目錄
PromptBench簡介
PromptBench的快速模型性能評估
PromptBench數據集介紹
PromptBench模型介紹
PromptBench模型加載遇到的問題
第一次在M1 Mac上加載模型
vicuna和llama系列模型
PromptBench各個模型加載情況總結
PromptBench的Prompt快速工程
chain of thought
emotion prompt
expert prompt
generated knowledge
least to most
PromptBench對抗性Prompt評估
PromptBench的動態評估
PromptBench總結
大語言模型真是火啊,火到每次我跟別人提到prompt(prangpt)這個單詞,都有人糾正我的讀法(promout),真討厭(你看懂我怎么讀的了么,不過不重要)。prompt又叫做提示語,在用大語言模型的過程中,是必不可少的輸入,它可以是一個問題、一段描述或者一些格式化的文本組合。優化prompt的目的通常是希望模型可以返回更加準確或者有針對性的輸出。不知道你有沒有聽過prompt工程師😳,大概就是要通過各種方式,整一個好的prompt讓結果一級棒。不過很多大能們都提到說,prompt engineering只是生成式AI的一個臨時狀態,畢竟大家還是希望最終形式是跟模型用自然語言溝通,不加條條框框的那種。
不過目前,在大語言模型應用的過程中,prompt工程師還是扮演著一定重要的角色。為了得到更好的結果,如果沒辦法改變LLM的性能,那只能從Prompt入手,并且需要系統性得在不同模型和數據集上測試其效果和魯棒性。
23年底的時候,微軟出了一個叫做PromptBench的GitHub項目(GitHub - microsoft/promptbench: A unified evaluation framework for large language models),一看就能猜出來這可能是要測prompt的bench mark,也就是看看這個prompt寫的好不好(這是一件關于evaluation的事情),項目有關論文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.07910。微盤鏈接:文件分享。本人主要是在家沒事干,翻paper的時候看到了這個東西,決定體驗一下。看完這篇文章,你不僅能了解一些LLM測試任務中常常使用的數據集,已成為歷史LLM的一些模型介紹,Prompt engineers的門門道道。
PromptBench簡介
首先,GitHub上作者們是這么描述PromptBench所能提供的功能:
1. 快速模型性能評估:可以快速構建模型、加載數據集和評估模型性能。
2. 快速工程:多種快速工程方法,例如:Few-shot Chain-of-Thought、情緒提示、專家提示等。
3. 評估對抗性提示:集成了提示攻擊,使研究人員能夠模擬對模型的黑盒對抗性提示攻擊并評估其魯棒性。
4. 動態評估:以減輕潛在的測試數據污染:集成了動態評估框架 DyVal ,動態生成具有受控復雜性的評估樣本。
簡單看看論文里描述Prompt Bench的框架圖(具體如下),可以發現,這個Prompt Bench給大家提供了一些benchmark所需的數據集和模型,看起來是可以直接調用的。

然后我們依次看看這些都是什么東西,以及怎么用。
Promptbench使用python3.9以上的版本,pip安裝即可:
pip install promptbench
PromptBench的快速模型性能評估
大家可以直接看這個promptbench的調用方式(model加載part報錯了不少):https://github.com/microsoft/promptbench/blob/main/examples/basic.ipynb
import promptbench as pb
print('All supported datasets: ')
print(pb.SUPPORTED_DATASETS)
print('All supported models: ')
print(pb.SUPPORTED_MODELS)可以看到目前可以做測試的數據集和模型有

PromptBench數據集介紹
首先,PromptBench里數據集加載代碼如下:
dataset = pb.DatasetLoader.load_dataset("name of the dataset you want to load")
數據集列表打印:['sst2', 'cola', 'qqp', 'mnli', 'mnli_matched', 'mnli_mismatched', 'qnli', 'wnli', 'rte', 'mrpc', 'mmlu', 'squad_v2', 'un_multi', 'iwslt2017', 'math', 'bool_logic', 'valid_parentheses', 'gsm8k', 'csqa', 'bigbench_date', 'bigbench_object_tracking', 'last_letter_concat', 'numersense', 'qasc']
簡單掃了一下,主要包括以下三類任務(框架圖里也有提及):

