?
本節內容
- Socket介紹
- Socket參數介紹
- 基本Socket實例
- Socket實現多連接處理
- 通過Socket實現簡單SSH
- 通過Socket實現文件傳送
- 作業:開發一個支持多用戶在線的FTP程序
?
?
1. Socket介紹
概念
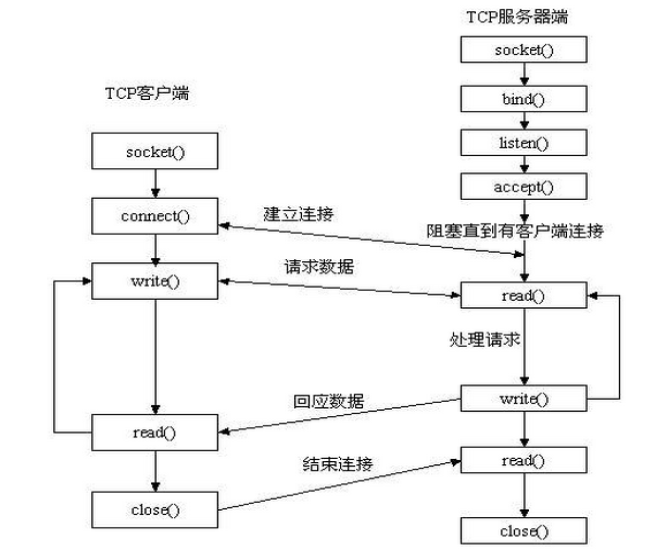
?
A?network socket?is an endpoint of a connection across a?computer network. Today, most communication between computers is based on the?Internet Protocol; therefore most network sockets are?Internet sockets. More precisely, a socket is a?handle?(abstract reference) that a local program can pass to the networking?application programming interface?(API) to use the connection, for example "send this data on this socket".
For example, to send "Hello, world!" via?TCP?to port 80 of the host with address 1.2.3.4, one might get a socket, connect it to the remote host, send the string, then close the socket.
實現一個socket至少要分以下幾步,(偽代碼)
| 1 2 3 4 | Socket socket?=?getSocket(type?=?"TCP")??#設定好協議類型connect(socket, address?=?"1.2.3.4", port?=?"80")?#連接遠程機器send(socket,?"Hello, world!")?#發送消息close(socket)?#關閉連接 |
A?socket API?is an?application programming interface?(API), usually provided by the?operating system, that allows application programs to control and use network sockets. Internet socket APIs are usually based on the?Berkeley sockets?standard. In the Berkeley sockets standard, sockets are a form of?file descriptor?(a?file?handle), due to the?Unix philosophy?that "everything is a file", and the analogies between sockets and files: you can read, write, open, and close both.?
A?socket address?is the combination of an?IP address?and a?port number, much like one end of a telephone connection is the combination of a?phone number?and a particular?extension. Sockets need not have an address (for example for only sending data), but if a program?binds?a socket to an address, the socket can be used to receive data sent to that address. Based on this address, internet sockets deliver incoming data packets to the appropriate application?process?or?thread.
Socket Families(地址簇)
socket.AF_UNIX unix本機進程間通信?
socket.AF_INET IPV4
socket.AF_INET6 ?IPV6
These constants represent the address (and protocol) families, used for the first argument to?socket(). If the?AF_UNIX?constant is not defined then this protocol is unsupported. More constants may be available depending on the system.
Socket Types
socket.SOCK_STREAM ?#for tcp
socket.SOCK_DGRAM ? #for udp?
socket.SOCK_RAW ? ? #原始套接字,普通的套接字無法處理ICMP、IGMP等網絡報文,而SOCK_RAW可以;其次,SOCK_RAW也可以處理特殊的IPv4報文;此外,利用原始套接字,可以通過IP_HDRINCL套接字選項由用戶構造IP頭。
socket.SOCK_RDM ?#是一種可靠的UDP形式,即保證交付數據報但不保證順序。SOCK_RAM用來提供對原始協議的低級訪問,在需要執行某些特殊操作時使用,如發送ICMP報文。SOCK_RAM通常僅限于高級用戶或管理員運行的程序使用。
socket.SOCK_SEQPACKET #廢棄了
These constants represent the socket types, used for the second argument to?socket(). More constants may be available depending on the system. (Only?SOCK_STREAM?and?SOCK_DGRAM?appear to be generally useful.)
?
