一、常量與變量
常量:程序中使用的具體的數、字符。在運行過程中,值無法更改
變量:表示一一個存儲單元,其中存儲的值可以修改 如:a=5,b=6
變量命名:
1、只能包含字母、數字、下劃線
2、只能以字母、下劃線開頭
3、不要使用關鍵字作為變量名稱
?
二、基礎數據類型
整數: int
浮點數: float (存在誤差)
字符串: str
布爾: bool
獲取變量類型: type函數
強制類型轉換 :
整數: int()
浮點數: float ()
字符串: str()
布爾: bool()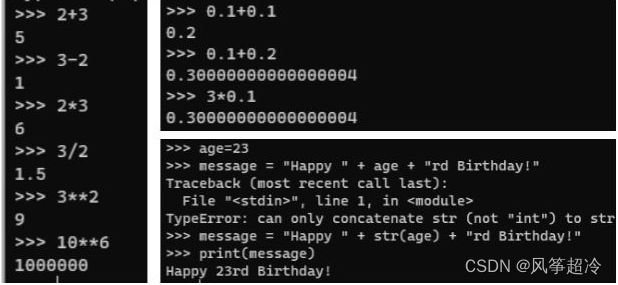
三、 數據類型轉換
int轉float:直接轉換? 7 -> 7.0
float轉int:舍棄小數
int轉bool:非0: True、 0: False
bool轉int: False: 0、 True: 1
轉str:直接轉換
四、常用運算符
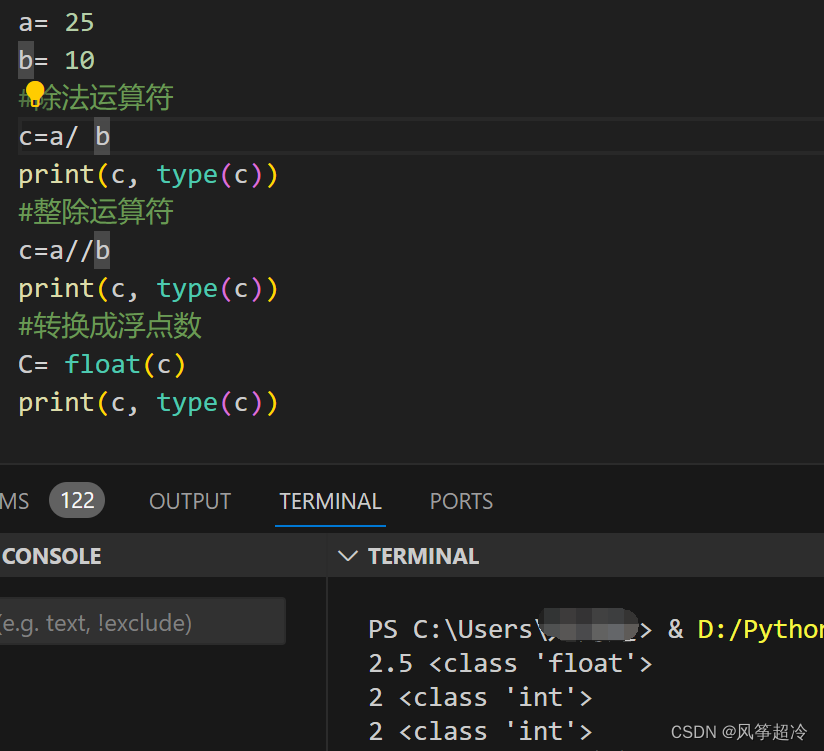
算術運算符:+、-、*、/、//(整除)、%(求余)、**(冪)
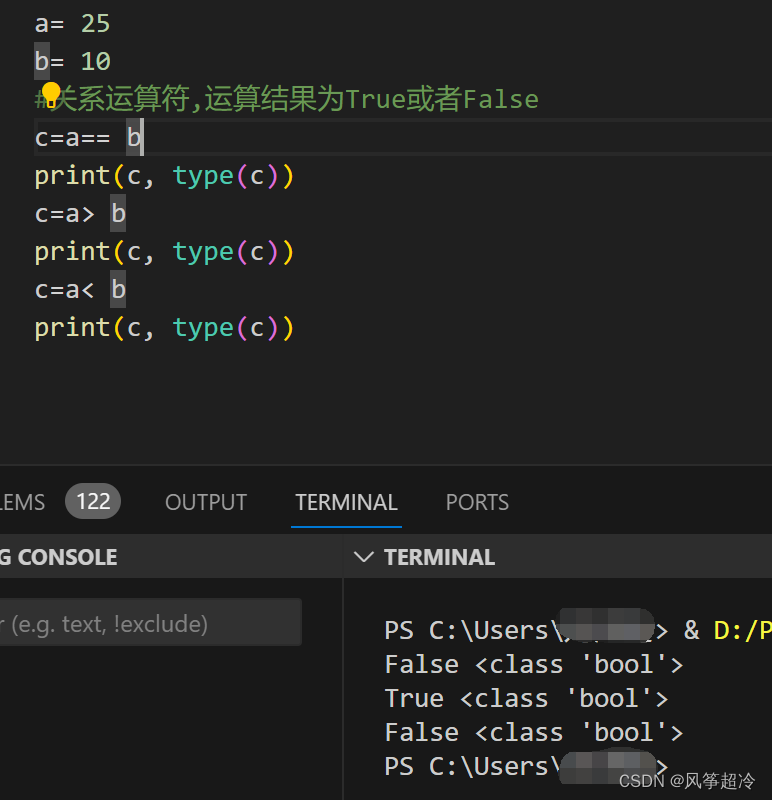
關系運算符:>、<、==、!=、>=、<=
賦值運算符: =、+=、-=、
*=、/=、%=、//=、**=
邏輯運算符: and、 or、 not

成員運算符: in、 not in
身份運算符: is、 is not?