- SST-2:二分類情感分析任務,https://huggingface.co/datasets/sst2,標簽0,1
- CoLA:判斷句子語法正確性,The Corpus of Linguistic Acceptability (CoLA),23種語言學出版物的10657個句子
- QQP:識別兩個句子是否語義相似,https://huggingface.co/datasets/merve/qqp
- MRPC:識別兩個句子是否語義相似,MRPC Dataset | Papers With Code
- MultiNLI(MNLI):自然語言推理,MultiNLI,433k個句子對(mnli_matched, mnli_mismatched in pb)
- Question-answering NLI(QNLI):自然語言推理,QNLI Dataset | Papers With Code,取自斯坦福問答數據集(SQuAD),由問題-段落對組成,其中段落中的一個句子包含相應問題的答案。
- Winograd NLI(WNLI):自然語言推理,WNLI Dataset | Papers With Code,包含成對的句子,任務是確定第二個句子是否是第一個句子的蘊涵。 該數據集用于訓練和評估模型理解句子之間關系的能力。
- Recognizing Textual Entailment(RTE):自然語言推理,RTE Dataset | Papers With Code,識別文本蘊含。
插播. 文本蘊含定義為一對文本之間的有向推理關系,如果人們依據自己的常識認為一個句子A的語義能夠由另一個句子B的語義推理得出的話,那么稱A蘊含B。
- Massive Multitask Language Understanding(MMLU):閱讀理解(選擇題),MMLU Dataset | Papers With Code,旨在通過僅在零樣本和少樣本設置中評估模型來衡量預訓練期間獲取的知識,更類似于評估人類的方式。 該基準涵蓋 STEM、人文、社會科學等領域的 57 個學科。
- SQuAD V2:閱讀理解,https://huggingface.co/datasets/squad_v2,段落、問題和答案,模型不僅需要根據問題和段落(上下文信息)回答問題,而且還要確定何時該段落不支持答案并放棄回答。
- Multilingual Corpus from United Nation Documents(UN Multi):多語言平行數據,聯合國網站平行語料庫,United Nations Parallel Corpus
- IWSLT 2017:多語言平行數據,https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/community_catalog/huggingface/iwslt2017,["ar-en", "de-en", "en-ar"] in pb
- Math:數學問題答案對,GitHub - hendrycks/math: The MATH Dataset (NeurIPS 2021),包含 12,500 個具有挑戰性的競賽數學問題的新數據集。 每個問題都有完整的分步解決方案,可用于訓練模型生成答案推導和解釋。
- GSM8K:數學問題答案對,GitHub - openai/grade-school-math,小學數學應用題數據集
- CommonsenseQA(csqa):多項選擇題回答數據集,https://huggingface.co/datasets/tau/commonsense_qa
- NummerSense:數值常識推理任務,https://huggingface.co/datasets/numer_sense,屏蔽從常識語料庫中挖掘的句子中0-10之間的數字,并評估語言模型是否可以正確預測屏蔽值。
- QASC:問答數據集,Question Answering via Sentence Composition (QASC) Dataset — Allen Institute for AI,9,980個有關小學科學的 8 向多項選擇題
- Last letter concat:合并多個單詞的最后一個字母,https://huggingface.co/datasets/ChilleD/LastLetterConcat
- BIG-Bench:多任務,GitHub - google/BIG-bench: Beyond the Imitation Game collaborative benchmark for measuring and extrapolating the capabilities of language models,200多個任務,包括傳統自然語言處理任務,問答,解答數學,寫代碼等,具體可以看https://github.com/google/BIG-bench/blob/main/bigbench/benchmark_tasks/keywords_to_tasks.md#summary-table,bool logic & valid parentheses & bigbench_date & bigbench_object_tracking in pb
PromptBench模型介紹
PromptBench里模型加載代碼如下(直接跑的話實際上沒load出來好幾個):
model = pb.LLMModel(model='name of the model you want to load', some parameters)
模型列表打印:['google/flan-t5-large', 'llama2-7b', 'llama2-7b-chat', 'llama2-13b', 'llama2-13b-chat', 'llama2-70b', 'llama2-70b-chat', 'phi-1.5', 'palm', 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'gpt-4', 'gpt-4-1106-preview', 'gpt-3.5-turbo-1106', 'vicuna-7b', 'vicuna-13b', 'vicuna-13b-v1.3', 'google/flan-ul2']
我們先來看看這些模型有什么:
- Google Flan系列
