類型:單鏈表,雙鏈表、循環鏈表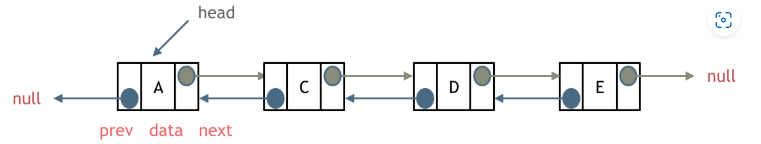
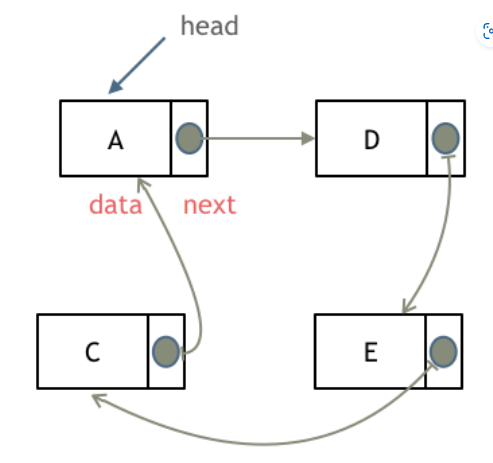
存儲:在內存中不是連續存儲
刪除操作:即讓c的指針指向e即可,無需釋放d,因為java中又內存回收機制
添加節點:?

鏈表的構造函數
public class ListNode {// 結點的值int val;// 下一個結點ListNode next;// 節點的構造函數(無參)public ListNode() {}// 節點的構造函數(有一個參數)public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}// 節點的構造函數(有兩個參數)public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val;this.next = next;}
}可以直接用java自帶的LinkedList類實現鏈表的初始化
import java.util.LinkedList;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建一個空的鏈表LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();// 向鏈表中添加元素list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);// 打印鏈表內容System.out.println(list);}
}
鏈表的聲明:
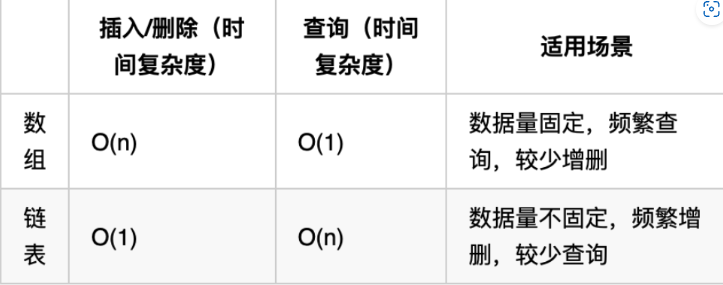
Java標準庫提供了LinkedList類,位于java.util包中。它的特點如下:
- 實現細節:
LinkedList底層通常實現為雙向鏈表,這意味著每個節點除了指向下一個節點,還保存對前一個節點的引用。 - 接口實現:除了實現
List接口外,LinkedList還實現了Deque接口,使其既可以當作列表使用,也可以當作隊列(或雙端隊列)使用。 - 增刪操作:
add(),remove(),offer(),poll()等方法在鏈表頭尾插入或刪除元素時性能較高。 - 遍歷操作:由于鏈表沒有下標索引,隨機訪問通常較慢。如果頻繁使用隨機訪問,可以考慮使用
ArrayList,ArrayList底層是基于動態數組實現的
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list1 =new LinkedList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list2 =new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList list3 = new LinkedList();?上述是常見的鏈表的聲明方式
第一種,變量的聲明類型和實際實現類型都是LinkedList,可直接調用 LinkedList 類中特有的方法,并且聲明了泛型Integer,確保只能存儲 Integer 類型的數據,編譯期間就能進行類型檢查,避免了類型轉換異常。
第二種,聲明類型是接口 List類型,實際實現的類型確實LinkedList,但只能調用 List 接口中定義的方法。如果需要使用 LinkedList 特有的方法(如隊列或雙端隊列相關的方法),則需要顯式地進行類型轉換。同樣使用了泛型 <Integer>,確保類型安全。
第三種聲明類型是接口List,實現的是ArrayList類型,ArrayList 支持快速隨機訪問,時間復雜度為 O(1)。在數組中間插入或刪除元素時需要移動元素,時間復雜度為 O(n);而 LinkedList 在任意位置添加或刪除(假如已經有相應節點引用)通常更高效。
第四種實現的是原始類型(因為沒有使用泛型),編譯器不會對集合中的數據進行類型檢查,
手搓鏈表
public class Linked {static class Node{int data;Node next;public Node(){};public Node(int data){this.data = data;this.next =null;}}public static class SingleLinkedList{private Node head;public void addFirst(int data){Node newNode = new Node(data);newNode.next = head;head = newNode;}public void addLast(int data){Node newNode = new Node(data);if(head ==null){head = newNode;return;}Node curr = head;while(curr.next != null){curr = curr.next;}curr.next = newNode;}public boolean remove(int data){if(head == null){//若鏈表為空,則刪除失敗return false;}if(head.data == data){//還要先判斷頭節點是否時要刪除的head = head.next;return true;}Node curr = head;while(curr.next != null && curr.next.data != data){curr = curr.next;}if (curr.next != null) {curr.next = curr.next.next;return true;}return false;}public void printList() {Node curr = head;while (curr != null) {System.out.print(curr.data + " ");curr = curr.next;}System.out.println("null");}}public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList list = new SingleLinkedList();list.addFirst(4);list.addFirst(3);list.addFirst(2);list.addFirst(1);list.addLast(5);list.addLast(6);list.printList();//1 2 3 4 5 6 nulllist.remove(6);list.printList();//1 2 3 4 5 null}