五、輸入輸出 函數
print()用于打印輸出,是最常見的一個函數。
語法: print(*objects, sep=' ', end="\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
參數說明:
1、objects:表示輸出一個或者多個對象。輸出多個對象需要用sep分隔。
2、sep:輸出多個對象時使用sep分隔,默認值是一一個空格。
3、end: 輸出結束以end結尾,默認值是換行符\n,可以換成其他字符串。
print(1)
print("Hello World")
a= 1
b= 'runoob '
print(a,b)
print("aa","bbb" )
print("aa" ,"bbb")
print("www",lanqiao, "cn",sep="+") #設置間隔符
input()輸入輸出函數
語法: input([prompt])
參數說明: prompt: 提示信息
輸入的變量均為str字符串類型
int()可以轉換成整數
a = input("請進行輸入:")
print(a,type(a))a = int(input("請進行輸入:"))
print(a,type(a))
?
?六、選擇結構
if語句
if condition:# 在條件滿足時執行的代碼塊# 可以是一條語句或多條語句,必須相同縮進級別
elif another_condition:# 如果上一個條件不滿足,但是這個條件滿足時執行的代碼塊# elif子句是可選的,可以有一個或多個
else:# 如果上面的條件都不滿足時執行的代碼塊# else子句也是可選的
Python使用縮進來表示代碼塊的層次結構,因此在if語句中,每個代碼塊都必須有相同的縮進級別。
在Python中可以在一個if語句塊內部嵌套另一個if語句:
x = 10
y = 5if x > 5:print("x is greater than 5")if y > 2:print("y is also greater than 2")else:print("y is not greater than 2")
else:print("x is not greater than 5")
for語句
range() 函數用于生成一系列數字,在 Python 中常用于 for 循環中,以便迭代一系列數字。
range(start, stop, step)
start:可選參數。序列的起始值,默認為0。stop:必需參數。序列的結束值。該值不包括在序列中。step:可選參數。序列的步長或增量值,默認為1。
range() 函數返回一個數字序列,從 start 開始,以 step 遞增,直到但不包括 stop。
for num in range(10, 0, -1):print(num)
for num in range(2, 10, 2):print(num)
for 變量 in 序列:執行代碼塊
變量:在每次迭代中,將序列中的元素賦值給變量。序列:可以是列表、元組、字符串等序列類型,或者是可迭代對象。執行代碼塊:在每次迭代中,執行縮進的代碼塊,這是循環體。
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for fruit in fruits:print(fruit)sum() 函數是 Python 內置函數之一
sum(iterable, start=0)
iterable:必需,一個可迭代的對象,如列表、元組等。start:可選,默認為0,指定初始值。
sum實現奇數求和
n = int(input("請輸入整數 n(實現n以內奇數求和):"))
result = sum( range(1,n+1,2))
print(result)
while語句
while 條件:執行代碼塊
條件是一個表達式,如果該表達式的值為True,則繼續執行循環體中的代碼塊;如果為False,則退出循環,繼續執行循環之后的代碼。執行代碼塊是循環體,包含在while循環中要重復執行的代碼。
total = 0
num = 1
while num <= 5:total += numnum += 1
print("1 到 5 的和為:", total)
?![]()
輾轉相除法?