google/flan-t5-large:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.11416.pdf;模型地址,https://huggingface.co/google/flan-t5-large。T5模型是2019年Google發布的語言模型,這個flan-t5可以看作是加了基于指令微調的T5,且這里的微調方案是多任務的。文章摘要里是這么描述的:
In this paper we explore instruction finetuning with a particular focus on (1) scaling the number of tasks, (2) scaling the model size, and (3) finetuning on chain-of-thought data. We find that instruction finetuning with the above aspects dramatically improves performance on a variety of model classes (PaLM, T5, U-PaLM), prompting setups (zero-shot, few-shot, CoT), and evaluation benchmarks (MMLU, BBH, TyDiQA, MGSM, open-ended generation, RealToxicityPrompts).
簡而言之:任務變多,模型變大,在思維鏈數據(chain-of-thought data)上微調。
google/flan-ul2:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.05131.pdf。ul2,指的是Unifying Language Learning Paradigms,即統一語言學習范式,具體看文章,回頭出講解。
- llama系列:論文鏈接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.13971v1.pdf
- gpt系列:論文鏈接:https://www.mikecaptain.com/resources/pdf/GPT-1.pdf,這個大家肯定很熟悉了。
- vicuna系列:文章鏈接:Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality | LMSYS Org
- Google PaLM:Pathways Language Model (PaLM),文章鏈接:https://blog.research.google/2022/04/pathways-language-model-palm-scaling-to.html。最近出到PaLM2了,https://ai.google/static/documents/palm2techreport.pdf。
- 微軟的phi:模型地址,https://huggingface.co/microsoft/phi-1_5。
PromptBench模型加載遇到的問題
第一次在M1 Mac上加載模型
首先,本人用的是M1 Mac機器,與NVIDIA GPU不兼容,無法使用CUDA加速。于是我的device cuda這種命令是nonono,不過可以放在mps(Metal Performance Shaders)上加速。如果調用模型,除了刪掉參數: device='cuda',還需要把promptbench/models/models.py文件中的代碼,如果有cuda的地方改成mps。比如:
input_ids = self.tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cuda")
cuda改成mps,即
input_ids = self.tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("mps")
另外,由于我的硬盤沒那么大,下載模型的時候可能會說沒空間,如果要刪除之前的模型,模型位置在:~/.cache/huggingface/hub/。
vicuna和llama系列模型
'llama2-7b', 'llama2-7b-chat', 'llama2-13b', 'llama2-13b-chat', 'llama2-70b', 'llama2-70b-chat', 'vicuna-7b', 'vicuna-13b', 'vicuna-13b-v1.3'如果直接填進去加載都失敗了,然后看了promptbench/models/__init__.py的代碼,目測要調用llama或者vicuna模型都需要提前下載的樣子。大家可以再多試試!!!萬一我說的是錯的呢😑。
if model_class == LlamaModel or model_class == VicunaModel:return model_class(self.model, max_new_tokens, temperature, system_prompt, model_dir)然后我就去下載llama和vicuna了,然后首先你需要下載git-lfs(Git Large File Storage | Git Large File Storage (LFS) replaces large files such as audio samples, videos, datasets, and graphics with text pointers inside Git, while storing the file contents on a remote server like GitHub.com or GitHub Enterprise.),下載了homebrew的朋友可以直接運行下面的代碼brew install git-lfs,然后運行git lfs install,如果顯示Git LFS initialized說明安裝成功。接著,俺下載了一個vicuna項目:https://huggingface.co/lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5/tree/main。
llama模型下載現在需要申請許可,就是點files and version,你要申請一下,然后還要去meta官網(https://llama.meta.com/llama-downloads/)上填寫一些信息,然后會給你發個郵件告訴你可以用了。

