React框架
1.前端展示解釋
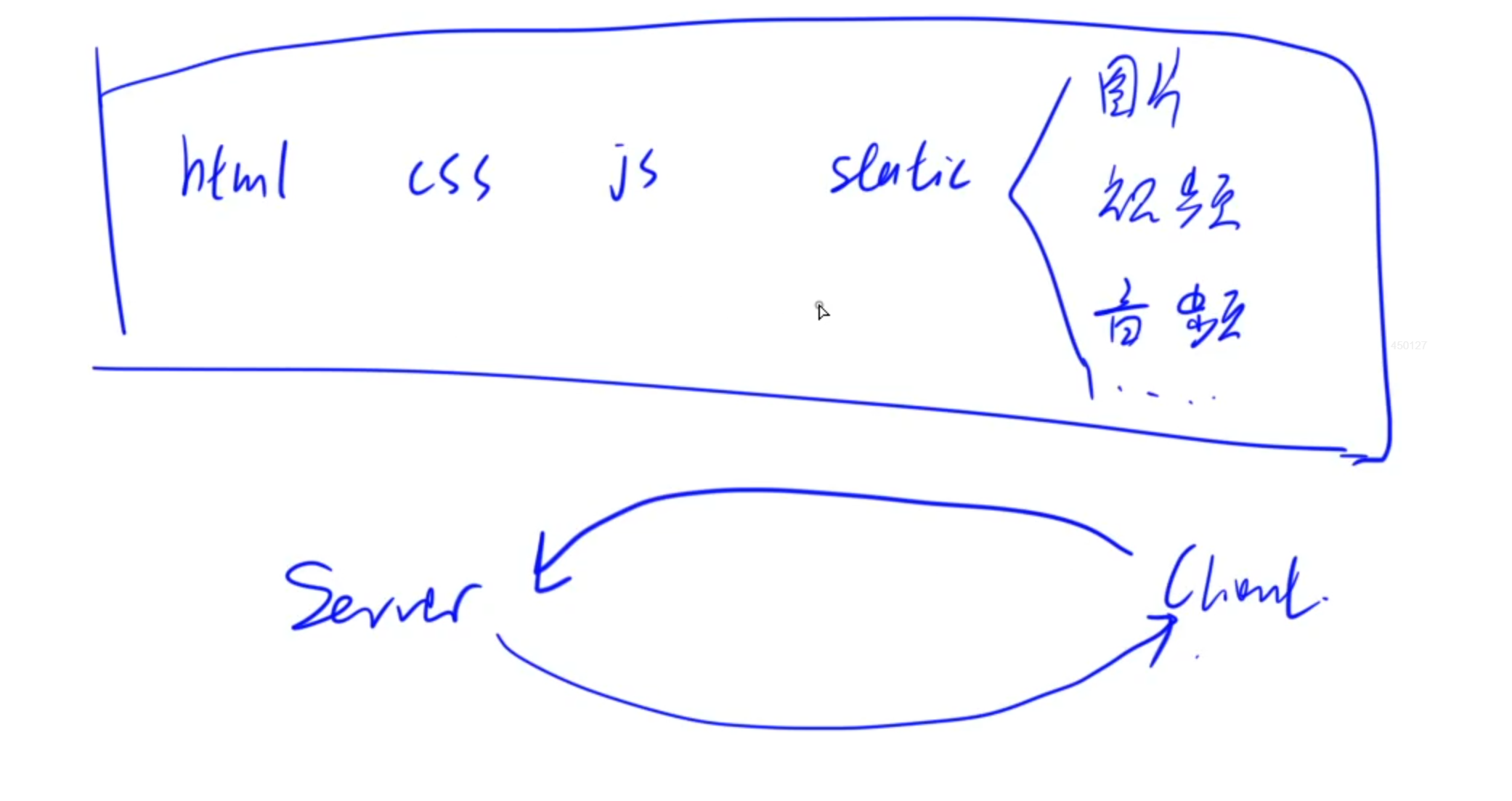
當客戶端訪問服務器時,會從服務器中下載很多靜態文件到本地,比如css、js等前端渲染文件
下載完成之后瀏覽器會將這些文件組合形成前端頁面渲染出來。
2.React概述
React是一個專注于構建用戶界面的JavaScript庫,它采用聲明式編程范式,使得代碼更加易于閱讀和理解。React的核心思想是組件化,即將用戶界面劃分為獨立的、可復用的組件。每個組件都有自己的狀態和生命周期,方便開發者進行維護和復用。
React特性1:虛擬DOM樹
DOM樹:是集中保存一個網頁中所有內容的樹形結構
而React框架會在內存中維護一個虛擬的DOM樹,它是實際DOM的輕量級內存表示。當網頁源代碼中網頁內容狀態或者屬性發生變化時,React會重新計算虛擬DOM樹,并通過比較新舊虛擬DOM樹的差異(Diffing),找出需要更新的部分。最后,將這些變化批量應用到實際DOM上,從而減少不必要的重繪和回流,提高性能。
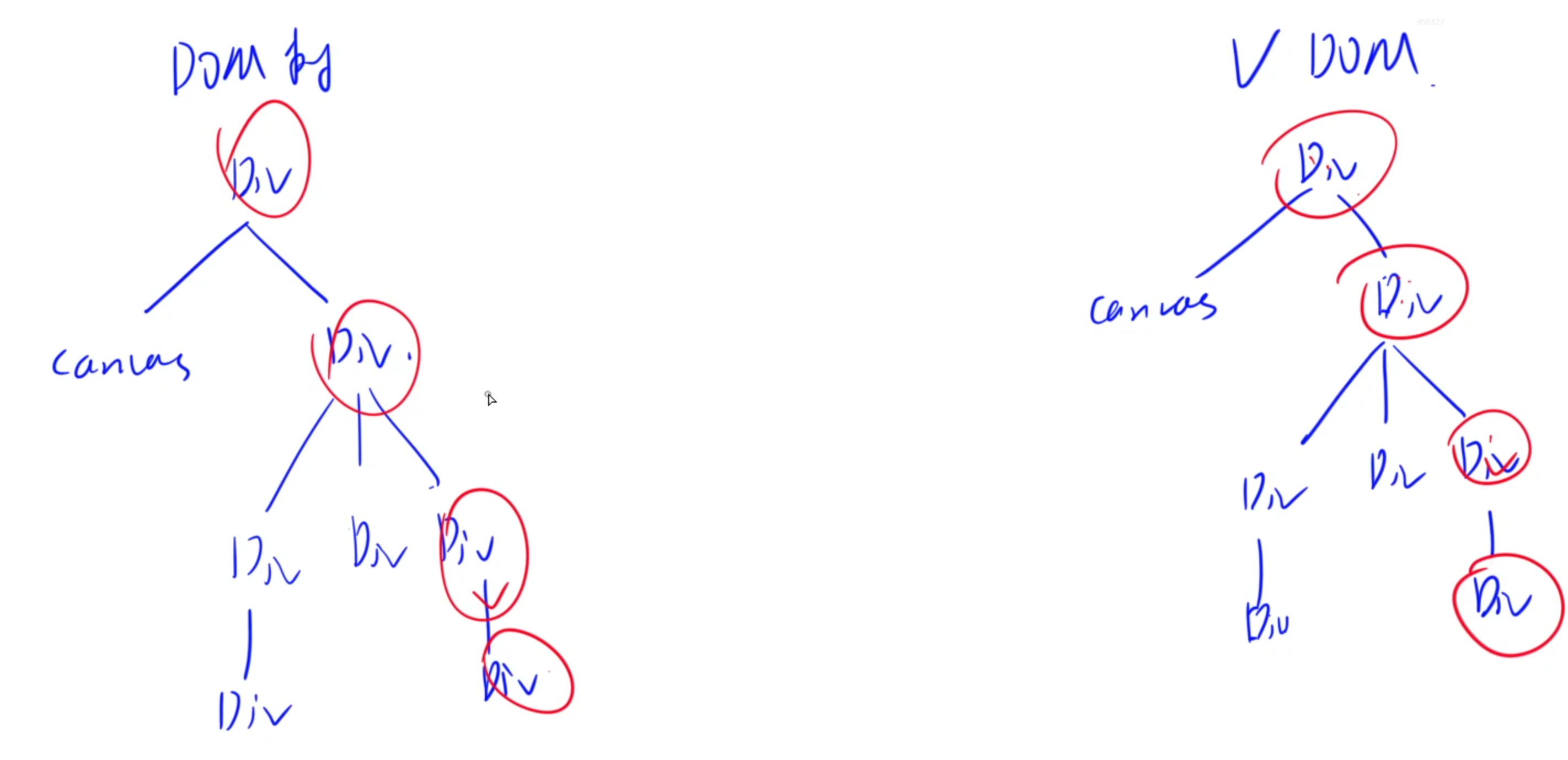
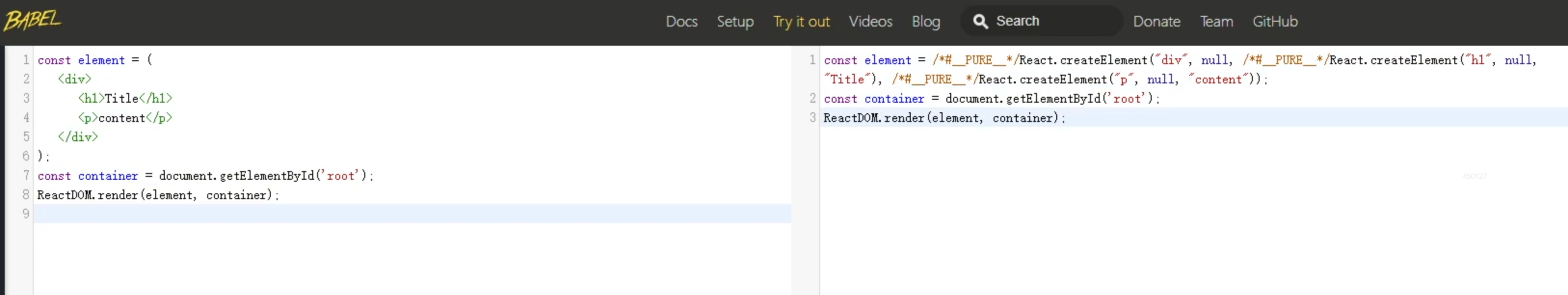
React特性2:JSX語法擴展
React引入了JSX(JavaScript XML)語法擴展,允許在JavaScript中編寫類似HTML的結構。這種語法使得開發者可以更加直觀地描述用戶界面,同時保持代碼的靈活性和可維護性。
JSX編譯成JS,編寫JSX的語法更加簡單靈活。
編譯通過React提供的Babel編譯器將JSX代碼編譯成JS代碼。
3.環境配置
1.按照終端Git Bash
安裝地址:Git Bash官網(windows)
2.安裝Nodejs
安裝地址:Nodejs
3.安裝create-react-app
打開Git Bash,執行:
npm i -g create-react-app
4.安裝VSCode插件
Simple React Snippets:提供一些react常用命令的自動補全Prettier - Code formatter:代碼高亮
5.創建React App
當需要使用React開發一個App時
在目標目錄下打開Git Bash,執行:
create-react-app react-app #可以替換為其他名稱cd react-app
npm start #啟動應用
4.React初始項目結構
1.node_modules
負責維護JS庫:各種JS相關的輪子
2.public
index.html:主頁面的渲染
以及一些靜態文件

3.src
主界面以及其他組件內容的css和js文件
5.ES6語法
1.使用bind()函數綁定this取值
在JavaScript中,函數里的this指向的是執行時的調用者,而不是定義時所在的對象。
例如:
const animal = {name: "dog",talk: function() {console.log(this);}
}animal.talk();const talk = animal.talk;
talk();
運行結果是:
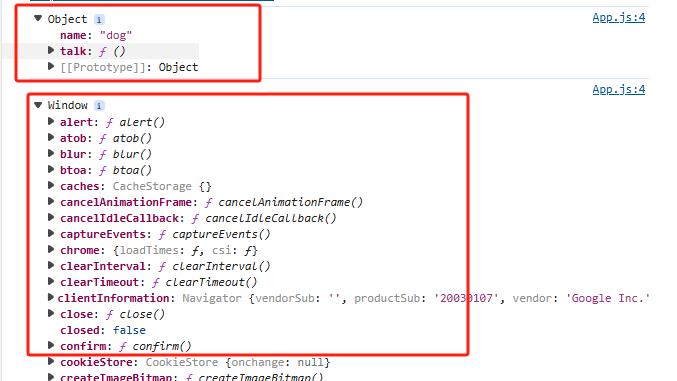
animal.talk()它會根據調用的對象來給talk()里面的this賦值
而將animal.talk()賦值給當前文件的成員,再執行該成員調用talk()方法時,由于當前文件是由window調用的,那么talk()里面的this就變成了Window。
而為了避免這種情況,使用bind()函數,可以綁定this的取值,例如:
const talk = animal.talk.bind(animal);
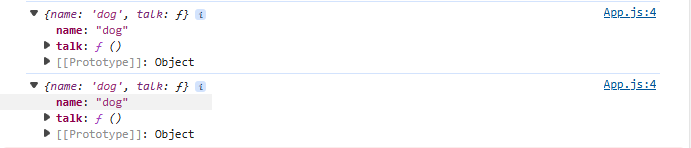
就可以將該對象綁定到重新賦值的成員上,不會導致錯誤的取值。
2.箭頭函數的簡寫
const f = (x) => {return x * x;
}
const f1 = x => x * x;console.log(f(3), f1(3));
運行結果:
9 9
3.通過箭頭函數綁定this的取值
const animal = {talk: function() {setTimeout(function() {console.log(this);}, 1000);}
};animal.talk();
在上述代碼中雖然talk()函數是由animal調用的,但是里面的function函數其實還是Window執行的,所以里面的函數取的this是當前Window。

為避免這種情況,一般的寫法是:
const animal = {talk: function() {let outer = this;setTimeout(function() {console.log(outer);}, 1000);}
};animal.talk();
讓里層的outer指向外層的animal對象。
而使用箭頭函數可以直接規避這種情況:
const animal = {talk: function() {setTimeout(() => {console.log(this);}, 1000);}
};animal.talk();
運行結果:

4.對象的解構
例如:
const animal = {name: "dog",age: 12,height: 100,
};const {name : new_name, age} = animal; //new_name是name的別名console.log(new_name, age);
打印結果:

5.數組和對象的展開
let a = [1, 2, 3];
let b = [4, 5, 6];
let c = [...a]; //c是a的復制let d = [...c, ...b]; //將c和b展開放到d中console.log(d);const A = {name: "dog"};
const B = {age: 12};
const C = {...A, ...B, heigth: 100}; //將對象元素展開并放入C中console.log(C);
打印結果:

6.Named 與 Default exports
- Named Export:可以export多個,import的時候需要加大括號,名稱需要匹配
- Default Export: 最多export一個,import的時候不需要加大括號,可以直接定義別名
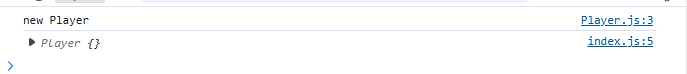
export default class Player {constructor() {console.log("new Player");}
}
import MyPlayer from './Player' //默認值不能加大括號let player = new MyPlayer();console.log(player);
打印結果:
6.Component
示例項目:實現兩個按鈕控制一個box左右移動
1)創建box-app項目:
crete-react-app box-app
cd box-app
npm start //啟動box-app
2)安裝bootstrap庫:
npm i bootstrap
在項目中導入bootstrap庫:
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstarp.css'
3)創建Component
一般將組件全部維護在一個component文件夾下
先創建component文件夾,然后創建box.jsx文件。
4)創建按鈕
當子節點數量大于1個時,需要用<div>或<React.Fragment>將其括起來。
同時整個部分用()括起來return
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { } render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></React.Fragment>);}
}export default Box;
5)內嵌表達式
JSX中使用{}嵌入表達式:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 1,};render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div>{this.state.x}</div><div>{this.toString()}</div><button>left</button><button>right</button></React.Fragment>);}toString() {return `x: ${this.state.x}`;}
}export default Box;
頁面展示:

6) 設置屬性
- 通過設置
className來對應屬性
通過bootstrap找到已經設計好的屬性類進行渲染。
bootstrap官網搜索需要的示例樣式:
- CSS屬性:不同于普通css,React中要求:中間使用
-連接的屬性需要改成駝峰命名,比如:background-color:backgrounColor,其他屬性類似。
設置屬性:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 1,};styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.styles}>{this.toString()}</div><button className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button></React.Fragment>);}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}export default Box;
簡寫方式:將屬性以數組的形式傳入style中
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 1,};render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={{width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}}>{this.toString()}</div><button className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button></React.Fragment>);}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:

7)數據驅動改變Style
通過改變一個變量的值從而改變組件的style樣式:
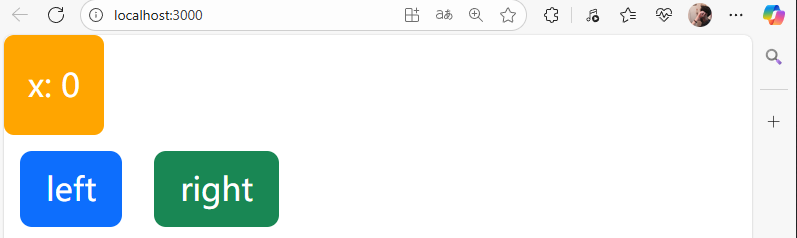
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,};render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;頁面展示: 當改變x的值時,<div>對應的樣式會發生改變。
8)渲染列表
- 使用map函數
- 每個元素需要具有唯一的
key屬性,用來幫助React快速找到被修改的DOM元素。
關于key的面試題:
面試題:react、vue中的key有什么作用?(key的內部原理)
虛擬DOM中key的作用:
key是虛擬DOM對象的標識,當數據發生變化時,Vue會根據【新數據】生成【新的虛擬DOM】
隨后Vue進行【新虛擬DOM】與【舊虛擬DOM】的差異比較,比較規則如下:
在舊虛擬DOM中找到與新虛擬DOM相同的key:
若虛擬DOM元素內容沒變, 直接使用之前的真實DOM元素!
若虛擬DOM元素內容變了, 則生成新的真實DOM元素,隨后替換掉頁面中之前的真實DOM元素。
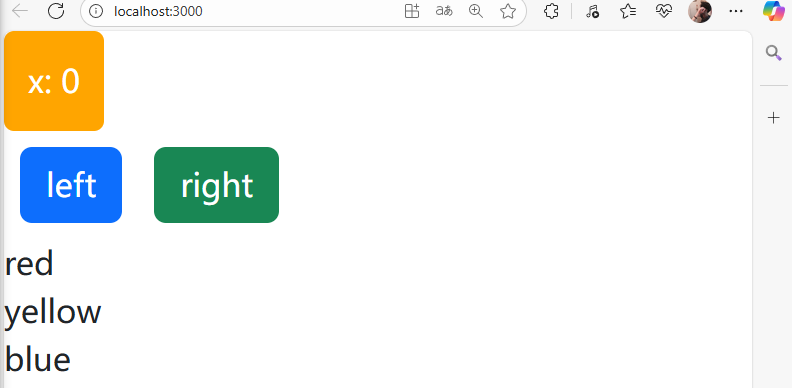
列表渲染示例: 使用map函數將列表中的元素內容渲染依次渲染出來。
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:
9)綁定事件
在添加綁定事件時需要注意:
這里同樣會發生this的值變成其他不明的指代,這就導致我們無法知道React在實現的時候是在什么東西調用的click函數,但是我們希望它在調用click時指向的是當前的結構體(box class).