輾轉相除法,也稱為歐幾里德算法,是一種用于計算兩個整數的最大公約數(Greatest Common Divisor,GCD)的算法。其基本原理是利用整數除法的性質以及兩個數的除余操作。
輾轉相除法的步驟如下:
- 將兩個整數中較大的數除以較小的數,并計算余數。
- 將較小的數與余數進行同樣的操作,直到余數為 0。
- 當余數為 0 時,最后一次的除數就是兩個整數的最大公約數。
def gcd(a, b):while b != 0:a, b = b, a % breturn a# 例子
num1 = 48
num2 = 18
print("48 和 18 的最大公約數是:", gcd(num1, num2))
初始時,a 為較大的數,b 為較小的數
break 和 continue
break 和 continue 是 Python 中用于控制循環的兩個關鍵字。
break 關鍵字:
break關鍵字用于跳出當前所在的最內層循環(for 或 while 循環),并繼續執行循環之后的代碼。- 當
break被執行時,循環立即終止,不再執行循環體中未執行的代碼,也不會繼續下一次循環。 break通常用于在滿足某些條件時強制退出循環,提前結束循環的執行。-
for i in range(5):if i == 3:breakprint(i)
continue 關鍵字:
continue關鍵字用于跳過當前循環中的剩余代碼,并直接進入下一次循環的迭代。- 當
continue被執行時,循環中continue之后的代碼不會被執行,而是直接開始下一次循環迭代。 continue通常用于在某些條件下跳過當前循環迭代,繼續下一次迭代。-
for i in range(5):if i == 2:continueprint(i)

七、基礎數據結構?
?7.1 列表
列表的創建
列表使用方括號 [] 來表示,其中的元素用逗號 , 分隔。
# 創建一個空列表
my_list = []# 創建一個包含整數元素的列表
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# 創建一個包含字符串元素的列表
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']# 列表中的元素可以是不同類型的
mixed_list = [1, 'apple', True, 3.14]
訪問列表元素
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']print(my_list[0]) # 輸出:'apple'
print(my_list[1]) # 輸出:'banana'
print(my_list[2]) # 輸出:'cherry'
列表的切片?
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# 獲取索引 1 到 3 的子列表(不包括索引 3)
sub_list = my_list[1:3]
print(sub_list) # 輸出:[2, 3]
修改列表元素
列表是可變的,可以通過索引來修改其中的元素。
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']my_list[1] = 'orange'
print(my_list) # 輸出:['apple', 'orange', 'cherry']
添加元素到列表
可以使用 append() 方法向列表末尾添加新元素,也可以使用 insert() 方法在指定位置插入新元素。
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']my_list.append('orange')
print(my_list) # 輸出:['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'orange']my_list.insert(1, 'grape')
print(my_list) # 輸出:['apple', 'grape', 'banana', 'cherry', 'orange']
刪除列表元素
可以使用 del 關鍵字、remove() 方法或 pop() 方法刪除列表中的元素。?
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']del my_list[1]
print(my_list) # 輸出:['apple', 'cherry']my_list.remove('cherry')
print(my_list) # 輸出:['apple']deleted_element = my_list.pop(0)
print(deleted_element) # 輸出:'apple'
print(my_list) # 輸出:[]
7.2 元組
在 Python 中,元組(Tuple)是一種有序、不可變的數據結構,用于存儲一組元素。元組使用圓括號 () 來表示,其中的元素用逗號 , 分隔。元組與列表相似,但元組是不可變的,即創建后不能修改、添加或刪除其中的元素。
元組的創建
元組使用圓括號 () 來表示,其中的元素用逗號 , 分隔。
# 創建一個空元組
my_tuple = ()# 創建一個包含整數元素的元組
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)# 創建一個包含字符串元素的元組
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')# 元組中的元素可以是不同類型的
mixed_tuple = (1, 'apple', True, 3.14)
訪問元組元素
元組中的元素可以通過索引來訪問,索引從 0 開始。
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')print(my_tuple[0]) # 輸出:'apple'
print(my_tuple[1]) # 輸出:'banana'
print(my_tuple[2]) # 輸出:'cherry'
元組的切片
可以使用切片操作從元組中獲取子元組。
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)# 獲取索引 1 到 3 的子元組(不包括索引 3)
sub_tuple = my_tuple[1:3]
print(sub_tuple) # 輸出:(2, 3)
元組的不可變性
元組是不可變的,一旦創建后,就不能修改其中的元素。
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')# 嘗試修改元組中的元素會引發錯誤
my_tuple[1] = 'orange' # TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
7.3 字符串(字符串對象不支持修改)
在Python中,字符串是一種表示文本數據的數據類型,它是一系列Unicode字符的有序序列。字符串可以由單引號(')、雙引號(")或三引號(''' 或 """)來表示。
字符串的創建
可以使用單引號、雙引號或三引號來創建字符串。
# 使用單引號創建字符串
single_quoted_string = 'Hello, world!'# 使用雙引號創建字符串
double_quoted_string = "Hello, world!"# 使用三引號創建多行字符串
multi_line_string = '''This is a
multi-line
string.'''
