java線程和操作系統線程
線程數 (Threads)
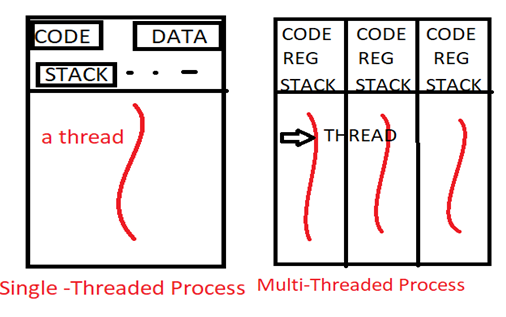
A thread is a unit of CPU utilization, which comprises the following parts that are program counter, register set, stack and a thread ID. Generally, it’s well known that the process is heavy weighted which means they consume lot more resources than the threads, and in this threads are light weighted. Basically, there are two types of threading process are there which are as follows:
線程是CPU利用率的單位,包括以下部分:程序計數器,寄存器集,堆棧和線程ID。 通常,眾所周知,進程的權重很重,這意味著它們比線程消耗更多的資源,而在這種情況下,線程的權重很輕。 基本上,有兩種類型的線程處理過程,如下所示:
Single Threaded process:
單線程進程:
Traditionally if a process has a single thread of control then it is termed as a single threaded process.
傳統上,如果進程具有單控制線程,則將其稱為單線程進程。
Multi Threaded process:
多線程進程:
If a process has multiple threads of control then it is termed as a Multithreaded process. It can be used to perform multiple tasks at a single time.
如果一個進程具有多個控制線程,則將其稱為多線程進程。 它可以一次執行多個任務。
Thread also plays a vital role in RPC which means Remote procedure call. It is used to call a function of some another program. The thread can also be used for the interprocess communication.
線程在RPC中也起著至關重要的作用,這意味著遠程過程調用。 它用于調用另一個程序的功能。 該線程也可以用于進程間通信。
多線程編程的好處 (Benefits of Multi-Threaded programming)
Responsiveness:
響應能力:
Since multithreading is an application which will allow a program to run even when a part of it is blocked. So it will increase the responsiveness to the particular user. For example suppose that a particular section is not responding in the above Multi-Threaded diagram instead of an entire process not responding, the two sections can respond to the user, which means Responsiveness.
由于多線程是一個應用程序,即使其中一部分被阻止,它也將允許程序運行。 因此,它將增加對特定用戶的響應。 例如,假設在上面的多線程圖中特定部分沒有響應,而不是整個過程沒有響應,則這兩個部分可以響應用戶,這意味著響應性。
Resource sharing:
資源共享:
It is a beneficial part in case of Multi-Threaded programming as it allows an application to have several different threads of venture within the same address space.
在多線程編程的情況下,它是有益的部分,因為它允許應用程序在同一地址空間內具有多個不同的冒險線程。
Boom Throughput:
動臂吞吐量:
Number of jobs completed per unit time is increased which is a favorable condition.
每單位時間完成的作業數量增加,這是一個有利條件。
Communication:
通訊:
As different threads have the same address space so it is very easier to communicate with the Multiple-Thread.
由于不同的線程具有相同的地址空間,因此與多線程通信非常容易。
Economy:
經濟:
As we know that threads share resources of the process for which they belong, by this it will be more economical to create threads for data and resource sharing.
眾所周知,線程共享它們所屬進程的資源,因此,創建用于數據和資源共享的線程將更加經濟。
Utilization of the Multiprocessor architectures:
多處理器體系結構的利用:
The benefits of Multi-Threading can be increased in an architecture which means threads can be made to run in parallel on a different processor, thus there will increment in a concurrency level.
在體系結構中可以增加多線程的好處,這意味著可以使線程在不同的處理器上并行運行,因此并發級別會增加。
多線程模型 (Multithreading Models)
Generally, there are two types of threads which are user thread and another one is kernel thread. In this type of system, the user-level threads are supported above the kernel and managed without kernel support, whereas kernel threads are directly supported and managed by the help of an operating system. On the basis of it there are generally three types of model governed:
通常,有兩種類型的線程是用戶線程,另一種是內核線程。 在這種類型的系統中,用戶級線程在內核之上受支持并且在沒有內核支持的情況下進行管理,而內核線程在操作系統的幫助下直接得到支持和管理。 在此基礎上,通常管理三種類型的模型:
Many to One model
多對一模型
In this mapping is done between the many user-level threads to the one kernel thread. So in this, we have many user levels which are mapped with one kernel thread.
在這種情況下,映射是在許多用戶級線程到一個內核線程之間完成的。 因此,在此,我們有許多用戶級別,它們被一個內核線程映射。
One to One Model
一對一模型
In this mapping is done between each user thread and the kernel thread.
在此,在每個用戶線程和內核線程之間完成映射。
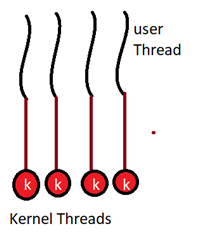
Many to Many Model
多對多模型
It is a type of model in which it multiplexes many user-level threads to a smaller or equal number of kernel threads. In this, if we have four user threads than we can have either four or less than four kernel thread.
它是一種模型,其中它將許多用戶級線程多路復用為更少或相等數量的內核線程。 在這種情況下,如果我們有四個用戶線程,那么我們可以有四個或少于四個內核線程。
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/operating-systems/threading.aspx
java線程和操作系統線程









)