}
反轉鏈表
題意:反轉一個單鏈表。
示例: 輸入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 輸出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL,即右移
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {// 如果鏈表為空,則直接返回nullif(head == null){return null;}// prev指針初始化為null,最后會成為反轉后鏈表的頭節點ListNode prev = null;// cur指針指向當前要處理的節點,開始時指向鏈表頭headListNode cur = head;// temp用于保存當前節點cur的下一個節點,防止在改變指針關系后丟失引用ListNode temp = null;// 當當前節點不為空時,循環執行反轉操作while (cur != null) {// 保存cur的下一個節點,防止鏈表斷裂temp = cur.next; // 此時temp指向cur的下一節點// 將當前節點的next指針指向前一個節點,實現局部反轉cur.next = prev; // 當前節點的next由原來的下一個節點變為前一個節點// 將prev移動到當前節點位置,為下一次反轉操作做準備prev = cur;// 將cur后移到下一個節點,也就是之前保存的tempcur = temp;}// 循環結束后,prev指向反轉后的鏈表頭節點,返回它作為新的鏈表起點return prev;}
}
鏈表內兩兩交換
給定一個鏈表,兩兩交換其中相鄰的節點,并返回交換后的鏈表。
你不能只是單純的改變節點內部的值,而是需要實際的進行節點交換。
解1:
- 創建一個虛擬頭節點dummy指向head,定義current指針真相虛擬頭節點
- 進入循環體內,確定current每次后面都能有兩個節點進行交換操作
- 定義first和second分別指向第一個節點和第二個節點,
- 然后讓第二個節點指向第一個節點,第一個節點指向下一個要交換的第一個節點,最后讓current指向交換后的第一個節點
- 2,3,4循環操作,直至不夠節點互換退出循環,返回虛擬頭節點之后的head
public class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {// 創建啞結點,它的 next 指向原鏈表的頭ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy.next = head;ListNode current = dummy;// 循環條件:當前結點后面至少有兩個節點while (current.next != null && current.next.next != null) {// 定義要交換的兩個節點ListNode first = current.next;ListNode second = current.next.next;// 交換節點:// 1. 先將 first 指向 second 的下一個節點first.next = second.next;// 2. second 指向 firstsecond.next = first;// 3. current 指向 second,完成與前面的連接current.next = second;// 移動 current,跳過剛才交換的兩個節點current = first;}// 返回啞結點的 next,即新的頭節點return dummy.next;}
}
解2:將鏈表轉換為隊列處理,在重建鏈表
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}// 1. 將鏈表節點存入數組List<ListNode> nodes = new ArrayList<>();ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {nodes.add(current);current = current.next;}// 2. 在數組中交換相鄰節點for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size() - 1; i += 2) {// 交換nodes[i]與nodes[i+1]ListNode temp = nodes.get(i);nodes.set(i, nodes.get(i+1));nodes.set(i+1, temp);}// 3. 重建鏈表(根據交換后的數組重設每個節點的next指針)for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size() - 1; i++) {nodes.get(i).next = nodes.get(i + 1);}// 最后一個節點的next設為nullnodes.get(nodes.size() - 1).next = null;// 4. 返回新的鏈表頭(數組中第一個元素)return nodes.get(0);}
}










)








