游發送數據out.collect(wordTuple2);}}});//4.按照word分組,按照tuple中第一個位置word的索引0,分組UnsortedGrouping<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOneGroupby = wordAndOne.groupBy(0);//傳入索引為0//5.各分組內聚合,按照二元組中第二個元素的位置進行聚合AggregateOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> sum = wordAndOneGroupby.sum(1);//6.輸出sum.print();}
}- Stateful stream Processing
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;public class WordCountStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//1.創建執行環境StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();//2.讀取數據DataStreamSource<String> lineDS=env.readTextFile("input/word.txt");//3.處理數據SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOneDS = lineDS.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() {@Overridepublic void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) throws Exception {//按照空格進行切分String[] words = value.split(" ");for (String word : words) {//數組轉成二元組(word,1)Tuple2<String, Integer> wordAndOne = Tuple2.of(word, 1);//通過采集器,向下游發送數據out.collect(wordAndOne);}}});//3.2 分組KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, String> wordAndOneKS = wordAndOneDS.keyBy(new KeySelector<Tuple2<String, Integer>, String>() {@Overridepublic String getKey(Tuple2<String, Integer> value) throws Exception {return value.f0;}});//3.3 聚合,從tuple第二個元素位置進行聚合SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> sumDS = wordAndOneKS.sum(1);//4.輸出數據sumDS.print();//5.執行:觸發啟動邏輯env.execute();}
}3. flink table api工作原理:
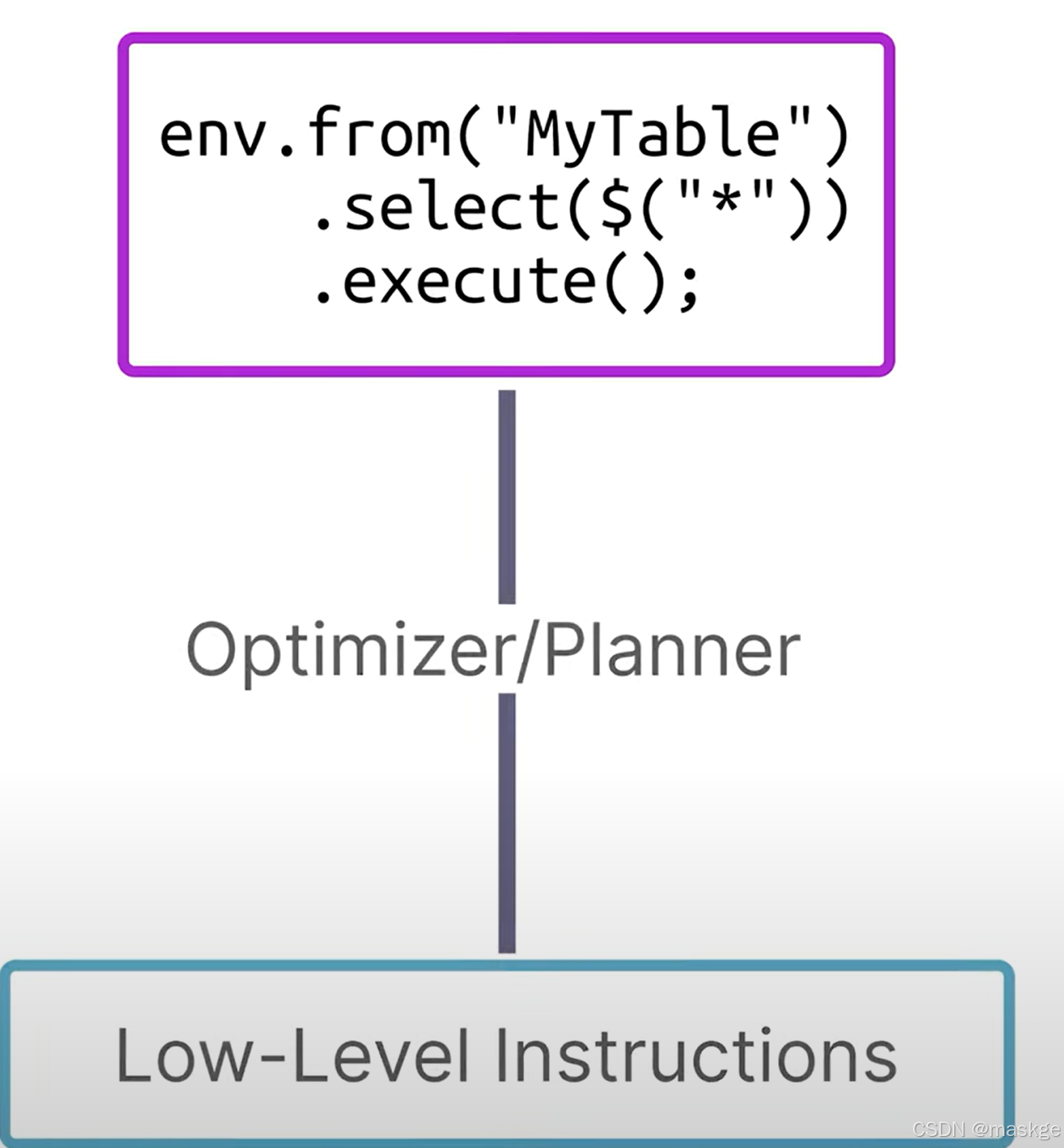
優化器、計劃器決定table api如何在flink集群上執行;
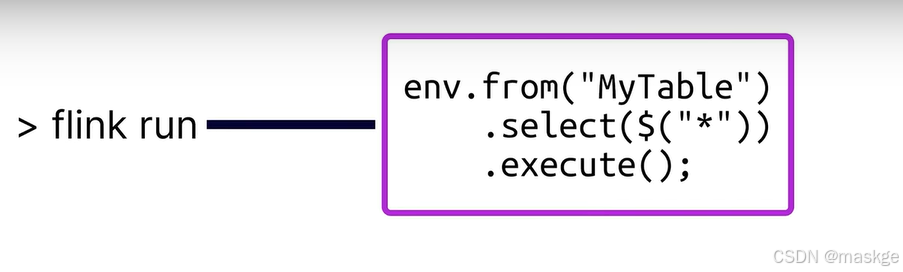
執行flink run命令運行,剩下的代碼執行由flink集群執行
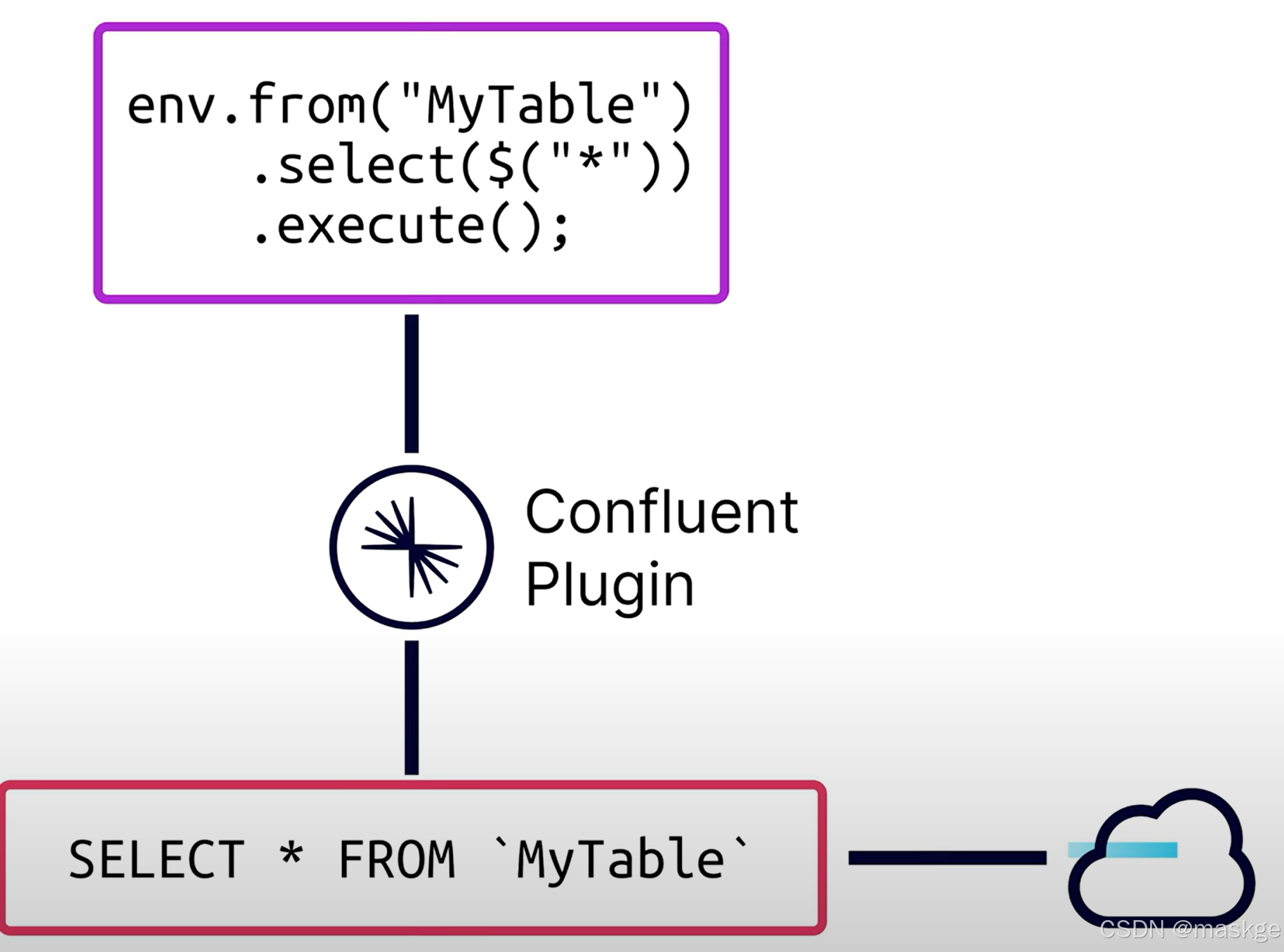 通過Confluent 插件,把flink java代碼轉換為SQL,然后交由云進行執行
通過Confluent 插件,把flink java代碼轉換為SQL,然后交由云進行執行
4. Flink table api 使用
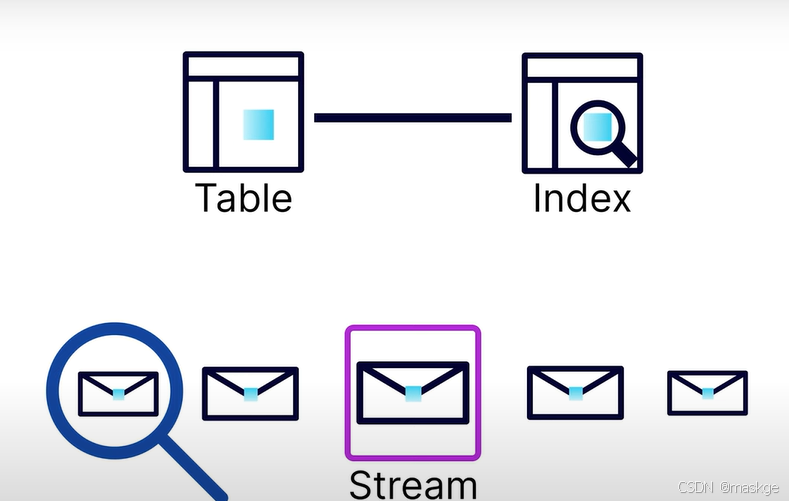
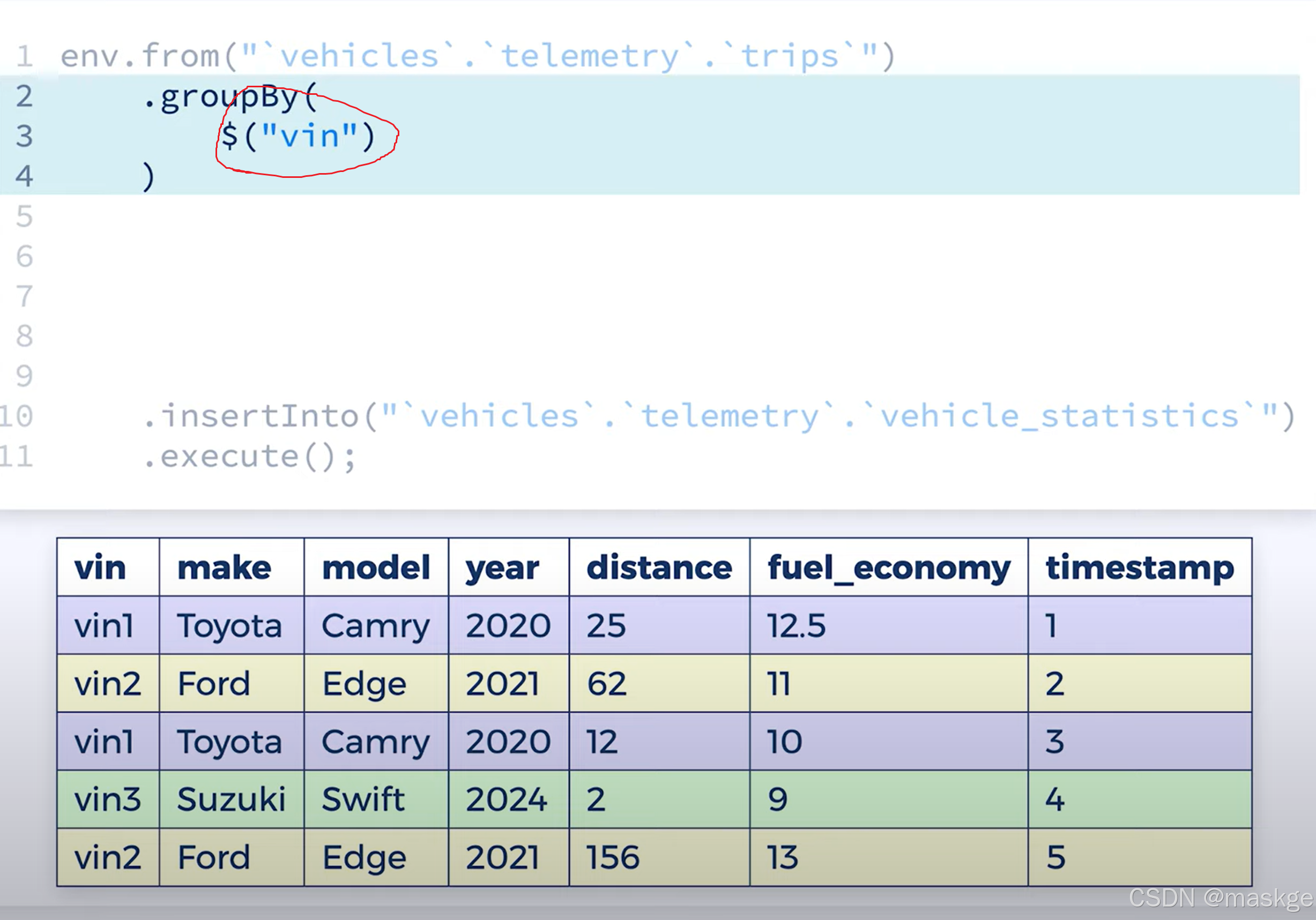
查詢數據庫中表數據可以通過讀取索引index查詢,但是查詢數據流,只能從開始讀取整個流
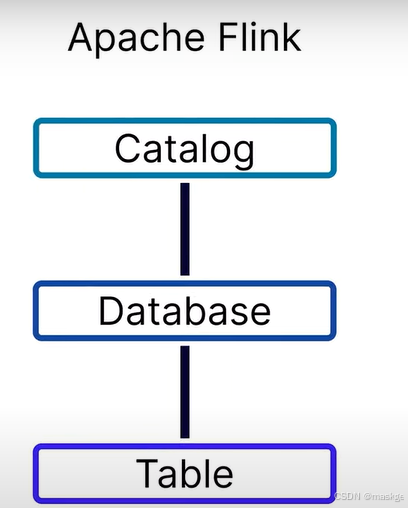
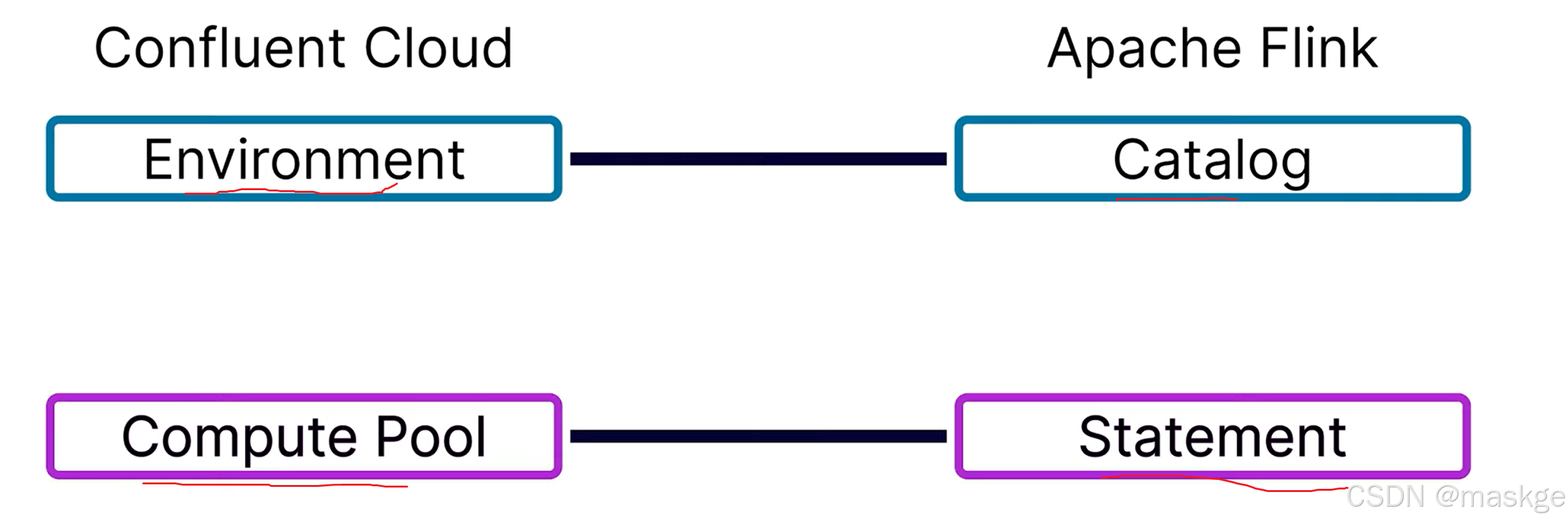
Flink table api 工作對象自定向下包含Catalog、database、table
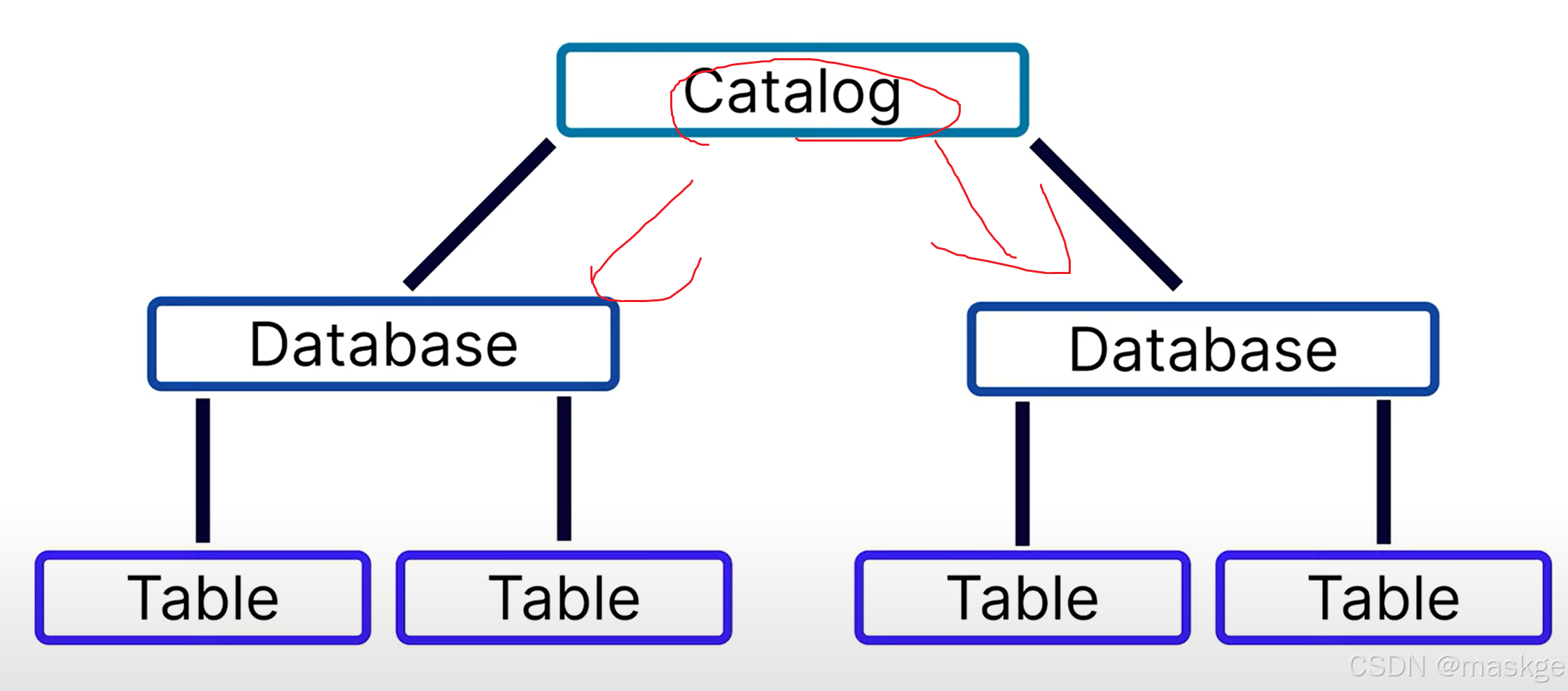
一個Catalog底下有1個或多個database,一個database底下有1個或多個table
調用方式:

例子:

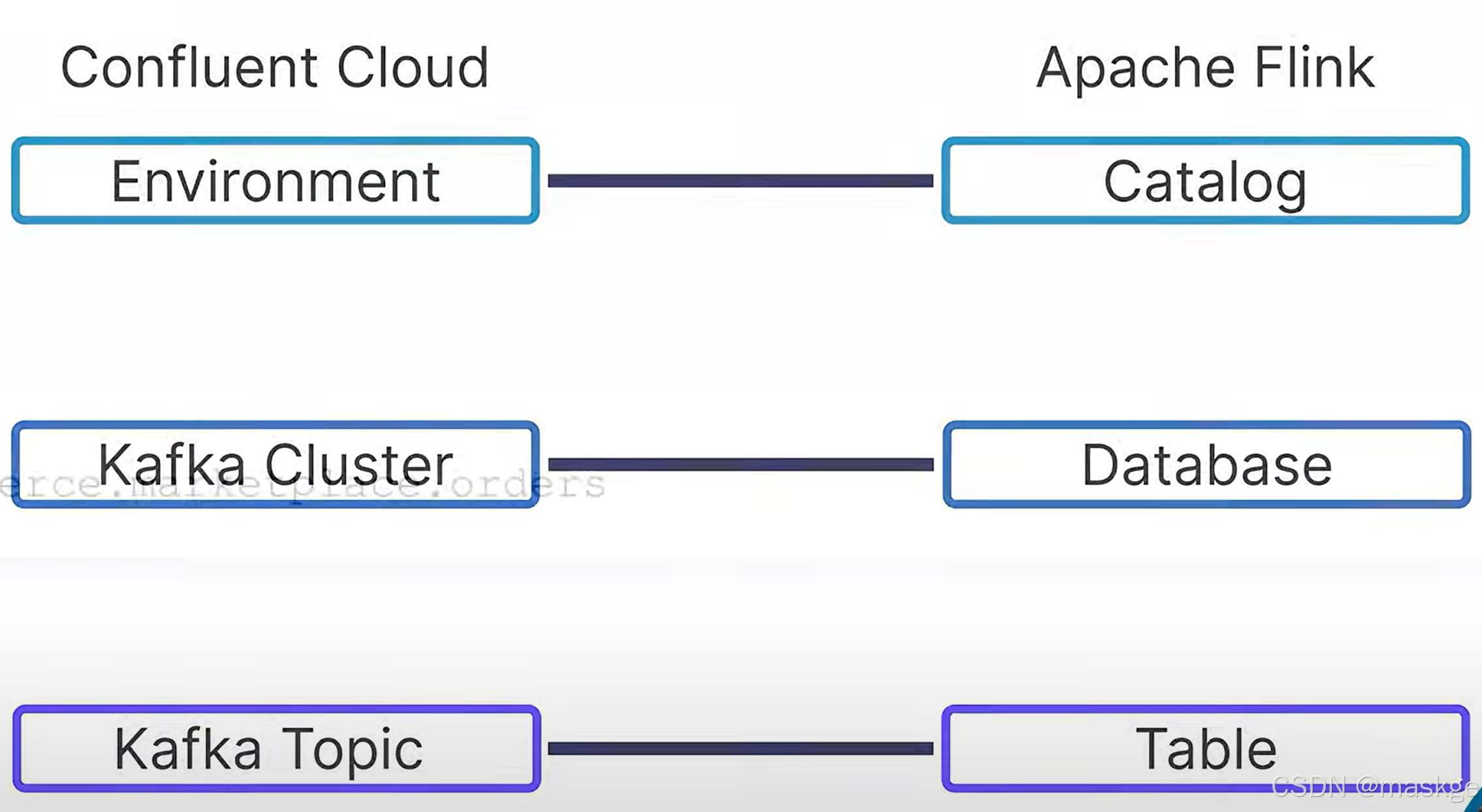 一個環境對應一個catalog,一個集群對應一個databse,一個Topic對應一個table,但是這塊topic與table的關系有點不一定
一個環境對應一個catalog,一個集群對應一個databse,一個Topic對應一個table,但是這塊topic與table的關系有點不一定
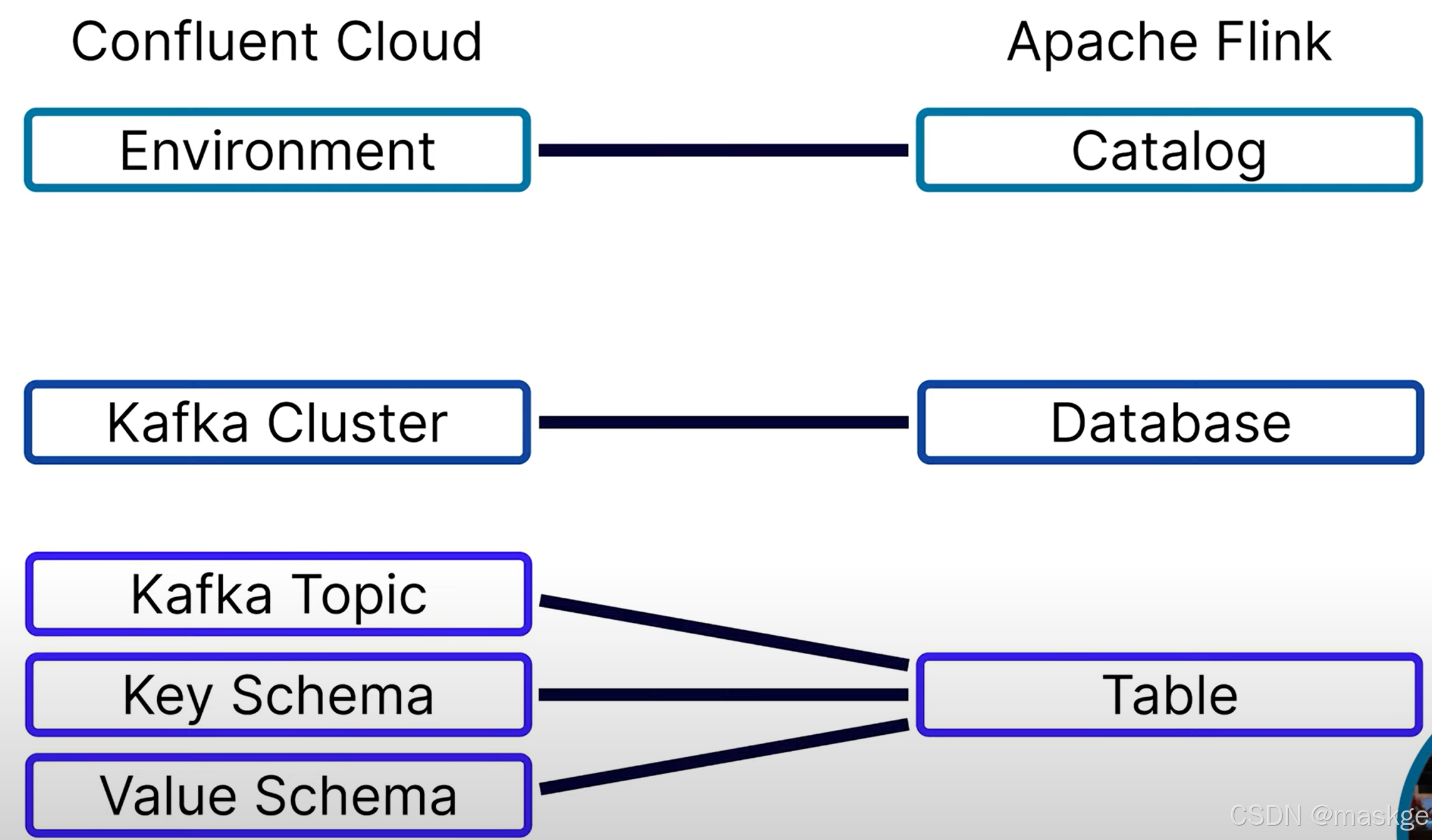
語句理解:
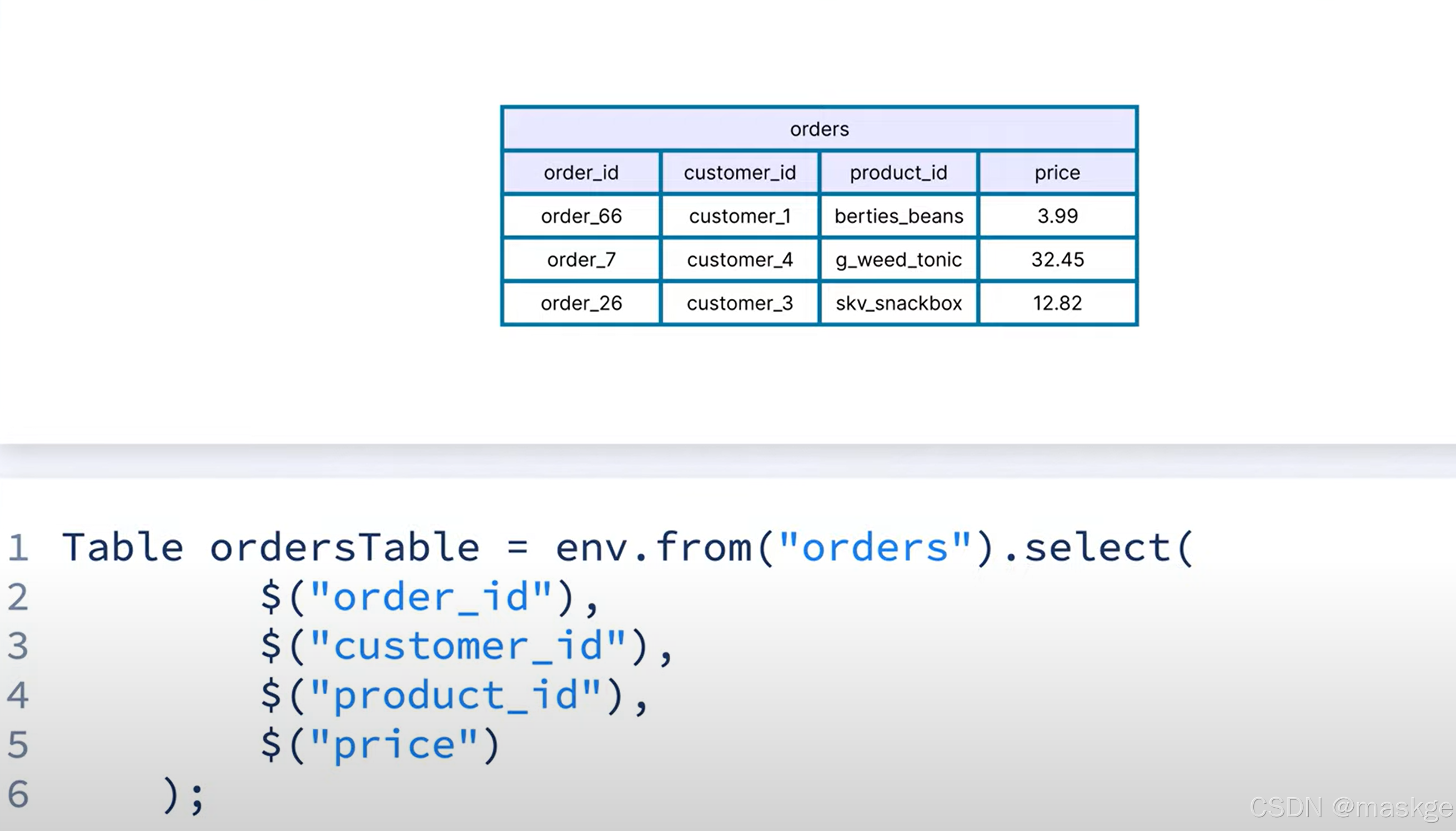
TableResult result=env.from("ecommerce.marketplace.orders").select($("*")).execute();result.print();執行上面的java代碼的效果與下面執行sql的效果等效:

5. select語句&flink table api:
//查詢結果TableResult result=env.from("ecommerce.marketplace.orders").select($("*"),$("vin").as("win")).insertInto("all_cars").execute();CloseableIterator<Row> rows=result.collect();//迭代結果while (rows.hasNext()){Row row=rows.next();row.getField("vin");}env.from("cars").select($("*")).where($("color").isEqual("Blue")).insertInto("blue_cars");env.from("cars").select($("*")).where($("year").isGreaterOrEqual(2022)).insertInto("cars_from_2022_or_later");env.from("cars").select($("*")).where(and($("year").isGreaterOrEqual(1900),$("year").isLess(2000))).insertInto("cars_from_the_1900s");env.from("cars").select($("*")).where($("year").cast(DataTypes.STRING()).like("19%")).insertInto("cars_from_the_1900s");
備注說明:flink中查詢出來的數據一般很少打印輸出,一般直接插入一張表
查看定義的表結構
SHOW CREATE TABLE examples.marketplace.orders;
