leetcode hot 100
- 雙指針
- 1.三數之和
- 2.接雨水
- 多維動態規劃
- 1.最長公共子序列
雙指針
1.三數之和
三數之和
排序 + 雙指針的方法,固定一個數nums[i], 用兩數和找target -= nums[i] 的數需要注意兩點:
1.需要去掉重復數字
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[--l]);
while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[++r]);
....
while (i < n - 1 && nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) i++;
2.如果用這種方法去掉重復數字,那么一定要先執行 l++ && r–再去執行去重,防止有不重復數字死循環的情況發生
l++, r--;
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l - 1]) l++;
while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r + 1]) r--;
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());int n = nums.size();vector<vector<int>> ans;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int l = i + 1, r = n - 1;int tmptar = -nums[i];while (l < r) {if (nums[l] + nums[r] < tmptar) {l++;} else if (nums[l] + nums[r] > tmptar) {r--;} else {ans.push_back({nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]});l++, r--;while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l - 1]) l++;while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r + 1]) r--;}}while (i < n - 1 && nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) i++;}return ans;}
};
2.接雨水
接雨水
- 圖1位置的水位由2,3位置決定
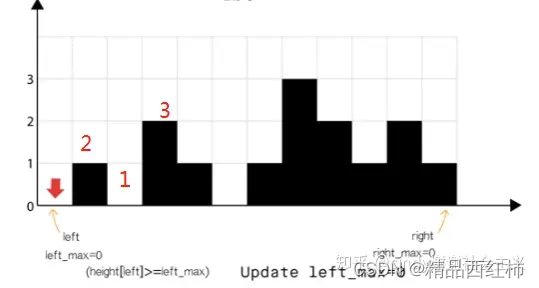
- 雙指針相向尋找,需要找到當前遍歷過的、左右兩側的最大高度l_max, r_max
- 如果 l_max 小于 r_max,那么左側一定能夠積水,如果 l_max 大于 r_max,右側一定能夠積水
- 左側,只有當前的高度height[l] < l_max時才能夠有積水,否則例如 [0,1,2,3,4,5]是沒辦法形成積水的
- 同理,右側,只有當前的高度height[r] < r_max時才能夠有積水
class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {int n = height.size();int l = 0, r = n - 1, l_max = 0, r_max = 0, ans = 0;while (l <= r) {if (l_max < r_max) {l_max = max(l_max, height[l]);if (l_max > height[l]) {ans += l_max - height[l];}l++; } else {r_max = max(r_max, height[r]);if (r_max > height[r]) {ans += r_max - height[r];}r--;}}return ans;}
};
多維動態規劃
1.最長公共子序列
1)確定狀態:對于兩個字符串的動態規劃問題,套路是通用的。
比如說對于字符串 s1 和 s2,它們的長度分別是 m、n,一般來說都要構造一個這樣的 DP table:dp[m + 1][n + 1]
2)轉移方程:對于 text1:abcde 和 text2:ace 兩個字符串,我們定義兩個指針進行遍歷 i 和 j。
遍歷 text1 長度為 m,定義指針 i,從 0~m。固定 i 指針(i == 1)位置,接下來開始遍歷 text2 長度為 n,定義指針 j,從 0~n。
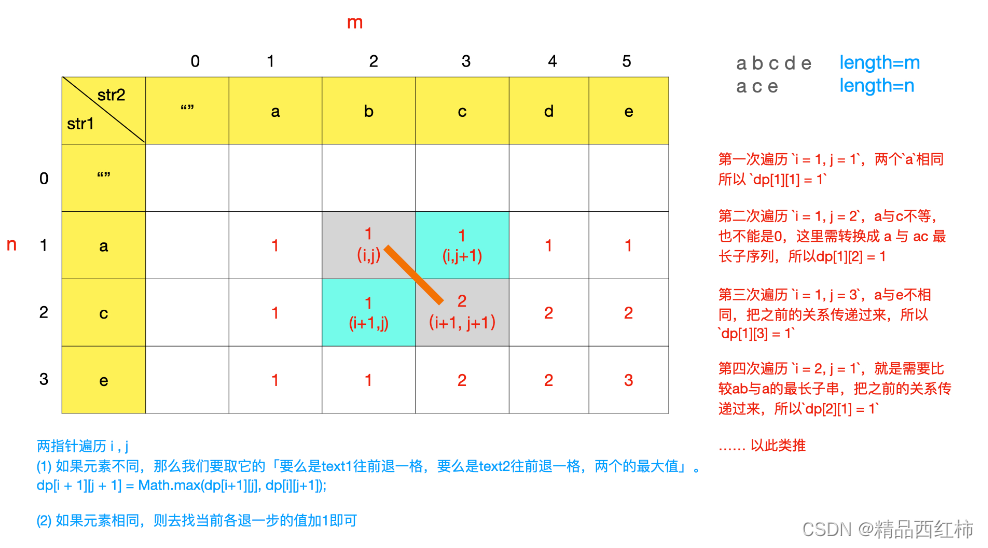
第一次遍歷 i = 1, j = 1,兩個a相同所以 dp[1][1] = 1
第二次遍歷 i = 1, j = 2,a與c不等,也不能是0,這里需轉換成 a 與 ac 最長子序列,這里需要把之前的關系傳遞過來,所以dp[1][2] = 1
第三次遍歷 i = 1, j = 3,a與e不相同,把之前的關系傳遞過來,所以dp[1][3] = 1
text2:ace 已經走完來第一輪,接下來text1:abcde 走到來b字符。
第四次遍歷 i = 2, j = 1,就是需要比較ab與a的最長子串,把之前的關系傳遞過來,所以dp[2][1] = 1
我們會發現遍歷兩個串字符,當不同時需要考慮兩層遍歷前面的值(關系傳遞),也就是左邊和上邊的其中較大的值,當相同時,需要考慮各自不包含當前字符串的子序列長度,再加上1。
因此可以得出:
現在對比的這兩個字符不相同的,那么我們要取它的「要么是text1往前退一格,要么是text2往前退一格,兩個的最大值」
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]);
對比的兩個字符相同,去找它們前面各退一格的值加1即可:dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
3)邊界條件:dp[0][X] = 0, dp[X][0] = 0;
4)計算順序:先行后列
class Solution {
public:int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {int n = text1.size(), m = text2.size();vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1, 0));for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) {for (int j = 1; j < m + 1; j++)if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1])dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j -1]);}return dp[n][m];}
};


)





,fgets(),get_s()))










)