這里寫目錄標題
- (一)原始圖像
- (二)雙線性插值原理
- (三)python實現
- 1. 安裝庫
- 2. python程序編寫
- 3. 效果
- 4. 工程文件
(一)原始圖像

(二)雙線性插值原理
一般情況下我們對圖像縮放的時候會進行上采樣或下采樣,上采樣常采用插值來實現,本文章使用雙線性插值實現圖像放大
雙線性插值的核心思想是在兩個方向上分別進行一次插值,關于下圖的解釋可以參考百度百科:雙線性插值
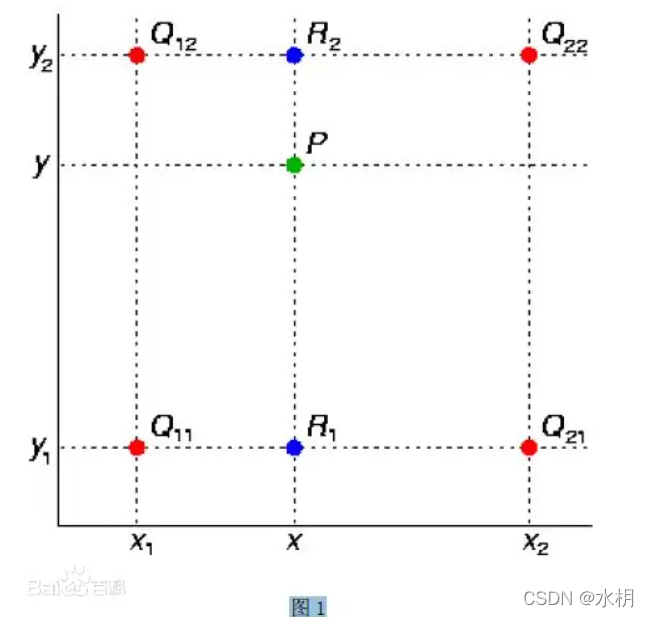
使用雙線性插值注意將目標圖形和原圖像幾何中心重合在計算插值,雙線性插值只會使用臨近的四個像素點坐標,先求x的單線性插值,再求y的單線性插值
這里舉例來說明:
關于中心對齊可以參考:雙線性插值,個人認為上面中心對齊時+0.5是因為圖像坐標從0開始,所以對于33的圖像只有(0 1 2)對應到55的圖像(0 1 2 3 4),它們的寬高比為5/3,對于33的2只能到25/3=3.3,永遠到不了4這個地方,只能先+0.5才能到4,(2+0.5)*5/3=4.1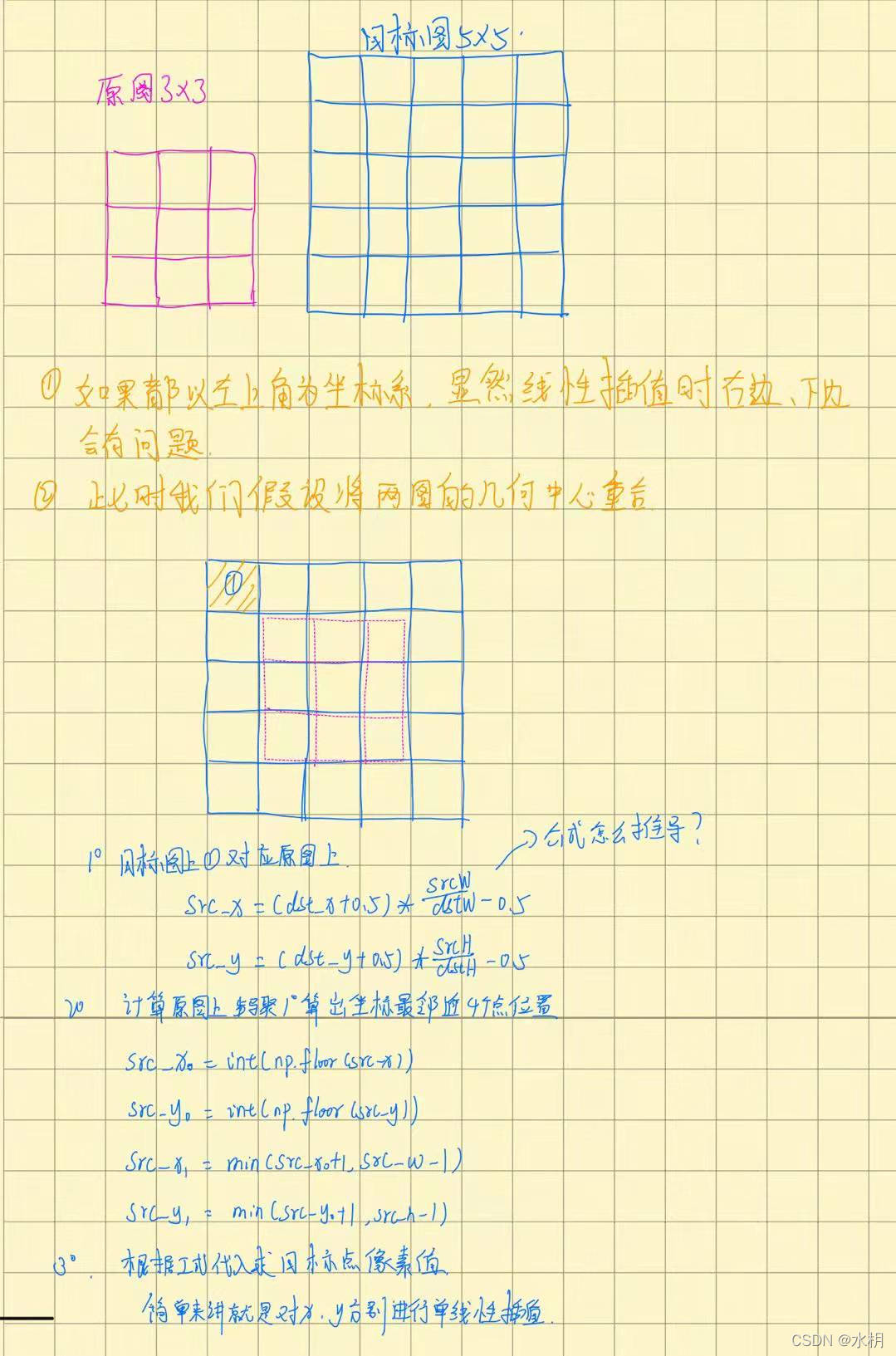
(三)python實現
python安裝可以參考:python安裝
1. 安裝庫
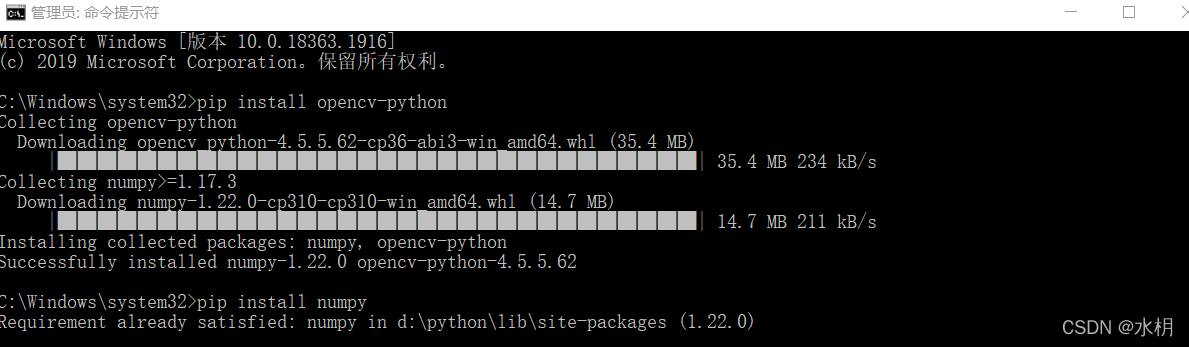
首先我們需要安裝用到的庫,按住win+r輸入cmd打開dos窗口,輸入下面的命令
pip install opencv-python
pip install numpy
2. python程序編寫
import cv2 # cv2 即opencv的庫
import numpy as np #給numpy起別名np,該庫Numerical Python是python的數學函數庫#雙線性插值實現
def bilinear_interpolation(img,out_dim):src_h,src_w,channels = img.shapedst_h,dst_w = out_dim[1],out_dim[0]print("src_h,src_w= ",src_h,src_w)print("dst_h,dst_w= ",dst_h,dst_w)if src_h == dst_h and src_w == dst_w:return img.copy()dst_img = np.zeros((dst_h,dst_w,3),dtype=np.uint8)scale_x,scale_y = float(src_w)/dst_w,float(src_h)/dst_hfor i in range(3):for dst_y in range(dst_h):for dst_x in range (dst_w):#根據幾何中心重合找出目標像素的坐標src_x = (dst_x+0.5)*scale_x -0.5src_y = (dst_y+0.5)*scale_y -0.5#找出目標像素最鄰近的四個點src_x0 = int(np.floor(src_x))src_x1 = min(src_x0 + 1,src_w -1)src_y0 = int(np.floor(src_y))src_y1 = min(src_y0 + 1,src_h -1)#代入公式計算temp0 = (src_x1 - src_x) * img[src_y0,src_x0,i] + (src_x - src_x0) * img[src_y0,src_x1,i]temp1 = (src_x1 - src_x) * img[src_y1,src_x0,i] + (src_x - src_x0) * img[src_y1,src_x1,i]dst_img[dst_y,dst_x,i] = int((src_y1 - src_y) * temp0 + (src_y - src_y0) * temp1)return dst_imgimg = cv2.imread("lenna.png")
dst = bilinear_interpolation(img,(700,700))
cv2.imshow("blinear",dst)
cv2.waitKey()3. 效果

打印信息:
======= RESTART: D:\AI\opencv\opencv\interpolation\bilinear_interpolation.py ======
src_h,src_w= 512 512
dst_h,dst_w= 700 7004. 工程文件
線性插值函數

圖像轉灰度圖Python實現)


)


)

)


)






