文章轉至
作者:林海山波
出處:https://me.csdn.net/lenbow
版權:本文版權歸作者和CSDN博客共有??
寫這篇博客只為自己學習路上做個筆記,方便自己學習記憶,大家如果想看詳細文章可以去原作者主頁去看,同時他的博客中還有很多tensorflow學習知識。感謝林海山波,資料統計的非常全面。
1、tensorflow的基本運作
為了快速的熟悉TensorFlow編程,下面從一段簡單的代碼開始:
import tensorflow as tf#定義‘符號’變量,也稱為占位符a = tf.placeholder("float")b = tf.placeholder("float")y = tf.mul(a, b) #構造一個op節點sess = tf.Session()#建立會話#運行會話,輸入數據,并計算節點,同時打印結果print sess.run(y, feed_dict={a: 3, b: 3})# 任務完成, 關閉會話.sess.close()2、tf函數
TensorFlow 將圖形定義轉換成分布式執行的操作, 以充分利用可用的計算資源(如 CPU 或 GPU。一般你不需要顯式指定使用 CPU 還是 GPU, TensorFlow 能自動檢測。如果檢測到 GPU, TensorFlow 會盡可能地利用找到的第一個 GPU 來執行操作. 并行計算能讓代價大的算法計算加速執行,TensorFlow也在實現上對復雜操作進行了有效的改進。大部分核相關的操作都是設備相關的實現,比如GPU。下面是一些重要的操作/核:
| 操作組 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| Maths | Add, Sub, Mul, Div, Exp, Log, Greater, Less, Equal |
| Array | Concat, Slice, Split, Constant, Rank, Shape, Shuffle |
| Matrix | MatMul, MatrixInverse, MatrixDeterminant |
| Neuronal Network | SoftMax, Sigmoid, ReLU, Convolution2D, MaxPool |
| Checkpointing | Save, Restore |
| Queues and syncronizations | Enqueue, Dequeue, MutexAcquire, MutexRelease |
| Flow control | Merge, Switch, Enter, Leave, NextIteration |
TensorFlow的算術操作如下:
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.add(x, y, name=None) | 求和 |
| tf.sub(x, y, name=None) | 減法 |
| tf.mul(x, y, name=None) | 乘法 |
| tf.div(x, y, name=None) | 除法 |
| tf.mod(x, y, name=None) | 取模 |
| tf.abs(x, name=None) | 求絕對值 |
| tf.neg(x, name=None) | 取負 (y = -x). |
| tf.sign(x, name=None) | 返回符號 y = sign(x) = -1 if x < 0; 0 if x == 0; 1 if x > 0. |
| tf.inv(x, name=None) | 取反 |
| tf.square(x, name=None) | 計算平方 (y = x * x = x^2). |
| tf.round(x, name=None) | 舍入最接近的整數 # ‘a’ is [0.9, 2.5, 2.3, -4.4] tf.round(a) ==> [ 1.0, 3.0, 2.0, -4.0 ] |
| tf.sqrt(x, name=None) | 開根號 (y = \sqrt{x} = x^{1/2}). |
| tf.pow(x, y, name=None) | 冪次方? # tensor ‘x’ is [[2, 2], [3, 3]] # tensor ‘y’ is [[8, 16], [2, 3]] tf.pow(x, y) ==> [[256, 65536], [9, 27]] |
| tf.exp(x, name=None) | 計算e的次方 |
| tf.log(x, name=None) | 計算log,一個輸入計算e的ln,兩輸入以第二輸入為底 |
| tf.maximum(x, y, name=None) | 返回最大值 (x > y ? x : y) |
| tf.minimum(x, y, name=None) | 返回最小值 (x < y ? x : y) |
| tf.cos(x, name=None) | 三角函數cosine |
| tf.sin(x, name=None) | 三角函數sine |
| tf.tan(x, name=None) | 三角函數tan |
| tf.atan(x, name=None) | 三角函數ctan |
張量操作Tensor Transformations
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.string_to_number (string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None) | 字符串轉為數字 |
| tf.to_double(x, name=’ToDouble’) | 轉為64位浮點類型–float64 |
| tf.to_float(x, name=’ToFloat’) | 轉為32位浮點類型–float32 |
| tf.to_int32(x, name=’ToInt32’) | 轉為32位整型–int32 |
| tf.to_int64(x, name=’ToInt64’) | 轉為64位整型–int64 |
| tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None) | 將x或者x.values轉換為dtype # tensor? a?is [1.8, 2.2], dtype=tf.floattf.cast(a, tf.int32) ==> [1, 2] # dtype=tf.int32 |
- 形狀操作Shapes and Shaping
操作 描述 tf.shape(input, name=None) 返回數據的shape
# ‘t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]]
shape(t) ==> [2, 2, 3]tf.size(input, name=None) 返回數據的元素數量
# ‘t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]]]
size(t) ==> 12tf.rank(input, name=None) 返回tensor的rank
注意:此rank不同于矩陣的rank,
tensor的rank表示一個tensor需要的索引數目來唯一表示任何一個元素
也就是通常所說的 “order”, “degree”或”ndims”
#’t’ is [[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]]
# shape of tensor ‘t’ is [2, 2, 3]
rank(t) ==> 3tf.reshape(tensor, shape, name=None) 改變tensor的形狀
# tensor ‘t’ is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
# tensor ‘t’ has shape [9]
reshape(t, [3, 3]) ==>?