查看flink是否正常啟動
ps aux | grep flink6. 使用flink table api 創建table
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.*;public class FlinkTableApi2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);//創建schemaSchema schemaTest=Schema.newBuilder().column("vin", DataTypes.STRING().notNull()).column("make", DataTypes.STRING().notNull()).column("model", DataTypes.STRING().notNull()).column("year",DataTypes.INT().notNull()).column("color",DataTypes.STRING().notNull()).build();//轉換上面schema成json或avro或protobuf schemaTableDescriptor descriptor=TableDescriptor.forConnector("confluents").schema(schemaTest).option("key.format","proto-registry")//注冊使用proto格式,當然也可以使用json-registry或avro-registry.option("value.format","proto-registry").option("kafka.retention.time","7 days").option("scan.startup.mode","latest-offset").partitionedBy("make")//設置分隔的key為make.build();//創建表env.createTable("cars",descriptor);}
}數據格式化的格式:
- proto-registry
- json-registry
- avro-registry
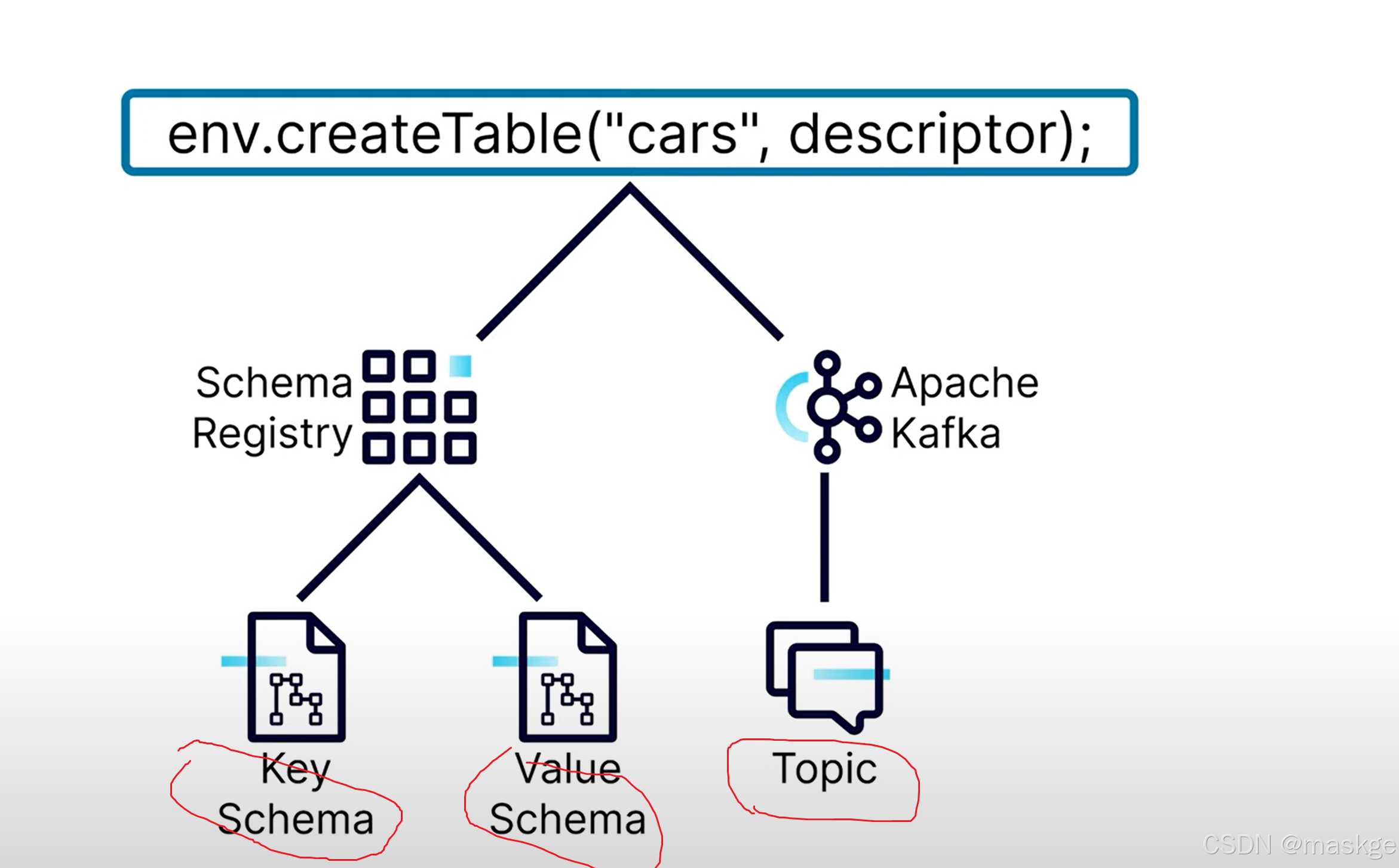
flink 創建表的原理:
- 創建表就是在創建 keyschema、value schema、topic;
- descriptor:描述如何這些資源被創建
flink table api 使用sql腳本創建表
//創建表方法2env.executeSql("""CREATE TABLE `cars` (`vin` VARCHAR(2147483647) NOT NULL,`make` VARCHAR(2147483647) NOT NULL,`model` VARCHAR(2147483647) NOT NULL,`year` INT NOT NULL,`color` VARCHAR(2147483647) NOT NULL) DISTRIBUTED BY (`vin`) INTO 6 BUCKETS WITH ('connector' = 'confluent','kafka.retention.time' = '7 days','scan.startup.mode' = 'latest-offset','key.format' = 'proto-registry','value.format' = 'proto-registry')""");
7. 使用flink table api 寫流式數據輸出到表或sink
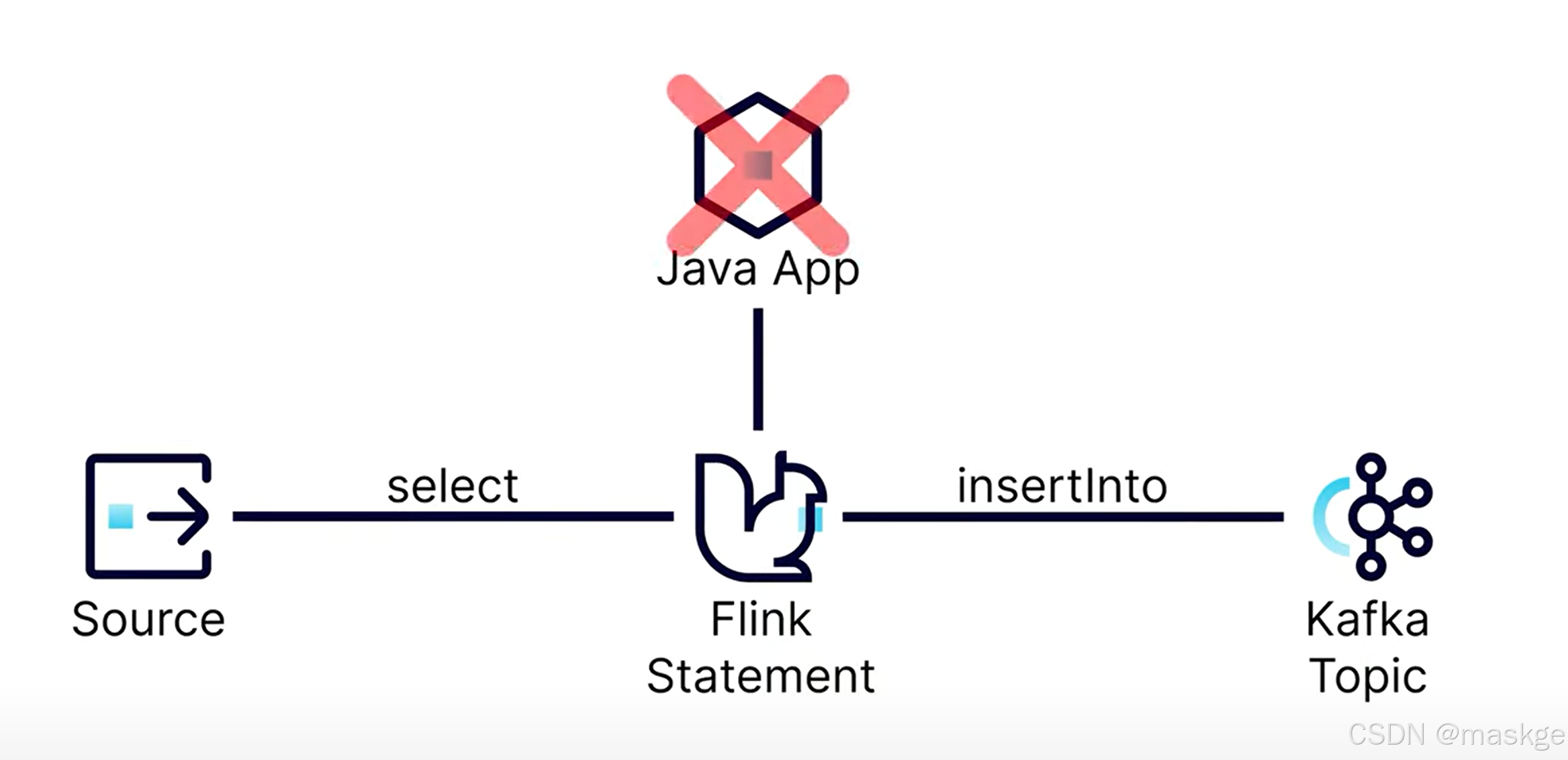
輸出到table



flink statement

 上面的sink即java APP
上面的sink即java APP
當javaApp,掛了出現的情況:只要kafka topic存在,可以把數據寫到kafka
flink table api 數據流寫入表(也可以是topics),并輸出結果到控制臺:
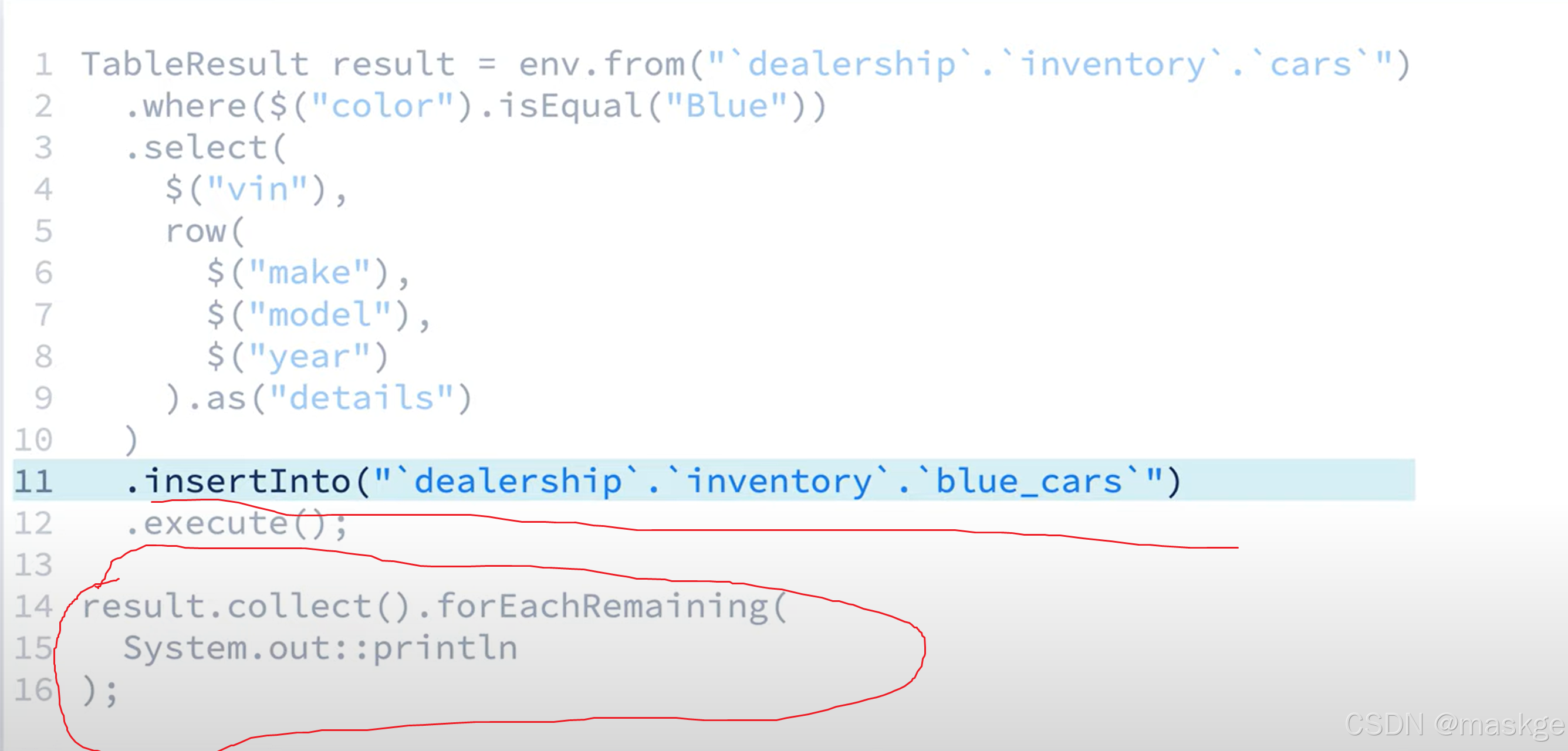
上面語句解釋:
執行execute()方法,就是在創建一個無界流,這也就意味著進行insertInfo()操作的時候,就一直往表中無限插入。這個特別需要注意,不能這樣做,不然會出現數據爆表
8. flink auto-scaling(自動伸縮)
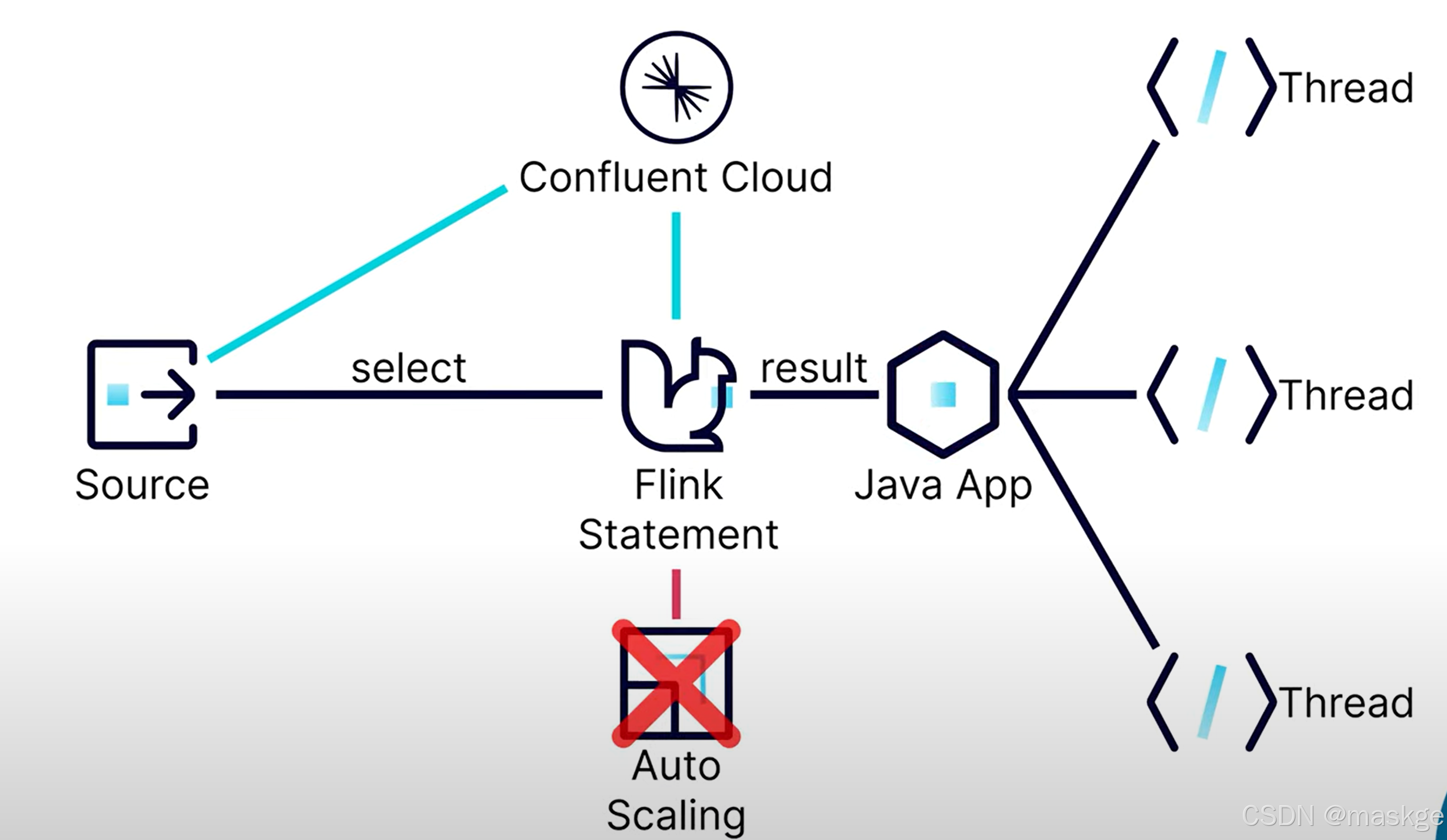 在flink java應用中,查詢是一個單線程,因此不能自動伸縮;
在flink java應用中,查詢是一個單線程,因此不能自動伸縮;
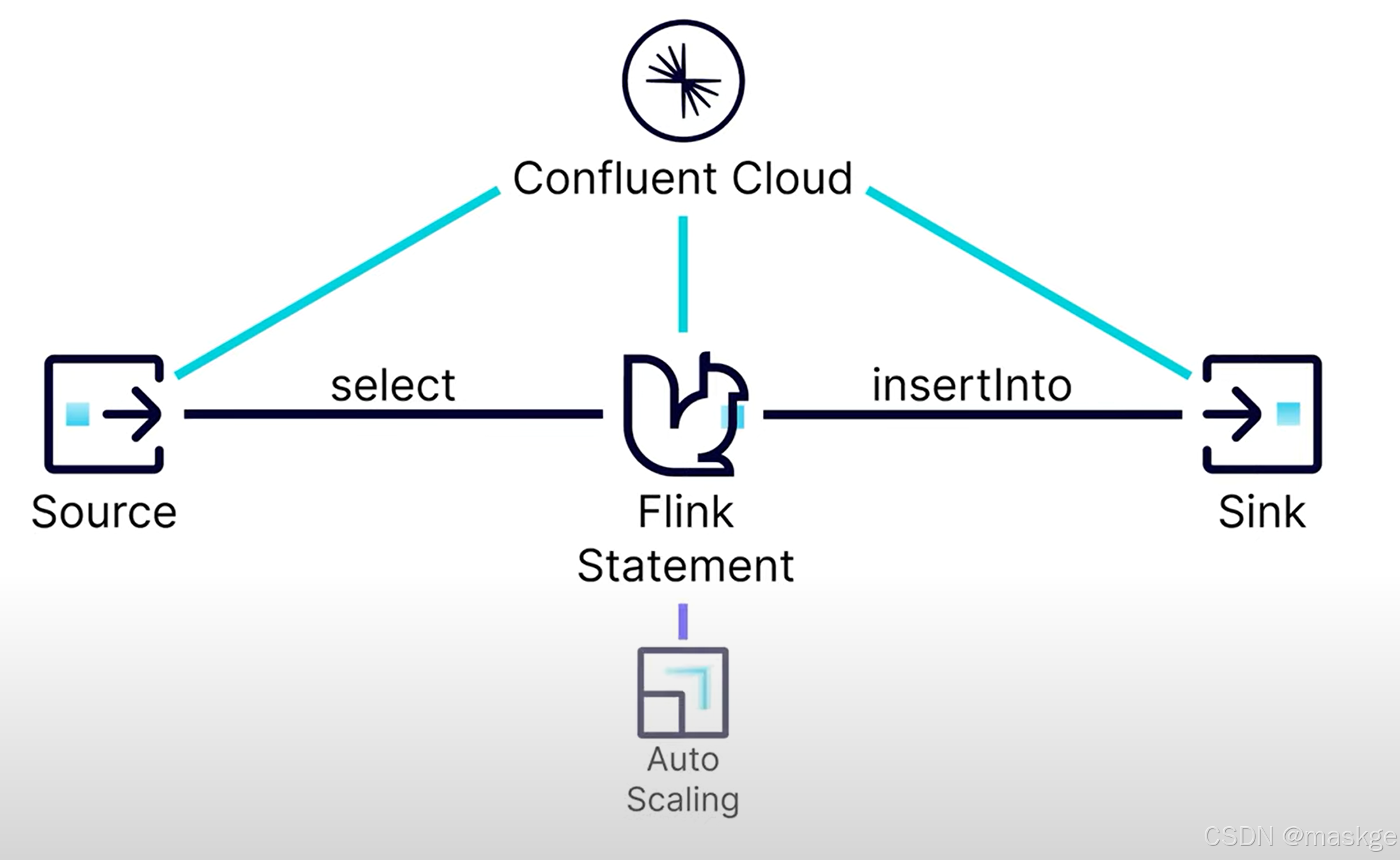
confluent cloud可以讓flink自動伸縮,更加高效的利用資源
中斷job:即使中斷了應用,無界流依然run,依然耗費資源。可以通過程序中斷job: tableresult.getJobClient().get().cancel();
TableResult tableresult=env.from("ecommerce.marketplace.orders").select($("*"),$("vin").as("win")).insertInto("all_cars").execute();tableresult.getJobClient().get().cancel();//中斷job
9. watermarks(水印)
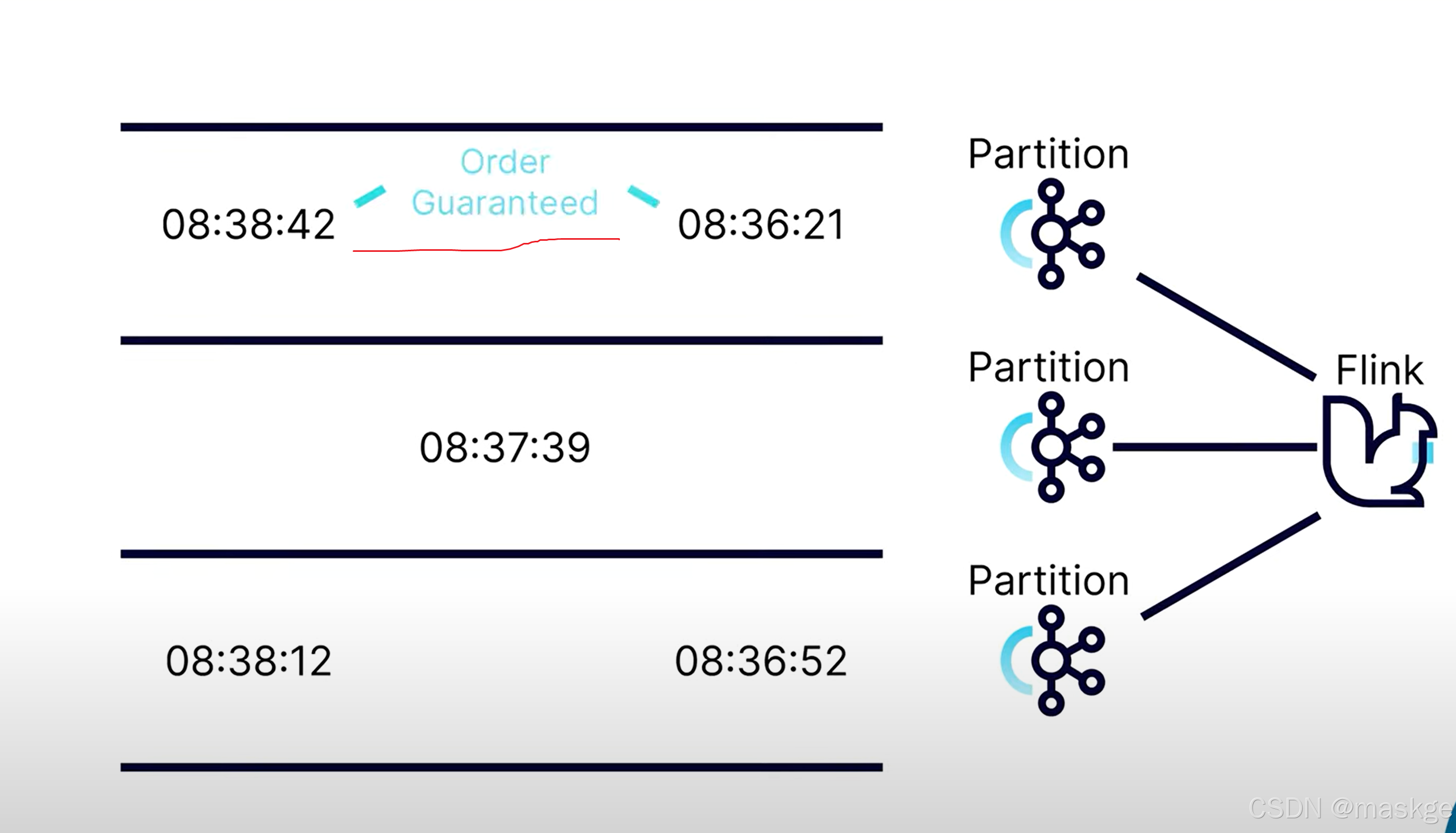
kafka可以確保分區內有序;但不確保跨多個分區有序;這也就產生了事件到達無序問題
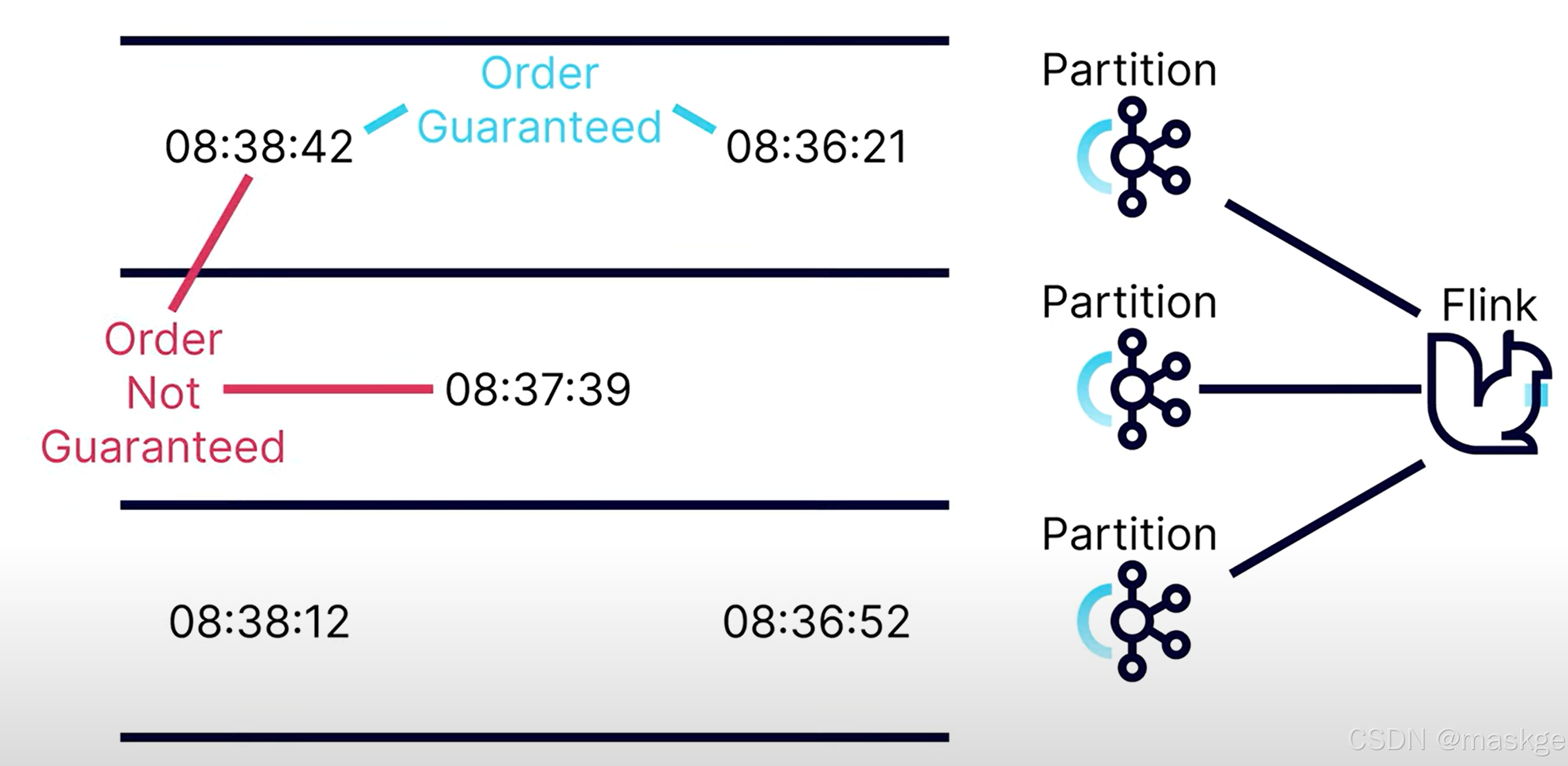
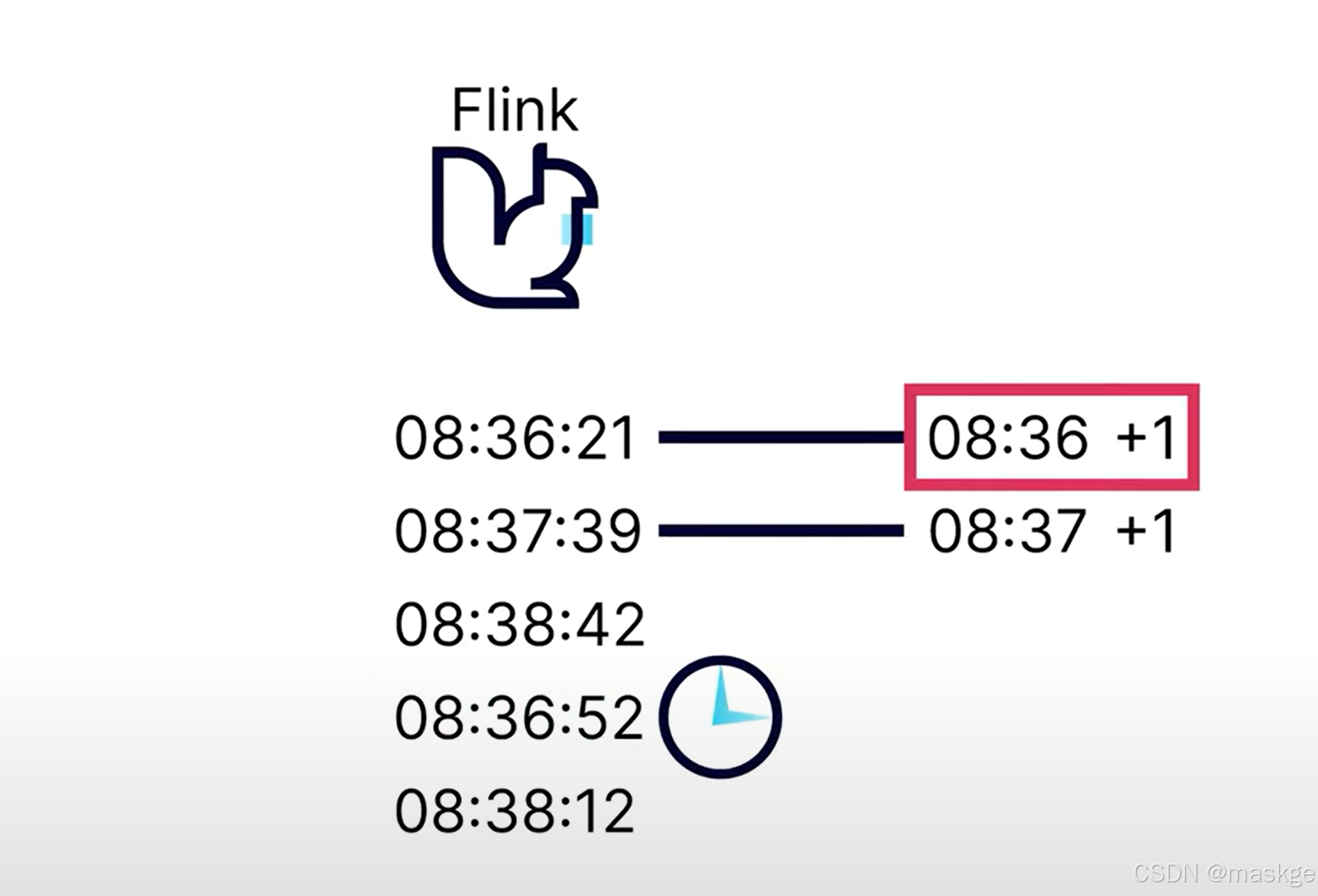
watermark的目標是提供一個最大的時間,等候無序事件
kafka ----> timeststamp
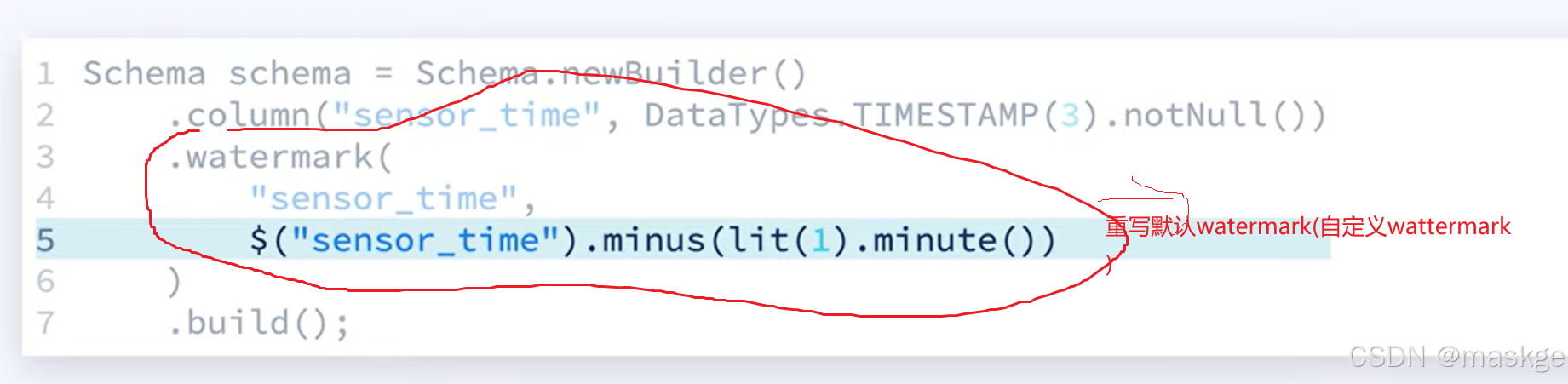
自定義watermark
10. 聚合數據(Aggregating Data)


語句解釋:把查詢匯總的結果,最終寫入topic: trips_overview中
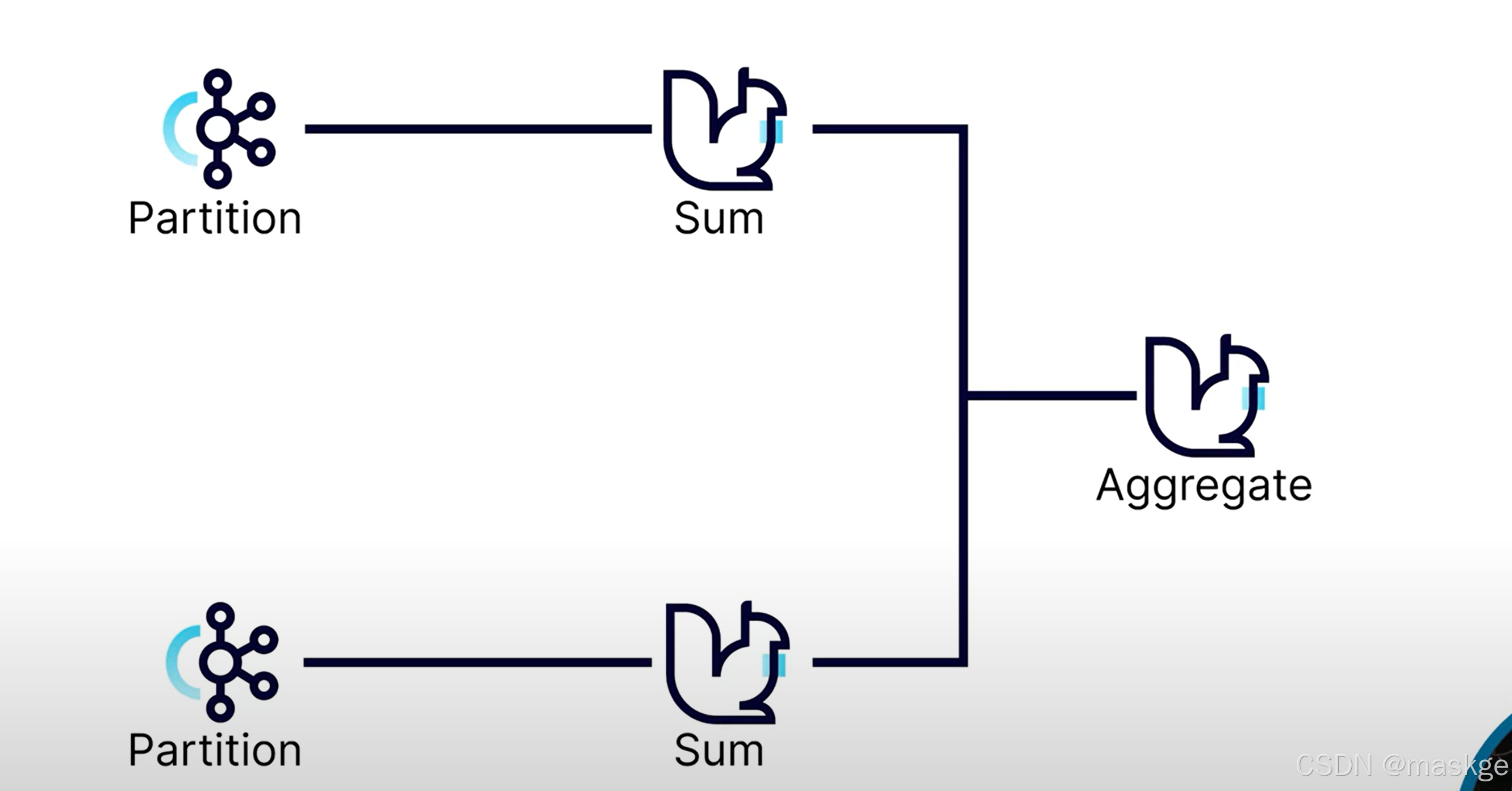
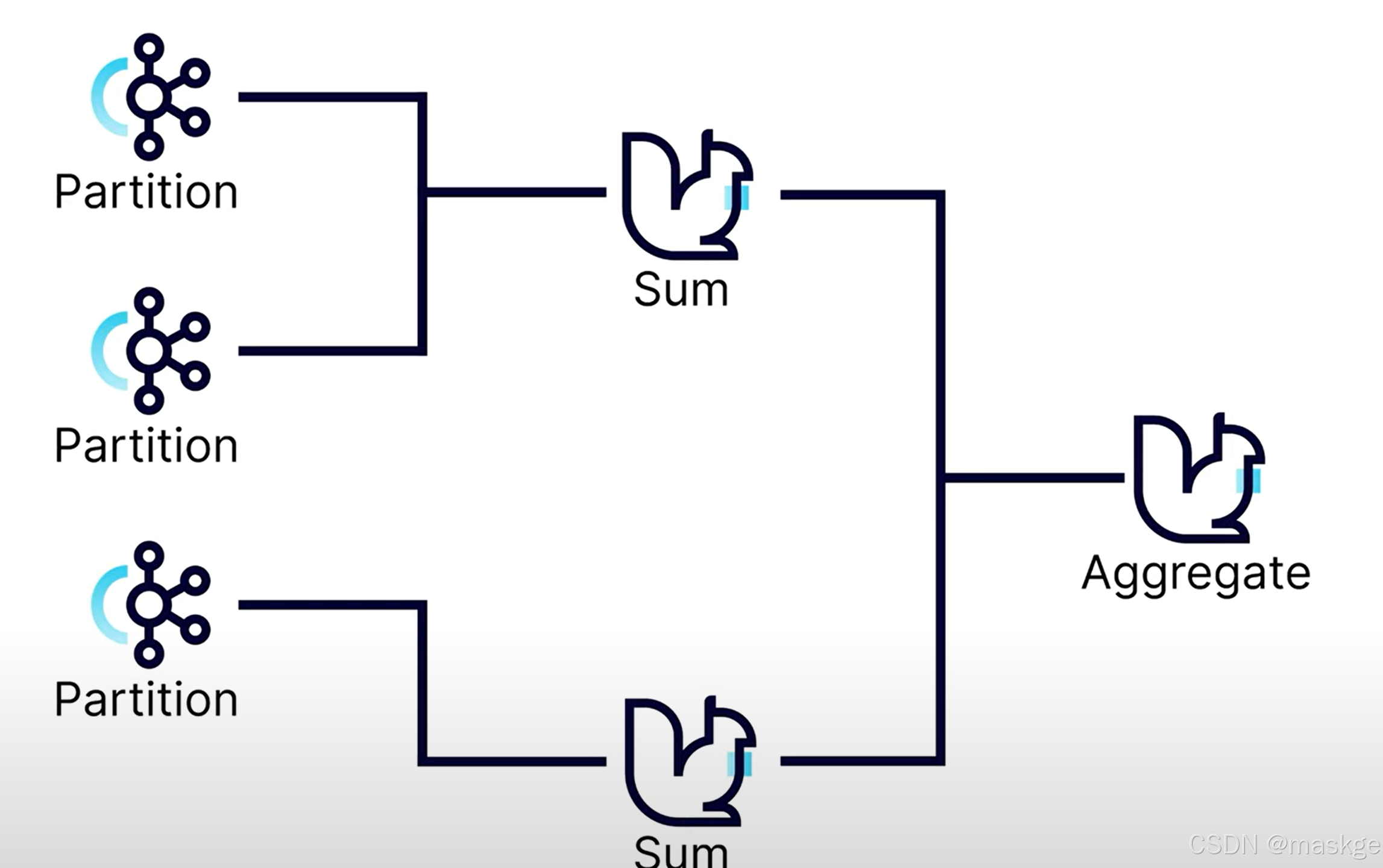
flink可以把各個分區sum的結果進行最終的聚合(Aggregate);
如果分區不夠,很容易出現數據偏移,最佳實踐是配置足夠多的分區空間,在擴展的時候,不會出現太多偏移
groupBy 可以分隔進入的數據流成為多個數據流

distinct():去重

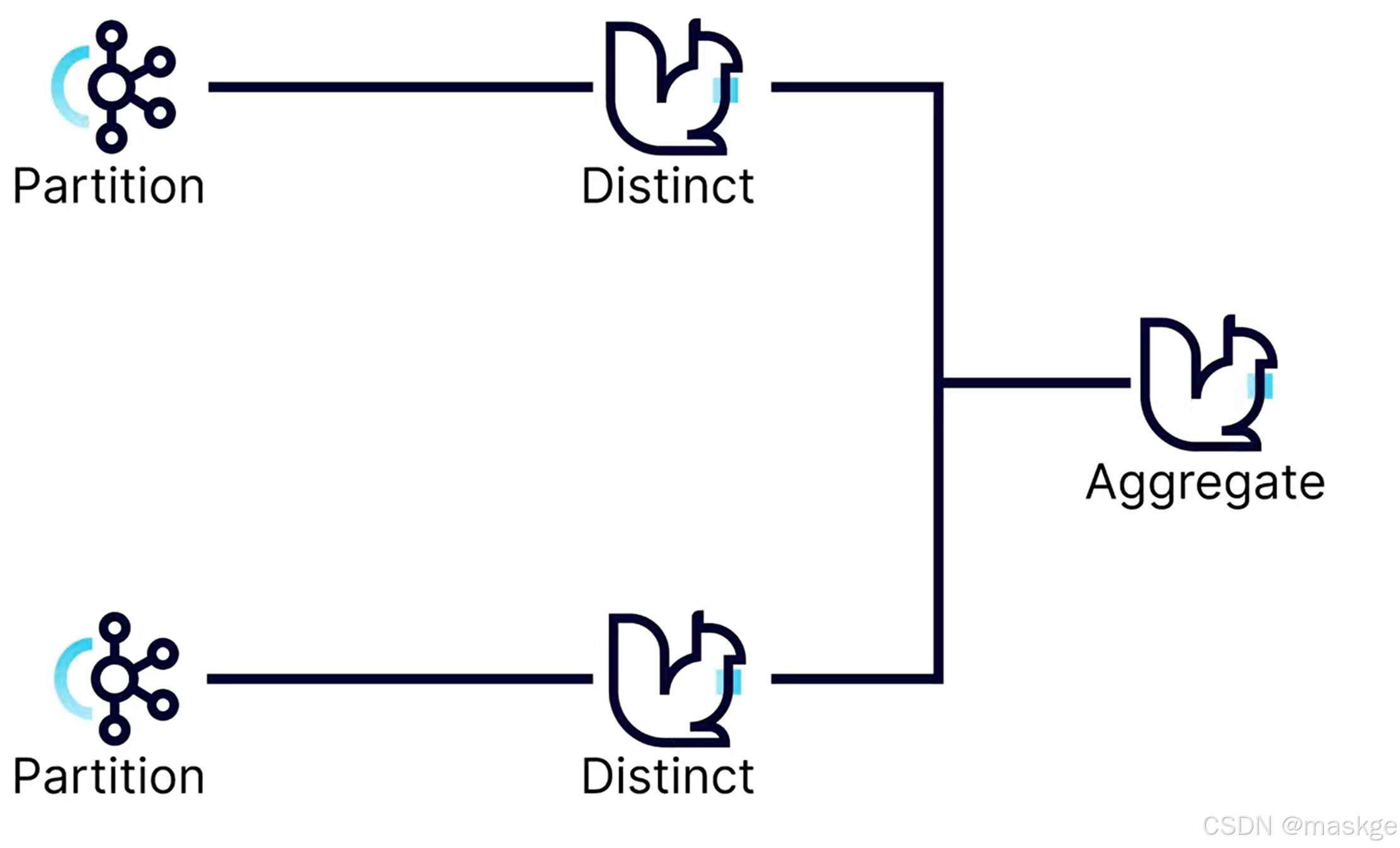
count 、 sum、average 通常是安全的并且可以完成最小的存儲; distinct需要更多的存儲,區間于如何配置它
11. 使用窗口聚合數據(using windows to aggregate data)
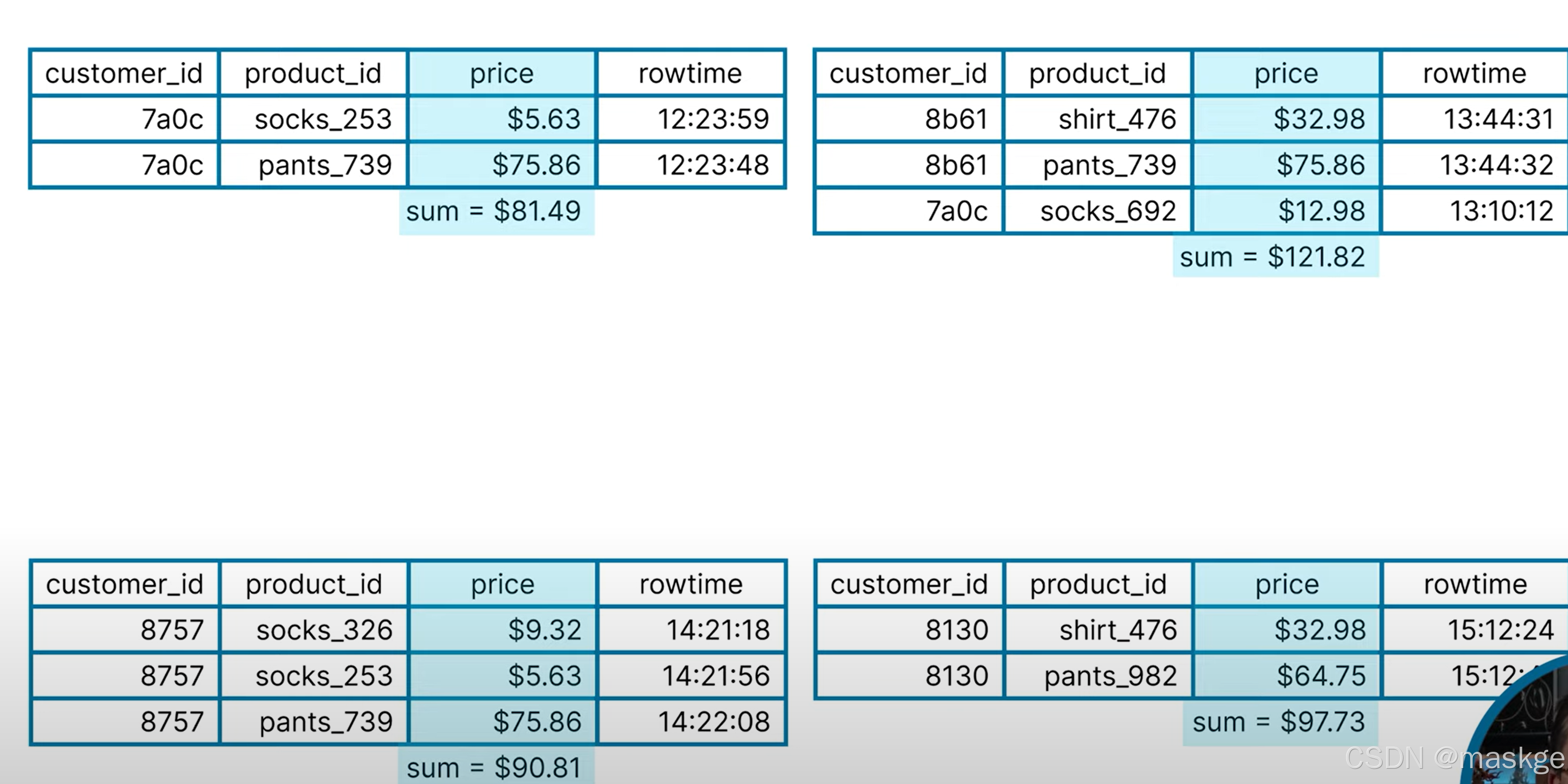
window API 允許flink對事件進行分組,基于時間窗口
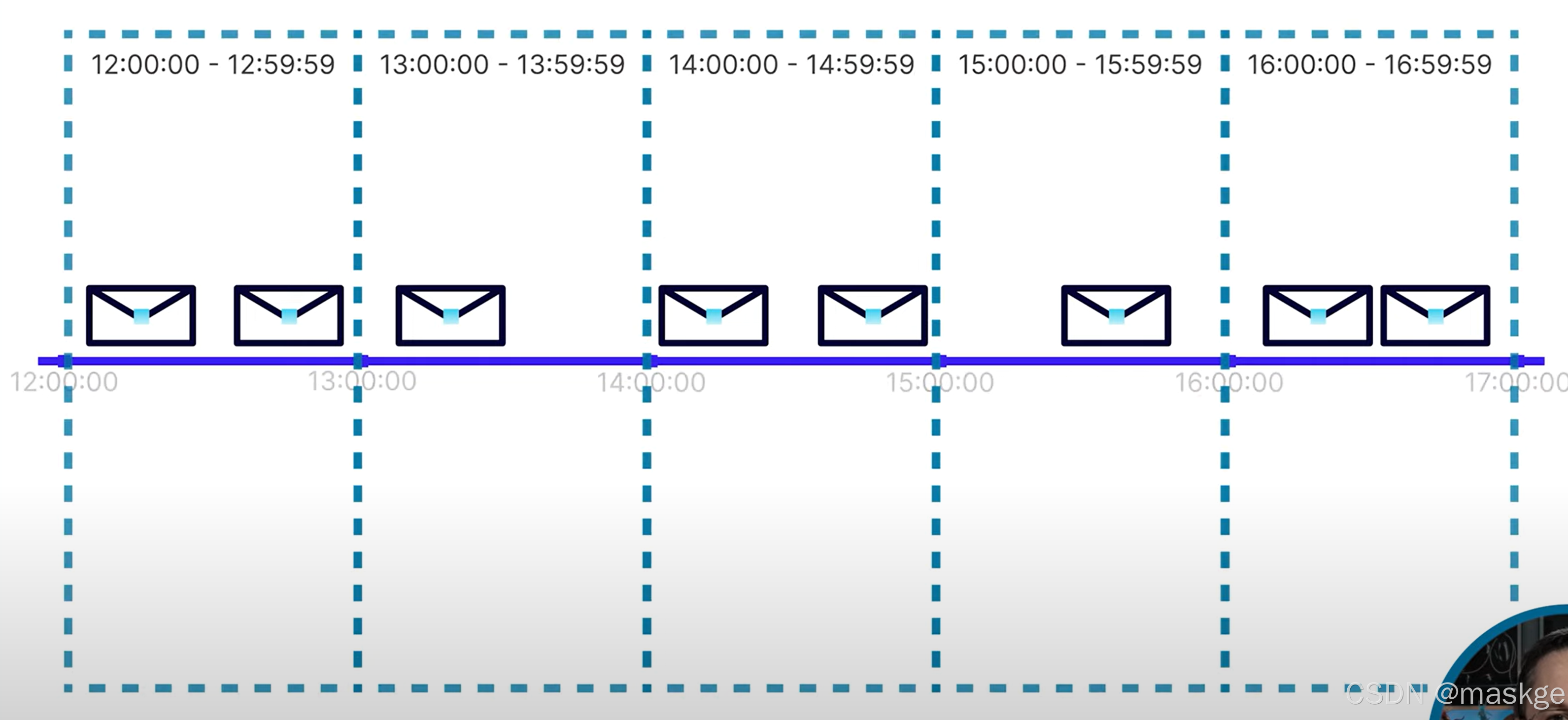
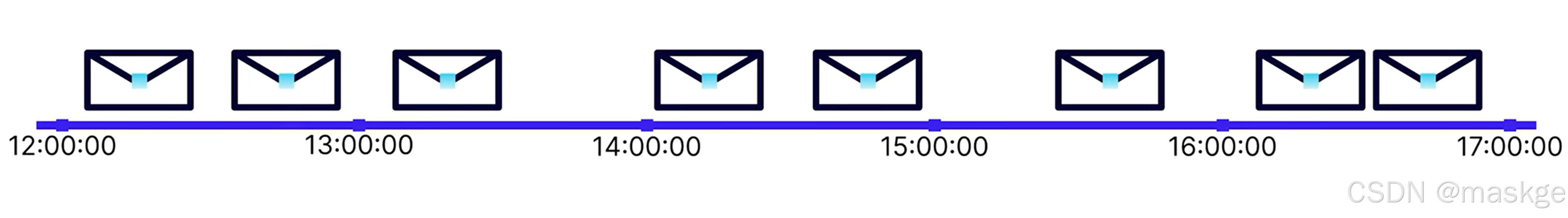
滾動窗口(tumbling windows): 窗口固定,無重疊
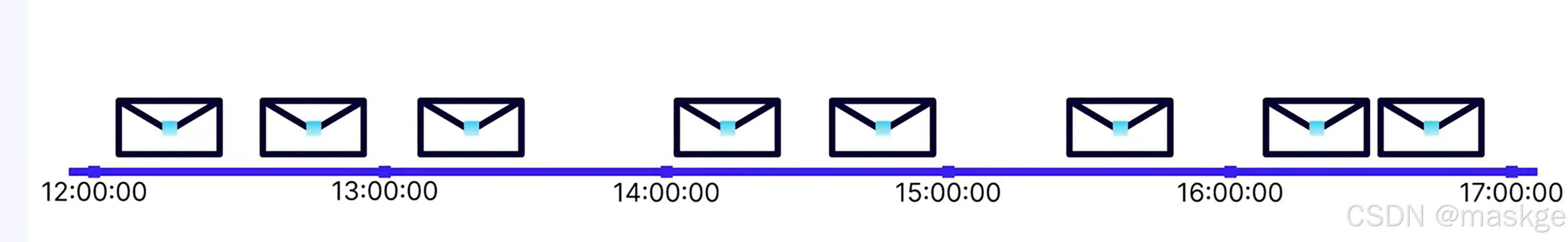