于是跟之前補充的ES6語法一致,要么通過箭頭函數(推薦),因為箭頭函數不會重新給this賦值,也就是說在調用箭頭函數實現的click函數時,它指向的this就是原本我們賦給它的this。
另外一種方法就是利用bind函數綁定this。
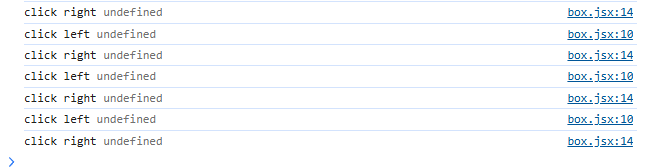
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft() {console.log("click left", this);}handleClickRight() { console.log("click right", this);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
這里打印this值會發現當前的this值是未定義的,也就是說確實不是當前結構體(box class)
兩種方式綁定this值不發生改變:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = () => {console.log("click left", this);}handleClickRight() { console.log("click right", this);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight.bind(this)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
打印展示:

10)修改state
- 需要使用
this.setState()函數 - 每次調用
this.setState()函數后,會重新調用this.render()函數,用來修改虛擬機DOM樹。React只會修改不同步的實際DOM樹節點。
當我們直接修改state里面的某個變量值時,雖然該變量確實發生改變,但是react無法將該變量的改變同步渲染,只有通過調用this.setState()函數來修改,react才會重新調用this.render()函數來修改虛擬DOM樹,從而修改不同步的實際DOM樹節點。
** 不調用this.setState()函數時:**
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = () => {this.state.x--;console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = () => { this.state.x++;console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
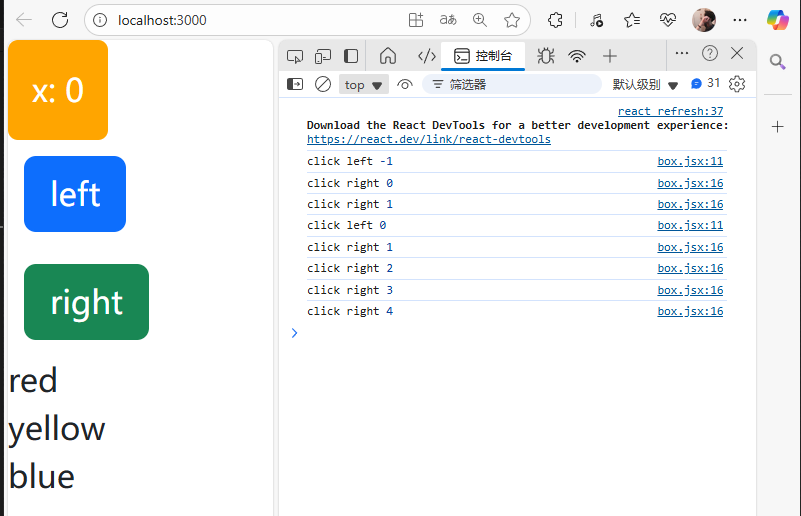
通過調用this.setState()函數來修改state:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = () => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - 1,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = () => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + 1,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue"}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
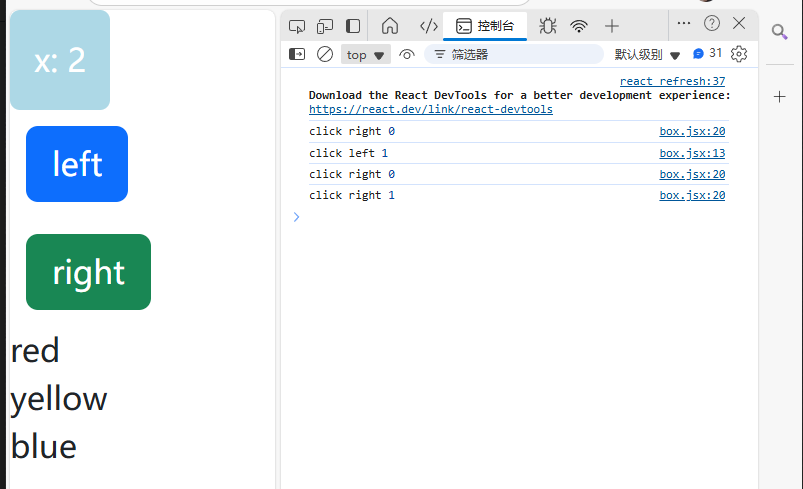
將marginLeft設置為當前this.state.x,這樣每次點擊左右就會改變this.state.x的值,通過this.setState()就會每次改變都會重新調用this.render()函數,而此時marginLeft的值與this.state.x相關,就能實現點擊right按鈕時,box塊往右移動(marginLeft變大),點擊left按鈕時,box塊往左移動(marginLeft變小)。
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = () => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - 1,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = () => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + 1,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;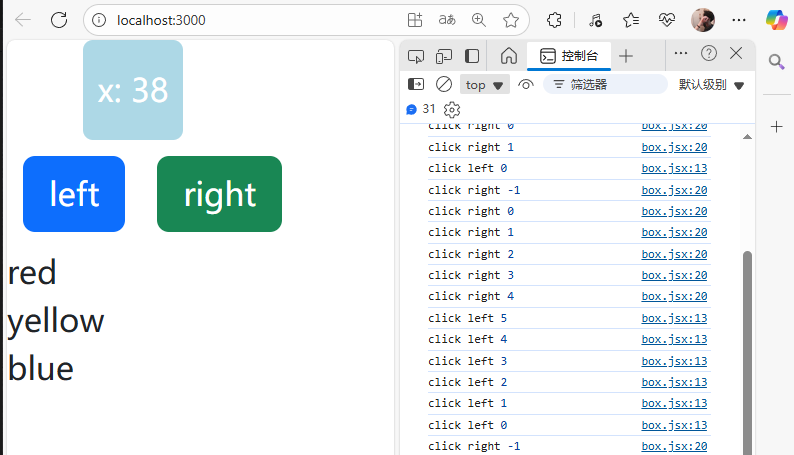
11)給事件函數添加參數
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = () => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + 1,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}handleClickLeftTmp = () => {return this.handleClickLeft(10);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeftTmp} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={this.handleClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面結果展示:
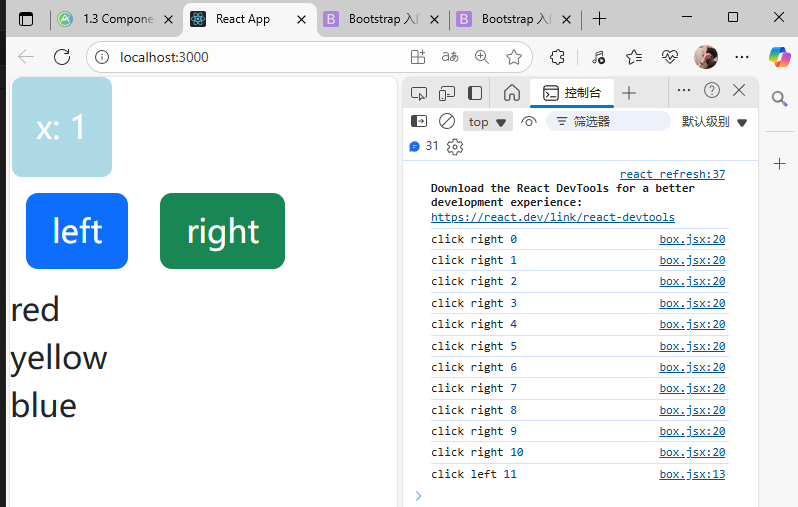
匿名函數寫法:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: 0,colors: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'],};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = (step) => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + step,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (/* <div><h1>hello world</h1><button>left</button><button>right</button></div> */<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={() => this.handleClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button>{this.state.colors.map(color => (<div key={color}>{color}</div>))}</React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
7.React組件化實現表格
實現表格的刪除和復制功能:將對應的元素刪除或者復制。
主要知識點:
- 1.使用map函數遍歷數組中的元素進行表格內容的填充
- 2.點擊事件的綁定
- 3.使用箭頭函數進行參數的傳遞
- 4.使用
this.setState()函數更新
注意事項:每個組件需要唯一的key進行標識,這里使用單獨設定的key,其他場景可以另外指代
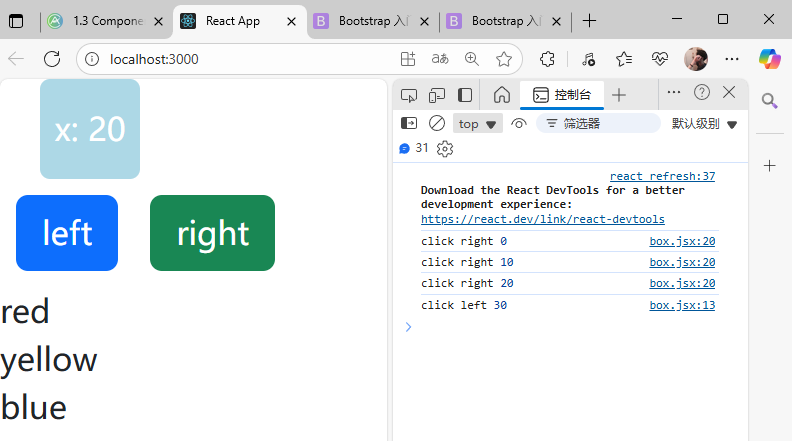
import React, { Component } from 'react';class Solution extends Component {state = { solutions: [{key: 51, number: 2000, title: "高質量文章1", views: 649, subscribes: 105293},{key: 52, number: 2001, title: "高質量文章2", views: 6491, subscribes: 105093},{key: 53, number: 2002, title: "高質量文章3", views: 6492, subscribes: 10593},{key: 54, number: 2003, title: "高質量文章4", views: 6493, subscribes: 105935},{key: 55, number: 2004, title: "高質量文章5", views: 6494, subscribes: 105593},{key: 56, number: 2005, title: "高質量文章6", views: 6495, subscribes: 105963},{key: 57, number: 2006, title: "高質量文章7", views: 6496, subscribes: 105793},{key: 58, number: 2007, title: "高質量文章8", views: 6497, subscribes: 105893},{key: 59, number: 2008, title: "高質量文章9", views: 6498, subscribes: 105993},{key: 60, number: 2009, title: "高質量文章10", views: 6499, subscribes: 105493},{key: 61, number: 2010, title: "高質量文章11", views: 6490, subscribes: 1059133},{key: 62, number: 2011, title: "高質量文章12", views: 6459, subscribes: 1059453},{key: 63, number: 2012, title: "高質量文章13", views: 64945, subscribes: 10594853}]} handleDelete = (s) => {console.log("delete");//將跟s不一樣的元素都保留下來,過濾掉sconst solutions = this.state.solutions.filter(solution => solution !== s);this.setState({solutions: solutions, //將當前的key更新為value: key:value});}handleIncrease = (s) => {const solutions = [...this.state.solutions, {key: s.key + 1, number: s.number, title: s.title, views: 0, subscribes: 0}]this.setState({solutions: solutions,})}render() { if (this.state.solutions.length == 0) {return <p>沒有文章啦~</p>}return (<table className="table"><thead><tr><th>文章序號</th><th>標題</th><th>閱讀</th><th>訂閱</th><th>操作</th></tr></thead><tbody>{this.state.solutions.map(solution => (<tr key={solution.key}><td>{solution.number}</td><td>{solution.title}</td><td>{solution.views}</td><td>{solution.subscribes}</td><td><button onClick={() => this.handleDelete(solution)} className="btn btn-danger">刪除</button><button onClick={() => this.handleIncrease(solution)} className="btn btn-success">復制</button></td></tr>))}</tbody></table>);}
}export default Solution;
頁面展示:
8.組合Components
1)創建Boxes組件
在Boxes組件中包含一系列Box組件: 將Box導入到Boxes中,然后在Boxes中創建多個Box組件
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 0},{id: 3, x: 0},{id: 4, x: 0},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;

2)從上往下傳遞數據
- 通過
this.props屬性可以從上到下傳遞數據
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}x={box.x}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: this.props.x,};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = (step) => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + step,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div><button onClick={() => this.handleClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:
在主組件中傳入參數,使得子組件的參數發生對應變化:

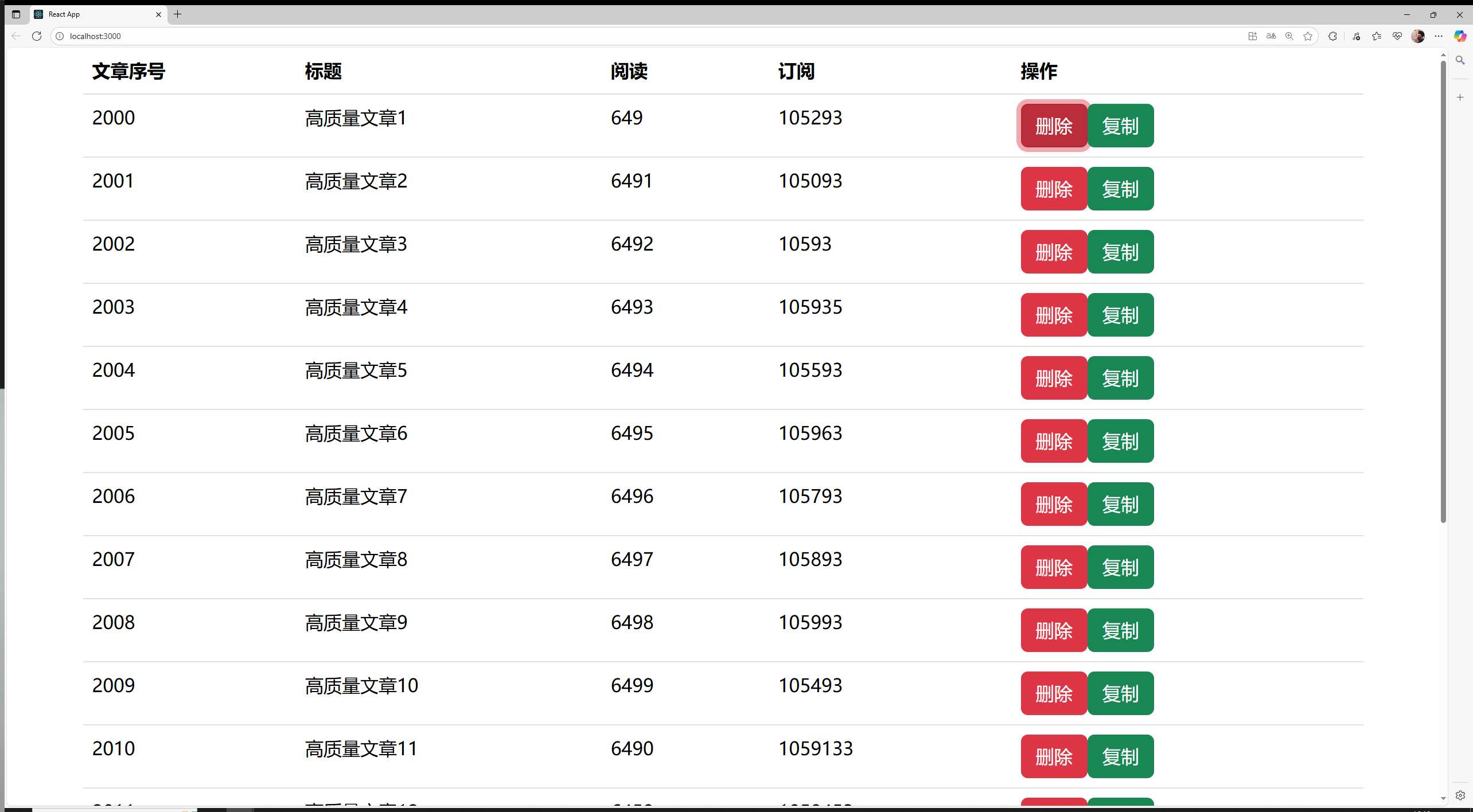
3)傳遞子節點
通過this.props.children屬性傳遞子節點
