一、? ? ? ? 主機驅動與外設驅動分離
? ? ? ? Linux中的SPI、I2c、USB等子系統都利用了典型的把主機驅動和外設驅動分離的想法,讓主機端負責產生總線上的傳輸波形,而外設端只是通過標準的API來讓主機端以適當的波形訪問自身。因此這里涉及了4個軟件模塊:
? ? ? ? 1)主機端的驅動。根據具體的I2c、SPI、USB等控制器的硬件的手冊,操作具體的i2c、SPI、USB等控制器,產生總線的各種波形。
? ? ? ? 2)連接主機和外設的紐帶。外設不直接調用主機端的驅動來產生波形,而是調一個標準的API。由這個標準的API把這個波形的傳輸請求間接“轉發”給具體的主機端驅動。當然,在這里,最好把關于波形的描述也以某種數據結構標準化。
? ? ? ? 3)外設端的驅動。外設接在I2c、SPI、USB這樣的總線上,但是它們本身可以是觸摸屏、網卡、聲卡或者任意一種類型的設備。我們在相關的i2c_driver、spi_driver、usb_driver這種xxx_driver的probe()函數中注冊具體的類型。當這些外設要去i2c、spi、usb等去訪問它的時候,它調用“連接主機和外設的紐帶”模塊的標準API。
? ? ? ? 4)板級邏輯。板級邏輯用來描述主機和外設是如何互聯,它相當于一個“路由表”。假設板子上有多個SPI控制器和多個SPI外設,那究竟誰接在誰上面?管理互聯關系,既不是主機端的責任,也不是外設端的責任,這屬于板級邏輯的責任。這部分通常在arch/arm/mach-xx或者arch/arm/boot/dts下面。
? ? ? ? 什么叫良好的軟件設計?一言以蔽之,讓正確的代碼出現在正確的位置。不要在錯誤的時間、錯誤的地點,編寫一段錯位的代碼。在LKML中,關于代碼出現在錯誤的位置,常見的臺詞是代碼“out of place”。
????????
二、? ? ? ? linux SPI主機和設備驅動
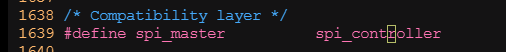
? ? ? ? 在linux中,用代碼的spi_maste結構體來描述一個spi主機控制器驅動,其主要成員是主機控制器的序號(系統中可能存在多個SPI主機控制器)、片選數量、SPI模式、時鐘設置用到的和數據傳輸用到的函數等。
????????
521 struct spi_controller {522 struct device dev;523 524 struct list_head list;525 526 /*527 * Other than negative (== assign one dynamically), bus_num is fully528 * board-specific. Usually that simplifies to being SoC-specific.529 * example: one SoC has three SPI controllers, numbered 0..2,530 * and one board's schematics might show it using SPI-2. Software531 * would normally use bus_num=2 for that controller.532 */533 s16 bus_num;534 535 /*536 * Chipselects will be integral to many controllers; some others537 * might use board-specific GPIOs.538 */539 u16 num_chipselect;540 541 /* Some SPI controllers pose alignment requirements on DMAable542 * buffers; let protocol drivers know about these requirements.543 */544 u16 dma_alignment;545 546 /* spi_device.mode flags understood by this controller driver */547 u32 mode_bits;548 549 /* spi_device.mode flags override flags for this controller */550 u32 buswidth_override_bits;551 552 /* Bitmask of supported bits_per_word for transfers */553 u32 bits_per_word_mask;554 #define SPI_BPW_MASK(bits) BIT((bits) - 1)555 #define SPI_BPW_RANGE_MASK(min, max) GENMASK((max) - 1, (min) - 1)556 557 /* Limits on transfer speed */558 u32 min_speed_hz;559 u32 max_speed_hz;560 561 /* Other constraints relevant to this driver */562 u16 flags;563 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_HALF_DUPLEX BIT(0) /* Can't do full duplex */564 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_NO_RX BIT(1) /* Can't do buffer read */565 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_NO_TX BIT(2) /* Can't do buffer write */566 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_MUST_RX BIT(3) /* Requires rx */567 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_MUST_TX BIT(4) /* Requires tx */568 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_GPIO_SS BIT(5) /* GPIO CS must select slave */569 #define SPI_CONTROLLER_SUSPENDED BIT(6) /* Currently suspended */570 571 /* Flag indicating if the allocation of this struct is devres-managed */572 bool devm_allocated;573 574 union {575 /* Flag indicating this is an SPI slave controller */576 bool slave;577 /* Flag indicating this is an SPI target controller */578 bool target;579 };580 581 /*582 * On some hardware transfer / message size may be constrained583 * the limit may depend on device transfer settings.584 */585 size_t (*max_transfer_size)(struct spi_device *spi);586 size_t (*max_message_size)(struct spi_device *spi);587 588 /* I/O mutex */589 struct mutex io_mutex;590 591 /* Used to avoid adding the same CS twice */592 struct mutex add_lock;593 594 /* Lock and mutex for SPI bus locking */595 spinlock_t bus_lock_spinlock;596 struct mutex bus_lock_mutex;597 598 /* Flag indicating that the SPI bus is locked for exclusive use */599 bool bus_lock_flag;600 601 /*602 * Setup mode and clock, etc (SPI driver may call many times).603 *604 * IMPORTANT: this may be called when transfers to another605 * device are active. DO NOT UPDATE SHARED REGISTERS in ways606 * which could break those transfers.607 */608 int (*setup)(struct spi_device *spi);609 610 /*611 * set_cs_timing() method is for SPI controllers that supports612 * configuring CS timing.613 *614 * This hook allows SPI client drivers to request SPI controllers615 * to configure specific CS timing through spi_set_cs_timing() after616 * spi_setup().617 */618 int (*set_cs_timing)(struct spi_device *spi);619 620 /*621 * Bidirectional bulk transfers622 *623 * + The transfer() method may not sleep; its main role is624 * just to add the message to the queue.625 * + For now there's no remove-from-queue operation, or626 * any other request management627 * + To a given spi_device, message queueing is pure FIFO628 *629 * + The controller's main job is to process its message queue,630 * selecting a chip (for masters), then transferring data631 * + If there are multiple spi_device children, the i/o queue632 * arbitration algorithm is unspecified (round robin, FIFO,633 * priority, reservations, preemption, etc)634 *635 * + Chipselect stays active during the entire message636 * (unless modified by spi_transfer.cs_change != 0).637 * + The message transfers use clock and SPI mode parameters638 * previously established by setup() for this device639 */640 int (*transfer)(struct spi_device *spi,641 struct spi_message *mesg);642 643 /* Called on release() to free memory provided by spi_controller */644 void (*cleanup)(struct spi_device *spi);645 646 /*647 * Used to enable core support for DMA handling, if can_dma()648 * exists and returns true then the transfer will be mapped649 * prior to transfer_one() being called. The driver should650 * not modify or store xfer and dma_tx and dma_rx must be set651 * while the device is prepared.652 */653 bool (*can_dma)(struct spi_controller *ctlr,654 struct spi_device *spi,655 struct spi_transfer *xfer);656 struct device *dma_map_dev;657 struct device *cur_rx_dma_dev;658 struct device *cur_tx_dma_dev;659 660 /*661 * These hooks are for drivers that want to use the generic662 * controller transfer queueing mechanism. If these are used, the663 * transfer() function above must NOT be specified by the driver.664 * Over time we expect SPI drivers to be phased over to this API.665 */666 bool queued;667 struct kthread_worker *kworker;668 struct kthread_work pump_messages;669 spinlock_t queue_lock;670 