把上面的消息分隔成1個小時一個窗口;
滾動窗口代碼如下:
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Tumble;import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.$;
import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.lit;public class FlinkTableApiWindowAggregate {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);env.from("examples.marketpalce.orders").window(Tumble.over(lit(1).hours()//設置一個滾動窗口持續時間為1小時).on($("$rowtime")//使用rowtime字段作為時間戳timestamp).as("window")//設置窗口名字為name).groupBy(//對查詢記錄進行分組$("customer_id"),$("window")).select(//查詢計算窗口數據$("customer_id"),$("window").start().as("window_start"),$("window").end().as("window_end"),$("price").sum().as("total_spend")).execute();}
}
fixed-size window(固定大小窗口)
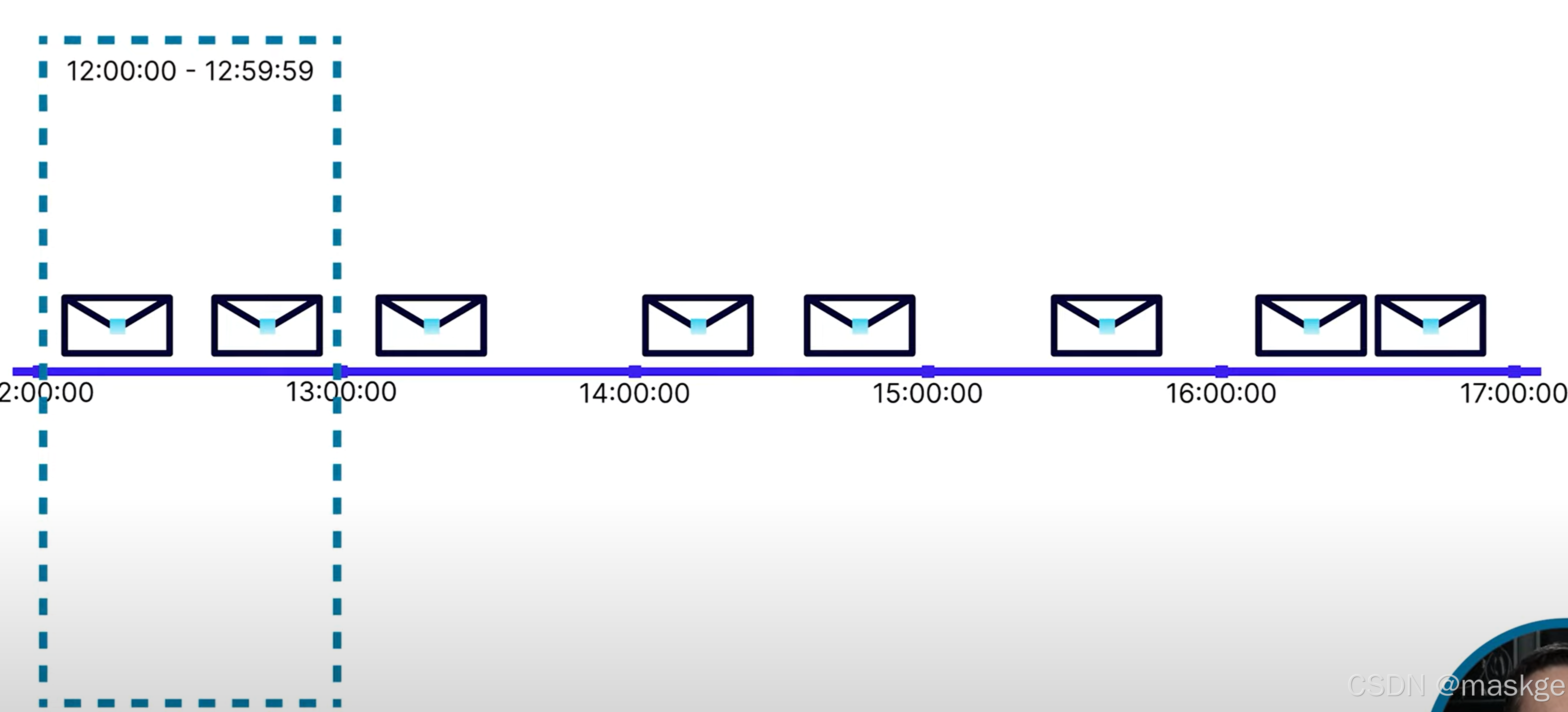
滑動窗口(sliding window):窗口與先前的窗口重疊;
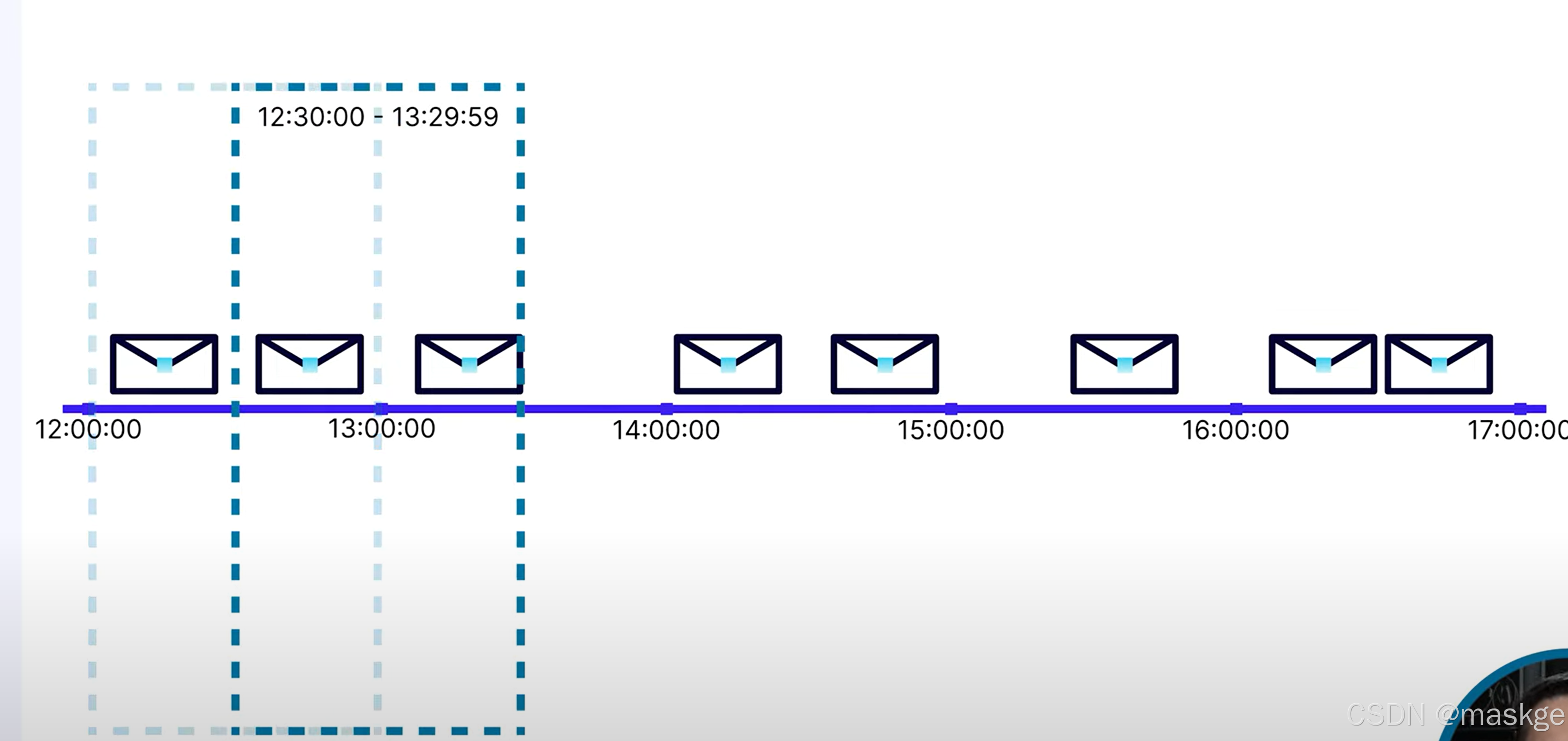
跳躍窗口(hopping window):
它是一種基于時間的窗口機制,用于將持續產生的流數據劃分成多個有固定長度的時間段(窗口),并按固定的 “跳躍間隔”(hop interval)向前移動。
- 核心特點:窗口有固定的長度(window size)和固定的跳躍間隔。跳躍間隔通常小于窗口長度,因此相鄰窗口之間會存在重疊部分。
例如:若窗口長度為 10 分鐘,跳躍間隔為 5 分鐘,那么第一個窗口覆蓋 [0:00, 0:10),第二個窗口覆蓋 [0:05, 0:15),以此類推,兩個窗口重疊 5 分鐘。 - 與其他窗口的區別:
- 滾動窗口(tumbling window):跳躍間隔等于窗口長度,無重疊;
- 滑動窗口(sliding window):邏輯上與跳躍窗口類似,有時可視為 “跳躍窗口” 的另一種表述(取決于具體語境),強調窗口隨時間滑動的特性。
跳躍窗口常用于需要高頻次統計一段連續時間數據的場景,例如 “每 5 分鐘計算過去 10 分鐘的訂單總量”。
滑動窗口代碼:
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Slide;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment;import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.$;
import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.lit;/*** 滑動窗口代碼*/
public class FlinkTableApiWindowAggregate2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);env.from("examples.marketpalce.orders").window(Slide.over(lit(1).hours()//設置一個滑動窗口持續時間為1小時).every(lit(30).minutes()//設置每30分鐘計算一個結果).on($("$rowtime")//使用rowtime字段作為時間戳timestamp).as("window")//設置窗口名字為name).groupBy(//對查詢記錄進行分組$("customer_id"),$("window")).select(//查詢計算窗口數據$("customer_id"),$("window").start().as("window_start"),$("window").end().as("window_end"),$("price").sum().as("total_spend")).execute();}
}12.flink 多表連接(joining flink tables)

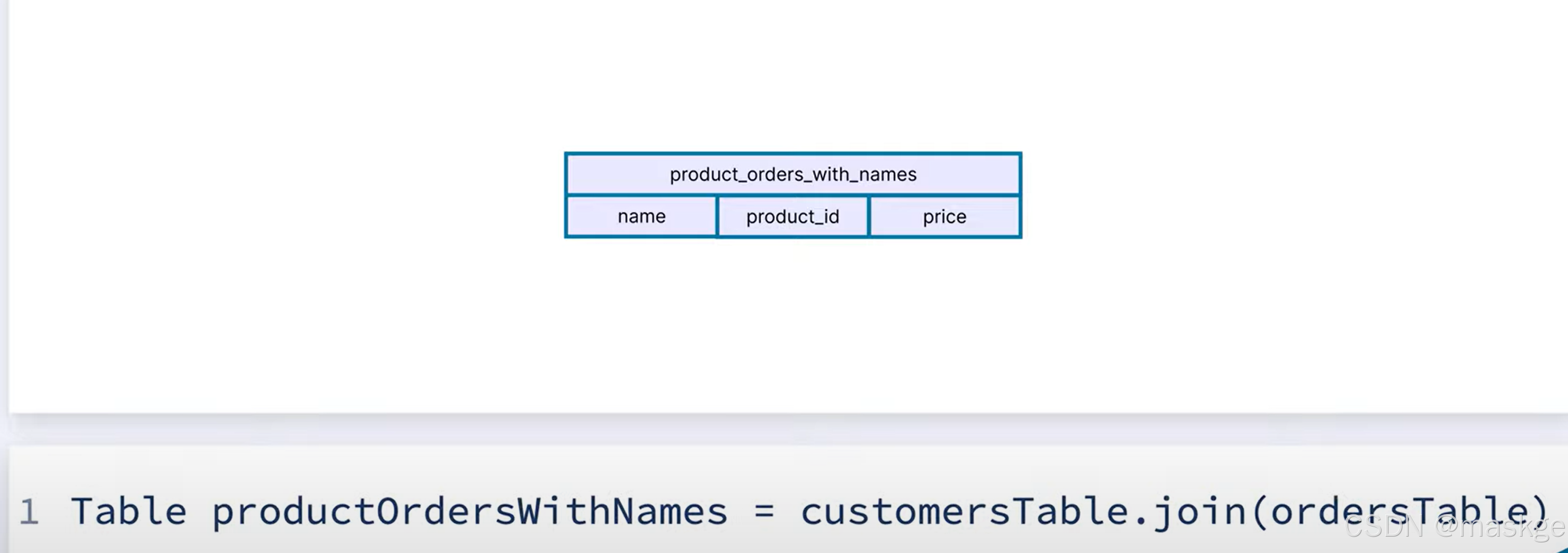
內連接(inner join)

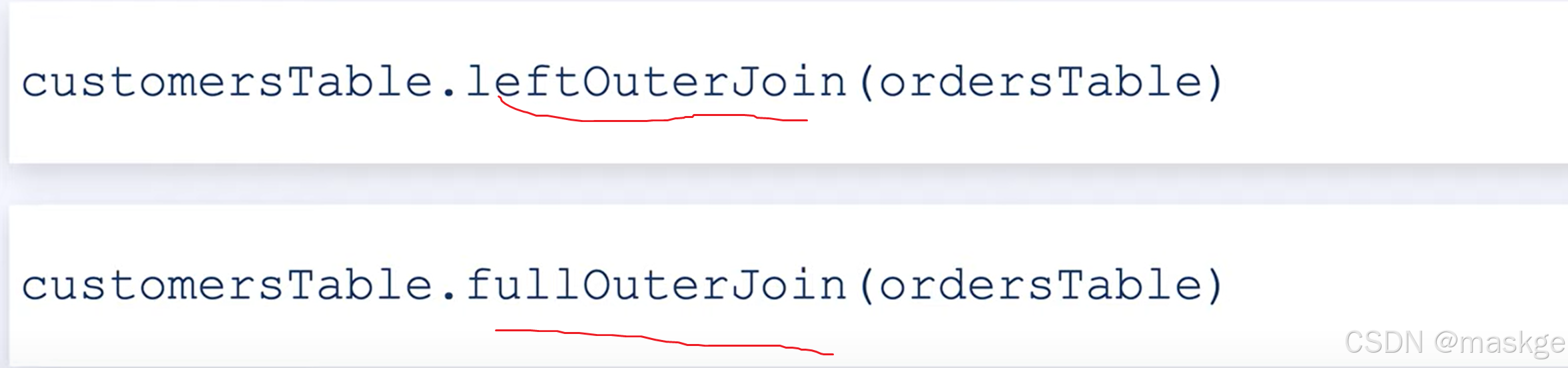
左連接&全連接

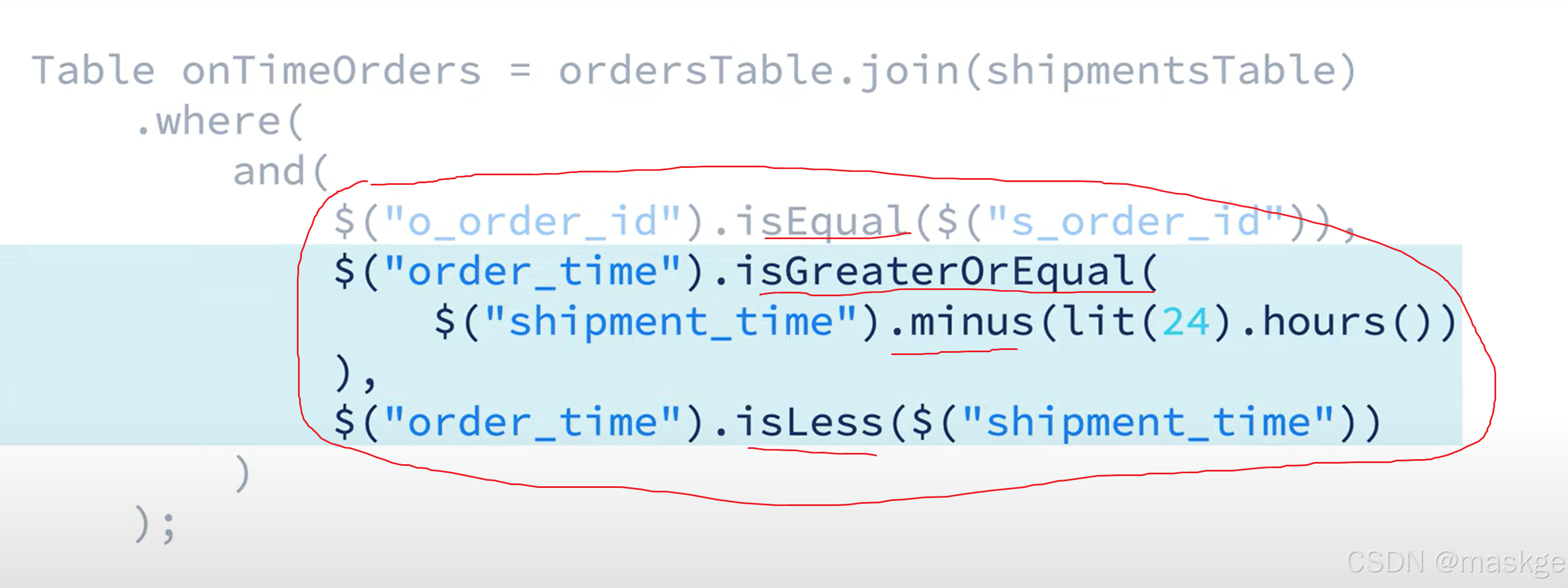
interval join(區間連接):在區間時間內的查詢有效,一旦超過區間時間,就舍棄窗口外無效狀態;
需要append-only 流,以避免級聯更新問題
13.flink table api 代碼
創建表代碼:
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.*;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.config.TableConfigOptions;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.DataType;import java.util.List;/*** A table program example that illustrates how to create a table backed by a Kafka topic.** <p>NOTE: This example requires write access to a Kafka cluster. Fill out the given variables* below with target catalog/database if this is fine for you.*/
public class CreatingTables {// Fill this with an environment you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_CATALOG = "";// Fill this with a Kafka cluster you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_DATABASE = "";// Fill this with names of the Kafka Topics you want to createstatic final String TARGET_TABLE1 = "MyExampleTable1";static final String TARGET_TABLE2 = "MyExampleTable2";public static void main(String[] args) {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();settings.getConfiguration().set(TableConfigOptions.LOCAL_TIME_ZONE,"UTC");//table.local-time-zone//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);env.useCatalog(TARGET_CATALOG);env.useDatabase(TARGET_DATABASE);System.out.println("Creating table... " + TARGET_TABLE1);// Create a table programmatically:// The table...