最近隔壁項目組的項目又出問題了,一直被用戶投訴太卡了,頁面白屏的那種,打開源代碼一看,全是非異步請求,類似于以下寫法:
@ResponseBody@RequestMapping(value = "/getTest")public String getTest() {System.out.println("主線程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(8000);//模擬業務執行時間} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("主線程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+System.currentTimeMillis());return "success...";}對于異步請求,用這個的好處呢是可以增大項目吞吐量,一個請求過來,將處理業務內容交于另外一個線程去執行,并且立即釋放主線程,請求少的時候其客戶端并感受不到,當請求多的時候,tomcat線程不夠用時,會有部分用戶客戶端出線等待或白屏狀態,體驗不佳,增加tomcat線程也可以,但是tomcat線程數和機器性能參數有關,極限一般是在3000~5000左右不等,而且線程越多,CPU響應時間也長,請求線程響應時間也會過長,所以,設置tomcat線程數最好是找到一個平衡點
官網介紹:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/4.3.12.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/html/mvc.html#mvc-ann-async
?從Servlet3.0和SpringMvc3.2以后開始支持異步請求,可以通過使用Callable這個回調接口實現,也可以通過DeferredResult這個對象進行實現,下面為具體官方介紹的用法,以下為兩種用法,還有一種是使用WebAsyncTask:
@PostMapping
public Callable<String> processUpload(final MultipartFile file) {return new Callable<String>() {public String call() throws Exception {// ...return "someView";}};}@RequestMapping("/quotes")
@ResponseBody
public DeferredResult<String> quotes() {DeferredResult<String> deferredResult = new DeferredResult<String>();// Save the deferredResult somewhere..return deferredResult;
}// In some other thread...
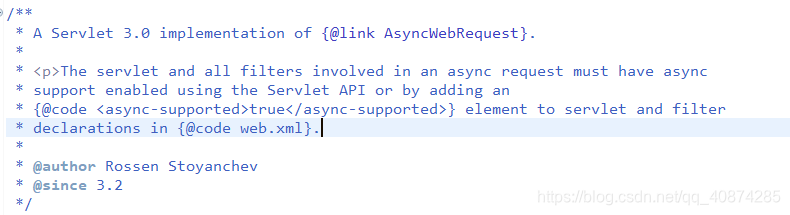
deferredResult.setResult(data); @RequestMapping("/getWebAsyncTask")@ResponseBodypublic WebAsyncTask<String> asyncTask(){System.out.println("主線程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+System.currentTimeMillis());// 1000 為超時設置,默認執行時間為10秒WebAsyncTask<String> webAsyncTask = new WebAsyncTask<String>(2000L,new Callable<String>(){public String