目錄
- (一)內核定時器介紹
- (二)內核定時器相關接口
- (三)使用步驟
- (四)實例代碼
(一)內核定時器介紹
內核定時器并不是用來簡單的定時操作,而是在定時時間后,觸發事件的操作,類似定時器中斷,是內核用來控制在未來某個時間點(基于jiffies)調度執行某個函數的一種機制,內核中采用的定時器以jiffies為單位。 單位秒=jiffies/HZ
幾個重要跟時間有關的名詞或變數
HZ:Linux核心每隔固定周期會發出timer interrupt (IRQ 0),HZ是用來定義每一秒有幾次timer interrupts。舉例來說,HZ為1000,代表每秒有1000次timer interrupts。
Tick:Tick是HZ的倒數,意即timer interrupt每發生一次中斷的時間。如HZ為250時,tick為4毫秒(millisecond)。
Jiffies:Jiffies為Linux核心變數(unsigned long),它被用來記錄系統自開機以來,已經過了多少tick。每發生一次timer interrupt,Jiffies變數會被加一。值得注意的是,Jiffies于系統開機時,并非初始化成零,而是被設為-300*HZ ,類似Linux系統中time(日歷時間)
(二)內核定時器相關接口
和定時器先關的數據結構:
struct timer_list {unsigned long expires; //未來時間點,即超時時間void (*function)(unsigned long);//超時回調函數unsigned long data; //傳遞給回調函數的數據,也就是定時器數據
};
初始化定時器相關的數據結構
1. 靜態定以定時器數據結構:
#define DEFINE_TIMER(_name, _function, _expires, _data) \struct timer_list _name = \TIMER_INITIALIZER(_function, _expires, _data)2. 動態初始化:-----手動對變量進行初始化
#define init_timer(timer) \do { \static struct lock_class_key __key; \init_timer_key((timer), #timer, &__key); \} while (0)
可延時定時:
#define init_timer_deferrable(timer) \do { \static struct lock_class_key __key; \init_timer_deferrable_key((timer), #timer, &__key); \} while (0)
設置定時時間
#define setup_timer(timer, fn, data) \
do { \static struct lock_class_key __key; \setup_timer_key((timer), #timer, &__key, (fn), (data));\
} while (0)
向內核添加定時器:
/*** add_timer - start a timer* @timer: the timer to be added** The kernel will do a ->function(->data) callback from the* timer interrupt at the ->expires point in the future. The* current time is 'jiffies'.** The timer's ->expires, ->function (and if the handler uses it, ->data)* fields must be set prior calling this function.** Timers with an ->expires field in the past will be executed in the next* timer tick.*/
void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
{BUG_ON(timer_pending(timer));mod_timer(timer, timer->expires);
}
從內核刪除定時器:
/*** del_timer - deactive a timer.* @timer: the timer to be deactivated** del_timer() deactivates a timer - this works on both active and inactive* timers.** The function returns whether it has deactivated a pending timer or not.* (ie. del_timer() of an inactive timer returns 0, del_timer() of an* active timer returns 1.)*/
int del_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
修改定時時間:
/*** mod_timer - modify a timer's timeout* @timer: the timer to be modified* @expires: new timeout in jiffies** mod_timer() is a more efficient way to update the expire field of an* active timer (if the timer is inactive it will be activated)** mod_timer(timer, expires) is equivalent to:** del_timer(timer); timer->expires = expires; add_timer(timer);** Note that if there are multiple unserialized concurrent users of the* same timer, then mod_timer() is the only safe way to modify the timeout,* since add_timer() cannot modify an already running timer.** The function returns whether it has modified a pending timer or not.* (ie. mod_timer() of an inactive timer returns 0, mod_timer() of an* active timer returns 1.)*/
int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires)
jiffies和時間的轉換:
extern unsigned int jiffies_to_msecs(const unsigned long j);
extern unsigned int jiffies_to_usecs(const unsigned long j);
extern unsigned long msecs_to_jiffies(const unsigned int m);
extern unsigned long usecs_to_jiffies(const unsigned int u);
(三)使用步驟
1、向內核添加定時器
setup_timer();設置定時器add_timer();.
2、解綁定時器
int del_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
(四)實例代碼
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>struct timer_list timer;
void function(unsigned long data)
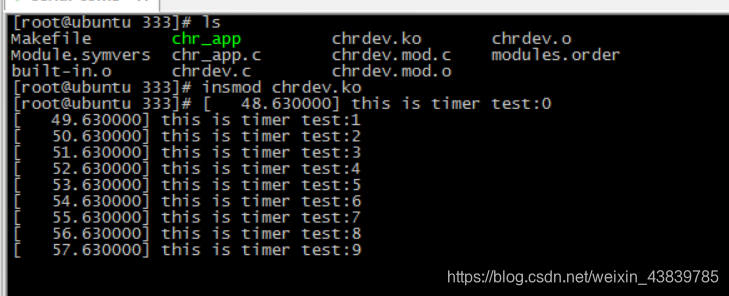
{static int count=0;printk("this is timer test:%d\n",count++);mod_timer(&timer,jiffies+1*HZ);
}
static int __init timer_module_init(void)
{timer.expires = jiffies+5*HZ;setup_timer(&timer,function,0);add_timer(&timer);return 0;
}
static void __exit timer_module_cleanup(void)
{del_timer(&timer);
}module_init(timer_module_init);
module_exit(timer_module_cleanup);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
本文章僅供學習交流用禁止用作商業用途,文中內容來水枂編輯,如需轉載請告知,謝謝合作
微信公眾號:zhjj0729
微博:文藝to青年
)
linux中斷底半部分處理機制)
 B. Pasha and Phone C. Duff and Weight Lifting)

與 $()區別)




)
)





)

)