// - is backed by an equally named Kafka topic// - stores its payload in JSON// - will reference two Schema Registry subjects for Kafka message key and value// - is distributed across 4 Kafka partitions based on the Kafka message key "user_id"env.createTable(TARGET_TABLE1,TableDescriptor.forManaged().schema(Schema.newBuilder().column("user_id", DataTypes.STRING()).column("name", DataTypes.STRING()).column("email", DataTypes.STRING()).build()).partitionedBy("user_id")//.distributedBy(4, "user_id").option("kafka.retention.time", "0").option("key.format", "json-registry").option("value.format", "json-registry").build());// Alternatively, the call above could also be executed with SQLenv.executeSql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `"+ TARGET_TABLE1+ "` (\n"+ " `user_id` STRING,\n"+ " `name` STRING,\n"+ " `email` STRING\n"+ ")\n"+ "DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`user_id`) INTO 4 BUCKETS\n"+ "WITH (\n"+ " 'kafka.retention.time' = '0 ms',\n"+ " 'key.format' = 'json-registry',\n"+ " 'value.format' = 'json-registry'\n"+ ")");System.out.println("Creating table... " + TARGET_TABLE2);// The schema builders can be quite useful to avoid manual schema work. You can adopt schema// from other tables, massage the schema, and/or add additional columnsDataType productsRow =env.from("examples.marketplace.products").getResolvedSchema().toPhysicalRowDataType();List<String> columnNames = DataType.getFieldNames(productsRow);List<DataType> columnTypes = DataType.getFieldDataTypes(productsRow);// In this example, the table will get all names/data types from the table 'products'// plus an 'additionalColumn' columnenv.createTable(TARGET_TABLE2,TableDescriptor.forManaged().schema(Schema.newBuilder().fromFields(columnNames, columnTypes).column("additionalColumn", DataTypes.STRING()).build()).build());}
}flink table pipeline(flink 流水線)代碼:
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.*;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.config.TableConfigOptions;import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.$;
import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.concat;
import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.row;/*** A table program example that demos how to pipe data into a table or multiple tables.** <p>NOTE: This example requires write access to a Kafka cluster. Fill out the given variables* below with target catalog/database if this is fine for you.** <p>ALSO NOTE: The example submits an unbounded background statement. Make sure to stop the* statement in the Web UI afterward to clean up resources.*/