字符串的訪問
字符串中的每個字符都有一個索引,索引從0開始。
my_string = "Hello, world!"print(my_string[0]) # 輸出:H
print(my_string[7]) # 輸出:w
字符串的切片
可以使用切片操作從字符串中獲取子字符串。
my_string = "Hello, world!"print(my_string[1:5]) # 輸出:ello
字符串的拼接
可以使用 + 運算符來拼接字符串。
string1 = "Hello, "
string2 = "world!"combined_string = string1 + string2
print(combined_string) # 輸出:Hello, world!
字符串的常用方法
Python自帶方法:
????????字符串長度: 使用 len() 方法可以獲取字符串的長度。
字符串內部函數:
????????字符串大小寫轉換:
upper(): 將字符串中的所有字符轉換為大寫。lower(): 將字符串中的所有字符轉換為小寫。capitalize(): 將字符串的第一個字符轉換為大寫,其他字符轉換為小寫。
my_string = "Hello, World!"print(my_string.upper()) # 輸出:HELLO, WORLD!
print(my_string.lower()) # 輸出:hello, world!
print(my_string.capitalize()) # 輸出:Hello, world!
????????字符串查找和替換:
find(substring): 查找子字符串在原字符串中的位置,如果找到返回索引值,否則返回 -1。replace(old, new): 將字符串中的指定子字符串替換為新的子字符串。
my_string = "Hello, world!"print(my_string.find("world")) # 輸出:7
print(my_string.find("Python")) # 輸出:-1new_string = my_string.replace("world", "Python")
print(new_string) # 輸出:Hello, Python!
????????字符串分割和連接:
split(delimiter): 將字符串根據指定的分隔符拆分成多個子字符串,并返回一個列表。join(iterable): 將可迭代對象中的字符串元素連接成一個字符串,以原字符串為連接符。
my_string = "apple,banana,orange"split_string = my_string.split(",")
print(split_string) # 輸出:['apple', 'banana', 'orange']my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
joined_string = ",".join(my_list)
print(joined_string) # 輸出:apple,banana,orange
????????字符串去除空白:
strip(): 去除字符串兩端的空白字符。lstrip(): 去除字符串左端的空白字符。rstrip(): 去除字符串右端的空白字符。
my_string = " Hello, world! "print(my_string.strip()) # 輸出:Hello, world!
print(my_string.lstrip()) # 輸出:Hello, world!
print(my_string.rstrip()) # 輸出: Hello, world!
字符串的格式化
可以使用字符串的格式化方法來創建具有動態內容的字符串。
name = "Alice"
age = 30formatted_string = f"My name is {name} and I am {age} years old."
print(formatted_string) # 輸出:My name is Alice and I am 30 years old.
使用 in 檢查成員關系
in運算符用于檢查某個值是否存在于序列中,如果存在,則返回True,否則返回False。
my_string = "Hello, world!"print('H' in my_string) # 輸出:True
print('X' in my_string) # 輸出:False
使用 not in 檢查非成員關系
not in運算符用于檢查某個值是否不存在于序列中,如果不存在,則返回True,否則返回False。
my_string = "Hello, world!"print('H' not in my_string) # 輸出:False
print('X' not in my_string) # 輸出:True
字符串轉義字符
\n:換行符,將光標移動到下一行開頭。\t:制表符,用于在文本中插入水平制表符。- \ : 續行符?

\\:反斜杠,用于插入一個反斜杠字符。\':單引號,用于插入一個單引號字符。\":雙引號,用于插入一個雙引號字符。
print("Hello\nWorld!")
# 輸出:
# Hello
# World!print("This is a\ttabbed\ttext.")
# 輸出:This is a tabbed text.print("C:\\path\\to\\file.txt")
# 輸出:C:\path\to\file.txtprint('He\'s a good boy.')
# 輸出:He's a good boy.print("She said, \"Hello!\"")
# 輸出:She said, "Hello!"
字符串強制轉換為List?
