目錄
一、什么是TopK問題
二、優先級隊列
優先級隊列介紹
代碼實現
三、使用優先級隊列解決TopK問題
四、快速選擇算法解決TopK問題
快速選擇
圖解快速選擇
代碼解決前k小個元素
五、優先級隊列與快速選則算法比較
優先級隊列
快速選擇
一、什么是TopK問題
TopK問題就是在一個數組中尋找出最小(大)的前K個數,或者尋找出第K大(小)的數
常見TopK問題圖示

常見TopK問題鏈接
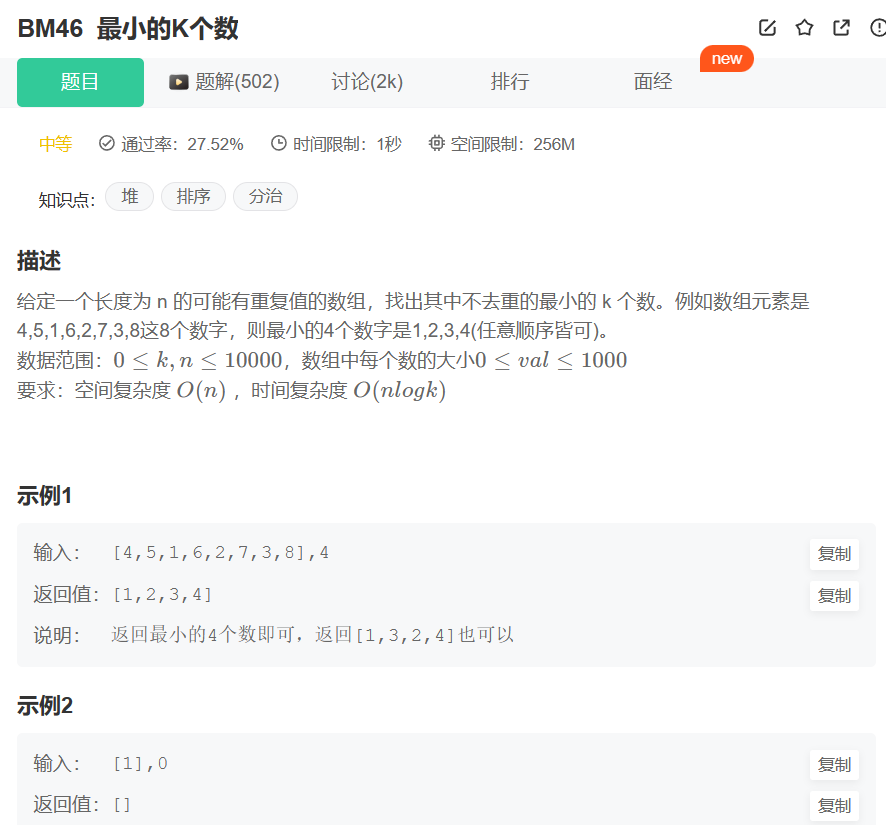
最小的K個數_牛客題霸_牛客網給定一個長度為 n 的可能有重復值的數組,找出其中不去重的最小的 k 個數。例如數組元素是。題目來自【牛客題霸】![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=295&tqId=23263&ru=/exam/oj&qru=/ta/format-top101/question-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=295&tqId=23263&ru=/exam/oj&qru=/ta/format-top101/question-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
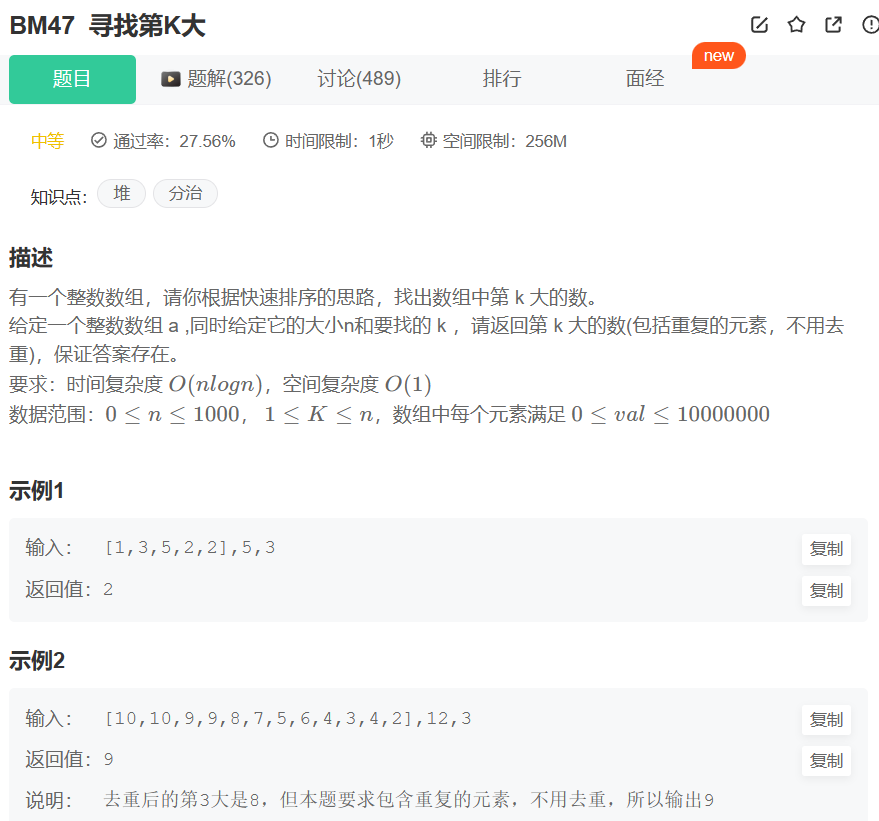
尋找第K大_牛客題霸_牛客網
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
二、優先級隊列
優先級隊列介紹
優先級隊列是一種數據結構,它根據元素的優先級來決定元素的插入和刪除順序。以下是一些關鍵特點:
- 基于優先級排序:每個元素在隊列中都有一個優先級,優先級最高的元素會首先被移除。
- 使用特定數據結構:優先級隊列通常可以使用堆(尤其是二叉堆)這種數據結構來實現,以保持隊列的有序狀態并高效地處理插入和刪除操作。
- 應用廣泛:它在很多算法中有廣泛應用,如任務調度、最短路徑尋找、事件驅動模擬等場合。
- 自定義比較:可以通過仿函數或運算符重載來支持自定義的數據類型和比較函數,從而定義元素的優先級。
- Java實現:在Java中,優先級隊列可以通過最小堆來實現,其中的元素按照自然順序或者根據提供的Comparator來確定優先級。
- 操作方法:主要操作包括插入元素(入隊)和刪除最高優先級的元素(出隊)。
- 性能優化:由于內部結構的優化,即使在大量元素的情況下,優先級隊列依然能夠快速地確定下一個要處理的元素。
總的來說,優先級隊列提供了一種有效的方式來管理那些需要按照特定順序處理的元素,是許多復雜算法和系統設計中不可或缺的工具。
優先級隊列博客
【數據結構】優先級隊列(堆)與PriorityQueue_unsortedpriorityqueue增加復雜度為1的getmax-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀504次,點贊2次,收藏2次。比如一組數據 1 2 3 4 5 6,我們將他創建成一個大根堆時,我們先從最后一個位置所在的樹開始進行調整,由于我們能獲取到數組的長度,且根據堆的性質父親節點的下標 * 2 + 1就孩子節點下標可知,知道孩子的下標(數組長度-1)就能知道父親的下標。比如我們在大根堆 4 3 2 2 1 1的堆里插入11,先將11存在最后,然后拿他與父親比較,如果大就交換,如果不比父親大那他就是大根堆不需要調整,此時交換后,要繼續更換父親與兒子的位置重復比較交換操作,直到孩子下標小于或者等于0時不在需要調整。_unsortedpriorityqueue增加復雜度為1的getmaxhttps://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/128423670?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522170929235016777224499491%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=170929235016777224499491&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-1-128423670-null-null.nonecase&utm_term=%E4%BC%98%E5%85%88%E7%BA%A7%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