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]
#如果shape有元素[-1],表示在該維度打平至一維
# -1 將自動推導得為 9:
reshape(t, [2, -1]) ==>?
[[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6]]tf.expand_dims(input, dim, name=None) 插入維度1進入一個tensor中
#該操作要求-1-input.dims()
# ‘t’ is a tensor of shape [2]
shape(expand_dims(t, 0)) ==> [1, 2]
shape(expand_dims(t, 1)) ==> [2, 1]
shape(expand_dims(t, -1)) ==> [2, 1] <= dim <= input.dims()
- 切片與合并(Slicing and Joining)
操作 描述 tf.slice(input_, begin, size, name=None) 對tensor進行切片操作
其中size[i] = input.dim_size(i) - begin[i]
該操作要求 0 <= begin[i] <= begin[i] + size[i] <= Di for i in [0, n]
#’input’ is?
#[[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]]
tf.slice(input, [1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 3]) ==> [[[3, 3, 3]]]
tf.slice(input, [1, 0, 0], [1, 2, 3]) ==>?
[[[3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4]]]
tf.slice(input, [1, 0, 0], [2, 1, 3]) ==>?
[[[3, 3, 3]],
[[5, 5, 5]]]tf.split(split_dim, num_split, value, name=’split’) 沿著某一維度將tensor分離為num_split tensors
# ‘value’ is a tensor with shape [5, 30]
# Split ‘value’ into 3 tensors along dimension 1
split0, split1, split2 = tf.split(1, 3, value)
tf.shape(split0) ==> [5, 10]tf.concat(concat_dim, values, name=’concat’) 沿著某一維度連結tensor
t1 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
t2 = [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat(0, [t1, t2]) ==> [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
tf.concat(1, [t1, t2]) ==> [[1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9], [4, 5, 6, 10, 11, 12]]
如果想沿著tensor一新軸連結打包,那么可以:
tf.concat(axis, [tf.expand_dims(t, axis) for t in tensors])
等同于tf.pack(tensors, axis=axis)tf.pack(values, axis=0, name=’pack’) 將一系列rank-R的tensor打包為一個rank-(R+1)的tensor
# ‘x’ is [1, 4], ‘y’ is [2, 5], ‘z’ is [3, 6]
pack([x, y, z]) => [[1, 4], [2, 5], [3, 6]]?
# 沿著第一維pack
pack([x, y, z], axis=1) => [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
等價于tf.pack([x, y, z]) = np.asarray([x, y, z])tf.reverse(tensor, dims, name=None) 沿著某維度進行序列反轉
其中dim為列表,元素為bool型,size等于rank(tensor)
# tensor ‘t’ is?
[[[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
#[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
#[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
#[[12, 13, 14, 15],
#[16, 17, 18, 19],
#[20, 21, 22, 23]]]]
# tensor ‘t’ shape is [1, 2, 3, 4]
# ‘dims’ is [False, False, False, True]
reverse(t, dims) ==>
[[[[ 3, 2, 1, 0],
[ 7, 6, 5, 4],
[ 11, 10, 9, 8]],
[[15, 14, 13, 12],
[19, 18, 17, 16],
[23, 22, 21, 20]]]]tf.transpose(a, perm=None, name=’transpose’) 調換tensor的維度順序
按照列表perm的維度排列調換tensor順序,
如為定義,則perm為(n-1…0)
# ‘x’ is [[1 2 3],[4 5 6]]
tf.transpose(x) ==> [[1 4], [2 5],[3 6]]
# Equivalently
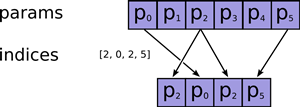
tf.transpose(x, perm=[1, 0]) ==> [[1 4],[2 5], [3 6]]tf.gather(params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None) 合并索引indices所指示params中的切片 tf.one_hot
(indices, depth, on_value=None, off_value=None,?
axis=None, dtype=None, name=None)indices = [0, 2, -1, 1]
depth = 3
on_value = 5.0?
off_value = 0.0?
axis = -1?