struct list_head queue;671 struct spi_message *cur_msg;672 struct completion cur_msg_completion;673 bool cur_msg_incomplete;674 bool cur_msg_need_completion;675 bool busy;676 bool running;677 bool rt;678 bool auto_runtime_pm;679 bool cur_msg_mapped;680 char last_cs;681 bool last_cs_mode_high;682 bool fallback;683 struct completion xfer_completion;684 size_t max_dma_len;685 686 int (*prepare_transfer_hardware)(struct spi_controller *ctlr);687 int (*transfer_one_message)(struct spi_controller *ctlr,688 struct spi_message *mesg);689 int (*unprepare_transfer_hardware)(struct spi_controller *ctlr);690 int (*prepare_message)(struct spi_controller *ctlr,691 struct spi_message *message);692 int (*unprepare_message)(struct spi_controller *ctlr,693 struct spi_message *message);694 union {695 int (*slave_abort)(struct spi_controller *ctlr);696 int (*target_abort)(struct spi_controller *ctlr);697 };698 699 /*700 * These hooks are for drivers that use a generic implementation701 * of transfer_one_message() provided by the core.702 */703 void (*set_cs)(struct spi_device *spi, bool enable);704 int (*transfer_one)(struct spi_controller *ctlr, struct spi_device *spi,705 struct spi_transfer *transfer);706 void (*handle_err)(struct spi_controller *ctlr,707 struct spi_message *message);708 709 /* Optimized handlers for SPI memory-like operations. */710 const struct spi_controller_mem_ops *mem_ops;711 const struct spi_controller_mem_caps *mem_caps;712 713 /* GPIO chip select */714 struct gpio_desc **cs_gpiods;715 bool use_gpio_descriptors;716 s8 unused_native_cs;717 s8 max_native_cs;718 719 /* Statistics */720 struct spi_statistics __percpu *pcpu_statistics;721 722 /* DMA channels for use with core dmaengine helpers */723 struct dma_chan *dma_tx;724 struct dma_chan *dma_rx;725 726 /* Dummy data for full duplex devices */727 void *dummy_rx;728 void *dummy_tx;729 730 int (*fw_translate_cs)(struct spi_controller *ctlr, unsigned cs);731 732 /*733 * Driver sets this field to indicate it is able to snapshot SPI734 * transfers (needed e.g. for reading the time of POSIX clocks)735 */736 bool ptp_sts_supported;737 738 /* Interrupt enable state during PTP system timestamping */739 unsigned long irq_flags;740 741 /* Flag for enabling opportunistic skipping of the queue in spi_sync */742 bool queue_empty;743 bool must_async;744 };? ? ? ? 分配、注冊和注銷SPI主機的API由SPI核心提供:
? ? ?
? ? ? ? 在linux中,用代碼清單的spi_driver結構體來描述一個SPI外設驅動,這個外設驅動可以認為是spi_master的客戶端驅動。
325 struct spi_driver {326 const struct spi_device_id *id_table;327 int (*probe)(struct spi_device *spi);328 void (*remove)(struct spi_device *spi);329 void (*shutdown)(struct spi_device *spi);330 struct device_driver driver;331 };? ? ? ? 可以看出,spi_driver結構體和platform_driver結構體有極大的相似性,都有probe()、remove()、suspend()、resume()這樣都接口和device_driver都實例。這幾乎是一切客戶端驅動常模板。?
? ? ? ? 在SPI外設驅動中,當通過SPI總線進行數據傳輸都時候,使用了一套與CPU無關的統一的接口。這套接口的第1個關鍵數據結構就是spi_transfer,它用于描述SPI傳輸,如下所示:
1030 struct spi_transfer {
1031 /*
1032 * It's okay if tx_buf == rx_buf (right?).
1033 * For MicroWire, one buffer must be NULL.
1034 * Buffers must work with dma_*map_single() calls, unless
1035 * spi_message.is_dma_mapped reports a pre-existing mapping.