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}x={box.x}><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: this.props.x,};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = (step) => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + step,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { console.log(this.props);return (<React.Fragment>{this.props.children[0]}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div>{this.props.children[1]}<button onClick={() => this.handleClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:
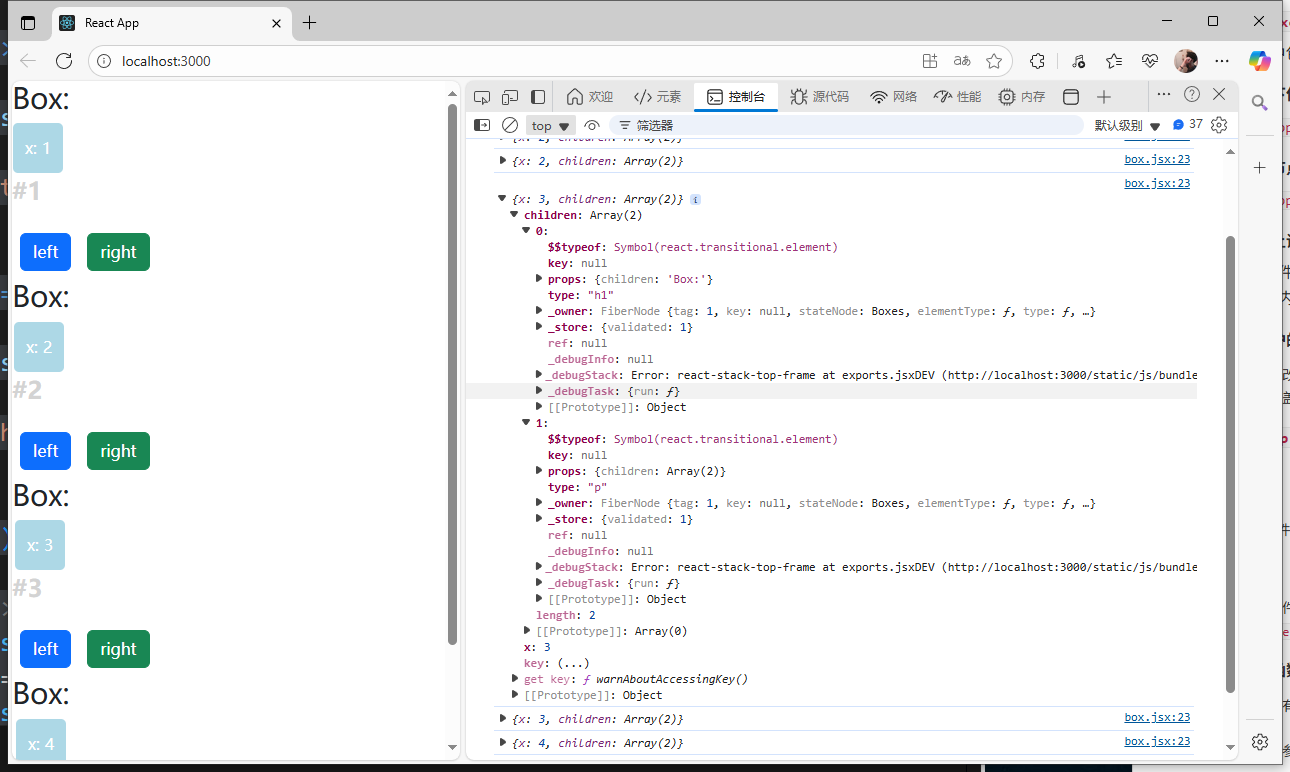
4)從下往上調用函數
- 注意:每個組件的
this.state只能在組件內部修改,不能在其他組件內修改
相當于私有組件,只能由自己調用和修改
子組件調用父組件的方法:通過this.props屬性將父組件的函數指代傳遞給子組件,當子組件獲取到父組件的函數指代后,可以通過該指代以及傳遞下來的參數去調用父組件的函數。
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} handleDelet = (boxId) => {console.log("handle delete", boxId);const boxes = this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: boxes});}render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}x={box.x}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件id={box.id}onDelete={this.handleDelet} //子組件在獲取到onDelete時,實際是獲取到了父組件的handleDelete方法的指代><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: this.props.x,};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = (step) => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + step,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.props.children[0]}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div>{this.props.children[1]}<button onClick={() => this.handleClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button><button //拿著父組件傳過來的參數去調用父組件傳的函數onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:
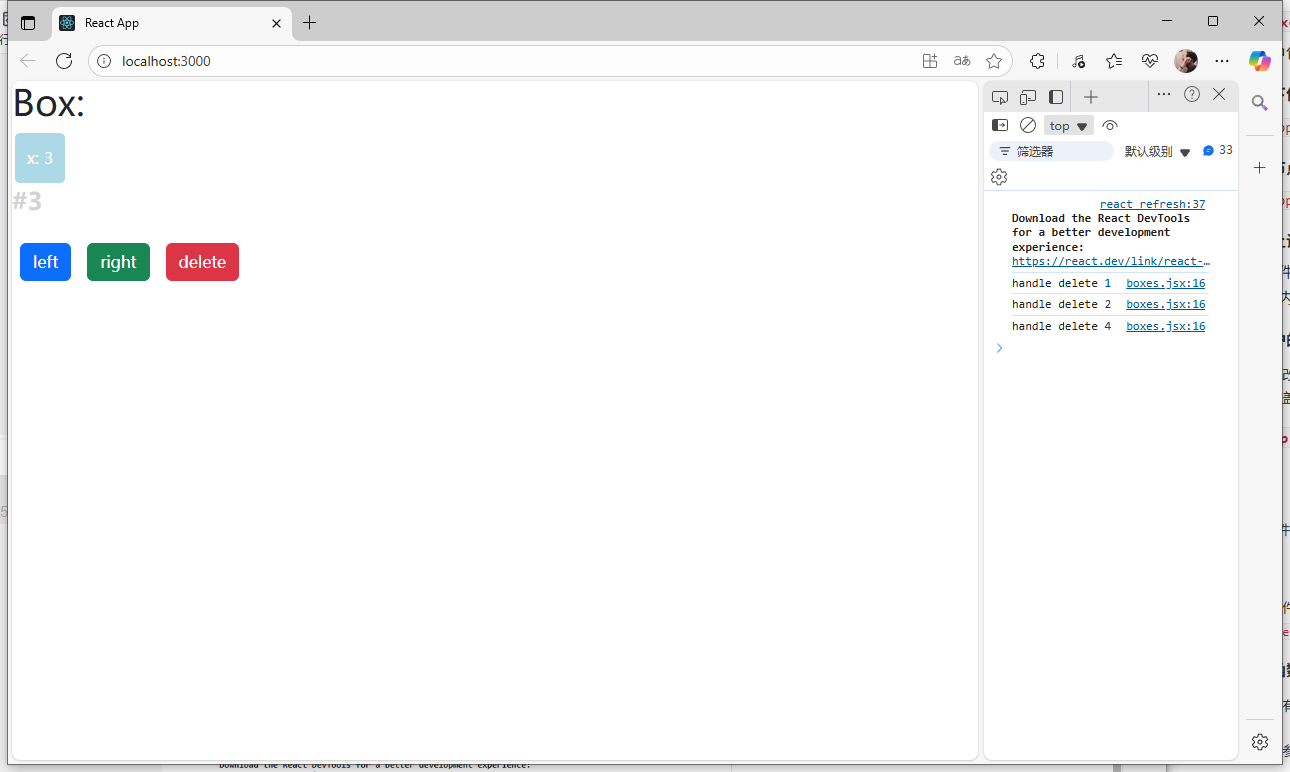
5)每個維護的數據僅能保存在一個this.state中
- 不要直接修改
this.state的值,因為setState函數可能會將修改覆蓋掉
例如:
1.在boxes.jsx中添加一個handleReset函數,通過reset按鈕觸發,來將四個子組件的值都變回初始值0,id則保持不變。
2.這時會發現,當點擊reset按鈕后,打印的boxes中的x值都變成0了,但是頁面的每個子組件的x渲染還是原來的值。
3.因為通過handleReset函數中的this.setState更新的是this.state.boxes里面的x,在實際渲染中,是通過box.jsx中的this.state.x來獲取,而該過程只會在初始化的時候執行一次,通過this.props.x傳過來的值獲取,后面每次修改的時候,該過程不會重復執行,所以不管怎么修改this.props.x的值,box.jsx里的x都不會發生變化了,因此實際的x渲染不會發生改變。
相當于在兩個地方存了同一個數據,在一邊修改可能無法影響兩邊的數據
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} handleReset = () => {const boxes = this.state.boxes.map(b => {return {id: b.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes});console.log(this.state);}handleDelet = (boxId) => {console.log("handle delete", boxId);const boxes = this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: boxes});}render() { return (<React.Fragment><button style={{marginBottom: "15px"}} className='btn btn-info'onClick={this.handleReset}>Reset</button>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}x={box.x}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件id={box.id}onDelete={this.handleDelet} //子組件在獲取到onDelete時,實際是獲取到了父組件的handleDelete方法的指代><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {state = { x: this.props.x,};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step,});console.log("click left", this.state.x);}handleClickRight = (step) => { this.setState({x: this.state.x + step,});console.log("click right", this.state.x);}render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.props.children[0]}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div>{this.props.children[1]}<button onClick={() => this.handleClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button><button //拿著父組件傳過來的參數去調用父組件傳的函數onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.state.x,}if (this.state.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.state.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
頁面展示:
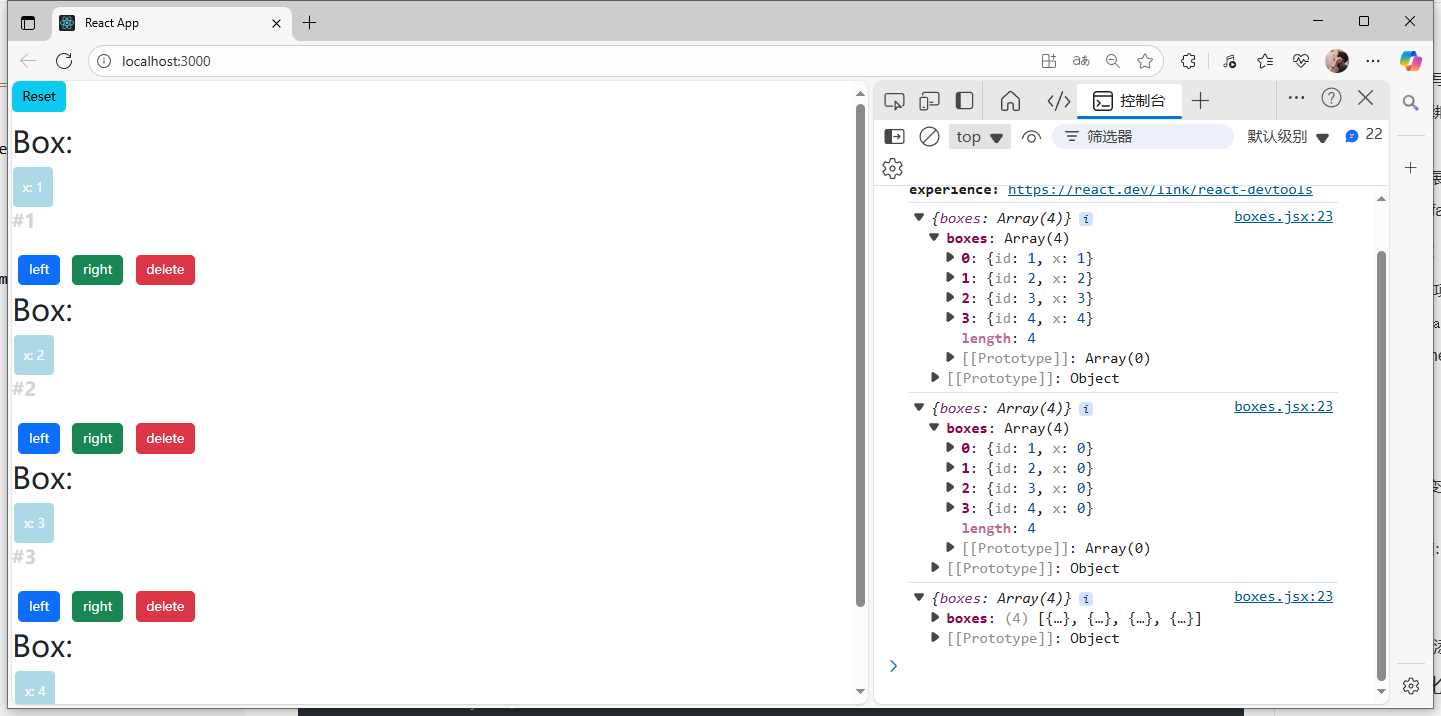
怎么使得子組件的x渲染能在外面進行修改呢?
1.將內部的state.x刪除
2.把x放到外部組件的this.state.boxes里面: 也就是只存一份x數據,然后兩邊都從這一份數據中讀取,就不會產生覆蓋的問題
如:
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} handleReset = () => {const boxes = this.state.boxes.map(b => {return {id: b.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes});console.log(this.state);}handleDelet = (boxId) => {console.log("handle delete", boxId);const boxes = this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: boxes});}handleClickLeft = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x --;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click left", this.boxes[k].x);}handleClickRight = (box) => { const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x ++;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click right", this.boxes[k].x);}render() { return (<React.Fragment><button style={{marginBottom: "15px"}} className='btn btn-info'onClick={this.handleReset}>Reset</button>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件id={box.id}box={box}onDelete={this.handleDelet} //子組件在獲取到onDelete時,實際是獲取到了父組件的handleDelete方法的指代onClickLeft={() => this.handleClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => this.handleClickRight(box)}><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx:
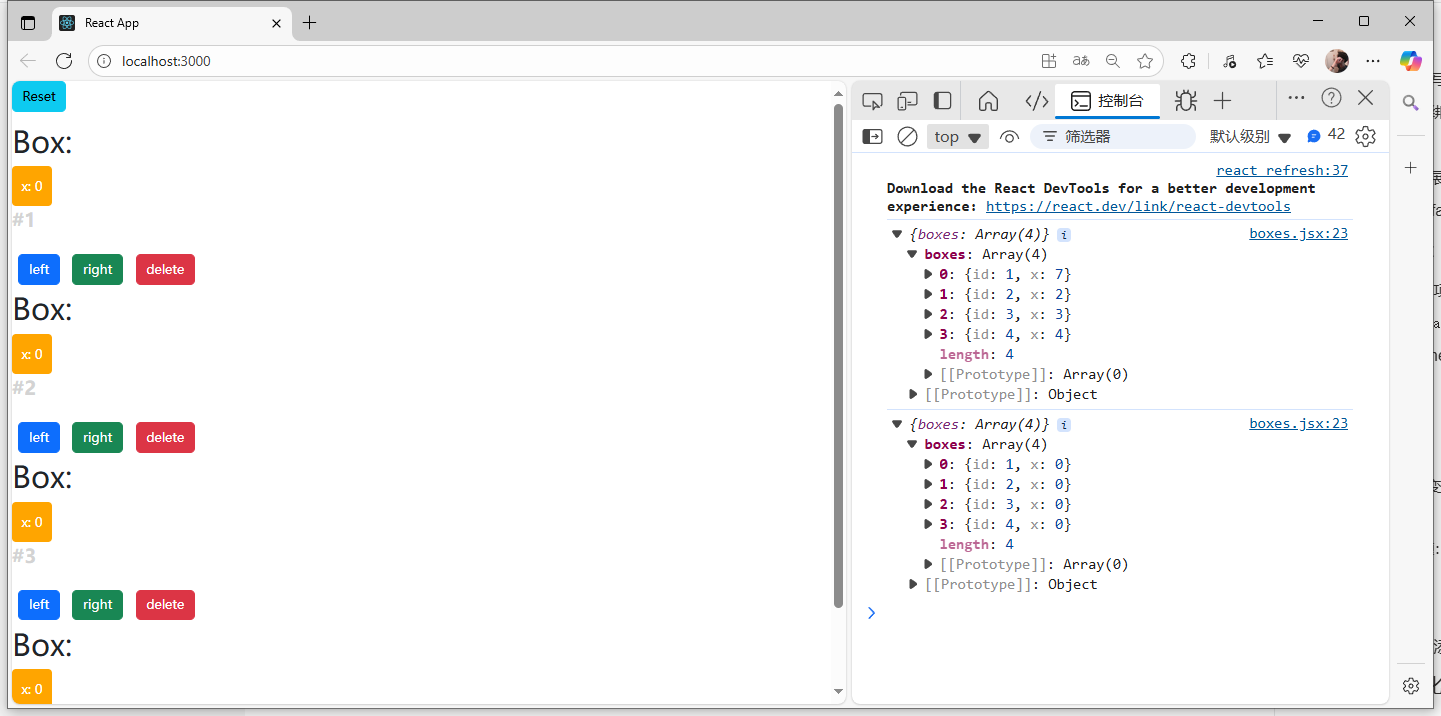
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.props.children[0]}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div>{this.props.children[1]}<button onClick={() => this.props.onClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.props.onClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button><button //拿著父組件傳過來的參數去調用父組件傳的函數onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.props.box.x,}if (this.props.box.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.props.box.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;頁面展示:
6)創建App組件
包含:
- 導航欄組件
Boxes組件
文件創建快捷縮寫(自動補全):
imrc + Tab = import React, { Component } from ‘react’;
cc + Tab =
class extends Component {state = { } render() { return ();}
}export default ;
注意:
- 要將多個組件共用的數據存放到最近公共祖先的
this.state中 - 比如:我們需要在另外一個組件中維護當前x不為0的組件個數,那我們則需要將當前組件(
Boxes)和另外一個組件(Navbar)放到新建的公共祖先組件(App)中
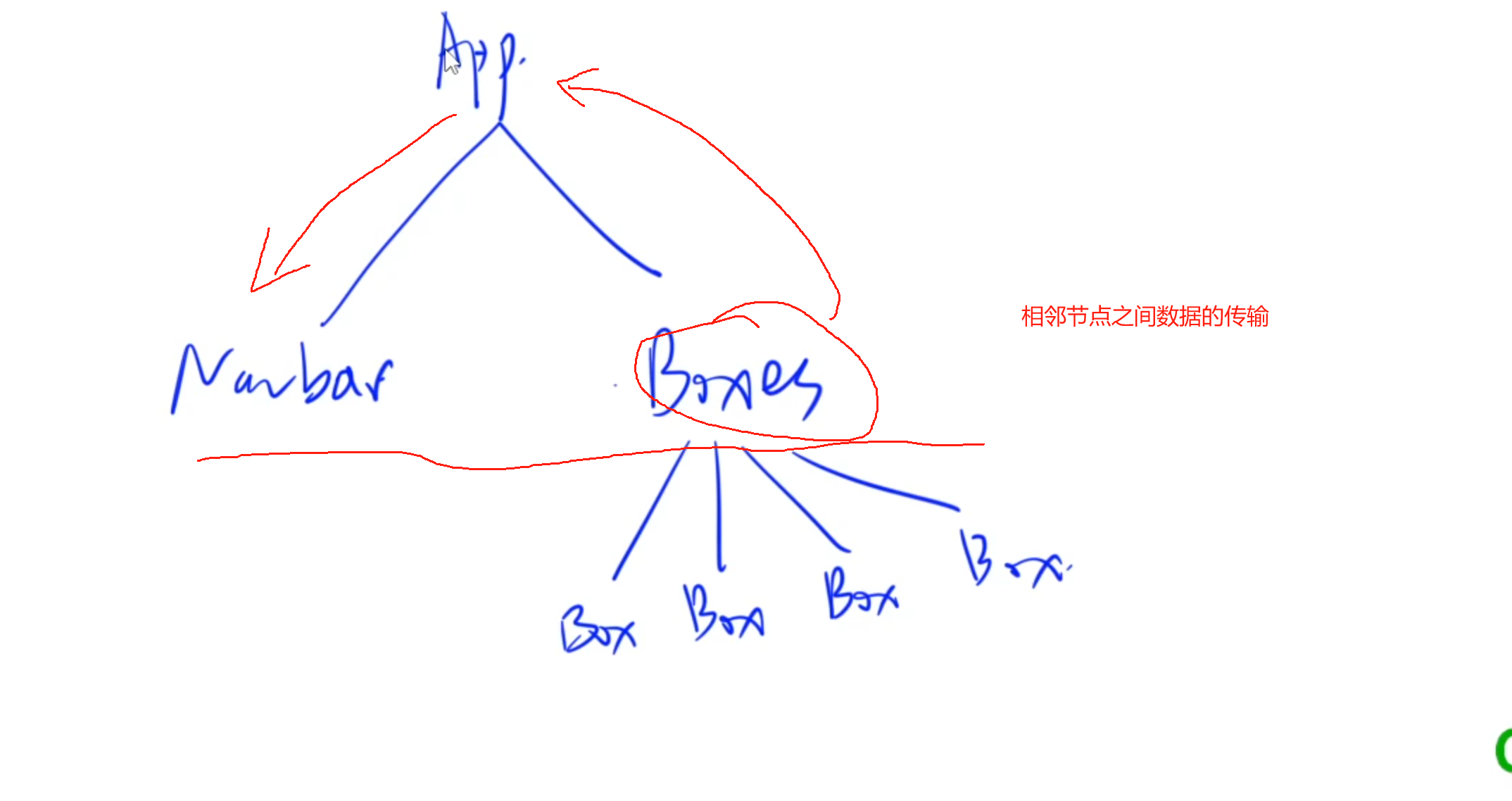
- 這里就需要將維護數據的state全部往上移,移動到公共祖先中維護。然后兩邊的節點通過公共祖先使用
props傳輸獲取數據。
app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Boxes from './boxes';class App extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} handleReset = () => {const boxes = this.state.boxes.map(b => {return {id: b.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes});console.log(this.state);}handleDelet = (boxId) => {console.log("handle delete", boxId);const boxes = this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: boxes});}handleClickLeft = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x --;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click left", this.boxes[k].x);}handleClickRight = (box) => { const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x ++;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click right", this.boxes[k].x);}render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar boxesCount={this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.x !== 0).length}/><div className='container'><Boxes boxes={this.state.boxes}onReset={this.handleReset}onClickLeft={this.handleClickLeft}onClickRight={this.handleClickRight}onDelete={this.handleDelet}/></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