#Then output is [4 x 3]:?
output =?
[5.0 0.0 0.0] // one_hot(0)?
[0.0 0.0 5.0] // one_hot(2)?
[0.0 0.0 0.0] // one_hot(-1)?
[0.0 5.0 0.0] // one_hot(1)
矩陣相關運算?
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.diag(diagonal, name=None) | 返回一個給定對角值的對角tensor # ‘diagonal’ is [1, 2, 3, 4] tf.diag(diagonal) ==>? [[1, 0, 0, 0] [0, 2, 0, 0] [0, 0, 3, 0] [0, 0, 0, 4]] |
| tf.diag_part(input, name=None) | 功能與上面相反 |
| tf.trace(x, name=None) | 求一個2維tensor足跡,即對角值diagonal之和 |
| tf.transpose(a, perm=None, name=’transpose’) | 調換tensor的維度順序 按照列表perm的維度排列調換tensor順序, 如為定義,則perm為(n-1…0) # ‘x’ is [[1 2 3],[4 5 6]] tf.transpose(x) ==> [[1 4], [2 5],[3 6]] # Equivalently tf.transpose(x, perm=[1, 0]) ==> [[1 4],[2 5], [3 6]] |
| tf.matmul(a, b, transpose_a=False,? transpose_b=False, a_is_sparse=False,? b_is_sparse=False, name=None) | 矩陣相乘 |
| tf.matrix_determinant(input, name=None) | 返回方陣的行列式 |
| tf.matrix_inverse(input, adjoint=None, name=None) | 求方陣的逆矩陣,adjoint為True時,計算輸入共軛矩陣的逆矩陣 |
| tf.cholesky(input, name=None) | 對輸入方陣cholesky分解, 即把一個對稱正定的矩陣表示成一個下三角矩陣L和其轉置的乘積的分解A=LL^T |
| tf.matrix_solve(matrix, rhs, adjoint=None, name=None) | 求解tf.matrix_solve(matrix, rhs, adjoint=None, name=None) matrix為方陣shape為[M,M],rhs的shape為[M,K],output為[M,K] |
復數操作
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.complex(real, imag, name=None) | 將兩實數轉換為復數形式 # tensor ‘real’ is [2.25, 3.25] # tensor? imag?is [4.75, 5.75]tf.complex(real, imag) ==> [[2.25 + 4.75j], [3.25 + 5.75j]] |
| tf.complex_abs(x, name=None) | 計算復數的絕對值,即長度。 # tensor ‘x’ is [[-2.25 + 4.75j], [-3.25 + 5.75j]] tf.complex_abs(x) ==> [5.25594902, 6.60492229] |
| tf.conj(input, name=None) | 計算共軛復數 |
| tf.imag(input, name=None) tf.real(input, name=None) | 提取復數的虛部和實部 |
| tf.fft(input, name=None) | 計算一維的離散傅里葉變換,輸入數據類型為complex64 |
歸約計算(Reduction)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.reduce_sum(input_tensor, reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 計算輸入tensor元素的和,或者安照reduction_indices指定的軸進行求和 # ‘x’ is [[1, 1, 1] # [1, 1, 1]] tf.reduce_sum(x) ==> 6 tf.reduce_sum(x, 0) ==> [2, 2, 2] tf.reduce_sum(x, 1) ==> [3, 3] tf.reduce_sum(x, 1, keep_dims=True) ==> [[3], [3]] tf.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) ==> 6 |
| tf.reduce_prod(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 計算輸入tensor元素的乘積,或者安照reduction_indices指定的軸進行求乘積 |
| tf.reduce_min(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 求tensor中最小值 |
| tf.reduce_max(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 求tensor中最大值 |
| tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 求tensor中平均值 |
| tf.reduce_all(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 對tensor中各個元素求邏輯’與’ # ‘x’ is? # [[True, True] # [False, False]] tf.reduce_all(x) ==> False tf.reduce_all(x, 0) ==> [False, False] tf.reduce_all(x, 1) ==> [True, False] |
| tf.reduce_any(input_tensor,? reduction_indices=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 對tensor中各個元素求邏輯’或’ |
| tf.accumulate_n(inputs, shape=None,? tensor_dtype=None, name=None) | 計算一系列tensor的和 # tensor ‘a’ is [[1, 2], [3, 4]] # tensor? b?is [[5, 0], [0, 6]]tf.accumulate_n([a, b, a]) ==> [[7, 4], [6, 14]] |
| tf.cumsum(x, axis=0, exclusive=False,? reverse=False, name=None) | 求累積和 tf.cumsum([a, b, c]) ==> [a, a + b, a + b + c] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True) ==> [0, a, a + b] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], reverse=True) ==> [a + b + c, b + c, c] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True, reverse=True) ==> [b + c, c, 0] |
分割(Segmentation)?