郵件大概長這個樣子:

然后我就去下載了Llama-2-7b-hf模型(不要問我為什么meta-llama/Llama-2-7b不可以加載,少了一個config.json文件)
git clone https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
如果你在這一步發現,你沒辦法下載,就算是輸入了你的huggingface的username和密碼。因為它說password authentication已經不管用了,那你就試試這個huggingface-cli login。

登陸以后記得還需要輸入access token,要提前申請哦!在你的hugging face賬戶信息里的Access Tokens(如下圖)。

加載代碼:model = pb.LLMModel(model="model name", model_dir='the file path of your vicuna or llama')
PromptBench各個模型加載情況總結
? google/flan-t5-large、google/flan-ul2、phi的調用,改完了mps后,直接修改model name即可
? llama系列和vicuna的調用,下載完了模型文件后,修改model name,加入model_dir參數即可
? palm模型,需要參數palm_key,申請地址:https://ai.google.dev/tutorials/setup
? gpt系列,需要參數openai_key,申請地址:https://platform.openai.com/api-keys
這個key的申請,或多或少需要翻墻之類的。
PromptBench的Prompt快速工程
大家可以直接看prompt engineering的示例代碼:https://github.com/microsoft/promptbench/blob/main/examples/prompt_engineering.ipynb
具體有五類:chain of thought,emotion prompt,expert prompt,generated knowledge和least to most。源碼的話在這里:https://github.com/microsoft/promptbench/tree/main/promptbench/prompt_engineering。本章節的話大概就是帶著大家過一遍這幾種工程方式。
chain of thought
chain of thought:簡稱Cot,文章鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.11903.pdf。為了提高LLM的推理能力,將推理步驟的內容喂給模型,下圖中高亮的部分就是咱們的chains of thought。

chain of thought prompting指在給出從開始到結束的step by step的步驟,而不是給出多個例子讓語言模型去理解,更多的是希望幫助“推理”。當任務涉及需要算術、常識和符號推理的復雜推理時,試試CoT, 此時模型需要理解并遵循中間步驟才能得出正確的答案。
emotion prompt
emotion prompt:文章鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.11760.pdf。大概意思就是你在告訴模型要做什么的時候,還要給它一些Psychology上的提示詞,比如,“這個問題對我來說很重要啊。”,“我相信你可以做得很好!”,“這件事情很緊急!”研究人員發現,給出這樣的一些emotion以后,LLM的效果有一定的提升。簡而言之,咱們需要PUA那個 LLM!!!

expert prompt
expert prompt:看了源代碼以后PromptBench里的expert prompt不太像角色扮演,一般提到expert prompt可能指的是告訴LLM你的專長是什么,引導其返回該領域的信息。比如在開始的時候說“我希望你是XX專家”,“我希望你扮演XX角色”,繼續PUA那個 LLM!!!
generated knowledge
generate knowledge:文章鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.08387.pdf。大概就是在回答問題時提供知識(其中包括從語言模型生成知識)作為prompt的附加輸入。比如在問答的情景下,除了Question這個輸入,Prompt里還有Knowledge這一項。

least to most
least to most:文章鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.10625.pdf。這個idea來自教育心理學,用于表示使用漸進的提示來幫助學生學習新知識的方式。 然后咱就是應用這種least to most來喂語言模型。 我覺得這個有一些子類似CoT,看起來是CoT的進階版,因為需要先拆分問題,然后再逐一解決。

PromptBench對抗性Prompt評估
原文還是說的很清楚的,主要分成了character-level,word-level,sentence-level和semantic-level。具體如下圖,看了下代碼,Semantic就用了textattack包里的wordembeddingdistance來做的。大概是做啥呢,就是大家之前發現如果我們對輸入樣本做了輕微的改動,模型就可能會犯錯,魯棒性就是有些差了。因此以textbugger為例,通過改變字母,生成稍微有改變的文本,且保留原來的語義信息,雖然不是百分百正確了,但是要的就是這個味兒。

- Textbugger:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.05271.pdf。

- Deepwordbug:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.04354.pdf。

- BertAttack:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.09984.pdf。
- TextFooler:論文鏈接,https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.11932.pdf。
- StressTest:論文鏈接,https://aclanthology.org/C18-1198.pdf。

