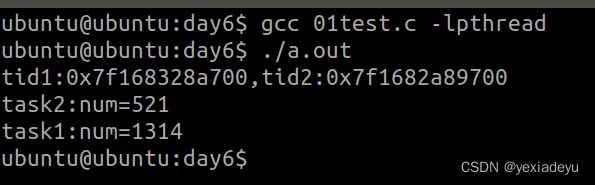
1、將互斥機制的代碼實現重新敲一遍。
#include<myhead.h>//臨界資源
int num=520;//1、創建一個互斥鎖變量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;void *task1(void *arg);
void *task2(void *arg);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//2、初始化互斥鎖pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//定義線程pthread_t tid1,tid2;if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){printf("tid1 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid2 create error\n");return 0;}//獲取tid號printf("tid1:%#lx,tid2:%#lx\n",tid1,tid2);//回收線程資源pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);//5、摧毀鎖資源pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);return 0;
}
//任務1函數
void *task1(void *arg)
{//3、獲取鎖資源pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);num = 1314;sleep(3);printf("task1:num=%d\n",num);//4、釋放鎖資源pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
//任務2函數
void *task2(void *arg)
{//3、獲取鎖資源pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);num ++;sleep(1);printf("task2:num=%d\n",num);//4、釋放鎖資源pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
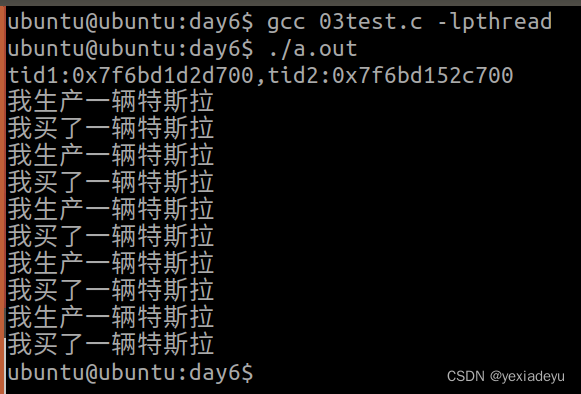
2、將無名信號量的代碼實現重新敲一遍。
#include<myhead.h>//1、創建無名信號量
sem_t sem;void *task1(void *arg);
void *task2(void *arg);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//2、初始化無名信號量sem_init(&sem,0,0);//定義線程pthread_t tid1,tid2;if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){printf("tid1 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid2 create error\n");return 0;}//獲取tid號printf("tid1:%#lx,tid2:%#lx\n",tid1,tid2);//回收線程資源pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);//5、釋放無名信號量sem_destroy(&sem);return 0;
}
//任務1函數
void *task1(void *arg)