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.segment_sum(data, segment_ids, name=None) | 根據segment_ids的分段計算各個片段的和 其中segment_ids為一個size與data第一維相同的tensor 其中id為int型數據,最大id不大于size c = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4], [-1,-2,-3,-4], [5,6,7,8]]) tf.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 0, 1])) ==>[[0 0 0 0]? [5 6 7 8]] 上面例子分為[0,1]兩id,對相同id的data相應數據進行求和, 并放入結果的相應id中, 且segment_ids只升不降 |
| tf.segment_prod(data, segment_ids, name=None) | 根據segment_ids的分段計算各個片段的積 |
| tf.segment_min(data, segment_ids, name=None) | 根據segment_ids的分段計算各個片段的最小值 |
| tf.segment_max(data, segment_ids, name=None) | 根據segment_ids的分段計算各個片段的最大值 |
| tf.segment_mean(data, segment_ids, name=None) | 根據segment_ids的分段計算各個片段的平均值 |
| tf.unsorted_segment_sum(data, segment_ids, num_segments, name=None) | 與tf.segment_sum函數類似, 不同在于segment_ids中id順序可以是無序的 |
| tf.sparse_segment_sum(data, indices,? segment_ids, name=None) | 輸入進行稀疏分割求和 c = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4], [-1,-2,-3,-4], [5,6,7,8]]) # Select two rows, one segment. tf.sparse_segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1]), tf.constant([0, 0]))? ==> [[0 0 0 0]] 對原data的indices為[0,1]位置的進行分割, 并按照segment_ids的分組進行求和 |
序列比較與索引提取(Sequence Comparison and Indexing)?
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.argmin(input, dimension, name=None) | 返回input最小值的索引index |
| tf.argmax(input, dimension, name=None) | 返回input最大值的索引index |
| tf.listdiff(x, y, name=None) | 返回x,y中不同值的索引 |
| tf.where(input, name=None) | 返回bool型tensor中為True的位置 # ‘input’ tensor is? #[[True, False] #[True, False]] # ‘input’ 有兩個’True’,那么輸出兩個坐標值. # ‘input’的rank為2, 所以每個坐標為具有兩個維度. where(input) ==> [[0, 0], [1, 0]] |
| tf.unique(x, name=None) | 返回一個元組tuple(y,idx),y為x的列表的唯一化數據列表, idx為x數據對應y元素的index # tensor ‘x’ is [1, 1, 2, 4, 4, 4, 7, 8, 8] y, idx = unique(x) y ==> [1, 2, 4, 7, 8] idx ==> [0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4] |
| tf.invert_permutation(x, name=None) | 置換x數據與索引的關系 # tensor? x?is [3, 4, 0, 2, 1]invert_permutation(x) ==> [2, 4, 3, 0, 1] |
神經網絡(Neural Network)
- 激活函數(Activation Functions)
操作 描述 tf.nn.relu(features, name=None) 整流函數:max(features, 0) tf.nn.relu6(features, name=None) 以6為閾值的整流函數:min(max(features, 0), 6) tf.nn.elu(features, name=None) elu函數,exp(features) - 1 if < 0,否則features
Exponential Linear Units (ELUs)tf.nn.softplus(features, name=None) 計算softplus:log(exp(features) + 1) tf.nn.dropout(x, keep_prob,?