1036 */
1037 const void *tx_buf;
1038 void *rx_buf;
1039 unsigned len;
1040
1041 #define SPI_TRANS_FAIL_NO_START BIT(0)
1042 u16 error;
1043
1044 dma_addr_t tx_dma;
1045 dma_addr_t rx_dma;
1046 struct sg_table tx_sg;
1047 struct sg_table rx_sg;
1048
1049 unsigned dummy_data:1;
1050 unsigned cs_off:1;
1051 unsigned cs_change:1;
1052 unsigned tx_nbits:3;
1053 unsigned rx_nbits:3;
1054 unsigned timestamped:1;
1055 #define SPI_NBITS_SINGLE 0x01 /* 1-bit transfer */
1056 #define SPI_NBITS_DUAL 0x02 /* 2-bit transfer */
1057 #define SPI_NBITS_QUAD 0x04 /* 4-bit transfer */
1058 u8 bits_per_word;
1059 struct spi_delay delay;
1060 struct spi_delay cs_change_delay;
1061 struct spi_delay word_delay;
1062 u32 speed_hz;
1063
1064 u32 effective_speed_hz;
1065
1066 unsigned int ptp_sts_word_pre;
1067 unsigned int ptp_sts_word_post;
1068
1069 struct ptp_system_timestamp *ptp_sts;
1070
1071 struct list_head transfer_list;
1072 };? ? ? ? 而一次完整的SPI傳輸流程可能不是只包含spi_transfer,它可能包含一個或多個spi_transfer,這些spi_transfer最終通過spi_message組織在一起。
1107 struct spi_message {
1108 struct list_head transfers;
1109
1110 struct spi_device *spi;
1111
1112 unsigned is_dma_mapped:1;
1113
1114 /* spi_prepare_message() was called for this message */
1115 bool prepared;
1116
1117 /*
1118 * REVISIT: we might want a flag affecting the behavior of the
1119 * last transfer ... allowing things like "read 16 bit length L"
1120 * immediately followed by "read L bytes". Basically imposing
1121 * a specific message scheduling algorithm.
1122 *
1123 * Some controller drivers (message-at-a-time queue processing)
1124 * could provide that as their default scheduling algorithm. But
1125 * others (with multi-message pipelines) could need a flag to
1126 * tell them about such special cases.
1127 */
1128
1129 /* Completion is reported through a callback */
1130 int status;
1131 void (*complete)(void *context);
1132 void *context;
1133 unsigned frame_length;
1134 unsigned actual_length;
1135
1136 /*
1137 * For optional use by whatever driver currently owns the
1138 * spi_message ... between calls to spi_async and then later
1139 * complete(), that's the spi_controller controller driver.
1140 */
1141 struct list_head queue;
1142 void *state;
1143
1144 /* List of spi_res resources when the SPI message is processed */
1145 struct list_head resources;
1146
1147 /* For embedding transfers into the memory of the message */
1148 struct spi_transfer t[];
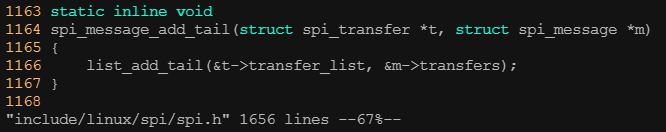
1149 };? ? ? ? 通過spi_message_init()可以初始化spi_message,而將spi_transfer添加到spi_message隊列的方法則是:
? ?? ?
?
? ? ? ? 發起一次spi_message的傳輸有同步和異步兩種方式,使用同步API時,會阻塞等待這個消息被處理完。同步操作時使用的API是: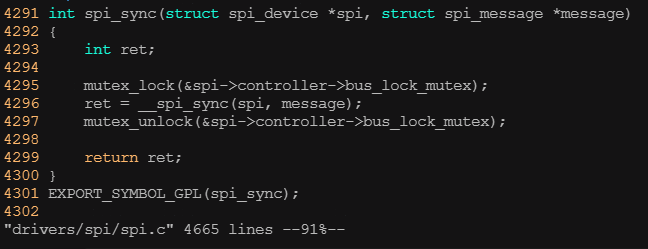 ?
?