{int num=5;while(num--){sleep(1);puts("我生產一輛特斯拉");//4、釋放資源sem_post(&sem);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
//任務2函數
void *task2(void *arg)
{int num=5;while(num--){//3、申請資源sem_wait(&sem);puts("我買了一輛特斯拉");}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
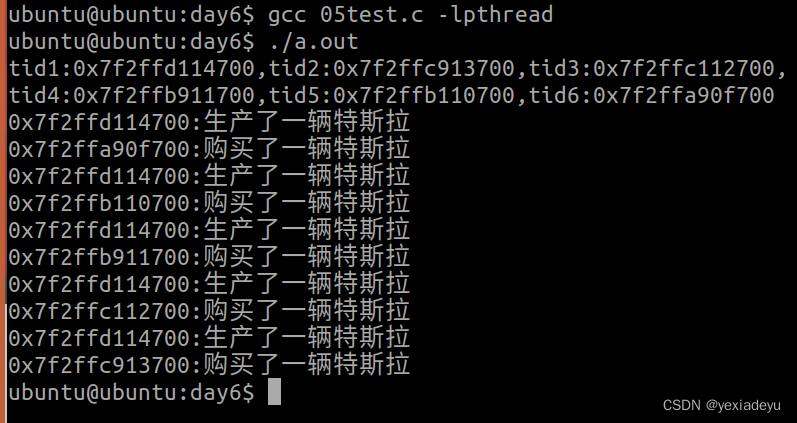
3、將條件變量的代碼實現重新敲一遍。
#include<myhead.h>//1、定義條件變量
pthread_cond_t cond;//11、定義互斥鎖變量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;void *task1(void *arg);
void *task2(void *arg);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//2、初始化條件變量pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);//22、初始化互斥鎖pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//定義線程pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3,tid4,tid5,tid6;if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){printf("tid1 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid2 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid3 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid4,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid4 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid5,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid5 create error\n");return 0;}if(pthread_create(&tid6,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){printf("tid6 create error\n");return 0;}printf("tid1:%#lx,tid2:%#lx,tid3:%#lx,tid4:%#lx,tid5:%#lx,tid6:%#lx\n",\tid1,tid2,tid3,tid4,tid5,tid6);//回收線程資源pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);pthread_join(tid3,NULL);pthread_join(tid4,NULL);pthread_join(tid5,NULL);pthread_join(tid6,NULL);//5、摧毀條件變量pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//55、摧毀互斥鎖pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);return 0;
}
//定義生產者函數