代碼實現
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author 1886**/
public class PriorityQueue <T extends Comparable<T>> {// 優先級隊列底層模擬堆的數組private Object[] queue;// 記錄當前優先級隊列元素個數private int size;private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;/*** 默認構造方法*/public PriorityQueue() {this.queue = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];}/*** 指定大小* @param capacity*/public PriorityQueue(int capacity) {this.queue = new Object[capacity];}/*** 傳入指定數組* @param queue*/public PriorityQueue(T[] queue) {// 1.初始化成員變量this.queue = queue;this.size = queue.length;// 2.將數組進行大根堆調整HeapIfy();}
}
/*** @author 1886**/
public class PriorityQueue <T extends Comparable<T>> {// 優先級隊列底層模擬堆的數組private Object[] queue;// 記錄當前優先級隊列元素個數private int size;private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;/*** 默認構造方法*/public PriorityQueue() {this.queue = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];}/*** 指定大小* @param capacity*/public PriorityQueue(int capacity) {this.queue = new Object[capacity];}/*** 傳入指定數組* @param queue*/public PriorityQueue(T[] queue) {// 1.初始化成員變量this.queue = queue;this.size = queue.length;// 2.將數組進行大根堆調整heapIfy();}/*** 堆化*/private void heapIfy() {for (int parent = (this.size - 1 - 1) >> 1; parent >= 0; parent--) {siftDown(parent, this.size);}}/*** 向下調整* @param parent 父親節點下標* @param len 向下調整的結束位置*/private void siftDown(int parent, int len) {// 計算出孩子節點位置int child = parent * 2 + 1;// 開始向下調整while (child < len) {// 尋找出兩個孩子節點中最大的if (child + 1 < len && ((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[child + 1])) < 0) {child++;}// 與父親節點進行判斷,如果孩子節點比父親節點大就進行調整 否則調整完畢if (((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[parent])) < 0) {break;} else {T tmp = (T)queue[child];queue[child] = (T)queue[parent];queue[parent] = tmp;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}}}