2. Socket 參數介紹
socket.socket(family=AF_INET,?type=SOCK_STREAM,?proto=0,?fileno=None) ?必會
Create a new socket using the given address family, socket type and protocol number. The address family should be?AF_INET?(the default),?AF_INET6,?AF_UNIX,?AF_CAN?or?AF_RDS. The socket type should beSOCK_STREAM?(the default),?SOCK_DGRAM,?SOCK_RAW?or perhaps one of the other?SOCK_?constants. The protocol number is usually zero and may be omitted or in the case where the address family is?AF_CAN?the protocol should be one of?CAN_RAW?or?CAN_BCM. If?fileno?is specified, the other arguments are ignored, causing the socket with the specified file descriptor to return. Unlike?socket.fromfd(),?fileno?will return the same socket and not a duplicate. This may help close a detached socket using?socket.close().
socket.socketpair([family[,?type[,?proto]]])
Build a pair of connected socket objects using the given address family, socket type, and protocol number. Address family, socket type, and protocol number are as for the?socket()?function above. The default family is?AF_UNIX?if defined on the platform; otherwise, the default is?AF_INET.
socket.create_connection(address[,?timeout[,?source_address]])
Connect to a TCP service listening on the Internet?address?(a 2-tuple?(host,?port)), and return the socket object. This is a higher-level function than?socket.connect(): if?host?is a non-numeric hostname, it will try to resolve it for both?AF_INET?and?AF_INET6, and then try to connect to all possible addresses in turn until a connection succeeds. This makes it easy to write clients that are compatible to both IPv4 and IPv6.
Passing the optional?timeout?parameter will set the timeout on the socket instance before attempting to connect. If no?timeout?is supplied, the global default timeout setting returned by?getdefaulttimeout()?is used.
If supplied,?source_address?must be a 2-tuple?(host,?port)?for the socket to bind to as its source address before connecting. If host or port are ‘’ or 0 respectively the OS default behavior will be used.
socket.getaddrinfo(host,?port,?family=0,?type=0,?proto=0,?flags=0) #獲取要連接的對端主機地址?必會
sk.bind(address)?必會
s.bind(address) 將套接字綁定到地址。address地址的格式取決于地址族。在AF_INET下,以元組(host,port)的形式表示地址。
sk.listen(backlog)?必會
開始監聽傳入連接。backlog指定在拒絕連接之前,可以掛起的最大連接數量。
? ? ? backlog等于5,表示內核已經接到了連接請求,但服務器還沒有調用accept進行處理的連接個數最大為5
? ? ? 這個值不能無限大,因為要在內核中維護連接隊列
sk.setblocking(bool)?必會
是否阻塞(默認True),如果設置False,那么accept和recv時一旦無數據,則報錯。
sk.accept()?必會
接受連接并返回(conn,address),其中conn是新的套接字對象,可以用來接收和發送數據。address是連接客戶端的地址。
接收TCP 客戶的連接(阻塞式)等待連接的到來
sk.connect(address)?必會
連接到address處的套接字。一般,address的格式為元組(hostname,port),如果連接出錯,返回socket.error錯誤。
sk.connect_ex(address)
同上,只不過會有返回值,連接成功時返回 0 ,連接失敗時候返回編碼,例如:10061
sk.close()?必會
關閉套接字
sk.recv(bufsize[,flag])?必會
接受套接字的數據。數據以字符串形式返回,bufsize指定最多可以接收的數量。flag提供有關消息的其他信息,通常可以忽略。
sk.recvfrom(bufsize[.flag])
與recv()類似,但返回值是(data,address)。其中data是包含接收數據的字符串,address是發送數據的套接字地址。
sk.send(string[,flag])?必會
將string中的數據發送到連接的套接字。返回值是要發送的字節數量,該數量可能小于string的字節大小。即:可能未將指定內容全部發送。
sk.sendall(string[,flag])?必會
將string中的數據發送到連接的套接字,但在返回之前會嘗試發送所有數據。成功返回None,失敗則拋出異常。
? ? ? 內部通過遞歸調用send,將所有內容發送出去。
sk.sendto(string[,flag],address)
將數據發送到套接字,address是形式為(ipaddr,port)的元組,指定遠程地址。返回值是發送的字節數。該函數主要用于UDP協議。
sk.settimeout(timeout)?必會
設置套接字操作的超時期,timeout是一個浮點數,單位是秒。值為None表示沒有超時期。一般,超時期應該在剛創建套接字時設置,因為它們可能用于連接的操作(如 client 連接最多等待5s )
sk.getpeername() ?必會
返回連接套接字的遠程地址。返回值通常是元組(ipaddr,port)。
sk.getsockname()?
返回套接字自己的地址。通常是一個元組(ipaddr,port)
sk.fileno()?
套接字的文件描述符
socket.sendfile(file,?offset=0,?count=None)
? ? ?發送文件 ,但目前多數情況下并無什么卵用。
?
SocketServer
The?socketserver?module simplifies the task of writing network servers.
There are four basic concrete server classes:
- class?
-
This uses the Internet TCP protocol, which provides for continuous streams of data between the client and server. If?bind_and_activate?is true, the constructor automatically attempts to invoke?
server_bind()?andserver_activate(). The other parameters are passed to the?BaseServer?base class.
socketserver.TCPServer(server_address,?RequestHandlerClass,?bind_and_activate=True)- class?