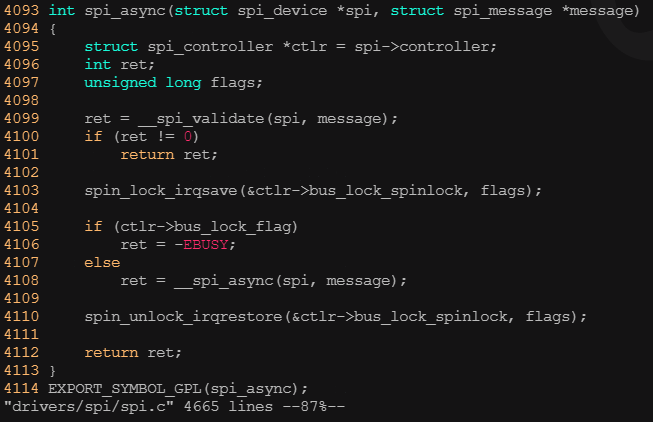
? ? ? ? 使用異步API時,不會阻塞等待這個消息被處理完,但是可以在spi_message的complete字段掛接一個回調函數,當消息被處理完成后,該函數會被調用。在異步操作時使用的API是:
? ? ?? ?
?
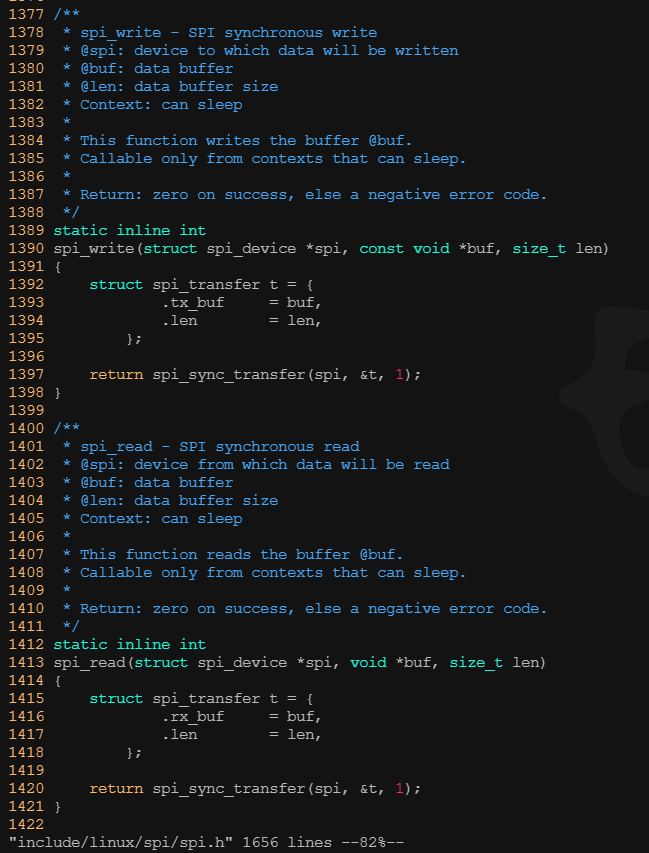
? ? ? ? 下圖是非常典型的初始化spi_transfer、spi_message并進行spi數據傳輸的例子,同時spi_write()、spi_read()也是spi核心層的兩個通用快捷API,在SPI外設驅動中可以直接調用它們進行簡單的純寫和純讀操作。
???????? ?
?