navbar.jsx:
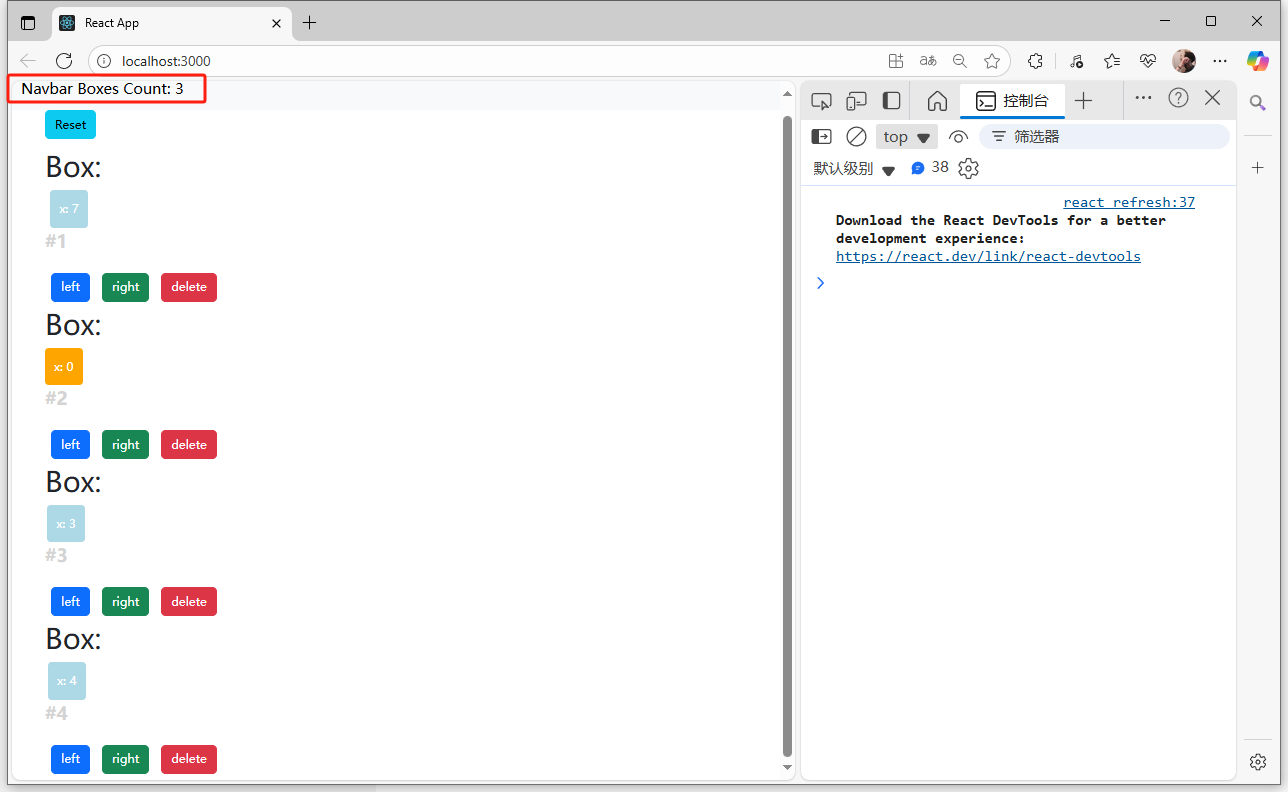
import React, { Component } from 'react';class NavBar extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<nav className='navbar navbar-light bg-light'><div className='container-fluid'><a className='navbar-brand' href = "/">Navbar <span>Boxes Count: {this.props.boxesCount} </span></a></div></nav>);}
}export default NavBar;
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {render() { return (<React.Fragment><button style={{marginBottom: "15px"}} className='btn btn-info'onClick={this.props.onReset}>Reset</button>{this.props.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件box={box}onDelete={this.props.onDelete}onClickLeft={() => this.props.onClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => this.props.onClickRight(box)}><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
box.jsx文件則保持不變
頁面展示:
7)無狀態函數組件
- 當組件中沒有用到
this.state時,可以簡寫為無狀態的函數組件 - 使用
sfc+Tab鍵補全:
const = () => {return ( );
}export default ;
- 函數的傳入參數為
props對象
比如上一小節中的boxes.jsx中沒有state屬性,那么可以修改為無狀態的函數組件:相當于只有render函數
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';const Boxes = (props) => {return (<React.Fragment><button style={{marginBottom: "15px"}} className='btn btn-info'onClick={props.onReset}>Reset</button>{props.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件box={box}onDelete={props.onDelete}onClickLeft={() => props.onClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => props.onClickRight(box)}><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);
}export default Boxes;
同樣的,navbar.jsx中也是沒有state屬性的,也可以轉換成無狀態函數組件:
navbar.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';const NavBar = (props) => {return (<nav className='navbar navbar-light bg-light'><div className='container-fluid'><a className='navbar-brand' href = "/">Navbar <span>Boxes Count: {props.boxesCount} </span></a></div></nav>);
}export default NavBar;
- 補充回憶:
解構也可以在參數里面解構(直接將props解構成參數列表):
boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import Box from './box';const Boxes = ({onReset, onDelete, onClickLeft, onClickRight, boxes}) => {return (<React.Fragment><button style={{marginBottom: "15px"}} className='btn btn-info'onClick={onReset}>Reset</button>{boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id}//將函數以及函數需要用到的參數傳遞給子組件box={box}onDelete={onDelete}onClickLeft={() => onClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => onClickRight(box)}><h1>Box:</h1><p>#{box.id}</p></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);
}export default Boxes;
8)組件的生命周期
Mount周期(掛載:第一次加載執行的函數),執行順序:
constructor() -> render() -> componentDisMount()
示例:
app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Boxes from './boxes';class App extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 1},{id: 2, x: 2},{id: 3, x: 3},{id: 4, x: 4},]} componentDidMount() {console.log("App - Mounted");}constructor() {super();console.log("App - Constructor");}handleReset = () => {const boxes = this.state.boxes.map(b => {return {id: b.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes});console.log(this.state);}handleDelet = (boxId) => {console.log("handle delete", boxId);const boxes = this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: boxes});}handleClickLeft = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x --;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click left", this.boxes[k].x);}handleClickRight = (box) => { const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box); //在當前boxes數組中找到當前元素的下標boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x ++;this.setState({boxes});//console.log("click right", this.boxes[k].x);}render() { console.log("App - rendered");return (<React.Fragment><NavBar boxesCount={this.state.boxes.filter(b => b.x !== 0).length}/><div className='container'><Boxes boxes={this.state.boxes}onReset={this.handleReset}onClickLeft={this.handleClickLeft}onClickRight={this.handleClickRight}onDelete={this.handleDelet}/></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
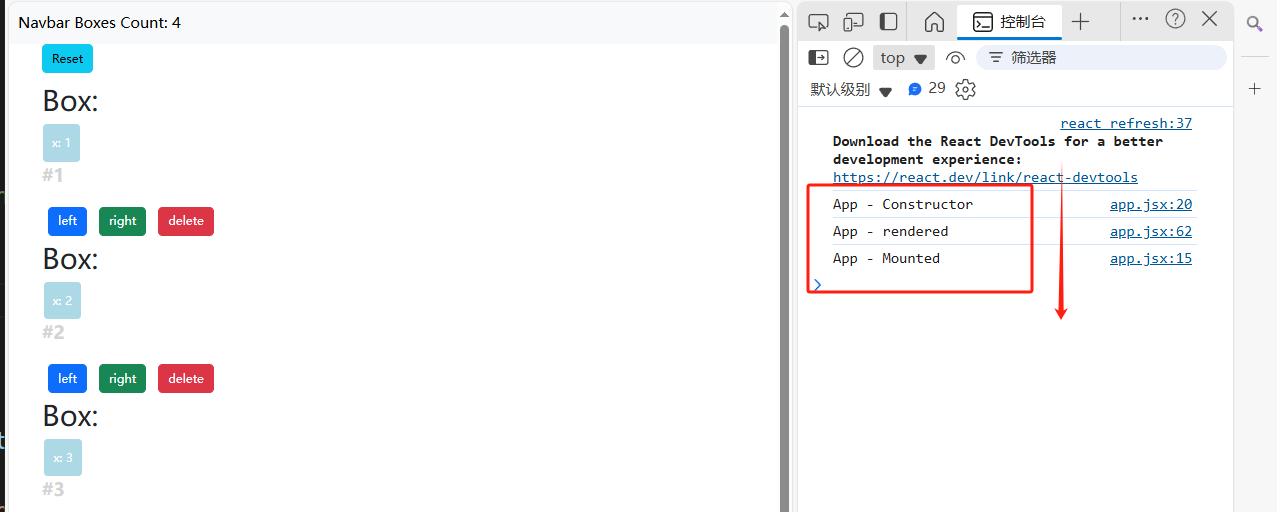
Update周期(修改),執行順序:
render() -> componentDidUpdate()
示例:
分別在box.jsx,boxes.jsx,navbar.jsx,app.jsx中的加入componentDidUpdate()函數,并在render()和更新函數中加入打印語句,觀察不同層級之間的執行順序:
結果如下:
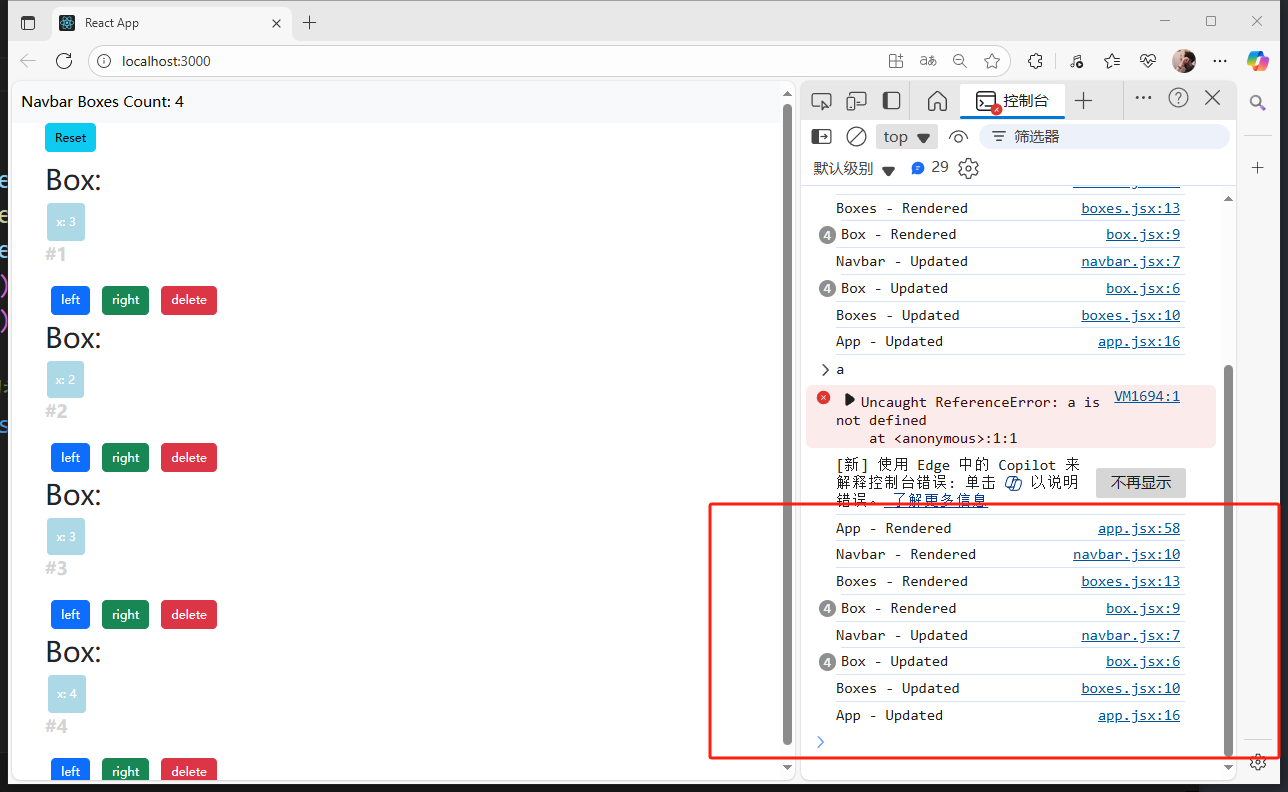
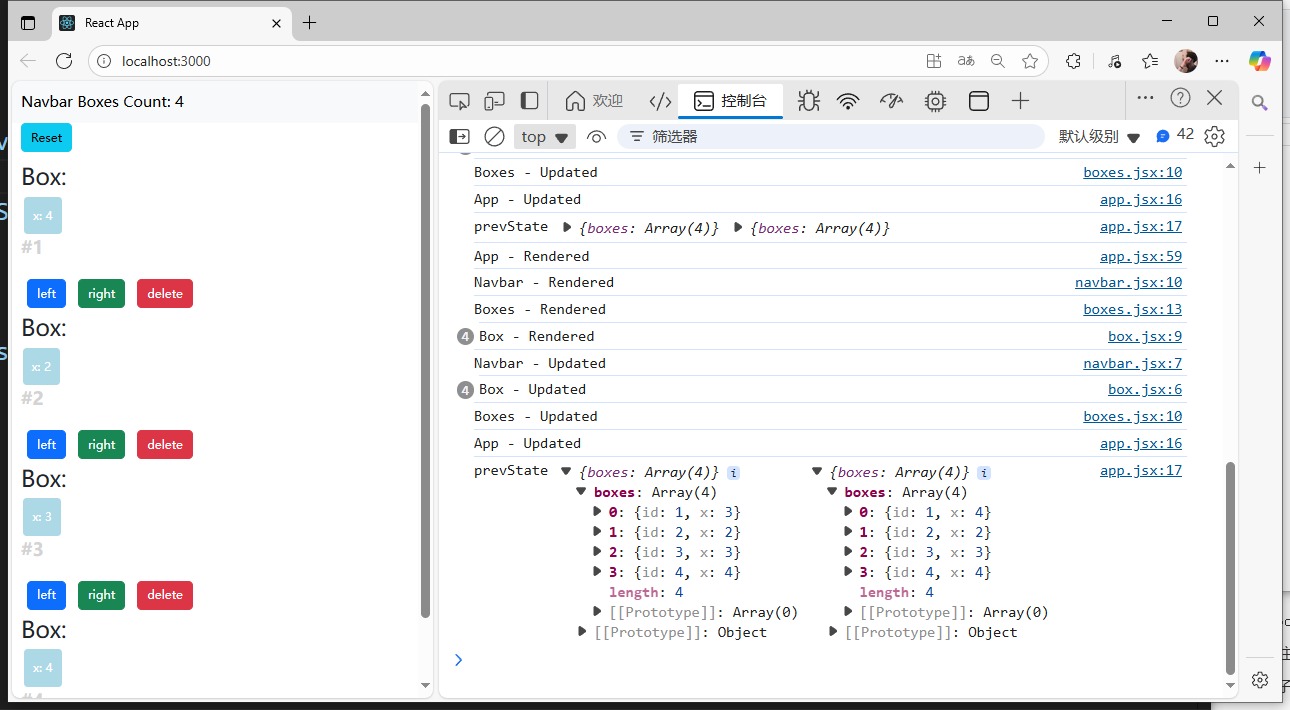
componentDidUpdate()中還有prevProps,prevState兩個參數:
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {console.log("App - Updated");console.log("prevState", prevState, this.state);}
可以通過這兩個參數,得到上一個狀態的state值。
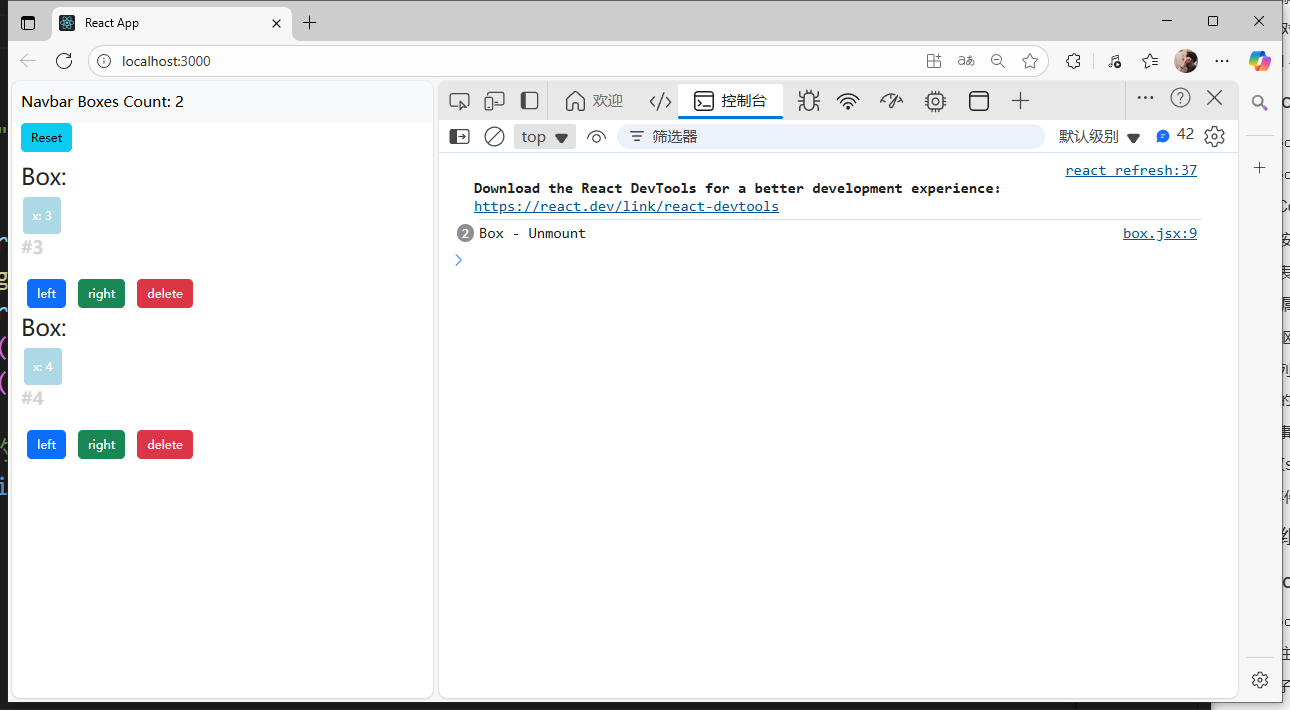
Unmount周期(刪除),執行順序:
componentWillUnmount()
每次刪除當前元素時會執行一次:
box.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react'class Box extends Component {// componentDidUpdate() {// console.log("Box - Updated");// }componentWillUnmount() {console.log("Box - Unmount");}render() { //console.log("Box - Rendered");return (<React.Fragment>{this.props.children[0]}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.toString()}</div>{this.props.children[1]}<button onClick={() => this.props.onClickLeft(10)} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>left</button><button onClick={() => this.props.onClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>right</button><button //拿著父組件傳過來的參數去調用父組件傳的函數onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.box.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: "50px",height: "50px",color: "white",textAlign: "center",lineHeight: "50px",borderRadius: "5px",backgroundColor: "lightblue",marginLeft: this.props.box.x,}if (this.props.box.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = "orange";}return styles;}toString() {const x = this.props.box.x;return `x: ${x}`;}
}
export default Box;
9.路由
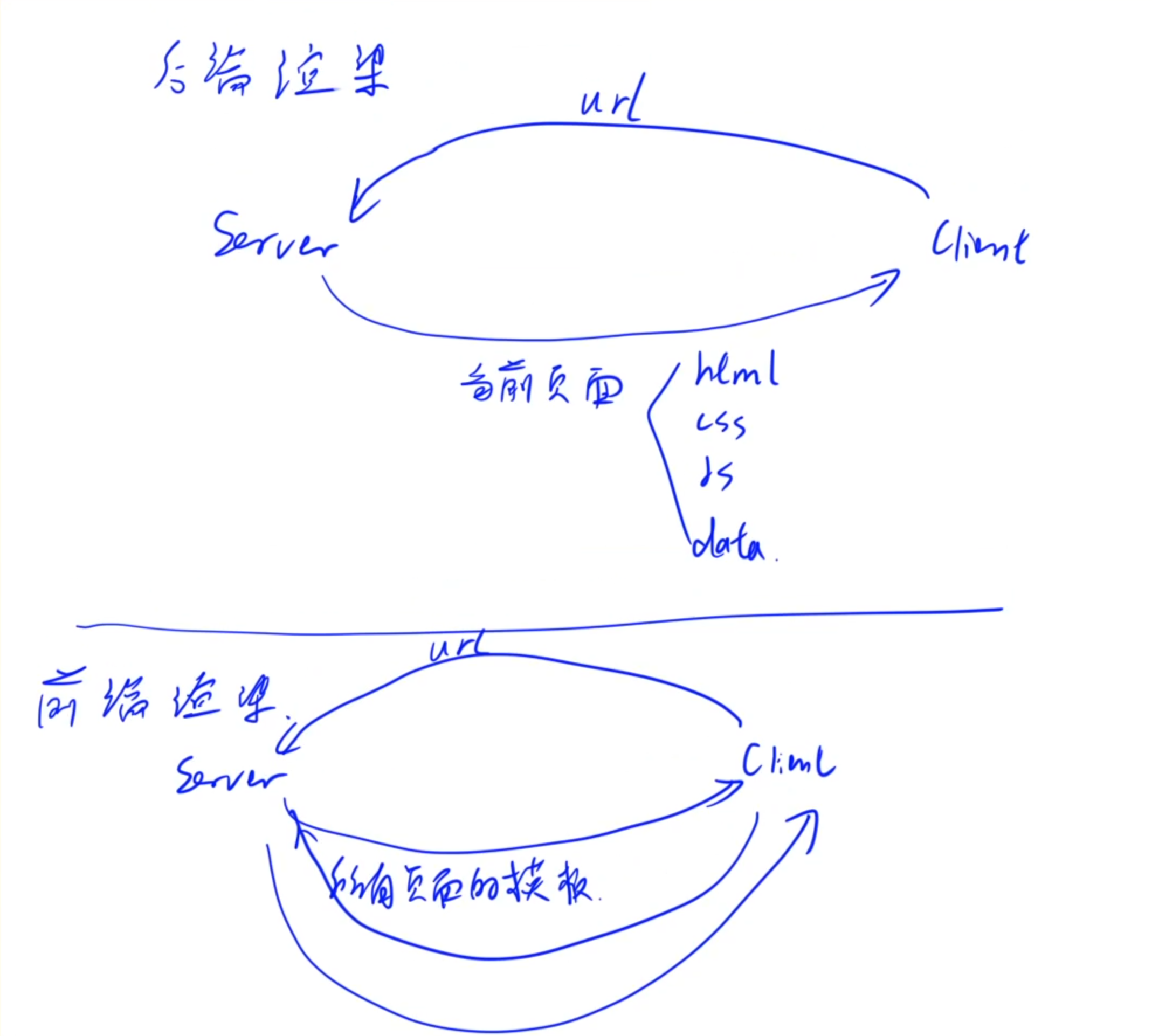
1.Web分類
- 靜態頁面:頁面里的數據是寫死的
- 動態頁面:頁面里的數據是動態填充的
- 后端渲染:數據在后端填充
- 前端渲染:數據在前端填充
2.安裝環境
- VsCode安裝插件:
Auto Import - ES6, TS, JSX, TSX - 安裝
Route插件:npm i react-router-dom
3.Route組件介紹
BrowserRouter:所有需要路由的組件,都需要包裹在BrowserRouter組件內Link:跳轉到某個鏈接,to屬性表示跳轉到的鏈接Routes:類似于C++中的switch,匹配第一個路徑Route:路由,path屬性表示路徑,element屬性表示路由到的內容
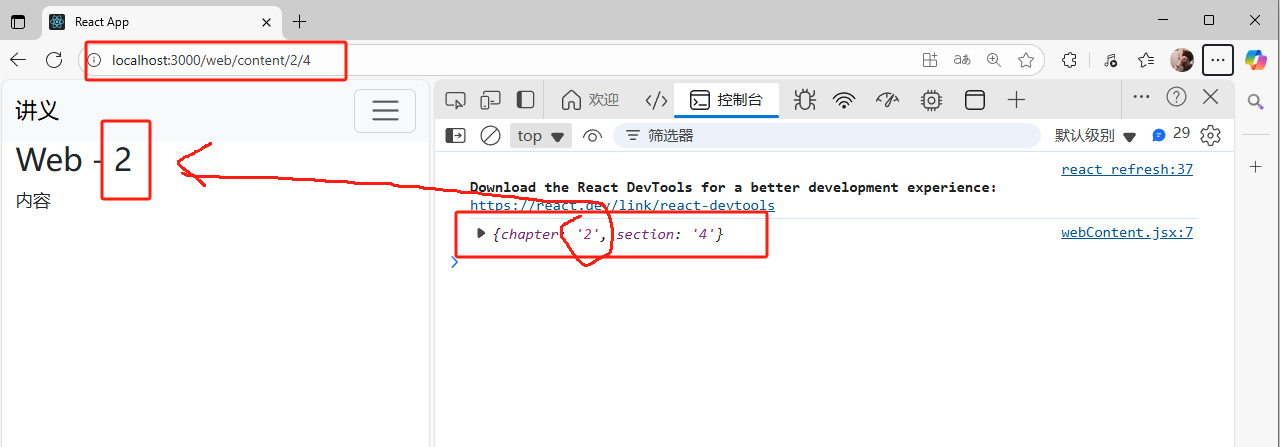
4.URL中傳遞參數
- 把URL中的某些部分變成變量讀取到組件中。
解析URL:
<Route path="/web/content/:chapter/:section/" element={<WebContent/>} />