s = "hello world"
print(list(s)) #['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']一行輸入兩個整數
s = input().split()a , b = list( map(int , s) )
print( a, b ) #1 2一行輸入多個整數
s = input().split()a = list(map(int , s))
print(a)修改字符串的常用方法
????????使用切片替換部分內容:
s = "hello, world"
s = s[:5] + "Python" # 將 "hello" 替換為 "Python"
print(s) # 輸出: "Python, world"
????????使用字符串的 replace() 方法:
s = "hello, world"
s = s.replace("hello", "Python")
print(s) # 輸出: "Python, world"
????????使用列表操作,然后使用字符串的 join() 方法
s = "hello, world"
s_list = list(s)
s_list[0] = 'P' # 替換第一個字符
s = ''.join(s_list)
print(s) # 輸出: "Pello, world"
????????使用字符串的格式化方法:
s = "hello, world"
s = "{} {}".format("Python", s.split(" ")[1])
print(s) # 輸出: "Python, world"
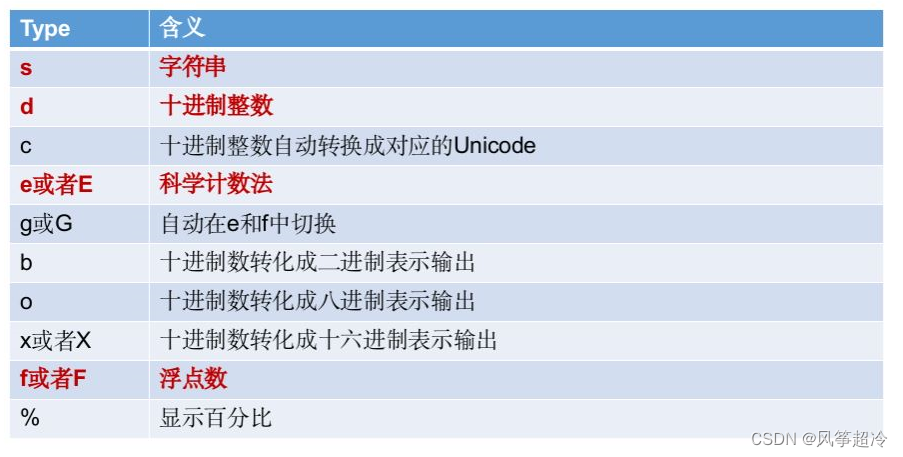
format 格式化
formatted_string = "Some text with {} and {}".format(value1, value2)
formatted_string = "Some text with {1} and {0}".format(value1, value2)
pi = 3.141592653589793
formatted_pi = "Value of pi: {:.2f}".format(pi) # 控制小數點后保留兩位
print(formatted_pi) # Output: Value of pi: 3.14

 ?
?
'''python實現下列需求開放式編程:對于給定的一.大段不規范的英文文本,對其進行排版:單詞和單詞之間有一個空格句子中的符號和前一個單詞之間沒有空格句子之間一一個空格分隔句子首字母大寫,其他字母小寫按照換行符劃分段落,輸出時每段空兩個空格輸出時每行80個字符,對于單個單詞-行超過80個單詞,直接下一-行輸出該單詞
'''
def format_text(text):formatted_text = ""paragraphs = text.split('\n\n') # 根據換行符劃分段落for paragraph in paragraphs:lines = []words = paragraph.split()line_length = 0line = ""for word in words:if line_length + len(word) + 1 <= 80: # 考慮空格的長度if line_length == 0:line += word.capitalize()else:line += " " + word.lower()line_length += len(word) + 1else:lines.append(line)line = word.capitalize()line_length = len(word)lines.append(line)formatted_paragraph = " ".join(lines) # 每段空兩個空格formatted_text += formatted_paragraph + "\n\n"return formatted_text# 示例文本
unformatted_text = """
this is a test. i am writing a python program to format text.
it's a simple program, but it should work well.
let's see how it goes.
"""formatted_text = format_text(unformatted_text)
print(formatted_text)
7.4 字典?
鍵: key, 值: value, 通過key來找value, key必須唯一, 因此同一個key只能對應著一個value
- Python中用{}表示字典,可以使用{}創建一個字典
- 字典中的key和value之間用冒號:分隔,元素之間用逗號,分隔。
- 字典的key只能為數字、字符串、元組,大多數情況使用字符串作為key
- 如果鍵重復,那么重復鍵對應的值后面會把前面的值覆蓋掉,但是位
置還是原來的位置 - value的類型沒有限制
#創建了一個空字典
a={}
print("type (a) = ", type (a) )
print("a = ", a)
#創建字典
a = {'a':123, 'b' :456, 0:789}
print("type (a) = ", type (a))
print("a = ", a)'''
type (a) = <class 'dict'>
a = {}
type (a) = <class 'dict'>
a = {'a': 123, 'b': 456, 0: 789}
'''擴展: 不定長參數(位置參數和關鍵字參數)
def func(*args):print(args)func(1,2,3,4)def func( a, *args ):print( args )func( 1, 2, 3, 4 )def func( *args, a ):print( args )func( 1, 2, 3, a = 4 )def func( a, **args ): #參數以字典形式傳輸,雙星號不定長放到關鍵字參數后print( args )func( a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, d = 4 )創建字典的六種方式
① 直接在空字典 {} 里面寫鍵值對
a = {'name': 'Tom', 'age': 28}
print(a)
② 定義一個空字典,再往里面添加鍵值對
a = {} # a = dict()
a['name'] = 'Tom'
a['age'] = 28
print(a)
③ 把鍵作為關鍵字傳入
a = dict(name="Tom", age=28)
print(a)
④ 可迭代對象方式來構造字典
a = dict([("name", "Tom"), ("age", 28)]) # 這里用元組/列表/集合都是可以的
print(a)
⑤ 通過 zip() 把對應元素打包成元組,類似于上一種方法
?