public class Example_05_TablePipelines {// Fill this with an environment you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_CATALOG = "";// Fill this with a Kafka cluster you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_DATABASE = "";// Fill this with names of the Kafka Topics you want to createstatic final String TARGET_TABLE1 = "PricePerProduct";static final String TARGET_TABLE2 = "PricePerCustomer";public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();settings.getConfiguration().set(TableConfigOptions.LOCAL_TIME_ZONE,"UTC");//table.local-time-zone//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);env.useCatalog(TARGET_CATALOG);env.useDatabase(TARGET_DATABASE);System.out.println("Creating tables... " + List.of(TARGET_TABLE1, TARGET_TABLE2));// Create two helper tables that will be filled with data from examplesenv.createTable(TARGET_TABLE1,TableDescriptor.forManaged().schema(Schema.newBuilder().column("product_id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull()).column("price", DataTypes.DOUBLE().notNull()).build()).build());env.createTable(TARGET_TABLE2,TableDescriptor.forManaged().schema(Schema.newBuilder().column("customer_id", DataTypes.INT().notNull()).column("price", DataTypes.DOUBLE().notNull()).build()).build());System.out.println("Executing table pipeline synchronous...");// A TablePipeline describes a flow of data from source(s) to sink.// In this case, from values to a Kafka-backed target tableTablePipeline pipeline =env.fromValues(row("1408", 27.71), row("1062", 94.39), row("42", 80.01)).insertInto(TARGET_TABLE1);// One can explain or execute a pipelinepipeline.printExplain();// Execution happens async by default, use await() to attach to the execution in case all// sources are finite (i.e. bounded).// For infinite (i.e. unbounded) sources, waiting for completion would not make much sense.pipeline.execute().await();System.out.println("Executing statement set asynchronous...");// The API supports more than a single sink, you can also fan out to different tables while// reading from a table once using a StatementSet:StatementSet statementSet =env.createStatementSet().add(env.from("`examples`.`marketplace`.`orders`").select($("product_id"), $("price")).insertInto(TARGET_TABLE1)).add(env.from("`examples`.`marketplace`.`orders`").select($("customer_id"), $("price")).insertInto(TARGET_TABLE2));// Executes a statement set that splits the 'orders' table into two tables,// a 'product_id | price' table and a 'customer_id | price' onestatementSet.execute();System.out.println("Reading merged data written by background statement...");// For this example, we read both target tables in again and union them into one output to// verify that the data arrivesTable targetTable1 =env.from(TARGET_TABLE1).select(concat($("product_id"), " event in ", TARGET_TABLE1));Table targetTable2 =env.from(TARGET_TABLE2).select(concat($("customer_id").cast(DataTypes.STRING())," event in ",TARGET_TABLE2));targetTable1.unionAll(targetTable2).as("status").execute().print();}
}flink values與datatype :
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.DataTypes;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Table;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.config.TableConfigOptions;
import org.apache.flink.table.expressions.Expression;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Map;import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.*;/** A table program example to create mock data. */