noise_shape=None, seed=None, name=None)計算dropout,keep_prob為keep概率
noise_shape為噪聲的shapetf.nn.bias_add(value, bias, data_format=None, name=None) 對value加一偏置量
此函數為tf.add的特殊情況,bias僅為一維,
函數通過廣播機制進行與value求和,
數據格式可以與value不同,返回為與value相同格式tf.sigmoid(x, name=None) y = 1 / (1 + exp(-x)) tf.tanh(x, name=None) 雙曲線切線激活函數
- 卷積函數(Convolution)
操作 描述 tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding,?
use_cudnn_on_gpu=None, data_format=None, name=None)在給定的4D input與 filter下計算2D卷積
輸入shape為 [batch, height, width, in_channels]tf.nn.conv3d(input, filter, strides, padding, name=None) 在給定的5D input與 filter下計算3D卷積
輸入shape為[batch, in_depth, in_height, in_width, in_channels]
- 池化函數(Pooling)
?
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.avg_pool(value, ksize, strides, padding,? data_format=’NHWC’, name=None) | 平均方式池化 |
| tf.nn.max_pool(value, ksize, strides, padding,? data_format=’NHWC’, name=None) | 最大值方法池化 |
| tf.nn.max_pool_with_argmax(input, ksize, strides, padding, Targmax=None, name=None) | 返回一個二維元組(output,argmax),最大值pooling,返回最大值及其相應的索引 |
| tf.nn.avg_pool3d(input, ksize, strides,? padding, name=None) | 3D平均值pooling |
| tf.nn.max_pool3d(input, ksize, strides,? padding, name=None) | 3D最大值pooling |
- 數據標準化(Normalization)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim, epsilon=1e-12, name=None) | 對維度dim進行L2范式標準化 output = x / sqrt(max(sum(x**2), epsilon)) |
| tf.nn.sufficient_statistics(x, axes, shift=None,? keep_dims=False, name=None) | 計算與均值和方差有關的完全統計量 返回4維元組,*元素個數,*元素總和,*元素的平方和,*shift結果 參見算法介紹 |
| tf.nn.normalize_moments(counts, mean_ss, variance_ss, shift, name=None) | 基于完全統計量計算均值和方差 |
| tf.nn.moments(x, axes, shift=None,? name=None, keep_dims=False) | 直接計算均值與方差 |
- 損失函數(Losses)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.l2_loss(t, name=None) | output = sum(t ** 2) / 2 |
- 分類函數(Classification)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits (logits, targets, name=None)* | 計算輸入logits, targets的交叉熵 |
| tf.nn.softmax(logits, name=None) | 計算softmax softmax[i, j] = exp(logits[i, j]) / sum_j(exp(logits[i, j])) |
| tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, name=None) | logsoftmax[i, j] = logits[i, j] - log(sum(exp(logits[i]))) |
| tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits (logits, labels, name=None) | 計算logits和labels的softmax交叉熵 logits, labels必須為相同的shape與數據類型 |
| tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits (logits, labels, name=None) | 計算logits和labels的softmax交叉熵 |
| tf.nn.weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits (logits, targets, pos_weight, name=None) | 與sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits()相似, 但給正向樣本損失加了權重pos_weight |
?
- 符號嵌入(Embeddings)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.embedding_lookup (params, ids, partition_strategy=’mod’,? name=None, validate_indices=True) | 根據索引ids查詢embedding列表params中的tensor值 如果len(params) > 1,id將會安照partition_strategy策略進行分割 1、如果partition_strategy為”mod”, id所分配到的位置為p = id % len(params) 比如有13個ids,分為5個位置,那么分配方案為: [[0, 5, 10], [1, 6, 11], [2, 7, 12], [3, 8], [4, 9]] 2、如果partition_strategy為”div”,那么分配方案為: [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]] |
| tf.nn.embedding_lookup_sparse(params,? sp_ids, sp_weights, partition_strategy=’mod’,? name=None, combiner=’mean’) | 對給定的ids和權重查詢embedding 1、sp_ids為一個N x M的稀疏tensor, N為batch大小,M為任意,數據類型int64 2、sp_weights的shape與sp_ids的稀疏tensor權重, 浮點類型,若為None,則權重為全’1’ |
- 循環神經網絡(Recurrent Neural Networks)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=None, dtype=None,? sequence_length=None, scope=None) | 基于RNNCell類的實例cell建立循環神經網絡 |
| tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, sequence_length=None,? initial_state=None, dtype=None, parallel_iterations=None,? swap_memory=False, time_major=False, scope=None) | 基于RNNCell類的實例cell建立動態循環神經網絡 與一般rnn不同的是,該函數會根據輸入動態展開 返回(outputs,state) |
| tf.nn.state_saving_rnn(cell, inputs, state_saver, state_name,? sequence_length=None, scope=None) | 可儲存調試狀態的RNN網絡 |
| tf.nn.bidirectional_rnn(cell_fw, cell_bw, inputs,? initial_state_fw=None, initial_state_bw=None, dtype=None, sequence_length=None, scope=None) | 雙向RNN, 返回一個3元組tuple (outputs, output_state_fw, output_state_bw) |
?