a = dict(zip(["name", "age"], ["Tom", 28]))
print(a)⑥ 利用類方法 fromkeys() 創建
d = my_dict( name = 'Tony', age = 28, height = 188 )
print( d )
dict(**kwarg) / dict(mapping) / dict(iterable)
用于創建一個字典并返回
print(dict(one=1, two=2, three=3)) # 傳入關鍵字來構造字典
print(dict(zip(["one", "two", "three"], [1, 2, 3]))) #映射函數方式來構造字典
print(dict([("one", 1), ("two", 2), ("three", 3)])) # 可迭代對象方式來構造字典def my_dict( **kwargs ):return kwargsd = my_dict( name = 'Tony', age = 28, height = 188 )
print( d )d = dict( name = 'Tony', age = 28, height = 188 )
print( d )
zip(*iterables)
- 返回一個元組的迭代器,其中的第 i 個元組包含來自每個可迭代對象
- 的第 i 個元素
- 當所輸入可迭代對象中最短的一個被耗盡時,迭代器將停止迭代
- 不帶參數時,它將返回一個空迭代器
- 當只有一個可迭代對象參數時,它將返回一個單元組的迭代器
result1 = zip( "abcd", "efgh" )
print(list( result1 ))result2 = zip( "abcd", "efg" )
print(list( result2 ))result3 = zip( )
print(list( result3 ))result4 = zip( "abcd" )
print(list( result4 ))字典的對象方法
????????
?7.5 集合
Python中的集合和數學中的集合概念一樣, 存儲不重復的元素。
集合中的元素都是唯一的,互不相同。
集合中只能存儲不可變的數據:數字、字符串、元組。
Python用{}表示集合,其中的元素用逗號分隔。
Python集合可以改變,不是序列,是無序的。
創建集合的方式:
- {元素1,元素2,元素3...}:把大括號中的所有元素構造成一個集合,如果有重復元素,只保留1個
- {}: 這是空字典,不是空集合
- set(x): 把x轉換成集合,x一般為列表、元組等
- set(): 空集
set([iterable])
●返回一個新的set對象,其元素來自于iterable, 如果未指定
iterable,則將返回空集合
frozenset([iterable])
●返回一個新的frozenset對象,即不可變的集合,其元素來自于
iterable,如果未指定參數,則返回凍結的空集合
●作用: set中的元素必須是不可變類型的,而frozenset是可以作為set元素的
利用集合特性進行 去重 和 關系測試
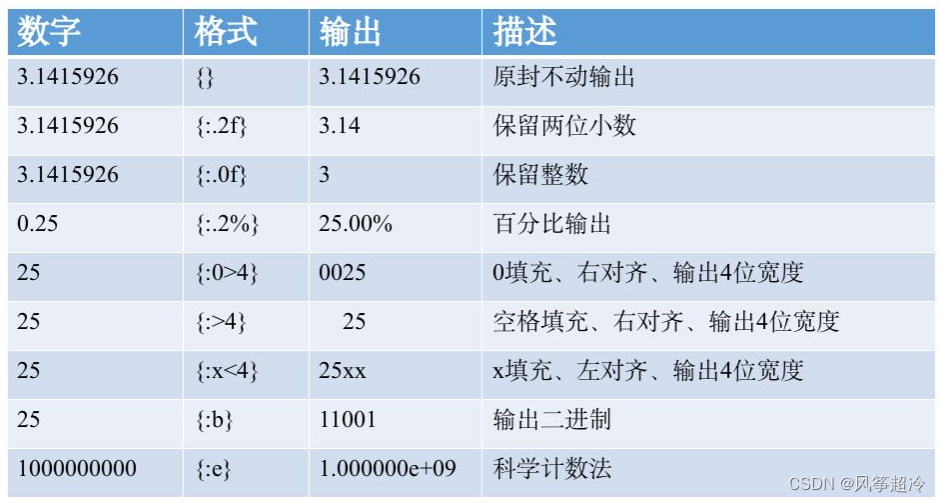
#把一個列表變成集合,就會自動去掉重復的元素
li=[1, 2, 5, 7, 7, 4, 5]
a = set( li )
print(a)
#測試多組集合數據之間的交集、差集、并集等關系
a =set("abdefga")
b = set("abc")
c = set("aef")
print(c <= a)
#判斷c是否是a的子集
print(a - b)
#返回a和b的差集
print(a| b)
#返回a和b的并集
print(a & b)
#返回a和b的交集
print(a ^ b)
#返回a和b中不同時存在的元素(對稱差)
print(a | b| c)
?集合對象的方法 set frozenset對象都可用
????????isdisjoint(other)
????????●other: Iterable
????????●如果集合中沒有與other共有的元素則返回True(注意變量類型)
str1 = "145"
list1 = [1, 4]
dic1 = {1:"1"}
set1 = {"1", 2, 3}
print(set1. isdisjoint(str1) )
#False
print(set1. isdisjoint(list1))
#True
print(set1. isdisjoint(dic1) )
#True
fset = frozenset(["1", 2, 3])
print(fset. isdisjoint(str1))