? ? ? ? SPI主機控制器驅動位于driver/spi/,這些驅動的主體是實現了spi_master的transfer()、transfer_one()、setup()這樣的成員函數,當然,也可能是實現spi_bitbang的txrx_bufs()、setup_transfer()、chipselect()這樣的成員函數。?下圖SPI主機端驅動完成的波形傳輸
摘取了./drivers/spi/spi-pl022.c的部分代碼。
1576 static int pl022_transfer_one_message(struct spi_controller *host,
1577 struct spi_message *msg)
1578 {
1579 struct pl022 *pl022 = spi_controller_get_devdata(host);
1580
1581 /* Initial message state */
1582 pl022->cur_msg = msg;
1583 msg->state = STATE_START;
1584
1585 pl022->cur_transfer = list_entry(msg->transfers.next,
1586 struct spi_transfer, transfer_list);
1587
1588 /* Setup the SPI using the per chip configuration */
1589 pl022->cur_chip = spi_get_ctldata(msg->spi);
1590 pl022->cur_cs = spi_get_chipselect(msg->spi, 0);
1591 /* This is always available but may be set to -ENOENT */
1592 pl022->cur_gpiod = spi_get_csgpiod(msg->spi, 0);
1593
1594 restore_state(pl022);
1595 flush(pl022);
1596
1597 if (pl022->cur_chip->xfer_type == POLLING_TRANSFER)
1598 do_polling_transfer(pl022);
1599 else
1600 do_interrupt_dma_transfer(pl022);
1601
1602 return 0;
1603 }1840 static int pl022_setup(struct spi_device *spi)
1841 {
1842 struct pl022_config_chip const *chip_info;
1843 struct pl022_config_chip chip_info_dt;
1844 struct chip_data *chip;
1845 struct ssp_clock_params clk_freq = { .cpsdvsr = 0, .scr = 0};
1846 int status = 0;
1847 struct pl022 *pl022 = spi_controller_get_devdata(spi->controller);
1848 unsigned int bits = spi->bits_per_word;
1849 u32 tmp;
1850 struct device_node *np = spi->dev.of_node;
..........
..........
2027 /* Stuff that is common for all versions */
2028 if (spi->mode & SPI_CPOL)
2029 tmp = SSP_CLK_POL_IDLE_HIGH;
2030 else
2031 tmp = SSP_CLK_POL_IDLE_LOW;
2032 SSP_WRITE_BITS(chip->cr0, tmp, SSP_CR0_MASK_SPO, 6);
2033
2034 if (spi->mode & SPI_CPHA)
2035 tmp = SSP_CLK_SECOND_EDGE;
2036 else
2037 tmp = SSP_CLK_FIRST_EDGE;
2038 SSP_WRITE_BITS(chip->cr0, tmp, SSP_CR0_MASK_SPH, 7);
2039
2040 SSP_WRITE_BITS(chip->cr0, clk_freq.scr, SSP_CR0_MASK_SCR, 8);
...........
...........
2057 err_config_params:
2058 spi_set_ctldata(spi, NULL);
2059 kfree(chip);
2060 return status;
2061 }2101 static int pl022_probe(struct amba_device *adev, const struct amba_id *id)
2102 {
2103 struct device *dev = &adev->dev;
2104 struct pl022_ssp_controller *platform_info =
2105 dev_get_platdata(&adev->dev);
2106 struct spi_controller *host;
2107 struct pl022 *pl022 = NULL; /*Data for this driver */
2108 int status = 0;
..........
..........
2133 /*
2134 * Bus Number Which has been Assigned to this SSP controller
2135 * on this board
2136 */
2137 host->bus_num = platform_info->bus_id;
2138 host->cleanup = pl022_cleanup;
2139 host->setup = pl022_setup;
2140 host->auto_runtime_pm = true;
2141 host->transfer_one_message = pl022_transfer_one_message;
2142 host->unprepare_transfer_hardware = pl022_unprepare_transfer_hardware;
2143 host->rt = platform_info->rt;
2144 host->dev.of_node = dev->of_node;
2145 host->use_gpio_descriptors = true;
2146
2147 /*
..........
..........