call() throws Exception {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());//業務邏輯處理Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());return "WebAsyncTask success..";}});webAsyncTask.onCompletion(new Runnable() {public void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"調用完成");}});webAsyncTask.onTimeout(new Callable<String>() {public String call() throws Exception {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"業務處理超時");return "<h1>Time Out</h1>";}});System.out.println("主線程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+System.currentTimeMillis());return webAsyncTask;}在異步請求的源碼中的注釋看到,在用異步的請求之前了都需要在web.xml加上的Servlet上面加上<async-supported>true</async-supported>:
?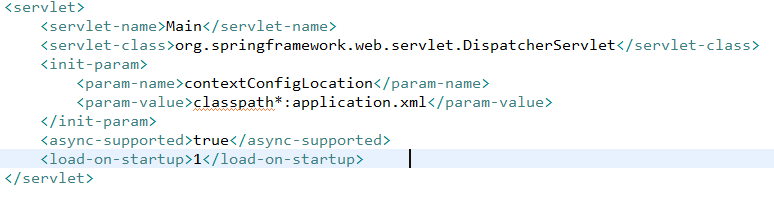
如果不加上會報以下錯誤(不過在使用SpringBoot項目的時候,這個會Spring被默認設置成true,所以在SpringBoot項目中無需設置):
嚴重: Servlet.service() for servlet [Main] in context with path [/TestWebMvc] threw exception [Request processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Async support must be enabled on a servlet and for all filters involved in async request processing. This is done in Java code using the Servlet API or by adding "<async-supported>true</async-supported>" to servlet and filter declarations in web.xml.] with root cause
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Async support must be enabled on a servlet and for all filters involved in async request processing. This is done in Java code using the Servlet API or by adding "<async-supported>true</async-supported>" to servlet and filter declarations in web.xml.at org.springframework.util.Assert.state(Assert.java:392)at org.springframework.web.context.request.async.StandardServletAsyncWebRequest.startAsync(StandardServletAsyncWebRequest.java:103)at