-
This uses datagrams, which are discrete packets of information that may arrive out of order or be lost while in transit. The parameters are the same as for?
TCPServer.
socketserver.UDPServer(server_address,?RequestHandlerClass,?bind_and_activate=True)- class?
-
These more infrequently used classes are similar to the TCP and UDP classes, but use Unix domain sockets; they’re not available on non-Unix platforms. The parameters are the same as for?
TCPServer.
socketserver.UnixStreamServer(server_address,?RequestHandlerClass,?bind_and_activate=True)class?socketserver.UnixDatagramServer(server_address,?RequestHandlerClass,bind_and_activate=True)These four classes process requests?synchronously; each request must be completed before the next request can be started. This isn’t suitable if each request takes a long time to complete, because it requires a lot of computation, or because it returns a lot of data which the client is slow to process. The solution is to create a separate process or thread to handle each request; the?ForkingMixIn?and?ThreadingMixIn?mix-in classes can be used to support asynchronous behaviour.
There are five classes in an inheritance diagram, four of which represent synchronous servers of four types:
+------------+
| BaseServer |
+------------+| v +-----------+ +------------------+ | TCPServer |------->| UnixStreamServer | +-----------+ +------------------+ | v +-----------+ +--------------------+ | UDPServer |------->| UnixDatagramServer | +-----------+ +--------------------+ Note that?UnixDatagramServer?derives from?UDPServer, not from?UnixStreamServer?— the only difference between an IP and a Unix stream server is the address family, which is simply repeated in both Unix server classes.
- class?
-
Forking and threading versions of each type of server can be created using these mix-in classes. For instance,?
ThreadingUDPServer?is created as follows:class ThreadingUDPServer(ThreadingMixIn, UDPServer): passThe mix-in class comes first, since it overrides a method defined in?
UDPServer. Setting the various attributes also changes the behavior of the underlying server mechanism.
socketserver.ForkingMixInclass?socketserver.ThreadingMixIn- class?
-
These classes are pre-defined using the mix-in classes.
?
?
?
Request Handler Objects
class?
socketserver.BaseRequestHandlerThis is the superclass of all request handler objects. It defines the interface, given below. A concrete request handler subclass must define a new?
handle()?method, and can override any of the other methods. A new instance of the subclass is created for each request.-
Called before the?
handle()?method to perform any initialization actions required. The default implementation does nothing.
setup()-
This function must do all the work required to service a request. The default implementation does nothing. Several instance attributes are available to it; the request is available as?
self.request; the client address as?self.client_address; and the server instance as?self.server, in case it needs access to per-server information.The type of?
self.request?is different for datagram or stream services. For stream services,self.request?is a socket object; for datagram services,?self.request?is a pair of string and socket.
handle()-
Called after the?
handle()?method to perform any clean-up actions required. The default implementation does nothing. If?setup()?raises an exception, this function will not be called.?
?
?
socketserver.TCPServer?Exampleserver side
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728import?socketserverclass?MyTCPHandler(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):????"""????The request handler class for our server.????It is instantiated once per connection to the server, and must????override the handle() method to implement communication to the????client.????"""????def?handle(self):????????# self.request is the TCP socket connected to the client????????self.data?=?self.request.recv(1024).strip()????????print("{} wrote:".format(self.client_address[0]))????????print(self.data)????????# just send back the same data, but upper-cased????????self.request.sendall(self.data.upper())if?__name__?==?"__main__":????HOST, PORT?=?"localhost",?9999????# Create the server, binding to localhost on port 9999????server?=?socketserver.TCPServer((HOST, PORT), MyTCPHandler)????# Activate the server; this will keep running until you????# interrupt the program with Ctrl-C????server.serve_forever()client side
123456789101112131415161718192021import?socketimport?sysHOST, PORT?=?"localhost",?9999data?=?" ".join(sys.argv[1:])# Create a socket (SOCK_STREAM means a TCP socket)sock?=?socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)try:????# Connect to server and send data????sock.connect((HOST, PORT))????sock.sendall(bytes(data?+?"\n",?"utf-8"))????# Receive data from the server and shut down????received?=?str(sock.recv(1024),?"utf-8")finally:????sock.close()print("Sent:???? {}".format(data))print("Received: {}".format(received))上面這個例子你會發現,依然不能實現多并發,哈哈,在server端做一下更改就可以了
把
1server?=?socketserver.TCPServer((HOST, PORT), MyTCPHandler)改成
?
1server?=?socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer((HOST, PORT), MyTCPHandler)?
finish() -
socketserver.ForkingTCPServerclass?socketserver.ForkingUDPServerclass?socketserver.ThreadingTCPServerclass?socketserver.ThreadingUDPServer


方法查找最大整數)





)







方法及示例)
)
