C
若序列為1 4 5 7 9 1 2 3,1 + 9一定大于1 + 1或1 + 4...所以只需要記錄當前數之前數字的最大值,然后遍歷取max即可,所以對于上面的序列有效的比較為1 + 9,2 + 9,3 + 9取max
代碼
//求大于當前數的最大值,然后取min即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N], mi[N];int T, n;
int main()
{cin >> T;while(T -- ){int ans = -1;cin >> n;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){cin >> a[i], mi[i] = max(a[i], mi[i - 1]);}for(int i = n; i >= 1; i --){if(mi[i - 1] > a[i])ans = max(ans, mi[i - 1] + a[i]);}//for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << mi[i] << ' ';if(ans == -1) cout << "0" << endl;else cout << ans << endl;}return 0;
}D
排序后尋找連續自然數的段數,答案就是段數-1
注意,當出現1?3 3 3 3?5 6 7,雖然自然數的段數為3,但是第二個段3 3 3 3前后都無絕對值之差為1的自然數,那么3 3 3 3的內部就需要互相連接才能保證與前后兩個段內的數進行互相連通,則答案為3(段數)?+ 3(內部相連) - 1(三段只需要兩條邊即可互相連通)
對于1 ?3 4 4 4?6 7,其中的每一個4都可以借助3與1進行互相連通,也可以借助最后一個4與6進行互相連通
代碼:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;//選用map的好處,可以記錄當前數字的個數,也等于變相去重
map<int, int> mp;
int t;
int n;void solve()
{cin >> n;mp.clear();for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){int x;cin >> x;mp[x] ++;}int ans = -1;for(auto & t : mp){int x = t.first, y = t.second;if(mp[x - 1] == 0)//當前數的前一個數不存在,則為一個單獨的段,答案+1{ans ++;if(mp[x - 1] == 0 && mp[x + 1] == 0)//前后都不存在,則該數字內部需要互相連通ans += y - 1;}}cout << ans << endl;
}int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cin >> t;while(t -- )solve();return 0;
}E
四種情況
1、只有兩行全為1
2、只有兩列全為1
3、一行一列全為1且交叉點為0
4、全為0
對上面四種情況分類討論即可,列出了一些簡單樣例
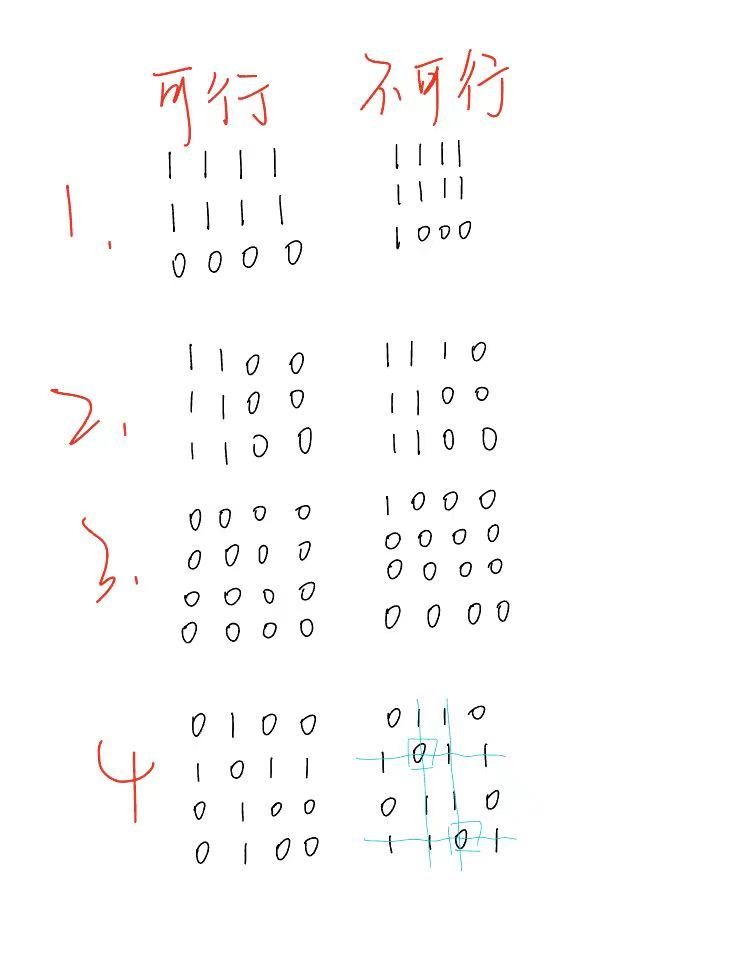
代碼:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1050;
int t;
map<int, int> mpx, mpy;//記錄每行以及每列中1的個數
int a[N][N];void solve()
{int n, m, ans = 0;memset(a, 0, sizeof a);mpx.clear(), mpy.clear();cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){string ch;//注意輸入格式,每行輸入為字符串cin >> ch;for(int j = 0; j < ch.size(); j ++){a[i][j] = (ch[j] == '1'? 1: 0);if(a[i][j]){ans ++;//記錄總體1的個數mpx[i] ++, mpy[j] ++;}}}bool st = true, sti = false, stj = false, stij = false;//若有兩行滿足全為1int mx = 0, my = 0, mxy = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) if(mpx[i] == m)mx ++;//只有僅有兩行全為1時才滿足條件,則此時所有1的個數應等于兩行1的個數sti = (mx == 2 && mx*m == ans ? true : false);//若有兩列滿足全為1for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++)if(mpy[j] == n)my ++;stj = (my == 2 && my*n == ans ? true : false);//同理int cnt = 0;//記錄一行一列時1的個數for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++){if(a[i][j] == 1) st = false;if(mpx[i] == m - 1 && mpy[j] == n - 1 && a[i][j] == 0){mxy ++;cnt += mpx[i] + mpy[j];}}//僅有一行一列滿足,無其他情況stij = (mxy == 1 && cnt == ans? true : false);//四類滿足一種即可if(sti || stj || stij || st) puts("YES");else puts("NO");return;
}int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cin >> t;while(t -- )solve();return 0;
}f等待補題ing
)


詳解:洪水猛獸的防御之道)



![[ctfshow web入門] web70](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[ctfshow web入門] web70)











:一文詳解three.js中的紋理映射UV)