print(fset. isdisjoint(list1) )
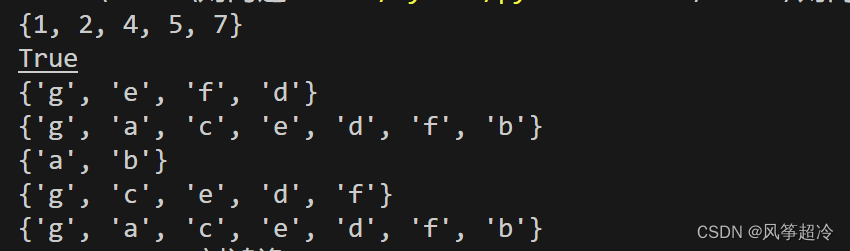
print(fset. isdisjoint(dic1) ) ?????????issubset(other)
?????????issubset(other)
????????●other: Iterable
????????●如果集合中的每個元素都在other之中,則返回True .
????????●對應的運算符版本set <= other要求參數為集合
str1 = "132"
list1 = [1, 4, "1", "2"]
dic1 = {1:"1", 2:"2"}
set1 = {"1", "2"}
print(set1. issubset(str1) )
#True
print(set1. issubset(list1) )
#True
print(set1. issubset(dic1) )
# False
fset = frozenset(["1", "2"])
print(fset. issubset(str1) )
print(fset. issubset(list1) )
print(fset. issubset(dic1) ) ?????????issuperset(other)
?????????issuperset(other)
????????●other: Iterable
????????●如果other中的每個元素都在集合之中,則返回True
????????●對應的運算符版本set >= other要求參數為集合
str1 = "12"
list1 = [1, "2"]
dic1 = {1:"1", 2:"2"}
set1 = {"1", "2", 1, 3}
print( set1.issuperset(str1) )
#True
print(set1. issuperset(list1) )
#True
print(set1. issuperset(dic1) )
# False
fset = frozenset(["1", "2", 1, 3])
print(fset. issuperset(str1) )
print(fset. issuperset(list1))
print(fset. issuperset(dic1) )
 ?????????union(*others)
?????????union(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●返回一個新集合,其中包含來自原集合以及others指定的所有集合中的元素(即并集)
????????●對應的運算符版本set|other|...要求參數為集合
s1 = {'a', 'c', 'f', 1, 2, 3}
print(s1.union('acf123', {4:5, 6:7}))????????intersection(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●返回一個新集合,其中包含原集合以及others指定的所有集合中共有的元素(即交集)
????????●對應的運算符版本set & other & ...要求參數為集合
s1 = {'a', 'c', 'f', 1, 2, 3}
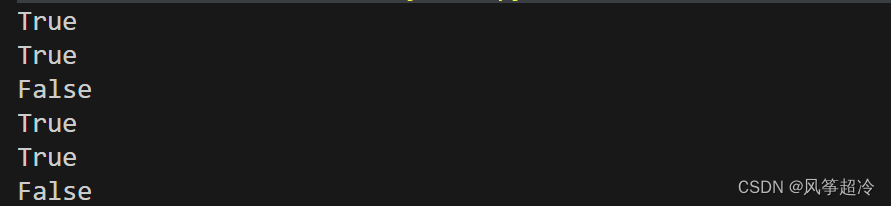
print(s1.intersection('acf123'))????????difference(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●返回一個新集合,其中包含原集合中在others指定的其他集合中不存在的元素(即差集)
????????●對應的運算符版本set - other- ... 要求參數為集合
str1 = "12"
list1 = [1, "2"]
dic1 = {"1":1, "2":2}
set1 ={"1", "2", 1, 3}
print(set1.difference(str1, list1, dic1) )
fset = frozenset(["1", "2", 1, 3] )
print( fset. difference(str1, list1, dic1))
????????symmetric_ difference(other)
????????●other: Iterable
????????●返回一個新集合,其中的元素或屬于原集合或屬于other指定的其他集合,但不能同時屬于兩者(即對稱差)
????????●對應的運算符版本set^ other要求參數為集合
?