void *task1(void *arg)
{int num=5;while(num--){sleep(1);printf("%#lx:生產了一輛特斯拉\n",pthread_self());//3、喚醒一個消費者pthread_cond_signal(&cond);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
//定義消費者函數
void *task2(void *arg)
{//33、上鎖pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//4、進入等待隊列pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);printf("%#lx:購買了一輛特斯拉\n",pthread_self());//4、解鎖pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);pthread_exit(NULL);
}
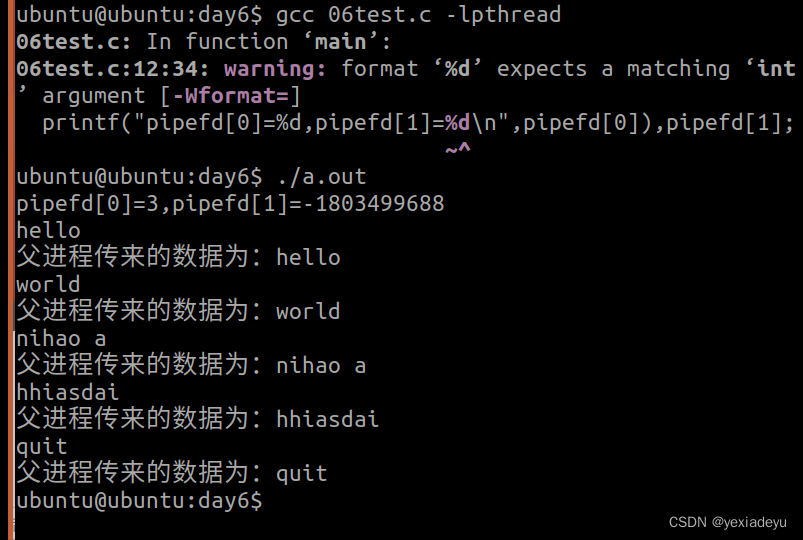
4、將無名管道的代碼實現重新敲一遍。
#include<myhead.h>
//管道進程傳輸
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//創建管道文件int pipefd[2]={0};if(pipe(pipefd)==-1){perror("pipe error");return -1;}printf("pipefd[0]=%d,pipefd[1]=%d\n",pipefd[0]),pipefd[1];//創建子進程pid_t pid=fork();if(pid>0){//父進程//關閉管道讀端close(pipefd[0]);char wbuf[128]="";while(1){//清空wbuf數組bzero(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));//終端輸入數據fgets(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf),stdin);wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]='\0';//將數據寫入管道文件中write(pipefd[1],wbuf,strlen(wbuf));//輸入結束條件if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉管道寫端close(pipefd[1]);//阻塞回收子進程資源wait(NULL);}else if(pid == 0){//子進程//關閉管道寫端close(pipefd[1]);char rbuf[128]="";while(1){//清空rbuf內容bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//從管道文件中讀取數據read(pipefd[0],rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//輸出rbuf的數據printf("父進程傳來的數據為:%s\n",rbuf);//讀取結束條件if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉管道讀端close(pipefd[0]);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}else{perror("fork error");return -1;}return 0;
}
5、將有名管道的代碼實現重新敲一遍。
