參考:
CompletableFuture原理與實踐-外賣商家端API的異步化 - 美團技術團隊
CompletableFuture 詳解 | JavaGuide
1.CompletableFuture介紹
CompletableFuture是由Java 8引入的,在Java8之前我們一般通過Future實現異步。
- Future用于表示異步計算的結果,只能通過阻塞或者輪詢的方式獲取結果,而且不支持設置回調方法,Java 8之前若要設置回調一般會使用guava的ListenableFuture,回調的引入又會導致臭名昭著的回調地獄。
- CompletableFuture對Future進行了擴展,可以通過設置回調的方式處理計算結果,同時也支持組合操作,支持進一步的編排,同時一定程度解決了回調地獄的問題。
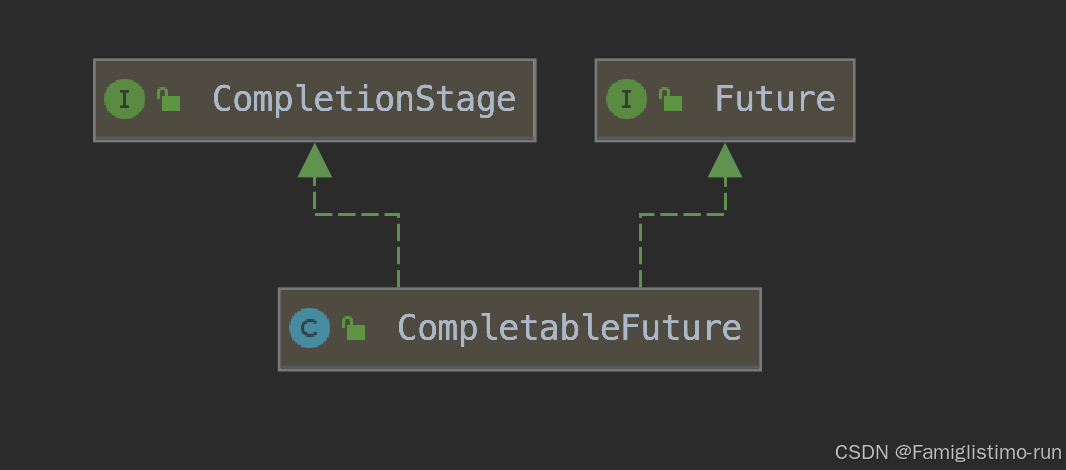
????????CompletableFuture實現了兩個接口(如上圖所示):Future、CompletionStage。Future表示異步計算的結果,CompletionStage用于表示異步執行過程中的一個步驟(Stage),這個步驟可能是由另外一個CompletionStage觸發的,隨著當前步驟的完成,也可能會觸發其他一系列CompletionStage的執行。從而我們可以根據實際業務對這些步驟進行多樣化的編排組合,CompletionStage接口正是定義了這樣的能力,我們可以通過其提供的thenAppy、thenCompose等函數式編程方法來組合編排這些步驟。
2.?CompletableFuture操作
2.1 使用
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
// 使用自定義線程池(推薦)
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
// 使用自定義線程池(推薦)
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);runAsync()?方法接受的參數是?Runnable?,這是一個函數式接口,不允許返回值。
supplyAsync()?方法接受的參數是?Supplier<U>?,這也是一個函數式接口,U?是返回結果值的類型。
2.2 處理異步計算的結果
????????當我們獲取到異步計算的結果之后,還可以對其進行進一步的處理,比較常用的方法有下面幾個:
thenApply()thenAccept()thenRun()whenComplete()
thenApply()?方法接受一個?Function?實例,用它來處理結果。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());
// 這次調用將被忽略。
future.thenApply(s -> s + "nice!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());????????如果你不需要從回調函數中獲取返回結果,可以使用?thenAccept()?或者?thenRun()。這兩個方法的區別在于?thenRun()?不能訪問異步計算的結果。
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenAccept(System.out::println);//hello!world!nice!CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenRun(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));//hello!???whenComplete()?的方法的參數是?BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable>?
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}
// 使用自定義線程池(推薦)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}2.3 異常處理
可以通過?handle()?方法來處理任務執行過程中可能出現的拋出異常的情況。
CompletableFuture<String> future= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");}return "hello!";
}).handle((res, ex) -> {// res 代表返回的結果// ex 的類型為 Throwable ,代表拋出的異常return res != null ? res : "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());還可以通過?exceptionally()?方法來處理異常情況。
CompletableFuture<String> future= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");}return "hello!";
}).exceptionally(ex -> {System.out.println(ex.toString());// CompletionExceptionreturn "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());

Ubuntu20.04復現KISS-ICP)

)
)



![P5967 [POI 2016] Korale 題解](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/P5967 [POI 2016] Korale 題解)










系統調用)