}import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author 1886**/
public class PriorityQueue <T extends Comparable<T>> {// 優先級隊列底層模擬堆的數組private Object[] queue;// 記錄當前優先級隊列元素個數private int size;private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;/*** 默認構造方法*/public PriorityQueue() {this.queue = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];}/*** 指定大小* @param capacity*/public PriorityQueue(int capacity) {this.queue = new Object[capacity];}/*** 傳入指定數組* @param queue*/public PriorityQueue(T[] queue) {// 1.初始化成員變量this.queue = queue;this.size = queue.length;// 2.將數組進行大根堆調整heapIfy();}/*** 入隊操作* @param data 進入優先級隊列的數據*/public void offer(T data) {// 如果優先級隊列滿 進行擴容if (this.size == this.queue.length) {grow();}// 將元素放到末尾this.queue[this.size] = data;// 進行向上調整siftUp(this.size++);}/*** 出隊操作* @return*/public T poll() {// 如果為空就返回空if (this.size == 0) return null;// 將堆頂元素與最后一個位置進行交換T top = (T)queue[0];queue[0] = this.queue[this.size - 1];queue[this.size - 1] = top;// 刪除元素this.size--;// 向下調整siftDown(0, this.size);// 返回return top;}/*** 排序*/public void sort() {int len = this.size - 1;while (len >= 0) {T tt = (T) queue[0];queue[0] = queue[len];queue[len] = tt;siftDown(0, len--);}}/*** 堆化*/private void heapIfy() {for (int parent = (this.size - 1 - 1) >> 1; parent >= 0; parent--) {siftDown(parent, this.size);}}/*** 向上調整* @param child*/private void siftUp(int child) {// 計算出父親節點的下標int parent = (child - 1) / 2;// 開始向上調整while (child > 0) {if (((T)queue[child]).compareTo((T)queue[parent]) >= 0) {T tmp = (T)queue[child];queue[child] = (T)queue[parent];queue[parent] = tmp;child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;} else {break;}}}/*** 向下調整* @param parent 父親節點下標* @param len 向下調整的結束位置*/private void siftDown(int parent, int len) {// 計算出孩子節點位置int child = parent * 2 + 1;// 