類組件獲取參數:
web.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';class Web extends Component {state = { webs: [{id: 1, title: "HTML"},{id: 2, title: "CSS"},{id: 3, title: "JavaScript"},{id: 4, title: "拳皇"},{id: 5, title: "React"},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment><h1>Web</h1><div>{this.state.webs.map(web => (<div key={web.id}><Link to={`/web/content/${web.id}`}>{web.id + "." + web.title}</Link></div>))}</div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default Web;
webContent.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom';class WebContent extends Component {state = { } render() { console.log(this.props.params);return (<React.Fragment><h1>Web - {this.props.params.chapter}</h1><div>內容</div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default (props) => (<WebContent {...props}params={useParams()}/>
);app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Home from './home';
import Linux from './linux';
import Django from './django';
import Web from './web';
import WebContent from './webContent';
import NotFound from './notFound';
import { Route, Routes } from 'react-router-dom';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar /><div className='container'><Routes><Route path="/" element={<Home/>} /><Route path="/linux" element={<Linux/> } /><Route path="/django" element={<Django/> } /><Route path="/web" element={<Web/>} /><Route path="/web/content/:chapter/:section/" element={<WebContent/>} /></Routes></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
參數打印:
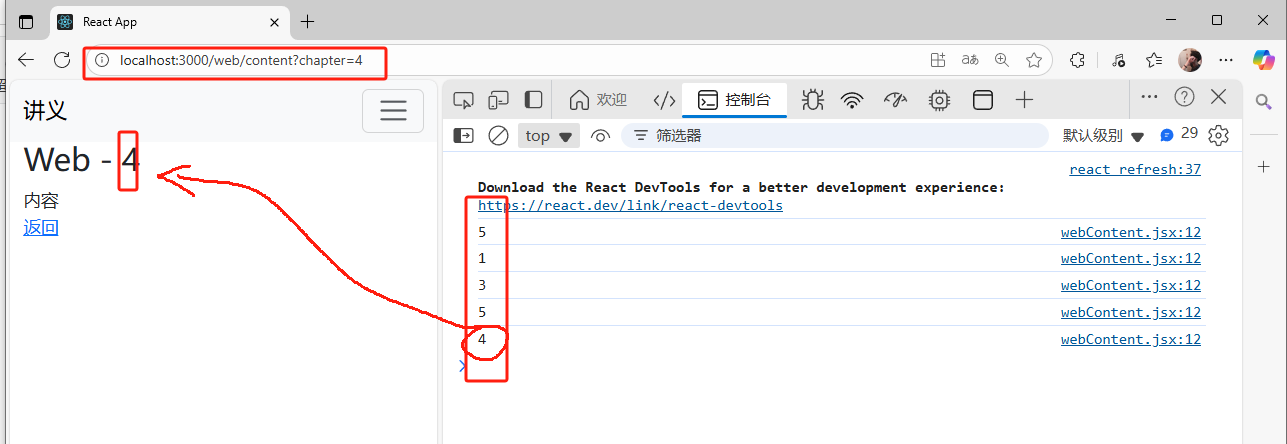
5.Search Param 傳遞參數
web.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';class Web extends Component {state = { webs: [{id: 1, title: "HTML"},{id: 2, title: "CSS"},{id: 3, title: "JavaScript"},{id: 4, title: "拳皇"},{id: 5, title: "React"},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment><h1>Web</h1><div>{this.state.webs.map(web => (<div key={web.id}><Link to={`/web/content?chapter=${web.id}`}>{web.id + "." + web.title}</Link></div>))}</div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default Web;
webContent.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { useSearchParams } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';class WebContent extends Component {state = { searchParams: this.props.params[0],setSearchParams: this.props.params[1],};render() { console.log(this.state.searchParams.get('chapter'));return (<React.Fragment><h1>Web - {this.state.searchParams.get('chapter')}</h1><div>內容</div><Link to="/web">返回</Link></React.Fragment>);}
}export default (props) => (<WebContent {...props}params={useSearchParams()}/>
);app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Home from './home';
import Linux from './linux';
import Django from './django';
import Web from './web';
import WebContent from './webContent';
import NotFound from './notFound';
import { Route, Routes } from 'react-router-dom';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar /><div className='container'><Routes><Route path="/" element={<Home/>} /><Route path="/linux" element={<Linux/> } /><Route path="/django" element={<Django/> } /><Route path="/web" element={<Web/>} /><Route path="/web/content" element={<WebContent/>} /></Routes></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
參數提取:
6.重定向
- 使用
Navigate組件可以重定向,Navigate是react實現好的組件。
<Route path="*" element={ <Navigate replace to="/404" /> } />
app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Home from './home';
import Linux from './linux';
import Django from './django';
import Web from './web';
import WebContent from './webContent';
import NotFound from './notFound';
import { Route, Routes, Navigate} from 'react-router-dom';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar /><div className='container'><Routes><Route path="/" element={<Home/>} /><Route path="/linux" element={<Linux/> } /><Route path="/django" element={<Django/> } /><Route path="/web" element={<Web/>} /><Route path="/web/content" element={<WebContent/>} /><Route path="/404" element={<NotFound/>} /><Route path="*" element={<Navigate replace to="/404"/>} /></Routes></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
notFound:
import React, { Component } from 'react';class NotFound extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<h1>NotFound</h1>);}
}export default NotFound;
7.嵌套路由
linux.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Outlet } from 'react-router-dom';class Linux extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><h1>Linux</h1><hr /> <Outlet /></React.Fragment>);}
}export default Linux;
app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Home from './home';
import Linux from './linux';
import Django from './django';
import Web from './web';
import WebContent from './webContent';
import NotFound from './notFound';
import { Route, Routes, Navigate} from 'react-router-dom';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar /><div className='container'><Routes><Route path="/" element={<Home/>} /><Route path="/linux" element={<Linux/> }><Route path="homework" element={<h4>homework</h4>}></Route><Route path="terminal" element={<h4>terminal</h4>}></Route><Route path="*" element={<h4>其他</h4>}></Route></Route><Route path="/django" element={<Django/> } /><Route path="/web" element={<Web/>} /><Route path="/web/content" element={<WebContent/>} /><Route path="/404" element={<NotFound/>} /><Route path="*" element={<Navigate replace to="/404"/>} /></Routes></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
頁面展示:
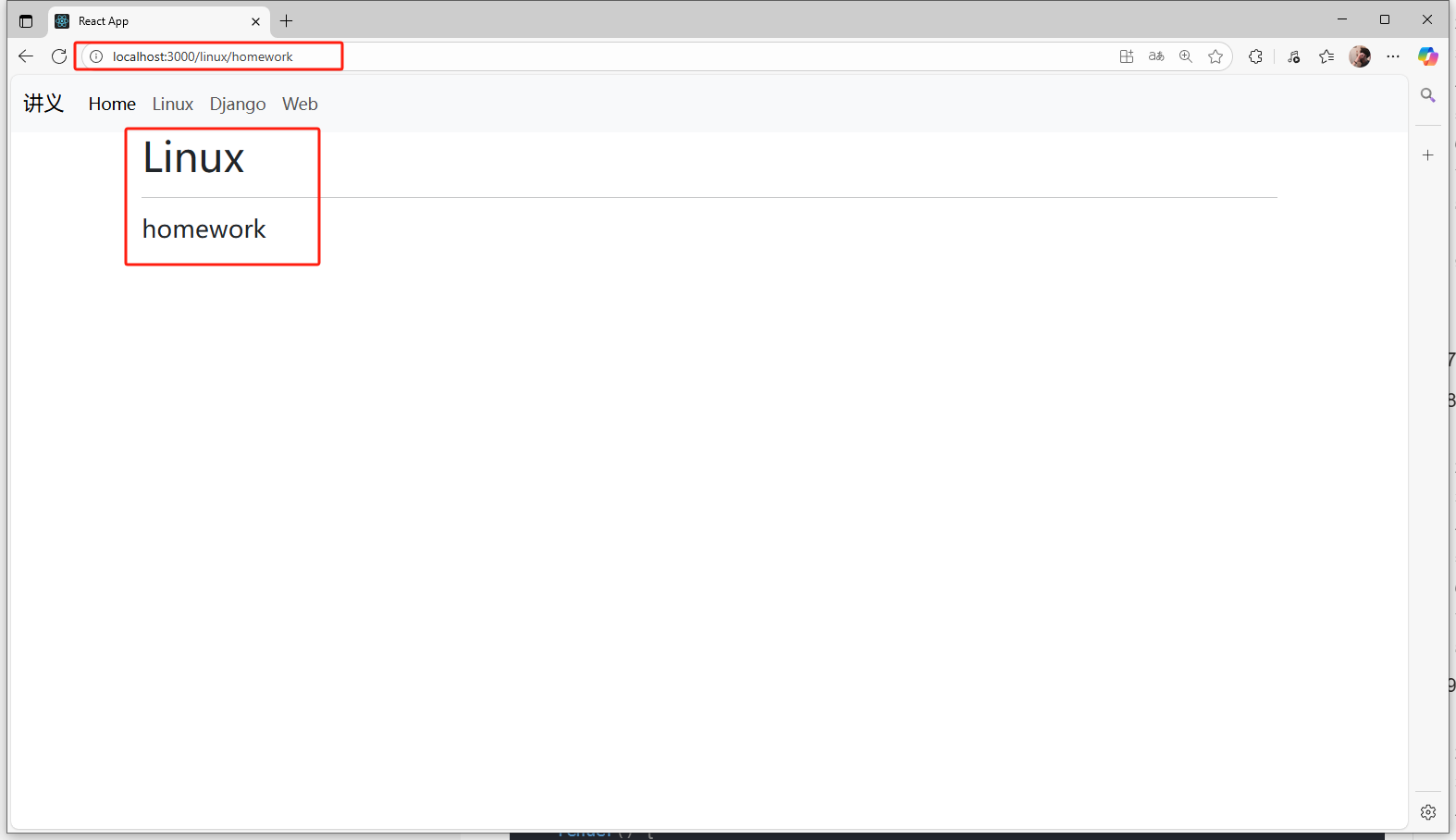
- 注意:需要在父組件中添加
<Outlet />組件,用來填充子組件的內容。
10.Redux
redux將所有數據存儲到樹中,并且樹是唯一的。
原本的DOM樹中,比如兩個組件之間的公共數據需要修改時,A組件修改數據使得B組件發生相應變化,需要將state數據提取到兩個組件的最近公共祖先,然后兩個組件同時綁定公共祖先內的state對應的數據,當層級較多時,這個關系維護起來就很麻煩:
比如這里想要在1號組件內修改數據使得2號組件的狀態發生改變,就需要一步一步往上提取到APP中,整個公共數據的維護就很冗余和麻煩。
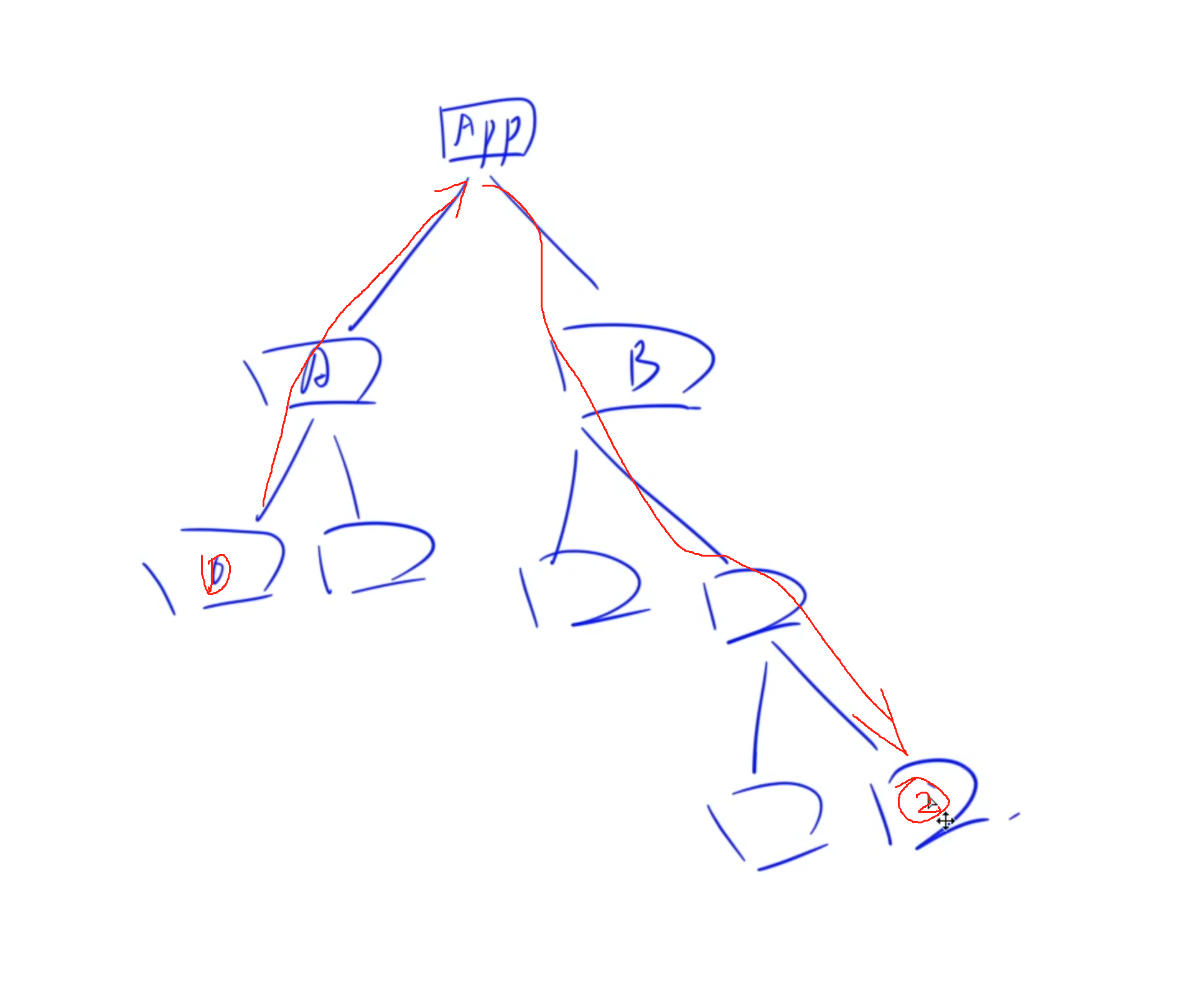
Redux的作用就是在整個DOM樹之外,用一個專門的地方存放類似于全局變量的數據,也就是將不同組件之間可能需要交互的數據放到全局變量中。當兩個組件需要交互時,就只需要這兩個組件單獨向該組件訪問即可。
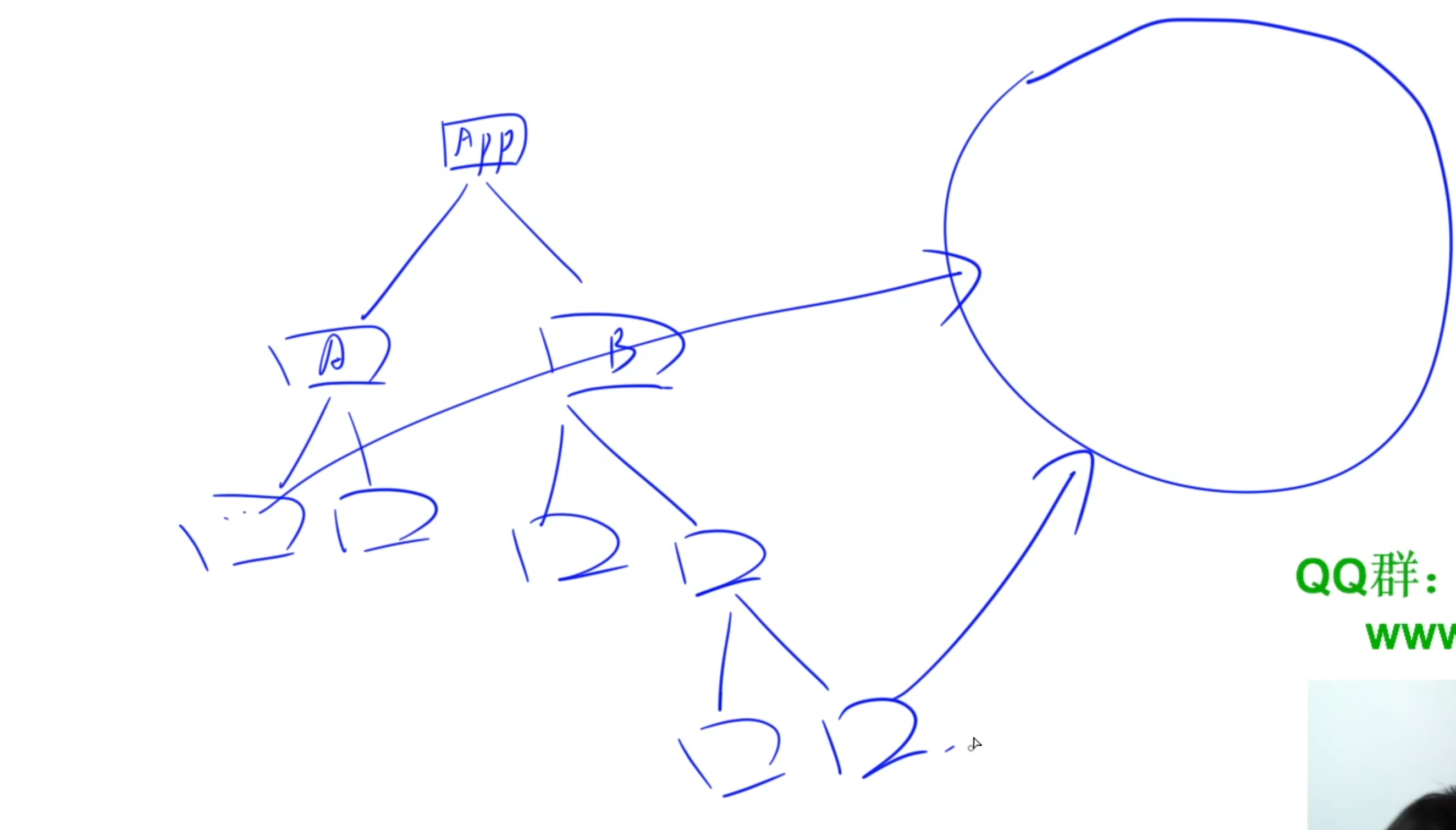
1)Redux基本概念
store:存儲樹結構state:維護的數據,一般維護成樹的結構。reducer: 對state進行更新的函數,每個state綁定一個reducer。傳入兩個參數:當前state和action,返回新的state。action:一個普通對象,存儲reducer的傳入參數,一般描述對state的更新類型。dispatch:傳入一個參數action,對整顆state樹操作一遍。
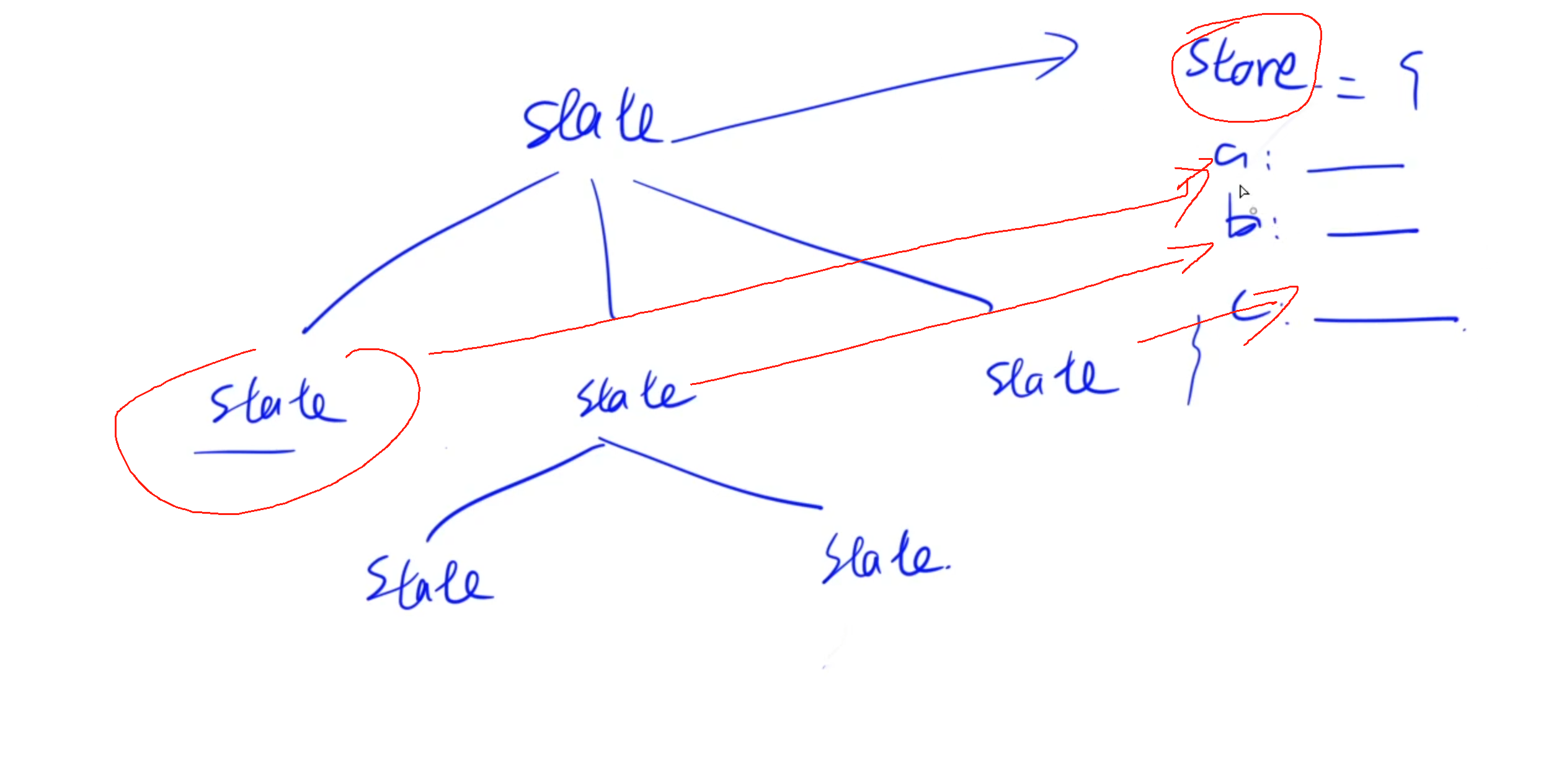
當我們想要修改某個state的值時,會遞歸調用所有的reducer,同時根據action中對state的更新類型作對比,如果是當前節點對應類型則會更新當前節點的state的值。
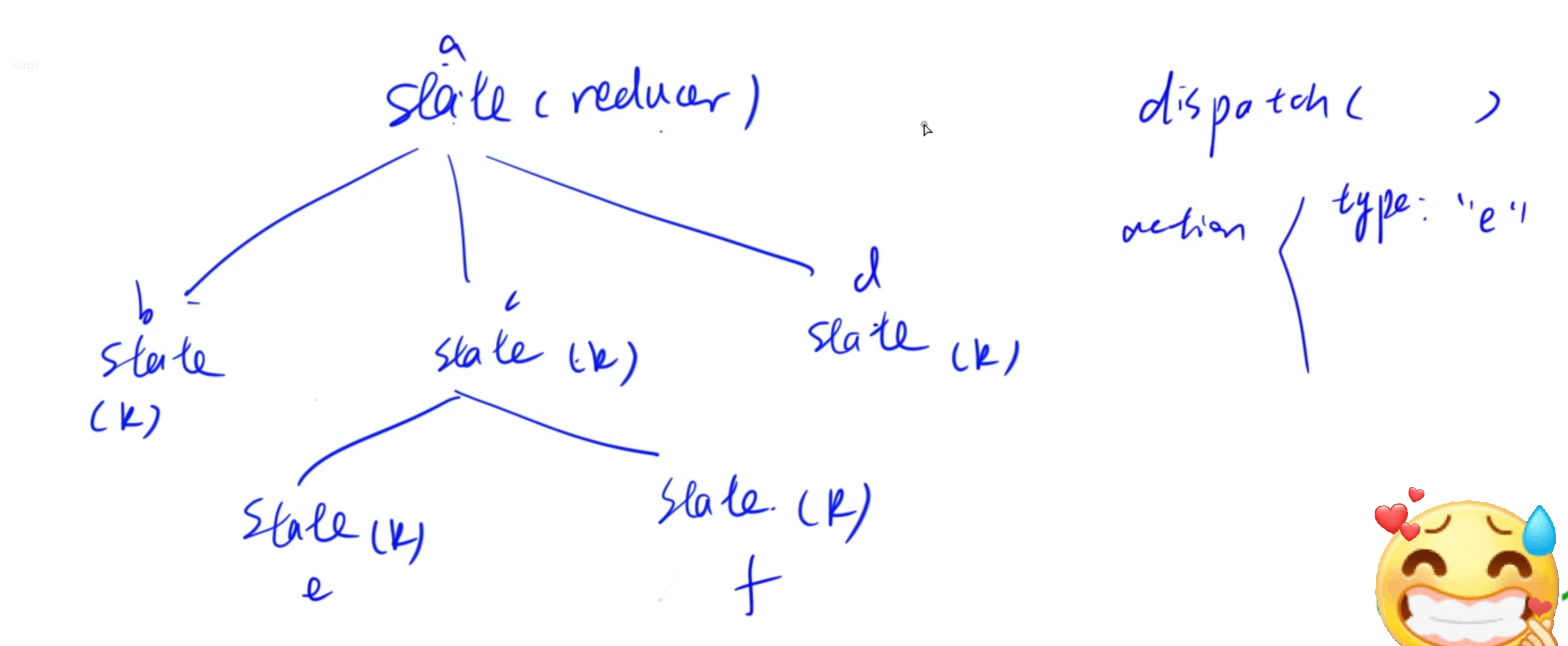
2)React-Redux基本概念
Provider:用來包裹整個項目,其store屬性用來存儲redux的store對象connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)函數:用來將store與組件關聯起來。mapStateToProps:每次store中的狀態更新后調用一次,用來更新組件中的值mapDispatchToProps:組件創建時調用一次,用來將store的1dispatch函數傳入組件。