public class Example_06_ValuesAndDataTypes {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();settings.getConfiguration().set(TableConfigOptions.LOCAL_TIME_ZONE,"UTC");//table.local-time-zone//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);// Values for each data type can be created...// (1) with Java objectsRow row = new Row(17);// BOOLEANrow.setField(0, true);// STRING / CHAR / VARCHARrow.setField(1, "Alice");// DATErow.setField(2, LocalDate.of(2024, 12, 23));// TIMErow.setField(3, LocalTime.of(13, 45, 59));// TIMESTAMProw.setField(4, LocalDateTime.of(2024, 12, 23, 13, 45, 59));// TIMESTAMP_LTZrow.setField(5, Instant.ofEpochMilli(1734957959000L));// BIGINTrow.setField(6, 42L);// INTrow.setField(7, 42);// SMALLINTrow.setField(8, (short) 42);// TINYINTrow.setField(9, (byte) 42);// DOUBLErow.setField(10, 42.0);// FLOATrow.setField(11, 42.0f);// DECIMALrow.setField(12, new BigDecimal("123.4567"));// BYTES / BINARY / VARBINARYrow.setField(13, new byte[] {1, 2, 3});// ARRAYrow.setField(14, new Integer[] {1, 2, 3});// MAProw.setField(15, Map.ofEntries(Map.entry("k1", "v1"), Map.entry("k2", "v2")));// ROWrow.setField(16, Row.of("Bob", true));Table fromObjects = env.fromValues(row);// (2) with Table API expressionsExpression rowExpr =row(// VARCHAR(200)lit("Alice").cast(DataTypes.VARCHAR(200)),// ARRAYarray(1, 2, 3),// MAPmap("k1", "v1", "k2", "v2"),// ROWrow("Bob", true),// NULLnullOf(DataTypes.INT()));Table fromExpressions = env.fromValues(rowExpr);// (3) with SQL expressionsTable fromSql =env.sqlQuery("VALUES ("// VARCHAR(200)+ "CAST('Alice' AS VARCHAR(200)), "// BYTES+ "x'010203', "// ARRAY+ "ARRAY[1, 2, 3], "// MAP+ "MAP['k1', 'v1', 'k2', 'v2', 'k3', 'v3'], "// ROW+ "('Bob', true), "// NULL+ "CAST(NULL AS INT), "// DATE+ "DATE '2024-12-23', "// TIME+ "TIME '13:45:59.000', "// TIMESTAMP+ "TIMESTAMP '2024-12-23 13:45:59.000', "// TIMESTAMP_LTZ+ "TO_TIMESTAMP_LTZ(1734957959000, 3)"+ ")");// Verify the derived data types and valuesSystem.out.println("Table from objects:");fromObjects.printSchema();fromObjects.execute().print();System.out.println("Table from Table API expressions:");fromExpressions.printSchema();fromExpressions.execute().print();System.out.println("Table from SQL expressions:");fromSql.printSchema();fromSql.execute().print();}
}flink confluent集成與部署代碼:
package com.flink.wc;import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableResult;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.config.TableConfigOptions;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
import org.apache.flink.util.CloseableIterator;import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;import static org.apache.flink.table.api.Expressions.*;/*** An example that illustrates how to embed a table program into a CI/CD pipeline for continuous* testing and rollout.** <p>Because we cannot rely on production data in this example, the program sets up some* Kafka-backed tables with data during the {@code setup} phase.** <p>Afterward, the program can operate in two modes: one for integration testing ({@code test}* phase) and one for deployment ({@code deploy} phase).** <p>A CI/CD workflow could execute the following:** <pre>* export EXAMPLE_JAR=./target/flink-table-api-java-examples-1.0.jar* export EXAMPLE_CLASS=io.confluent.flink.examples.table.Example_08_IntegrationAndDeployment* java -jar $EXAMPLE_JAR $EXAMPLE_CLASS setup* java -jar $EXAMPLE_JAR $EXAMPLE_CLASS test* java -jar $EXAMPLE_JAR $EXAMPLE_CLASS deploy* </pre>** <p>NOTE: This example requires write access to a Kafka cluster. Fill out the given variables* below with target catalog/database if this is fine for you.** <p>ALSO NOTE: The example submits an unbounded background statement. Make sure to stop the* statement in the Web UI afterward to clean up resources.** <p>The complete CI/CD workflow performs the following steps:** <ol>* <li>Create Kafka table 'ProductsMock' and 'VendorsPerBrand'.* <li>Fill Kafka table 'ProductsMock' with data from marketplace examples table 'products'.* <li>Test the given SQL on a subset of data in 'ProductsMock' with the help of dynamic options.* <li>Deploy an unbounded version of the tested SQL that write into 'VendorsPerBrand'.* </ol>*/