開始向下調整while (child < len) {// 尋找出兩個孩子節點中最大的if (child + 1 < len && ((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[child + 1])) < 0) {child++;}// 與父親節點進行判斷,如果孩子節點比父親節點大就進行調整 否則調整完畢if (((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[parent])) < 0) {break;} else {T tmp = (T)queue[child];queue[child] = (T)queue[parent];queue[parent] = tmp;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}}}/*** 擴容方法*/private void grow() {this.queue = Arrays.copyOf(this.queue, this.queue.length * 2);}private void display() {for (Object x : this.queue) {System.out.println(x);}}
}
三、使用優先級隊列解決TopK問題
從上面優先級隊列的介紹可知道,我們只需要創建出一個大小為K的優先級隊列。當我們求前K的最小的元素時,我們只需要創建出一個大小為K的大根堆。首先讓數組中k個元素進入堆中,然后從k+1開始遍歷數組,在遍歷過程中與堆頂的元素進行比較,這個時候堆頂的元素一定是這個堆中最大的一個,如果此時的值比堆頂的元素小就讓這個元素替換堆頂的元素,依次往復,在遍歷完整個數組后,這個堆中就會存儲前K個最小元素。相反如果要尋找出最小的前K個數就創建大根堆重復操作
前K小的元素
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution (int[] input, int k) {// write code hereArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();if (k <= 0 || input == null) return ret;PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(k, (o1, o2)->{return o2 - o1;});for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {if (i < k) queue.offer(input[i]);else {if (input[i] < queue.peek()) {queue.poll();queue.offer(input[i]);}}}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {ret.add(queue.poll());}return ret;}import java.util.*;/*** @author 1886**/public class Solution {static class PriorityQueue <T extends Comparable<T>> {// 優先級隊列底層模擬堆的數組private Object[] queue;// 記錄當前優先級隊列元素個數private int size;private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;/*** 默認構造方法*/public PriorityQueue() {this.queue = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];}/*** 指定大小* @param capacity*/public PriorityQueue(int capacity) {this.queue = new Object[capacity];}/*** 傳入指定數組* @param queue*/public PriorityQueue(T[] queue) {// 1.