redux相關依賴安裝:
npm i redux react-redux @reduxjs/toolkit
3)快速入門
index.js:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';const f1 = (state = 1, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'multiple':return state * 2;case 'cut':return state - 1;default:return state; }
};
const store = configureStore({reducer: f1
});console.log(`native value: ${store.getState()}`);//調用dispatch時傳入action對象,對象中指定type,從而實現對應的更新
store.dispatch({type:'multiple'});
store.dispatch({type:'multiple'}); //多次調用則多次更新console.log(`after update: ${store.getState()}`);const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<React.StrictMode></React.StrictMode>
);state打印:
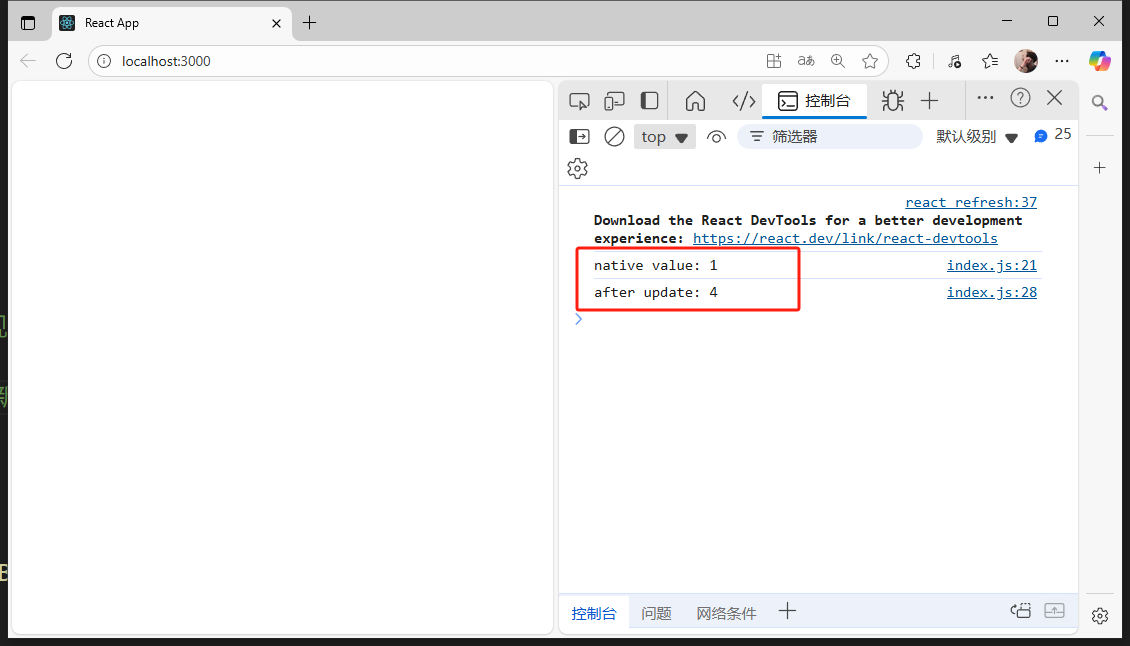
subscribe:
//每次dispatch更新之后會調用一次
store.subscribe(() => {console.log(`after update: ${store.getState()}`)})
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';const f1 = (state = 1, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'multiple':return state * 2;case 'cut':return state - 1;default:return state; }
};
const store = configureStore({reducer: f1
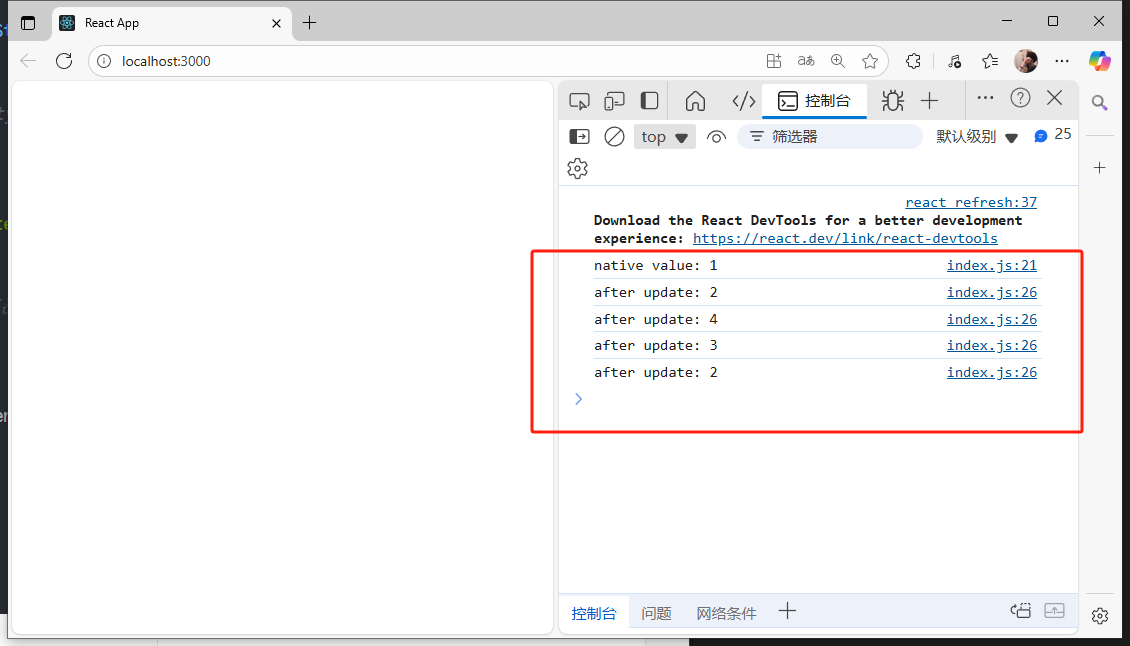
});console.log(`native value: ${store.getState()}`);//調用dispatch時傳入action對象,對象中指定type,從而實現對應的更新//每次dispatch更新之后會調用一次
store.subscribe(() => {console.log(`after update: ${store.getState()}`)}) store.dispatch({type:'multiple'});
store.dispatch({type:'multiple'}); //多次調用則多次更新
store.dispatch({type:'cut'});
store.dispatch({type:'cut'});const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<React.StrictMode></React.StrictMode>
);
參數傳入
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';const f1 = (state = 1, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'multiple':return state * action.value;case 'cut':return state - action.value;default:return state; }
};
const store = configureStore({reducer: f1
});console.log(`native value: ${store.getState()}`);//調用dispatch時傳入action對象,對象中指定type,從而實現對應的更新//每次dispatch更新之后會調用一次
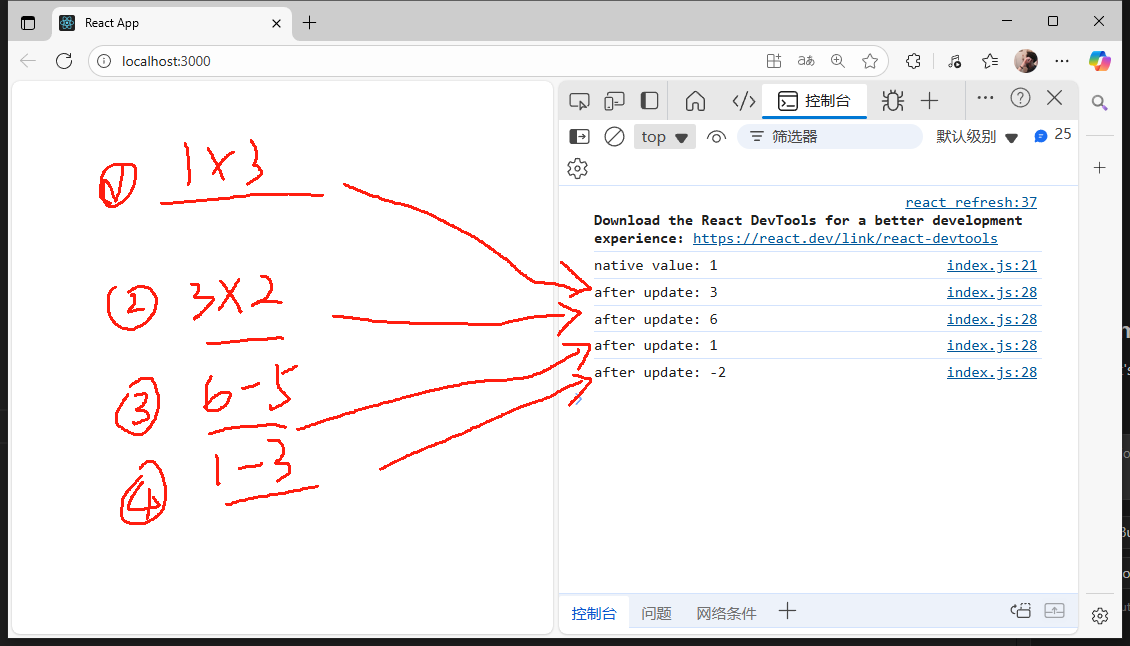
store.subscribe(() => {console.log(`after update: ${store.getState()}`)}) store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 3});
store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 2}); //多次調用則多次更新
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 5});
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 3});const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<React.StrictMode></React.StrictMode>
);
子節點的狀態更新
1.手動實現
具體看代碼注釋:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';const f1 = (state = 1, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'multiple':return state * action.value;case 'cut':return state - action.value;default:return state; }
};const f2 = (state = "", action) => {switch(action.type) {case 'concat':return state + action.character;default:return state;}
};//將兩個state作為f3的子節點
const f3 = (state = {}, action) => {return {f1: f1(state.f1, action),f2: f2(state.f2, action),}
}//以f3作為樹根
const store = configureStore({reducer: f3
});console.log(`native value: ${store.getState()}`);//調用dispatch時傳入action對象,對象中指定type,從而實現對應的更新//每次dispatch更新之后會調用一次
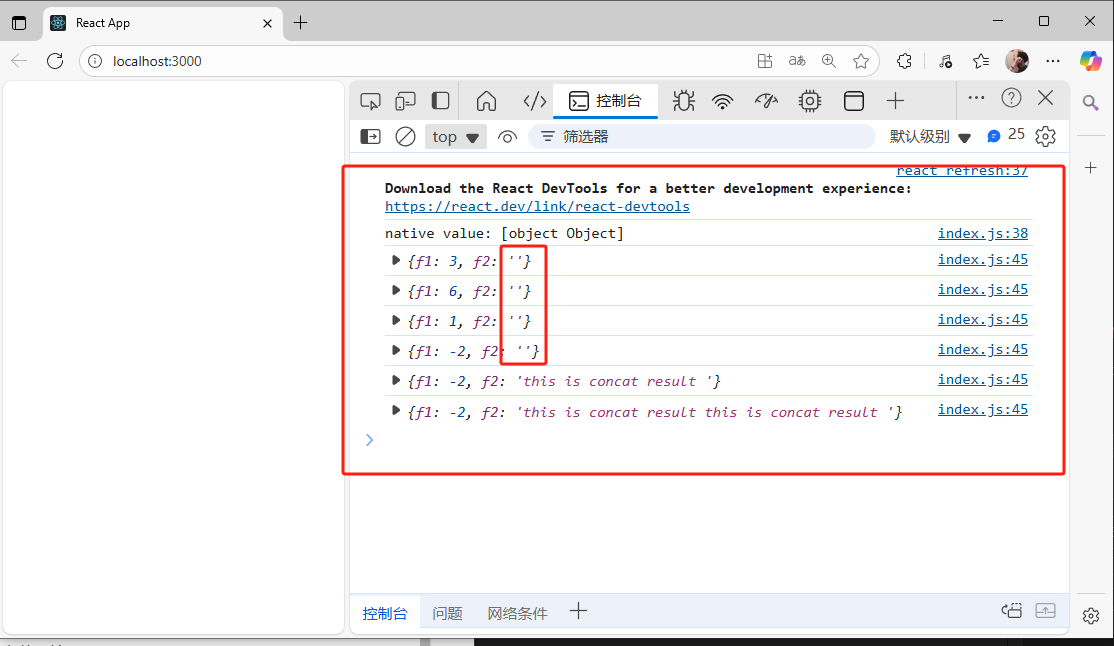
store.subscribe(() => {console.log(store.getState())}) store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 3});
store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 2});
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 5});
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 3});//同樣是調用樹根的值,傳入type實現不同子節點的狀態更新
store.dispatch({type: 'concat', character: "this is concat result "})
store.dispatch({type: 'concat', character: "this is concat result "})const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<React.StrictMode></React.StrictMode>
);
2.API實現
combineReducers:
直接使用該API效果和上面手動實現的效果一致。
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { combineReducers } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';const f1 = (state = 1, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'multiple':return state * action.value;case 'cut':return state - action.value;default:return state; }
};const f2 = (state = "", action) => {switch(action.type) {case 'concat':return state + action.character;default:return state;}
};// //將兩個state作為f3的子節點
// const f3 = (state = {}, action) => {
// return {
// f1: f1(state.f1, action),
// f2: f2(state.f2, action),
// }
// }const f3 = combineReducers({f1: f1,f2: f2,
});//以f3作為樹根
const store = configureStore({reducer: f3
});console.log(`native value: ${store.getState()}`);//調用dispatch時傳入action對象,對象中指定type,從而實現對應的更新//每次dispatch更新之后會調用一次
store.subscribe(() => {console.log(store.getState())}) store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 3});
store.dispatch({type:'multiple', value: 2});
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 5});
store.dispatch({type:'cut', value: 3});//同樣是調用樹根的值,傳入type實現不同子節點的狀態更新
store.dispatch({type: 'concat', character: "this is concat result "})
store.dispatch({type: 'concat', character: "this is concat result "})const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<React.StrictMode></React.StrictMode>
);4)實戰演練
實現一個app:
- 包含兩個組件:number和string
- 在
number組件中可以通過添加按鈕,給string組件中的內容添加指定的內容 - 在
string組件中可以通過加或者減按鈕,給number組件中的x增加或者減去指定內容
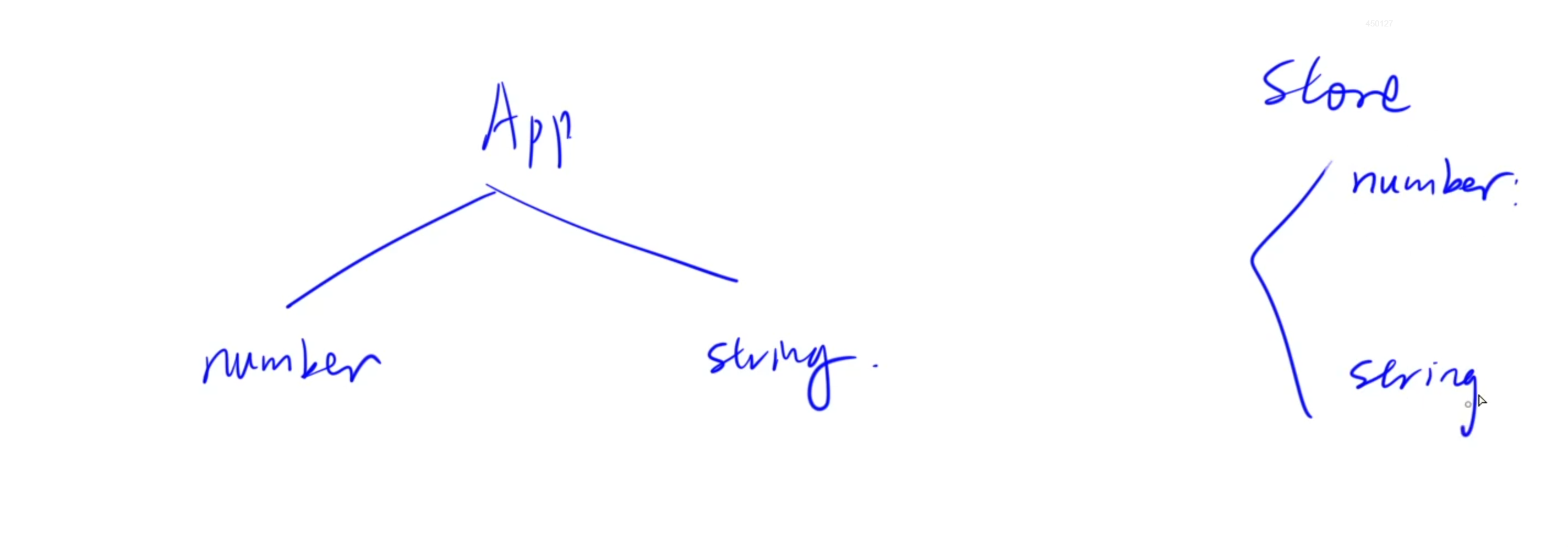
分析: - 首先使用redux去維護每個組件的state值,通過傳入action對象指定操作類型,從而實現指定組件的state更新
- 需要將state值從redux中取出并顯示在組件中(訪問存儲的全局變量):通過
connect(mapStateToProps)將store與組件關聯起來。每次store中的狀態更新后調用一次,用來更新組件中的值。 - 按下按鈕后,修改對應組件中的state值,也就是如何更新全局變量:
說明:
mapStateToProps:將state映射到props中,用來更新組件中的值mapDispatchToProps:將dispatch函數映射到props中,用來操作改變組件中的值
1.index.js:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { combineReducers } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import App from './components/app';import { Provider } from 'react-redux';const f1 = (state = 0, action) => {switch(action.type) {//規定對應類型執行怎么樣的state更新操作case 'add':return state + action.value;case 'cut':return state - action.value;default:return state; }
};const f2 = (state = "the concat string is:", action) => {switch(action.type) {case 'concat':return state + action.character;default:return state;}
};}const f3 = combineReducers({number: f1,string: f2,
});//以f3作為樹根
const store = configureStore({reducer: f3
});
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<Provider store={store}><App /></Provider>
);2.app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Number from './number';
import String from './string';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><Number /><hr /><String /></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