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//創建一個管道文件if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664)==-1){perror("mkfifo error");return -1;}//阻塞getchar();//清楚文件system("rm myfifo");return 0;
}
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//打開管道文件int wfd=-1;//以只寫的形式打開文件if((wfd=open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char wbuf[128]="";while(1){printf("please enter>>>");fgets(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf),stdin);//把'\n'變為'\0'wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]='\0';//數據寫入管道write(wfd,wbuf,strlen(wbuf));//終端輸入結束條件if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(wfd);return 0;
}
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//打開管道文件int rfd=-1;//以只讀形式打開文件if((rfd = open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char rbuf[128]="";while(1){//清空rbuf數組bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//讀取管道文件的數據read(rfd,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//輸出結果printf("收到的數據為:%s\n",rbuf);//讀取結束條件if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(rfd);return 0;
}
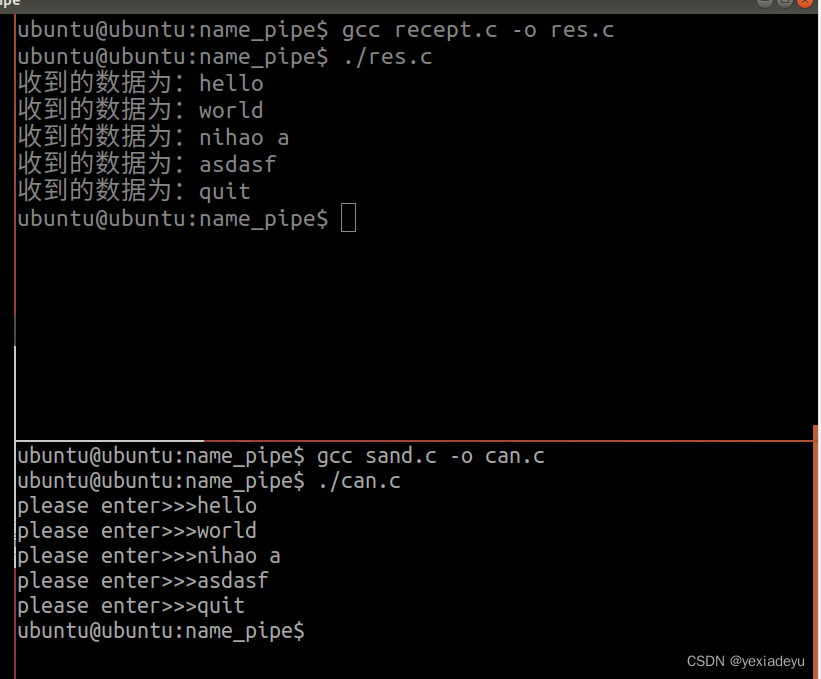
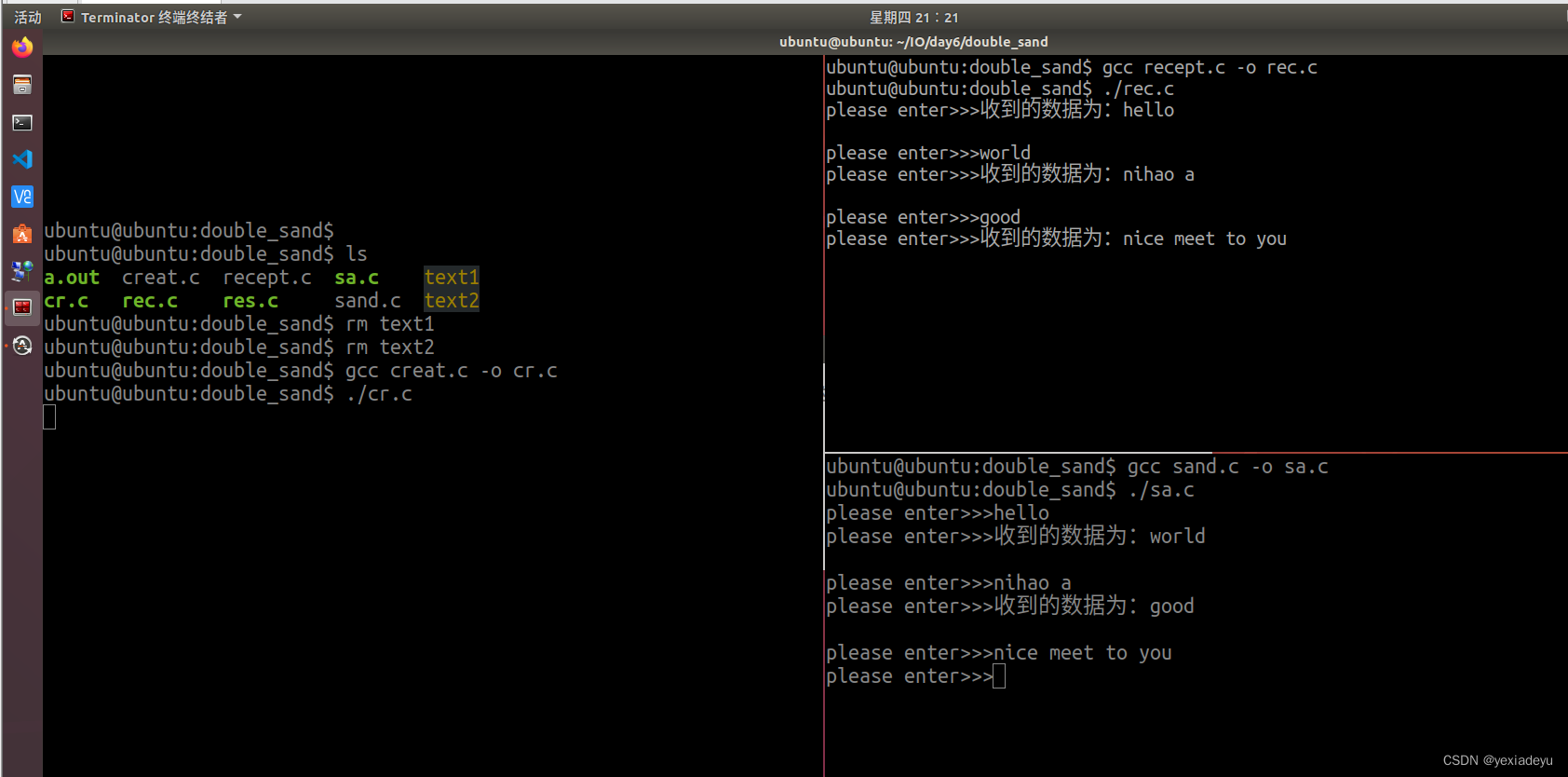
6、使用有名管道完成兩個進程的相互通信(提示:可以使用多進程或多線程完成)。
//管道創建函數
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//創建二個管道文件if(mkfifo("./text1",0664)==-1){perror("text1 error");return -1;}if(mkfifo("./text2",0664)==-1){perror("text2 error");return -1;}//阻塞getchar();//清楚文件system("rm text1");system("rm text2");return 0;
}
//用戶1發送和接受函數