初始化成員變量this.queue = queue;this.size = queue.length;// 2.將數組進行大根堆調整heapIfy();}/*** 入隊操作* @param data 進入優先級隊列的數據*/public void offer(T data) {// 如果優先級隊列滿 進行擴容if (this.size == this.queue.length) {grow();}// 將元素放到末尾this.queue[this.size] = data;// 進行向上調整siftUp(this.size++);}/*** 出隊操作* @return*/public T poll() {// 如果為空就返回空if (this.size == 0) return null;// 將堆頂元素與最后一個位置進行交換T top = (T)queue[0];queue[0] = this.queue[this.size - 1];queue[this.size - 1] = top;// 刪除元素this.size--;// 向下調整siftDown(0, this.size);// 返回return top;}/*** 排序*/public void sort() {int len = this.size - 1;while (len >= 0) {T tt = (T) queue[0];queue[0] = queue[len];queue[len] = tt;siftDown(0, len--);}}/*** 堆化*/private void heapIfy() {for (int parent = (this.size - 1 - 1) >> 1; parent >= 0; parent--) {siftDown(parent, this.size);}}/*** 向上調整* @param child*/private void siftUp(int child) {// 計算出父親節點的下標int parent = (child - 1) / 2;// 開始向上調整while (child > 0) {if (((T)queue[child]).compareTo((T)queue[parent]) >= 0) {T tmp = (T)queue[child];queue[child] = (T)queue[parent];queue[parent] = tmp;child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;} else {break;}}}/*** 向下調整* @param parent 父親節點下標* @param len 向下調整的結束位置*/private void siftDown(int parent, int len) {// 計算出孩子節點位置int child = parent * 2 + 1;// 開始向下調整while (child < len) {// 尋找出兩個孩子節點中最大的if (child + 1 < len && ((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[child + 1])) < 0) {child++;}// 與父親節點進行判斷,如果孩子節點比父親節點大就進行調整 否則調整完畢if (((T)queue[child]).compareTo(((T)queue[parent])) < 0) {break;} else {T tmp = (T)queue[child];queue[child] = (T)queue[parent];queue[parent] = tmp;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}}}public T peek() {return this.size == 0 ? null : (T)queue[0];}/*** 擴容方法*/private void grow() {this.queue = Arrays.copyOf(this.queue, this.queue.length * 2);}private void display() {for (Object x : this.queue) {System.out.println(x);}}