org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager.startAsyncProcessing(WebAsyncManager.java:428)at org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager.startCallableProcessing(WebAsyncManager.java:308)at org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager.startCallableProcessing(WebAsyncManager.java:255)
?進入到源碼里面可以看到,報錯的地方是在StandardServletAsyncWebRequest.java:103
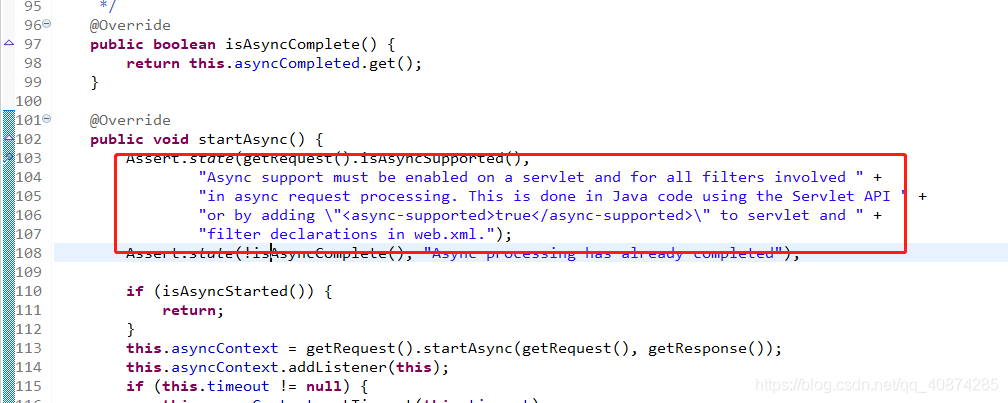
其實就是直接的看到getRequest()這個對象的一個屬性而已(request對象地址:org.apache.catalina.connector.Request@79b39c31,說明這個請求是tomcat中的一個對象):
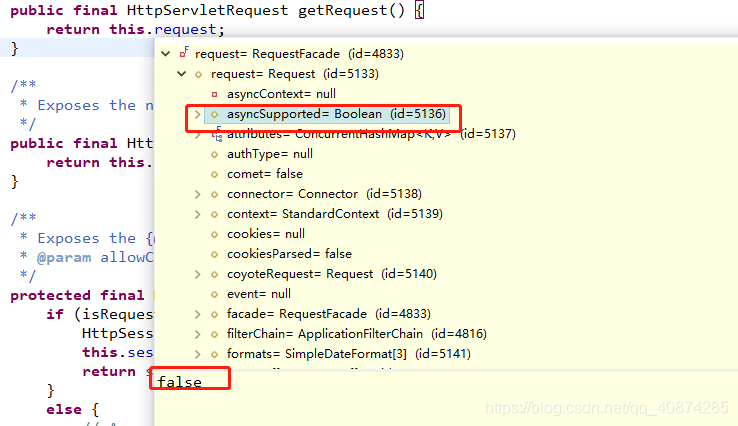
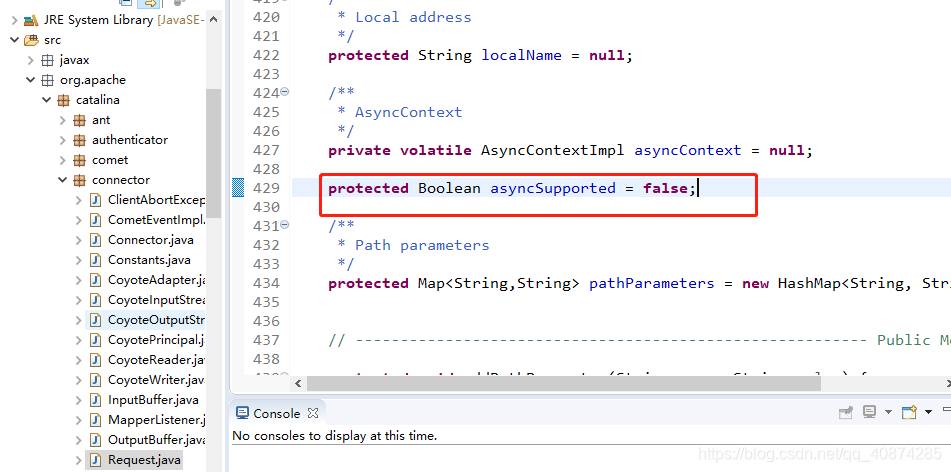
在tomcat源碼中,該對象的屬性默認為false:
在公司的加上那個屬性標簽后,結果發現屬性被公司的破平臺jar包吃掉了,這時不慌,可以先設置一個攔截器或者過濾器,在這個里面加上一個屬性,這樣也可以設置異步屬性:
request.setAttribute("org.apache.catalina.ASYNC_SUPPORTED", true);結果發現還是不行,這時逼我改源碼呀!最后將StandardServletAsyncWebRequest.java這個類重寫了一下,在判斷之前設置一下請求屬性,這樣才好,現在回到異步使用那里,其實在官方還是一種異步的方法,使用WebAsyncTask這個類這個可以增加超時回調結果,在調用中,我們打印一下異步線程名稱: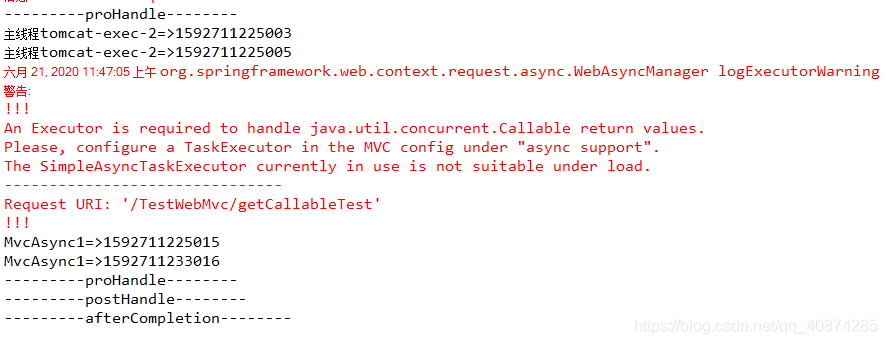
運行時時候會提示你請配置一個線程池,并且采用的線程為:MvcAsync,這個是SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor線程,但這個并非線程池,打開這個源碼看的時候發現,他就是創建了一個新的Thread用來執行異步線程:
/*** Template method for the actual execution of a task.* <p>The default implementation creates a new Thread and starts it.* @param task the Runnable to execute* @see #setThreadFactory* @see #createThread* @see java.lang.Thread#start()*/protected void doExecute(Runnable task) {Thread thread = (this.threadFactory != null ? this.threadFactory.newThread(task) : createThread(task));thread.start();}那我們就先配置一個線程池:創建一個類繼承WebMvcConfigurer接口,實現configureAsyncSupport方法:
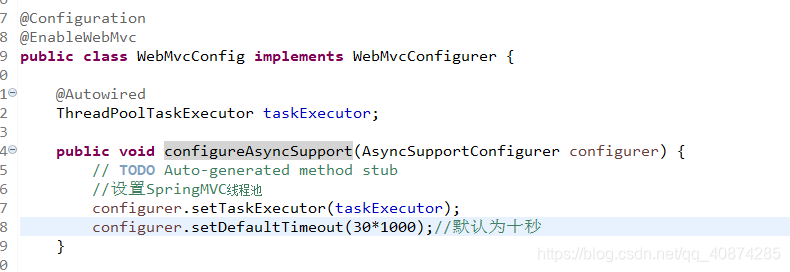
現在就可以正常使用異步線程啦!