—?tf.nn.rnn簡要介紹—?
cell: 一個RNNCell實例?
inputs: 一個shape為[batch_size, input_size]的tensor?
initial_state: 為RNN的state設定初值,可選?
sequence_length:制定輸入的每一個序列的長度,size為[batch_size],值范圍為[0, T)的int型數據?
其中T為輸入數據序列的長度?
@?
@針對輸入batch中序列長度不同,所設置的動態計算機制?
@對于在時間t,和batch的b行,有?
(output, state)(b, t) = ? (zeros(cell.output_size), states(b, sequence_length(b) - 1)) : cell(input(b, t), state(b, t - 1))
- 求值網絡(Evaluation)
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.nn.top_k(input, k=1, sorted=True, name=None) | 返回前k大的值及其對應的索引 |
| tf.nn.in_top_k(predictions, targets, k, name=None) | 返回判斷是否targets索引的predictions相應的值 是否在在predictions前k個位置中, 返回數據類型為bool類型,len與predictions同 |
- 監督候選采樣網絡(Candidate Sampling)
?對于有巨大量的多分類與多標簽模型,如果使用全連接softmax將會占用大量的時間與空間資源,所以采用候選采樣方法僅使用一小部分類別與標簽作為監督以加速訓練。
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Sampled Loss Functions | ? |
| tf.nn.nce_loss(weights, biases, inputs, labels, num_sampled, num_classes, num_true=1, sampled_values=None, remove_accidental_hits=False, partition_strategy=’mod’, name=’nce_loss’) | 返回noise-contrastive的訓練損失結果 |
| tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss(weights, biases, inputs, labels,? num_sampled, num_classes, num_true=1, sampled_values=None, remove_accidental_hits=True, partition_strategy=’mod’,? name=’sampled_softmax_loss’) | 返回sampled softmax的訓練損失 參考- Jean et al., 2014第3部分 |
| Candidate Samplers | ? |
| tf.nn.uniform_candidate_sampler(true_classes, num_true,? num_sampled, unique, range_max, seed=None, name=None) | 通過均勻分布的采樣集合 返回三元tuple 1、sampled_candidates 候選集合。 2、期望的true_classes個數,為浮點值 3、期望的sampled_candidates個數,為浮點值 |
| tf.nn.log_uniform_candidate_sampler(true_classes, num_true, num_sampled, unique, range_max, seed=None, name=None) | 通過log均勻分布的采樣集合,返回三元tuple |
| tf.nn.learned_unigram_candidate_sampler (true_classes, num_true, num_sampled, unique,? range_max, seed=None, name=None) | 根據在訓練過程中學習到的分布狀況進行采樣 返回三元tuple |
| tf.nn.fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler(true_classes, num_true, num_sampled, unique, range_max, vocab_file=”,? distortion=1.0, num_reserved_ids=0, num_shards=1,? shard=0, unigrams=(), seed=None, name=None) | 基于所提供的基本分布進行采樣 |
保存與恢復變量
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 類tf.train.Saver(Saving and Restoring Variables) | ? |
| tf.train.Saver.__init__(var_list=None, reshape=False,? sharded=False, max_to_keep=5,? keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=10000.0,? name=None, restore_sequentially=False, saver_def=None, builder=None) | 創建一個存儲器Saver var_list定義需要存儲和恢復的變量 |
| tf.train.Saver.save(sess, save_path, global_step=None,? latest_filename=None, meta_graph_suffix=’meta’, write_meta_graph=True) | 保存變量 |
| tf.train.Saver.restore(sess, save_path) | 恢復變量 |
| tf.train.Saver.last_checkpoints | 列出最近未刪除的checkpoint 文件名 |
| tf.train.Saver.set_last_checkpoints(last_checkpoints) | 設置checkpoint文件名列表 |
| tf.train.Saver.set_last_checkpoints_with_time(last_checkpoints_with_time) | 設置checkpoint文件名列表和時間戳 |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?










)




WS-DAN (弱監督數據增強))

)

)