public class Example_08_IntegrationAndDeployment {// Fill this with an environment you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_CATALOG = "";// Fill this with a Kafka cluster you have write access tostatic final String TARGET_DATABASE = "";// Fill this with names of the Kafka Topics you want to createstatic final String SOURCE_TABLE = "ProductsMock";static final String TARGET_TABLE = "VendorsPerBrand";// The following SQL will be tested on a finite subset of data before// it gets deployed to production.// In production, it will run on unbounded input.// The '%s' parameterizes the SQL for testing.static final String SQL ="SELECT brand, COUNT(*) AS vendors FROM ProductsMock %s GROUP BY brand";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {if (args.length == 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("No mode specified. Possible values are 'setup', 'test', or 'deploy'.");}//1.創建設置EnvironmentSettings settings=EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();settings.getConfiguration().set(TableConfigOptions.LOCAL_TIME_ZONE,"UTC");//table.local-time-zone//2.創建table環境TableEnvironment env = TableEnvironment.create(settings);env.useCatalog(TARGET_CATALOG);env.useDatabase(TARGET_DATABASE);String mode = args[0];switch (mode) {case "setup":setupProgram(env);break;case "test":testProgram(env);break;case "deploy":deployProgram(env);break;default:throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown mode: " + mode);}}// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Setup Phase// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------private static void setupProgram(TableEnvironment env) throws Exception {System.out.println("Running setup...");System.out.println("Creating table..." + SOURCE_TABLE);// Create a mock table that has exactly the same schema as the example `products` table.// The LIKE clause is very convenient for this task which is why we use SQL here.// Since we use little data, a bucket of 1 is important to satisfy the `scan.bounded.mode`// during testing.env.executeSql(String.format("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `%s`\n"+ "DISTRIBUTED INTO 1 BUCKETS\n"+ "LIKE `examples`.`marketplace`.`products` (EXCLUDING OPTIONS)",SOURCE_TABLE));System.out.println("Start filling table...");// Let Flink copy generated data into the mock table. Note that the statement is unbounded// and submitted as a background statement by default.TableResult pipelineResult =env.from("`examples`.`marketplace`.