說一下MVC異步走向原理:
在上面那個執行截圖來看,會發現在執行異步是,會多調用一次攔截器的preHandle方法:
其實就是,請求過來時,經過攔截器后發現該請求為異步,會將tomcat中的Servlet以及Filter退出容器,保持一個response的響應連接,當業務執行完畢后,會自動去請求一次容器,將結果返回到客戶端上。
而且異步執行時,SpringMVC會先調用自己的前置處理器,在源碼的WebAsyncManager.java類中:
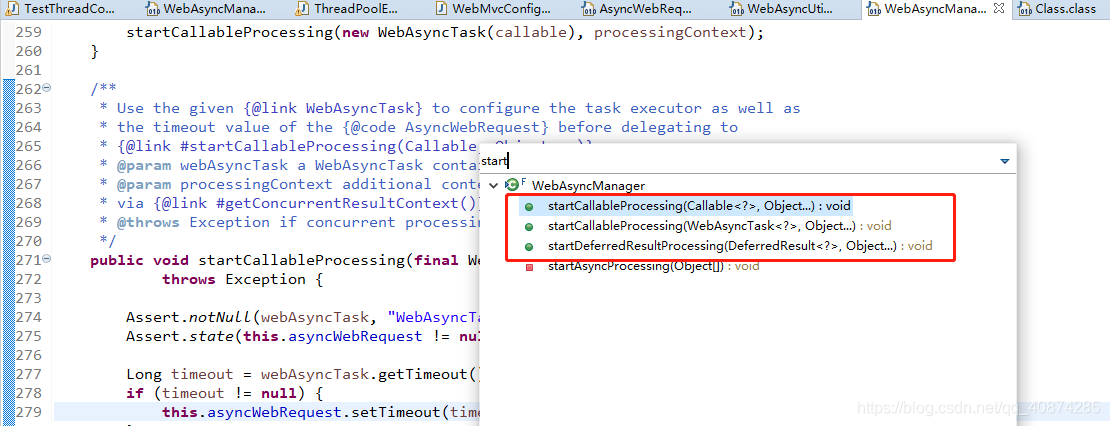
三種前置處理器分別對應三種使用方式,其實使用Callable異步運行和使用WebAsyncTask在源碼中是一致的,而且異步調用的源代碼也是使用Future<?>這個類執行的(這里用到了并發這一塊)保證執行的效率:
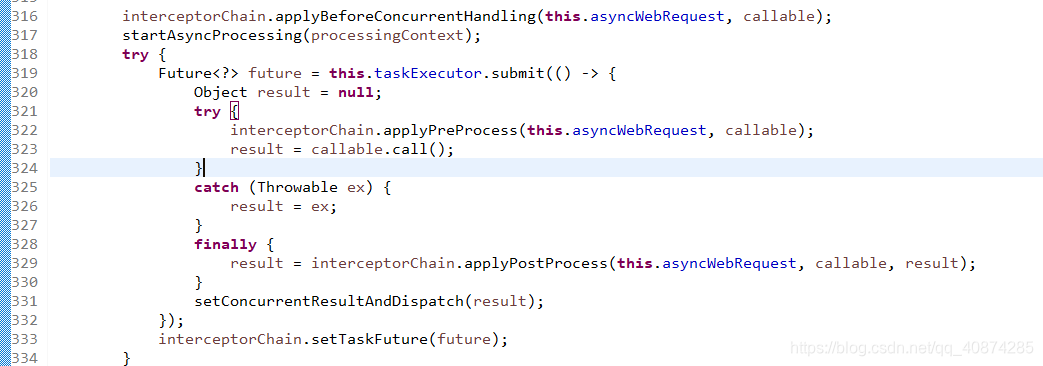
好了,這就是SpringMVC簡單的異步調用,以及部分源碼的解讀,有問題請各位社區大佬指教!



:開啟net.tcp端口)


![Sgen.exe: Speed up XmlSerializer's Startup Performance [.NET 2.0, XML Serialization]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/Sgen.exe: Speed up XmlSerializer's Startup Performance [.NET 2.0, XML Serialization])






使用)


源碼解析)