3.number.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';class Number extends Component {state = { } handleClick = () => {this.props.concat('y ');console.log("click concat");}render() { console.log(this.props);return (<React.Fragment><h3>Nubmer:</h3><div>{this.props.number}</div><button onClick={this.handleClick}>添加</button></React.Fragment>);}
}//將state綁定到參數中
const mapStateToProps = (state, props) => {return {number: state.number,}
}//將dispatch函數綁定到props上
const mapDisPatchToProps = {concat: (c) => {return {type: 'concat',character: c,}}
}export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDisPatchToProps)(Number);
4.string.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';class String extends Component {state = { } handleClickAdd = () => {this.props.add(10);console.log("click add");}handleClickCut = () => {this.props.cut(1);console.log("click cut");}render() { return (<React.Fragment><h3>String:</h3><div>{this.props.string}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickAdd}>加</button><button onClick={this.handleClickCut}>減</button></React.Fragment>);}
}const mapStateToProps = (state, props) => {return {string: state.string,};
};const mapDisPatchToProps = {add: (c) => {return {type: 'add',value: c,}},cut: (c) => {return {type: 'cut',value: c,}}
};export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDisPatchToProps)(String);
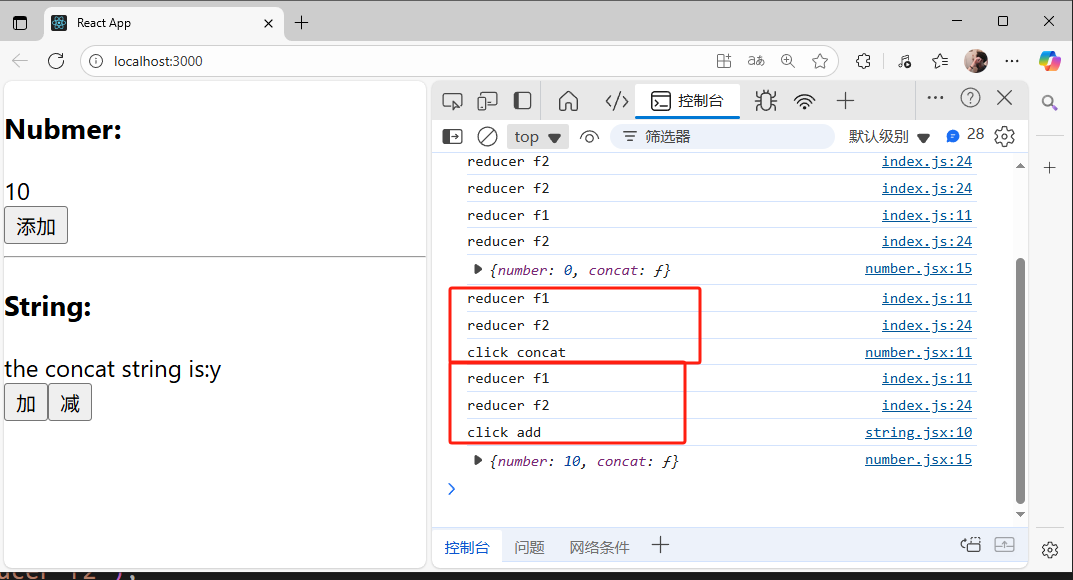
效果展示:
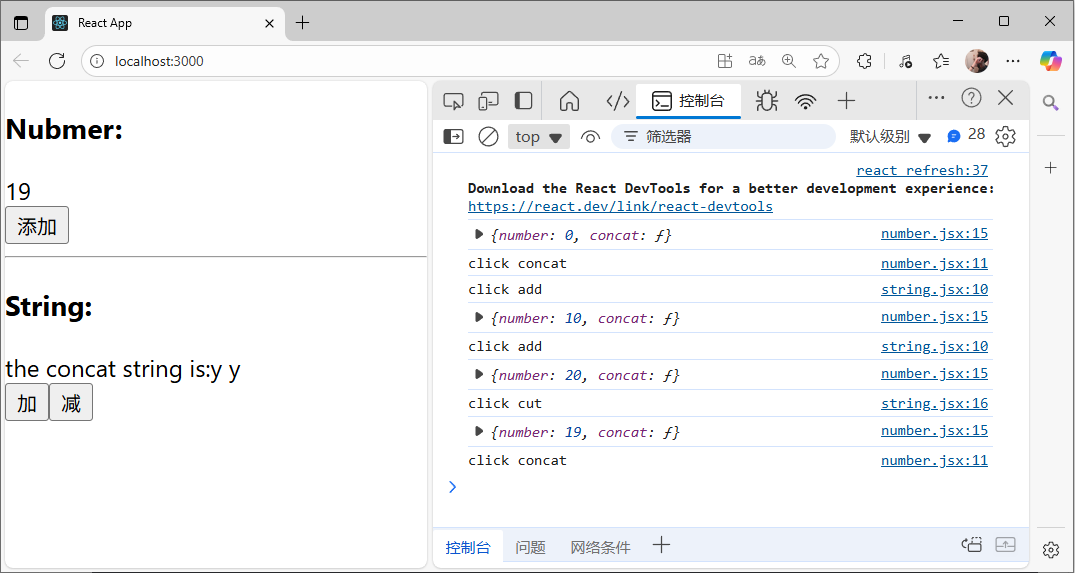
過程解釋
整個流程分為兩步(以string的操作為例):
-
1.數值的改變
點擊添加按鈕 ->調用handleClick函數->handleClick函數觸發this.props.concat(通過mapDispatchToProps將concat綁定到props上)->concat函數會返回一個對象(包含type:concat和參數:c) ->通過connect(mapDispatchToProps)會傳遞到所有節點的reducer上,這里concat返回的對象就會作為action傳入reducer中,對于f1來說,會對比type發現均不匹配,所以無操作,對于f2來說,type與concat匹配,于是會執行對應的state操作 ->完成f2的操作,在原本的state值上添加傳入的參數字符 -
2.數值的更新同步
store是根節點,由于store傳入到了<Provider>組件中,于是會重新渲染整個Provider組件-> 重新渲染App組件->String組件-> 通過mapStateToProps已經將f3中的string代表的state綁定到了String組件的props中-> 通過this.props.string獲取到更新之后的state->完成同步
注意這里不管調用那個組件的參數更新,都會將所有的reducer執行一遍
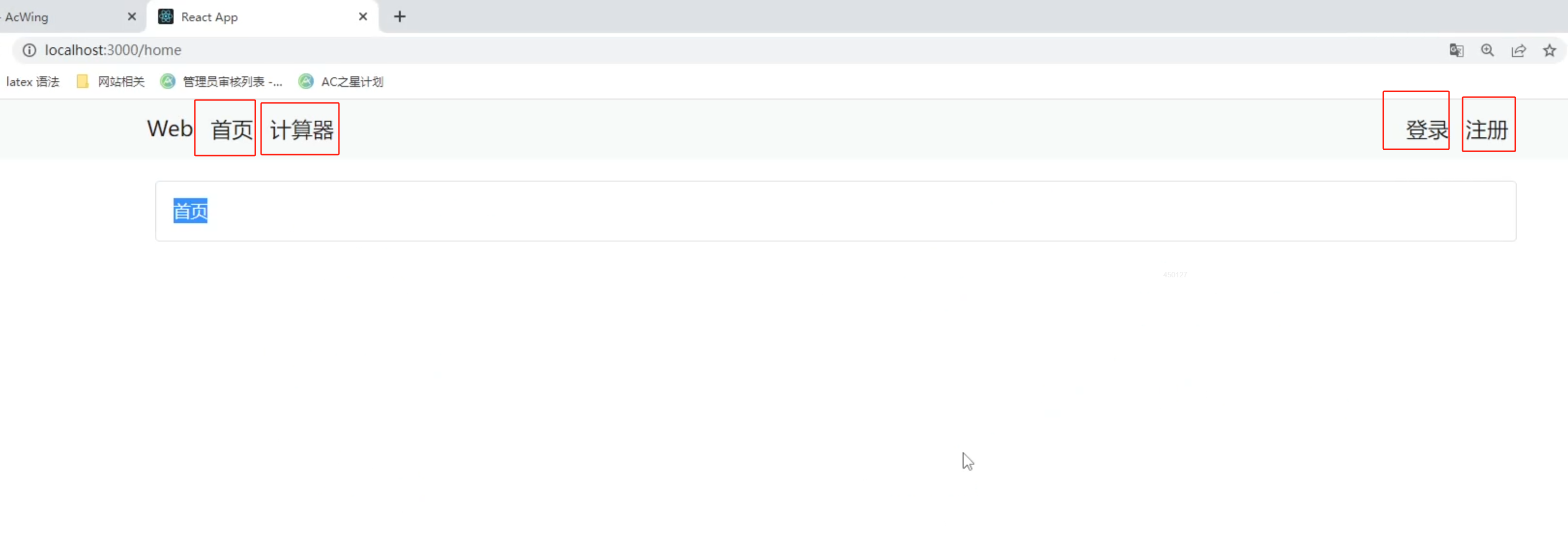
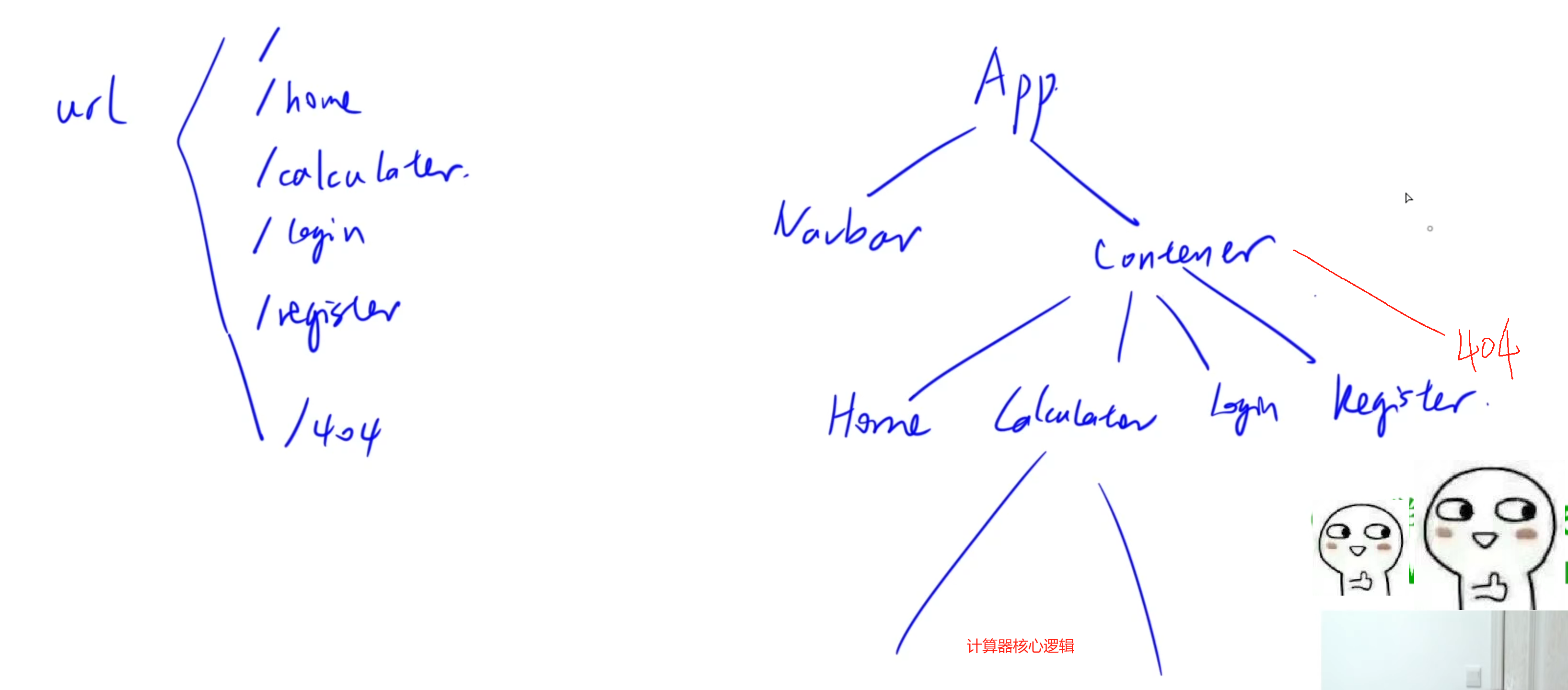
11. React實戰項目——計算器
總體效果預覽:
1.創建項目以及配置環境
- 1.創建app:
create-react-app calculator-app - 2.配置環境:
- 配置redux,用于組件之間的交互:
npm i redux react-redux @reduxjs/toolkit - 配置路由router:
npm i react-router-dom - 配置bootstrap,前端常用樣式庫:
npm i bootstrap,文件中引入bootstrap:import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css';
- 配置redux,用于組件之間的交互:
- 3.啟動項目:進入calculator-app文件夾,運行git bash,執行
npm start
2.創建各個組件以及建立路由
- 需要用到路由的組件必須:
- 引入:
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'; - 將該組件使用
<BrowserRouter>組件包裹起來,比如:
- 引入:
<BrowserRouter><App />
</BrowserRouter>
1.url的切換
創建navbar.jsx來實現各個組件之間的url的轉換:
- 1.在bootstrap官網找到合適的樣式,并復制過來,將class改為className
- 2.添加并修改對應的內容,使得符合預期樣式:
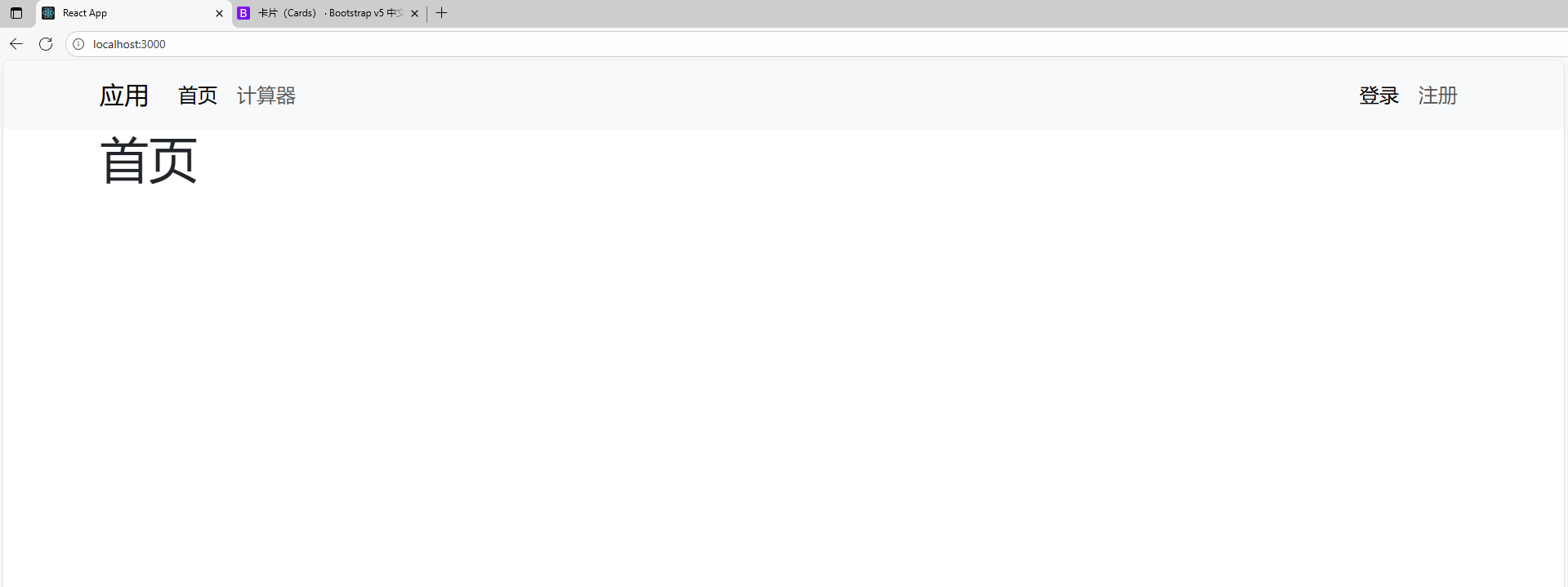
- 3.寫路由:引入Link:
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom'; - 4.將所有需要路由跳轉的地方用
<Link>包圍,to屬性寫上跳轉的url地址:比如to='/login'表示會跳轉到localhost:3000/login
navbar.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';class NavBar extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<nav className="navbar navbar-expand-lg bg-body-tertiary"><div className="container"><Link className="navbar-brand" to='/'>應用</Link><button className="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#navbarText" aria-controls="navbarText" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation"><span className="navbar-toggler-icon"></span></button><div className="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarText"><ul className="navbar-nav me-auto mb-2 mb-lg-0"><li className="nav-item"><Link className="nav-link active" aria-current="page" to='/'>首頁</Link></li><li className="nav-item"><Link className="nav-link" to='/calculator'>計算器</Link></li></ul><ul className="navbar-nav"><li className="nav-item"><Link className="nav-link active" aria-current="page" to='/login'>登錄</Link></li><li className="nav-item"><Link className="nav-link" to='register'>注冊</Link></li></ul></div></div></nav>);}
}export default NavBar;
2.頁面跳轉
新建components文件夾,并在文件夾中依次創建:home.jsx, login.jsx, register.jsx, notFound.jsx, calculator.jsx
創建出Home, Login, Register, Calculator, NotFound五個組件,并導入到app.jsx中:
導入<Routes>和<Route>:
import { Route, Routes, Navigate } from 'react-router-dom';
其中:如果不屬于定義的url則需要實現重定向到404url展示NotFound組件
<Route path="*" element={ <Navigate replace to="/404" /> } />
app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import { Route, Routes, Navigate } from 'react-router-dom';
import Home from './content/home';
import Login from './content/login';
import Register from './content/register';
import Calculator from './content/calculator';
import NotFound from './content/notFound';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><NavBar /><div className='container'><Routes><Route path='/' element={ <Home /> } /><Route path='/login' element={ <Login /> } /><Route path='/register' element={ <Register /> } /><Route path='/calculator' element={ <Calculator /> } /><Route path='/404' element={ <NotFound /> } /><Route path="*" element={ <Navigate replace to="/404" /> } /></Routes></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
3.組合組件以及Redux應用
這的計算器實現主要由calculator.jsx來完成計算器前端顯示以及數據的交互:
calculator.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Base from './base';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import NumberButton from './calculator/numberButton';
import OperationButton from './calculator/operationButton';
import ACTIONS from '../../redux/action';class Calculator extends Component {state = { formater: Intl.NumberFormat('en-us')};format = number => {if (number === "") return "";//將一個數分為整數部分和小數部分const [integer, decimal] = number.split('.');//如果小數部分不存在,就只返回整數部分的formatif (decimal === undefined) {return this.state.formater.format(integer);}//否則的話整數部分format,小數部分保持不變return `${this.state.formater.format(integer)}.${decimal}`;}render() { return (<Base><div className="calculator"><div className='screen'><div className='up-screen'>{this.format(this.props.lastResult)} {this.props.operation}</div><div className='down-screen'>{this.format(this.props.currentResult)}</div></div><button className='button-AC' onClick={this.props.clear}>AC</button><button onClick={this.props.delete_number}>Del</button><OperationButton operation={'÷'} /> <NumberButton className='button-number' number={'7'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'8'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'9'} /><OperationButton operation={'×'} /> <NumberButton className='button-number' number={'4'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'5'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'6'} /><OperationButton operation={'-'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'1'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'2'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'3'} /><OperationButton operation={'+'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'0'} /><NumberButton className='button-number' number={'.'} /><button className='button-equal' onClick={this.props.evaculate}>=</button></div></Base>);}