}/*** 代碼中的類名、方法名、參數名已經指定,請勿修改,直接返回方法規定的值即可** * @param input int整型一維數組 * @param k int整型 * @return int整型ArrayList*/public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution (int[] input, int k) {// write code hereArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();if (k <= 0 || input == null) return ans;PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(k);for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {if (i < k) queue.offer(input[i]);else if (input[i] < queue.peek()) {queue.poll();queue.offer(input[i]);}}while (queue.peek() != null) {ans.add(queue.poll());}return ans;}
}四、快速選擇算法解決TopK問題
快速選擇
快速選擇算法(Quickselect)是用于在未排序的數組中查找第k小或第k大元素的高效算法,它的時間復雜度為O(n)。該算法與快速排序有密切的聯系,但它不對整個數組進行完整的排序,而是只關注于找到所需的特定順序的元素。以下是它的一些關鍵點:
- 基本思想:
- 選擇一個基準值(pivot),按照這個基準值將數組分為兩部分,左側部分的所有元素都小于等于基準值,右側部分的所有元素都大于基準值。
- 遞歸搜索:
- 確定基準值的位置后,根據k與基準值的位置關系,選擇數組的哪一部分繼續進行遞歸搜索。如果k小于基準值的索引,則在第一部分(小于等于基準值的部分)繼續搜索;否則,在第二部分(大于基準值的部分)繼續搜索。
- 時間復雜度:
- 快速選擇算法的平均時間復雜度為O(n),但最壞情況下的時間復雜度會退化到O(n^2)。盡管如此,由于其不需要完全排序數組,它在實際操作中通常比完全的排序算法更加高效。
- 實際應用:
- 快速選擇算法及其變種是在實際應用中最常使用的高效選擇算法之一,尤其適用于解決Top K問題等場景。
總的來說,快速選擇算法是一種基于快速排序的選擇算法,它高效地解決了在不完全排序的數組中尋找特定順序元素的問題,并因此在各種算法競賽和實際應用場景中得到了廣泛的使用。
圖解快速選擇
圖解
對下面這個數組尋找到前k小的元素
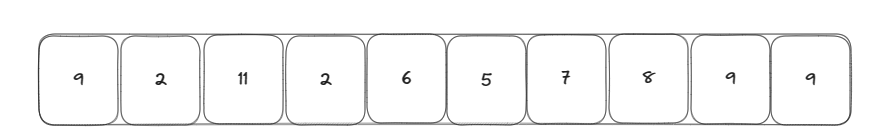
首先我隨機生成一個下標指向一個基準元素
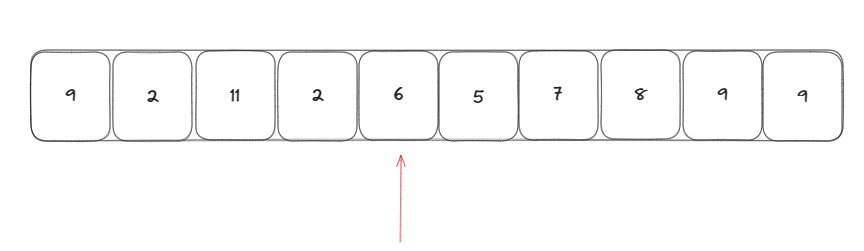
然后使用一個指針指向開始位置依次往后遍歷,如果當前元素比基準元素大則將該元素放在末尾,也就是基準元素后面,如果比當前元素小則將他放在基準元素前面
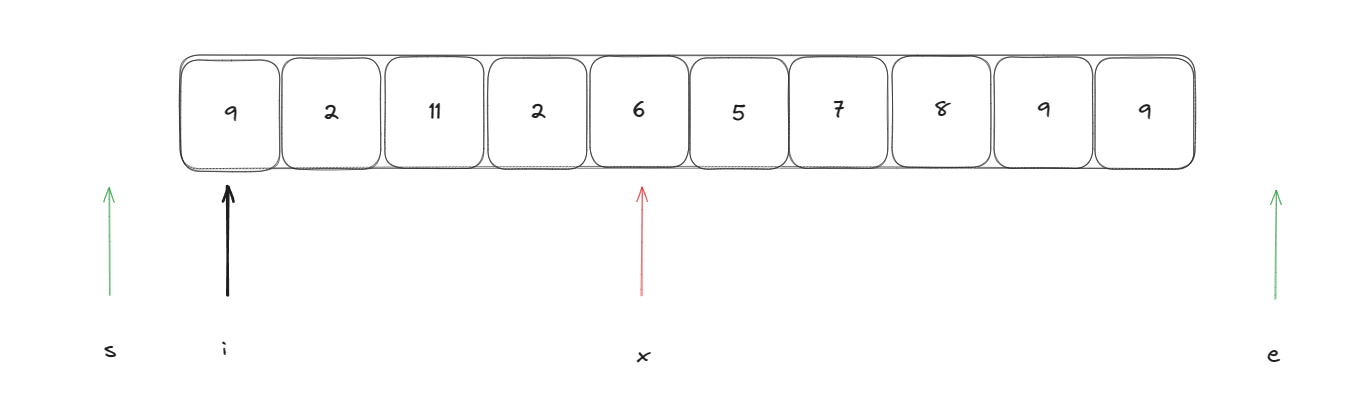
此時遍歷指針i指向的值比基準元素大,此時需要執行以下操作進行交換:swap(arr[--e], arr[i])
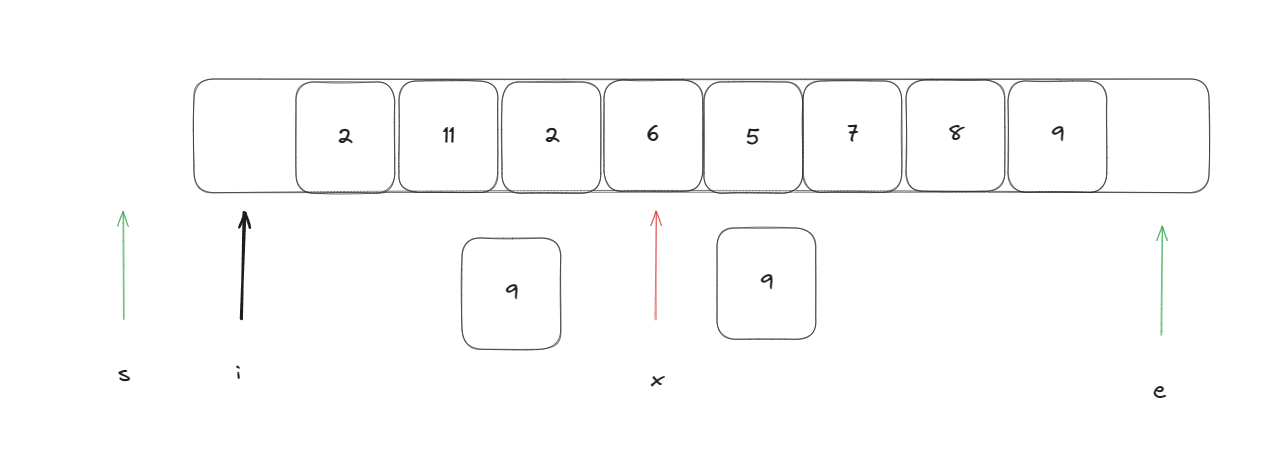
此時進行將遍歷指針指向的元素與基準元素進行比較依次重復此操作,當遍歷指針指向的元素比基準元素小時執行:swap(arr[i++], arr[++s]) ,當與基準元素相等時只需要執行i++即可。當遍歷指針與末尾指針e相遇時即可停止。
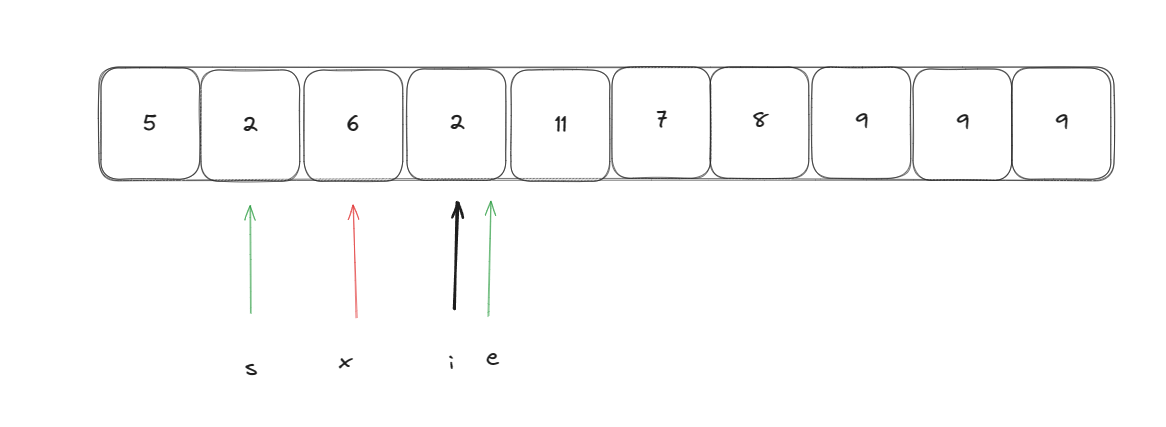
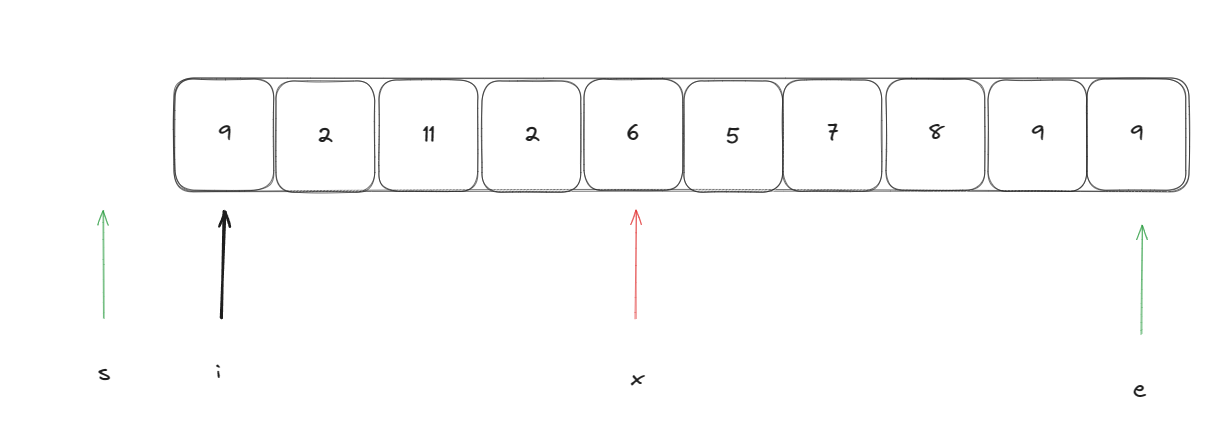
此時在l到s,e到r重復執行上述操作,知道l >= r時結束遞歸就是基于快速選擇的快排算法。但是此時我們需要尋找前k小個元素,而數組已經被分成了三部分
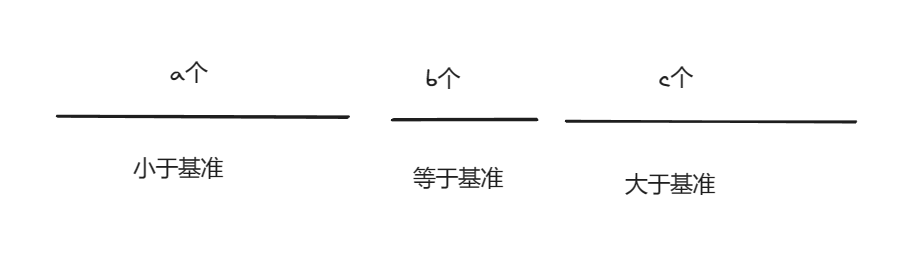