集合遍歷操作:
- 與遍歷list一樣, for x in a,其中a是set, x是循環變量
- s.clear():清空集合
- X in S:
- 判斷是否存在
- len(s):集合元素個數
s = {1,2 ,3,4}
for x in s:print (x)
print ( sum(s), max(s) , min(s) )?集合對象的方法 僅set 對象都可用
????????set.update(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●更新集合,添加來自others中的所有元素
????????set.intersection_ _update(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●更新集合,只保留其中在所有others中也存在的元素.
?
????????set.difference_ update(*others)
????????●others: Iterable
????????●更新集合,移除其中也存在于任意一個others中的元素
?
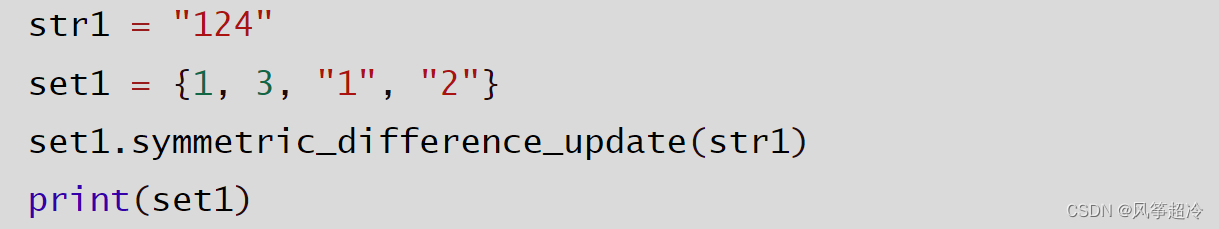
????????set.symmetric_ difference_ update(other)
????????●other: Iterable
????????●更新集合,只保留存在于一-方而非共同存在的元素
?
????????set. add(elem)
????????●將元素elem添加到集合中。如果元素已經存在,則沒有影響
?
????????set.remove(elem)
????????●從集合中移除元素elem。 如果elem不存在于集合中則會引發KeyError
?
????????set.discard(elem)
????????●從集合中移除元素elem。如果elem不存在于集合中則不做任何操作
?
????????set.pop()
????????●從集合中移除并返回任意一個元素。如果集合為空則會引發KeyError ?????????set.clear()
?????????set.clear()
????????●從集合中移除所有元素

s = {1, 2, 3}
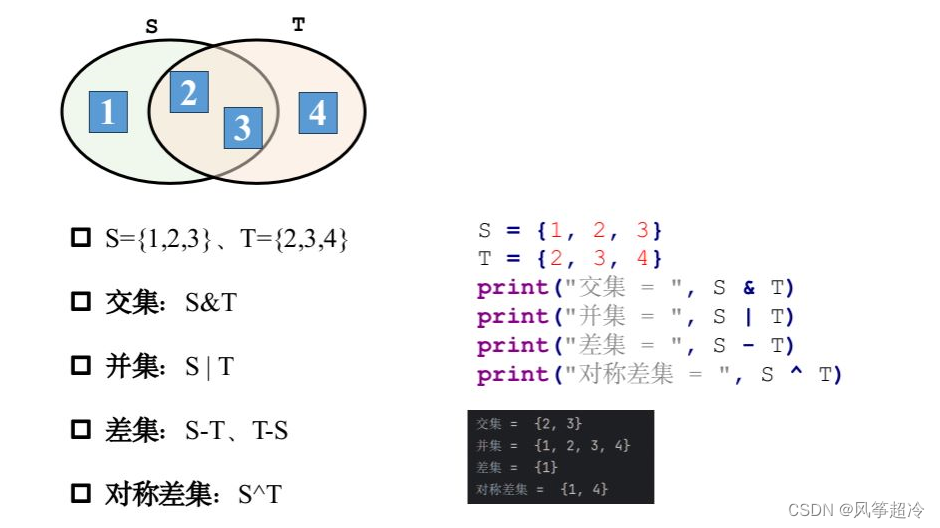
t = {2, 3, 4}print ( "交集:", s.intersection(t) )
print ( "并集:", s.union(t) )
print ("差集:", s.difference(t) )
print ("對稱集:", s.symmetric_difference(t) )輸入若干數字,將所有元素去重后輸出數字:
s = list (map(int, input().split()))
a = set (s)
print (a)'''
維護-一個數據結構管理表格,初始-個n行m列的表格,元素均為
空,需要完成若干次操作:set x y value:將表格第x行第y列設置為valuefindxy:查詢第x行第y列對應的值del x y:刪除第x行第y列的值Many value:查找value 是否在表格中,如果在表格中則出現次
數為多少
'''


