`products`").select($("*")).insertInto(SOURCE_TABLE).execute();System.out.println("Waiting for at least 200 elements in table...");// We start a second Flink statement for monitoring how the copying progressesTableResult countResult = env.from(SOURCE_TABLE).select(lit(1).count()).as("c").execute();// This waits for the condition to be met:try (CloseableIterator<Row> iterator = countResult.collect()) {while (iterator.hasNext()) {Row row = iterator.next();long count = row.getFieldAs("c");if (count >= 200L) {System.out.println("200 elements reached. Stopping...");break;}}}// By using a closable iterator, the foreground statement will be stopped automatically when// the iterator is closed. But the background statement still needs a manual stop.ConfluentTools.stopStatement(pipelineResult);//countResult.getJobClient().get().cancel()System.out.println("Creating table..." + TARGET_TABLE);// Create a table for storing the results after deployment.env.executeSql(String.format("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `%s` \n"+ "(brand STRING, vendors BIGINT, PRIMARY KEY(brand) NOT ENFORCED)\n"+ "DISTRIBUTED INTO 1 BUCKETS",TARGET_TABLE));}// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Test Phase// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------private static void testProgram(TableEnvironment env) {System.out.println("Running test...");// Dynamic options allow influencing parts of a table scan. In this case, they define a// range (from start offset '0' to end offset '100') how to read from Kafka. Effectively,// they make the table bounded. If all tables are finite, the statement can terminate.// This allows us to run checks on the result.String dynamicOptions ="/*+ OPTIONS(\n"+ "'scan.startup.mode' = 'specific-offsets',\n"+ "'scan.startup.specific-offsets' = 'partition: 0, offset: 0',\n"+ "'scan.bounded.mode' = 'specific-offsets',\n"+ "'scan.bounded.specific-offsets' = 'partition: 0, offset: 100'\n"+ ") */";System.out.println("Requesting test data...");TableResult result = env.executeSql(String.format(SQL, dynamicOptions));Iterator<Row> rows = result.collect();List<Row> lists=new ArrayList<>();while (rows.hasNext()){Row row=rows.next();lists.add(row);}System.out.println("Test data:\n"+ lists.stream().map(Row::toString).collect(Collectors.joining("\n")));// Use the testing framework of your choice and add checks to verify the// correctness of the test databoolean testSuccessful =lists.stream().map(r -> r.<String>getFieldAs("brand")).anyMatch(brand -> brand.equals("Apple"));if (testSuccessful) {System.out.println("Success. Ready for deployment.");} else {throw new IllegalStateException("Test was not successful");}}// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Deploy Phase// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------private static void deployProgram(TableEnvironment env) {System.out.println("Running deploy...");// It is possible to give a better statement name for deployment but make sure that the name// is unique across environment and region.String statementName = "vendors-per-brand-" + UUID.randomUUID();env.getConfig().set("client.statement-name", statementName);// Execute the SQL without dynamic options.// The result is unbounded and piped into the target table.TableResult insertIntoResult =env.sqlQuery(String.format(SQL, "")).insertInto(TARGET_TABLE).execute();// The API might add suffixes to manual statement names such as '-sql' or '-api'.// For the final submitted name, use the provided tools.String finalName = ConfluentTools.getStatementName(insertIntoResult);System.out.println("Statement has been deployed as: " + finalName);}
}




)
適配CmBacktrace錯誤追蹤)






)



和移動網絡(蜂窩數據)的環境下,使用安卓平板,通過USB數據線(而不是Wi-Fi)來控制電腦(版本2))