此時我們可以通過判斷k是否小于等于a,如果k小于等于a那么前k小的元素一定是在左邊這段區域,如果k小于等于a+b時說明此時第k小就在中間這個區域,只需要返回他就可以。如果上面兩種情況都不成立,那么我們只需要區右邊區域找到第k - a - b個最小的元素,找到該元素后,該元素之前的元素就是最小的K個數
代碼解決前k小個元素
最小的K個數_牛客題霸_牛客網給定一個長度為 n 的可能有重復值的數組,找出其中不去重的最小的 k 個數。例如數組元素是。題目來自【牛客題霸】![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=295&tqId=23263&ru=/exam/oj&qru=/ta/format-top101/question-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=295&tqId=23263&ru=/exam/oj&qru=/ta/format-top101/question-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
/*** 代碼中的類名、方法名、參數名已經指定,請勿修改,直接返回方法規定的值即可** * @param input int整型vector * @param k int整型 * @return int整型vector*/
int rand_num(int l, int r) {srand(time(0));return rand() % (r - l + 1) + l;
}int qselect(vector<int>& arr, int l, int r, int k) {if (l >= r) return arr[l];int i = l, s = l - 1, e = r + 1, x = arr[rand_num(l,r)];while (i < e) {if (arr[i] > x) swap(arr[i], arr[--e]);else if (arr[i] < x) swap(arr[i++], arr[++s]);else i++;}int a = s - l + 1, b = e - s - 1;if (a >= k) return qselect(arr, l, s, k);else if (a + b >= k) return x;else return qselect(arr, e, r, k - a - b);
}vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int>& input, int k) {// write code herevector<int> ans(k);if (k <= 0 || input.size() < 1) return ans;qselect(input, 0, input.size() - 1, k);for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) ans[i] = input[i];return ans;
}
};null有一個整數數組,請你根據快速排序的思路,找出數組中第 k 大的數。 給定一個整數數組。題目來自【牛客題霸】![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/e016ad9b7f0b45048c58a9f27ba618bf?tpId=295&tqId=44581&ru=%2Fpractice%2F6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf&qru=%2Fta%2Fformat-top101%2Fquestion-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/e016ad9b7f0b45048c58a9f27ba618bf?tpId=295&tqId=44581&ru=%2Fpractice%2F6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf&qru=%2Fta%2Fformat-top101%2Fquestion-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj
import java.util.*;public class Solution {/*** 代碼中的類名、方法名、參數名已經指定,請勿修改,直接返回方法規定的值即可*** @param a int整型一維數組* @param n int整型* @param K int整型* @return int整型*/private int randNum(int l, int r) {Random random = new Random();return l + random.nextInt(r - l + 1);}private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {int t = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = t;}private int qSelect(int[] arr, int l, int r, int k) {if (l >= r) return arr[l];int i = l, s = l - 1, e = r + 1, x = arr[randNum(l, r)];while (i < e) {if (arr[i] > x) swap(arr, i, --e);else if (arr[i] < x) swap(arr, ++s, i++);else i++;}int c = r - e + 1, b = e - s - 1;if (c >= k) return qSelect(arr, e, r, k);else if (b + c >= k) return x;else return qSelect(arr, l, s, k - c - b); }public int findKth (int[] a, int n, int K) {// write code herereturn qSelect(a, 0, n - 1, K);}
}五、優先級隊列與快速選則算法比較
優先級隊列
使用優先級隊列(通常實現為堆)解決TopK問題的時間復雜度是O(NlogK)。具體分析如下:
- 建堆:首先對K個元素進行建堆操作,建堆的時間復雜度是O(K)。這是因為堆的構建過程涉及到對K個元素進行排序,以形成一個最大堆或最小堆。
- 維護堆:然后遍歷剩余的N-K個元素,對于每個元素,執行堆調整操作以維護堆的性質。每次插入或刪除操作的時間復雜度是O(logK),因為堆的高度大約是logK,而單次堆調整的時間復雜度與堆的高度成正比。因此,對于N-K個元素的遍歷,總的時間復雜度是O((N-K)logK)。
- 總時間復雜度:綜合以上兩個步驟,總的時間復雜度是O(K + (N-K)logK),由于通常情況下K遠小于N,可以簡化為O(NlogK)。
快速選擇
快速選擇算法的平均時間復雜度是 O(N),但最壞情況下的時間復雜度是 O(N^2)。以下是關于快速選擇算法時間復雜度的詳細分析:
- 平均時間復雜度:
- 在平均情況下,快速選擇算法的時間復雜度是O(N)。這是因為每次分區操作平均只需要遍歷數組的一半長度。在快速選擇算法中,我們選擇一個樞紐元素(pivot),并將數組分為兩部分,一部分包含小于樞紐的元素,另一部分包含大于樞紐的元素。這個過程與快速排序相似,但是快速選擇只遞歸地處理包含第K小元素的那一部分數組,而不是整個數組。由于每次遞歸調用處理的數組大小大約減半,所以平均時間復雜度為O(N)。
- 最壞情況時間復雜度:
- 在最壞的情況下,如果每次選擇的樞紐都是最大或最小元素,那么每次分區操作只能減少一個元素的大小,導致需要進行N次分區操作,因此最壞情況下的時間復雜度是O(N^2)。為了減少這種情況的發生,可以通過隨機選擇樞紐來提高算法的效率。
- 優化措施:
- 為了優化快速選擇算法并避免最壞情況的發生,可以采用“中位數的中位數”作為樞紐,這種方法被稱為BFPRT算法。通過計算近似中位數并將其作為樞紐,可以有效地將數組分為大致相等的兩部分,從而保持算法的平均時間復雜度。
- 數學推導:
- 快速選擇算法的時間復雜度也可以通過數學歸納法進行推導。可以將數組分成若干組,每組選取中位數,然后從中選取中位數的中位數作為樞紐。這樣的分組策略可以保證至少有一部分數組的大小顯著減少,從而在數學上證明算法的平均時間復雜度為O(N)。具體的推導過程涉及到遞歸式和分組策略的詳細分析。

)
)






——常用標簽(1))


 詳解)