}const mapStateToProps = (state, props) => {return {currentResult: state.currentResult,lastResult: state.lastResult,operation: state.operation,}
}const mapDispatchToProps = {delete_number: () => {return {type: ACTIONS.DELETE_NUMBER,}},clear: () => {return {type: ACTIONS.CLEAR,}},evaculate: () => {return {type: ACTIONS.EVACULATE,}}
}export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Calculator);
1.在index.css中定義按鈕以及計算器頁面樣式:
body {margin: 0;font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, 'Segoe UI', 'Roboto', 'Oxygen','Ubuntu', 'Cantarell', 'Fira Sans', 'Droid Sans', 'Helvetica Neue',sans-serif;-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}code {font-family: source-code-pro, Menlo, Monaco, Consolas, 'Courier New',monospace;
}* {box-sizing: border-box;
}.calculator {display: grid;grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 6rem);grid-template-rows: minmax(6rem, auto) repeat(5, 4rem);gap: 1px;background-color: rgba(191, 191, 191, 0.75);width: calc(24rem + 5px);margin: 0 auto;border: 2px solid black;}.button-AC {grid-column: 1 / span 2;
}
.button-equal {grid-column: 3 / span 2;
}.button-number {background-color: white
}.screen {grid-column: 1 / span 4;display: flex;flex-direction: column;align-items: flex-end;justify-content: space-around;padding: 10px;word-wrap: break-word;word-break: break-all;
}.up-screen {font-size: 1rem;
}.down-screen {font-size: 3rem;
}.calculator > button:hover {background-color: #b5b5b5;
}
2.組合Components:
1)數字按鍵組件numberButton
對于數字鍵來說,按下數字鍵就會將數字鍵對應的數字添加到輸入結果中,于是將他們的邏輯全部抽取成一個NumberButton組件:
numberButton.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ACTIONS from '../../../redux/action';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';//將點擊按鈕對應的內容添加到對應的狀態上
class NumberButton extends Component {state = { } render() { return (//當點擊這個按鈕時,會獲取這個按鈕的內容,作為參數傳入add_number中<button onClick={() => this.props.add_number(this.props.number)}>{this.props.number}</button>);}
}const mapDispatchToProps = {//add_number已經綁定到Dispatch中,會將對應的type傳到reducer中進行匹配add_number: number => {return {type: ACTIONS.ADD_NUMBER,number: number,}}
}export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(NumberButton);
2)運算符按鍵組件operationButton
對于加減乘除四個按鍵來說,按下時,也就是執行對應的運算邏輯,所以也可以統一抽取為一個組件operationButton:
operationButton.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ACTIONS from '../../../redux/action';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';class OperationButton extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<button onClick={() => {this.props.choose_operation(this.props.operation)}}>{this.props.operation}</button>);}
}const mapDispatchToProps = {choose_operation: operation => {return {type: ACTIONS.CHOOSE_OPERATION,operation: operation,}}
}export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(OperationButton);
最后只需要將對應的按鍵用組件進行包圍即可完成高效的復用。
3.Redux使用五個行為維護四個狀態
1)創建store樹根
store.js:
import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import reducer from "./reducer";const store = configureStore({reducer: reducer,
});export default store;
2)定義靜態的行為集合
action.js:
const ACTIONS = {ADD_NUMBER: "add-number",DELETE_NUMBER: "delete-number",CHOOSE_OPERATION: "choose-operation",CLEAR: "clear",EVACULATE: "evaculate"
};export default ACTIONS;
3)reducer觸發每個狀態的更新
reducer.js:
import ACTIONS from "./action";const evaluate = state => {let {lastResult, operation, currentResult} = state;let last = parseFloat(lastResult);let cur = parseFloat(currentResult);let res = 0;switch(operation) {case '+':res = last + cur;break;case '-':res = last - cur;break;case '÷':res = last / cur;break;case '×':res = last * cur;break; }return res.toString();
}const reducer = (state={currentResult: "",lastResult: "",operator: "",overwrite: false, //用于判斷當前輸入結果是否需要覆蓋,默認為false,只有按下等號得到結果之后,再輸入內容才需要覆蓋
}, action) => {switch(action.type) {case ACTIONS.ADD_NUMBER://如果overwrite為true,則說明這是在計算結果之后輸入數字//需要將計算結果清空,輸入結果顯示為當前輸入的數字if (state.overwrite) { return {...state,currentResult: action.number,overwrite: false,}}//如果當前的顯示為0,并且當前位也為0,則說明是00,則不添加if (state.currentResult === '0' && action.number === '0') {return state;}//當前結果為0,如果下一位不是'.',構成'0.x'的話,說明是'0x',直接替換掉0,變成'x'if (state.currentResult === '0' && action.number !== '.') {return {...state,currentResult: action.number,}}//如果輸入的結果是包含'.'的,則再次點擊'.'則不添加if (action.number === '.' && state.currentResult.includes('.')) {return state;}//如果當前輸入的結果直接是'.'則需要在前面補上'0'變成'0.'if (action.number === '.' && state.currentResult === "") {return {...state,currentResult: "0" + action.number,}}return {...state,currentResult: state.currentResult + action.number,}case ACTIONS.DELETE_NUMBER://當得到計算結果再按del鍵時,應該將計算結果作為一個整體刪除,而不是一位一位刪除if (state.overwrite) {return {...state,currentResult: "",overwrite: false,}}//當前輸入結果為空時,就不需要再刪除了if (state.currentResult === "") {return state;}return {...state,//slice(0, -1):刪除從0開始的-1個元素,也就是把這個結果的最后一個元素刪除currentResult: state.currentResult.slice(0, -1),}case ACTIONS.CHOOSE_OPERATION://如果上一個計算結果為0,并且當前的輸入結果也是空的,則不添加if (state.lastResult === "" && state.currentResult === "") {return state;}//當上面沒有結果,并且輸入結果不為空,但是按了運算符時// 需要將當前結果發送到上面的結果中,并且運算符變為當前按下的運算符//當前輸入結果清空if (state.lastResult === "" ) {return {//這里...state,會將state解構出來,然后后面列舉的值會被替換成指定的內容...state,lastResult: state.currentResult,operation: action.operation,currentResult: "",}}//當當前輸入結果為空,再次點擊運算符時,表示需要將運算符替換掉if (state.currentResult === "") {return {...state,operation: action.operation}}//最后就是其他情況//當上一個計算結果不為空,并且當前輸入結果不為空,// 再次點擊運算符就需要將 上一個計算結果 (運算符) 當前輸入結果 = 最終結果//放入到上一個計算結果中,并且將當前按下的運算符放到對應位置return {...state,lastResult: evaluate(state),operation: action.operation,currentResult: ""}case ACTIONS.CLEAR:return {...state,lastResult: "",operation: "",currentResult: ""}case ACTIONS.EVACULATE:if (state.currentResult === "" ||state.operation === "" || state.lastResult === "")return state;return {...state,currentResult: evaluate(state),lastResult: "",operation: "",overwrite: true,}default:return state;}
};export default reducer;
12.總結
上述只是支離破碎的片段,可能觀感不佳,請諒解,完整項目放在acgit倉庫
*注:以上內容來自acwing平臺的web應用課學習整理,僅作為學習交流,不作為商業用途,如有侵權,聯系刪除。






)







)



- DRM簡介)