- StressTest:PromptBench是用的length mismatch來做的stress test。texts = [" and true is true ", " and false is not true ", " and true is true "*5]
- CheckList:論文鏈接,https://aclanthology.org/2020.acl-main.442.pdf。
PromptBench的動態評估
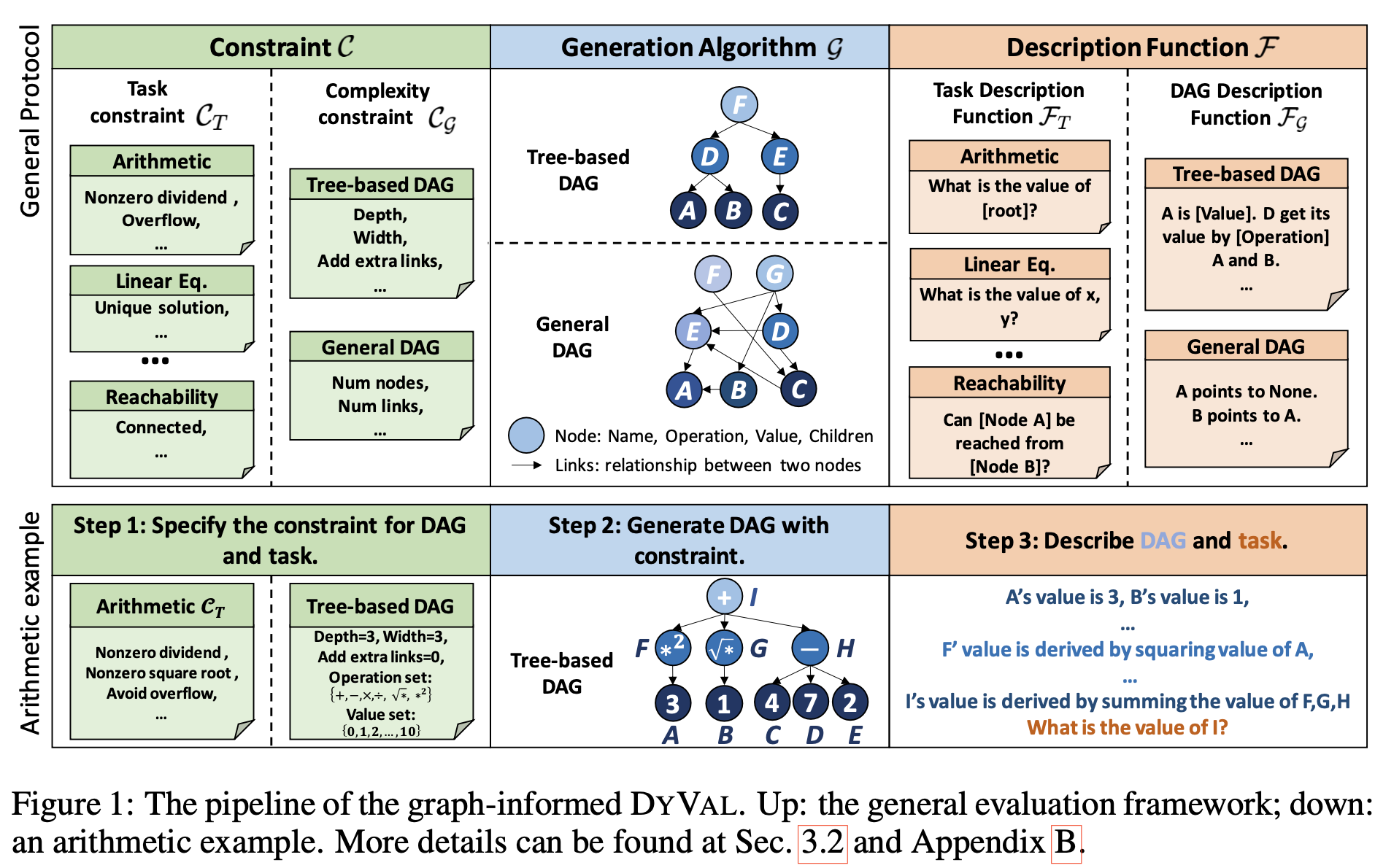
這里的動態評估部分,主要是文章https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.17167.pdf提出的Dyval的應用,相比于固定的數據來做測試,Dyval是動態實時生成評估樣本的。原文是這么描述Dyval的:
DYVAL consists of three components: 1) the generation algorithm G to generate test samples with diversities; 2) the constraint C to modulate sample complexity and validity; and 3) the description function F to translate the generated samples into natural languages.
具體步驟大家去看原文吧!
PromptBench總結
反正我整個用下來,就覺得好像不是那么好用。我的電腦硬盤沒那么大,下載模型的時候時常沒空間,因此能跑起來就主動暫停,刪模型換下一個嘗試了,更不用說本人還沒有GPU。LLM可真的有夠大的,自己玩玩,是玩不動的。總的來說,bench越來越多,model越來越大,prompt也是各種花樣。懷念傳統NLP,或者說不用LLM的NLP。

)

【Jmeter】線程(Threads(Users))之開放模型線程組(Open Model Thread Group))



)