2239 err_spi_register:
2240 if (platform_info->enable_dma)
2241 pl022_dma_remove(pl022);
2242 err_no_irq:
2243 clk_disable_unprepare(pl022->clk);
2244 err_no_clk_en:
2245 err_no_clk:
2246 err_no_ioremap:
2247 amba_release_regions(adev);
2248 err_no_ioregion:
2249 spi_controller_put(host);
2250 return status;
2251 }? ? ? ? SPI外設驅動遍布內核的drivers、sound的各個子目錄之下,SPI只是一種總線,spi_driver的作用只是將SPI外設掛接在該總線上,因此在spi_driver的probe()函數中,將注冊SPI外設本身所屬設備驅動的類型。
? ? ? ? 和platform_driver對應一個platform_device一樣,spi_driver也對應一個spi_device,platform_device需要在BSP的板文件中添加板信息數據,而spi_device也同樣需要。spi_device的板信息用spi_board_info結構體描述,該結構體記錄著spi外設使用的主機控制器序號、片選序號、數據比特率、SPI傳輸模式(即CPOL、CPHA)等。諾基亞770上的兩個SPI設備的板信息數據如下圖所示,位于板文件的arch/arm/mach-omap1/board-nokia770.c中。
151 static struct spi_board_info nokia770_spi_board_info[] __initdata = {
152 [0] = {
153 .modalias = "lcd_mipid",
154 .bus_num = 2,
155 .chip_select = 3,
156 .max_speed_hz = 12000000,
157 .platform_data = &nokia770_mipid_platform_data,
158 .swnode = &nokia770_mipid_swnode,
159 },
160 [1] = {
161 .modalias = "ads7846",
162 .bus_num = 2,
163 .chip_select = 0,
164 .max_speed_hz = 2500000,
165 .swnode = &nokia770_ads7846_swnode,
166 },
167 };? ? ? ? 在linux啟動過程中,在機器的init_machine()函數中,會通過如下語句注冊這些spi_board_info:
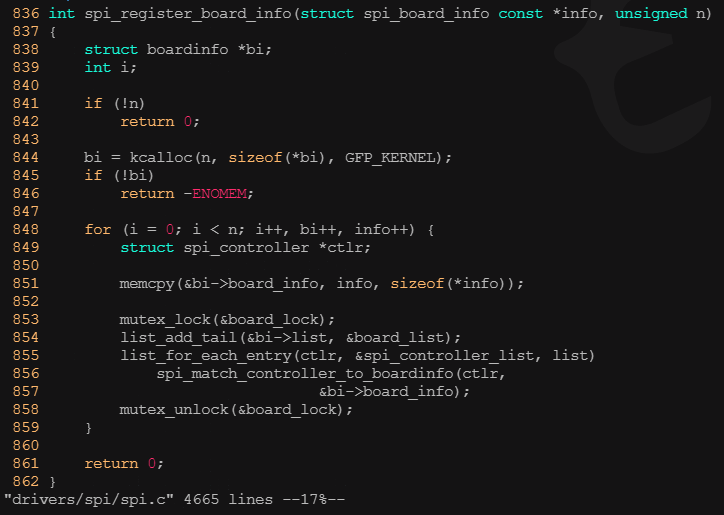
? ? ? ? 這一點和啟動時通過platform_add_device()添加platform_device非常相似。
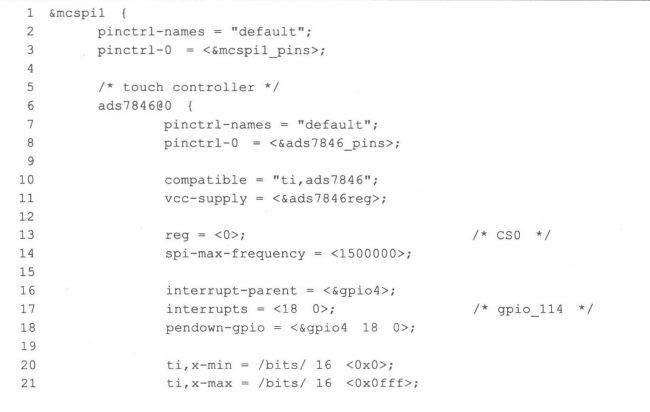
? ? ? ? ARM Linux 3.x之后的內核在改為設備樹,不再需要在arch/arm/mach-xxx中編碼SPI的板級信息了。而傾向于在SPI控制器節點下填寫子節點,如下圖通過設備樹添加SPI外設。
????????
???????? ?
?
????????



)



、淺拷貝,原理講解與示例代碼)

)
-- 基礎語法與數據類型)