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid>0){//打開管道文件int wfd=-1;//以只寫的形式打開文件if((wfd=open("./text1",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char wbuf[128]="";while(1){printf("please enter>>>");fgets(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf),stdin);//把'\n'變為'\0'wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]='\0';//數據寫入管道write(wfd,wbuf,strlen(wbuf));//終端輸入結束條件if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(wfd); //打開管道文件}else if(pid==0){//打開管道文件int rfd=-1;//以只讀形式打開文件if((rfd = open("./text2",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char rbuf[128]="";while(1){//清空rbuf數組bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//讀取管道文件的數據read(rfd,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//輸出結果printf("收到的數據為:%s\n",rbuf);//讀取結束條件if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(rfd);}else {perror("fork error");return -1;}return 0;
}
//用戶2發送接受函數
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid>0){//打開管道文件int rfd=-1;//以只讀形式打開文件if((rfd = open("./text1",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char rbuf[128]="";while(1){//清空rbuf數組bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//讀取管道文件的數據read(rfd,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//輸出結果printf("收到的數據為:%s\n",rbuf);//讀取管道文件的數據取結束條件if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(rfd);}else if(pid==0){ //打開管道文件int wfd=-1;//以只寫的形式打開文件if((wfd=open("./text2",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}//定義容器char wbuf[128]="";while(1){printf("please enter>>>");fgets(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf),stdin);//把'\n'變為'\0'wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]='\0';//數據寫入管道write(wfd,wbuf,strlen(wbuf));//終端輸入結束條件if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)break;}//關閉文件close(wfd);}else {perror("fork error");return -1;}return 0;
}
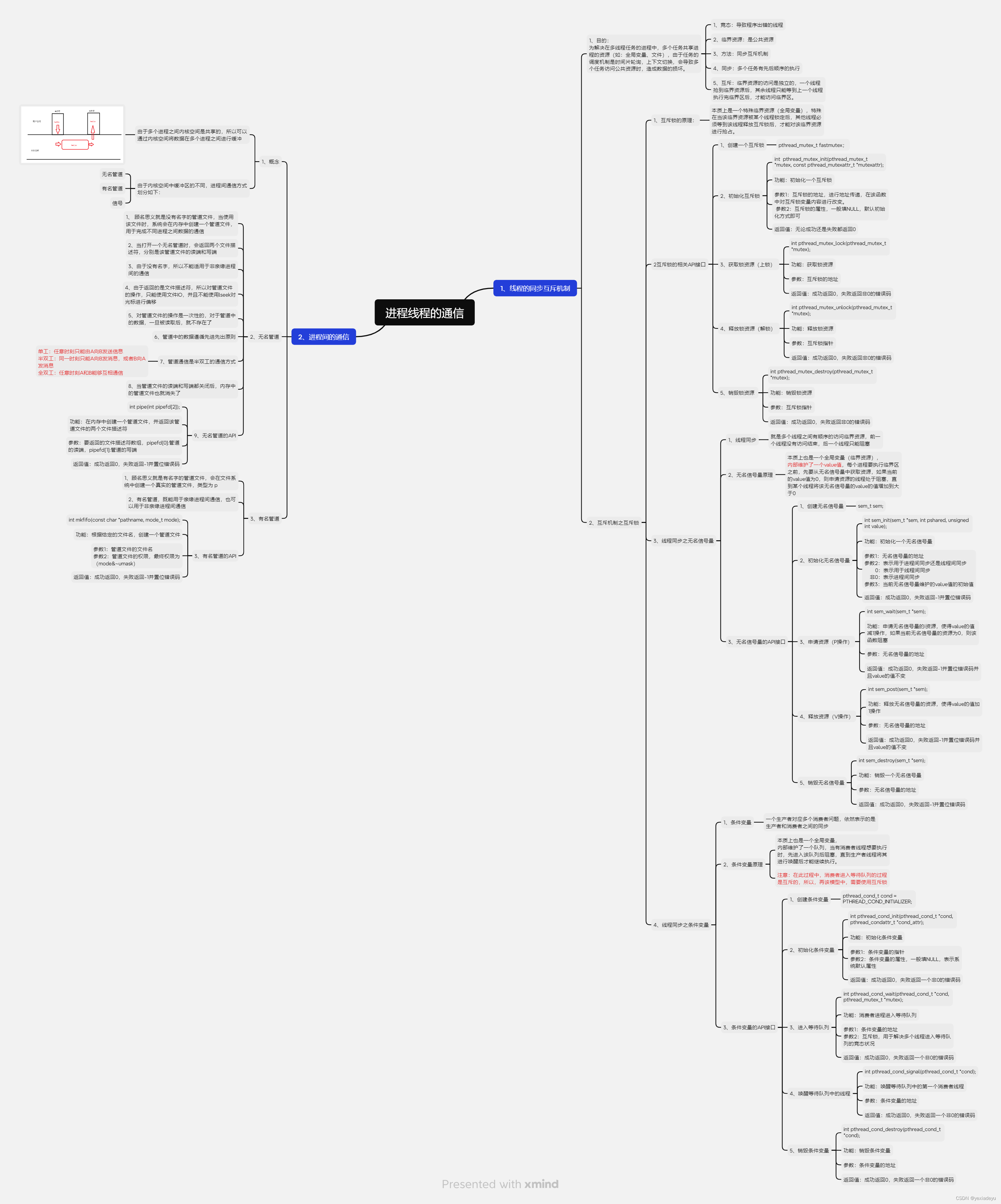
7、思維導圖









)













———配置及使用控制臺)
拖動組件的設計)

