ArrayBuffer對象作為內存區域可以存放多種類型的數據。同一段內存,不同數據有不同的解讀方式,這種解讀方式稱為“視圖(view)”。ArrayBuffer有兩種類型的視圖,一種是類型化數組視圖(TypedArray),另一種是數據視圖(DataView)。類型化數組視圖的數組成員都是同一個數據類型,后者的數組成員可以是不同的數據類型。
TypedArray視圖一共有9種類型,每一種視圖都是一個構造函數。
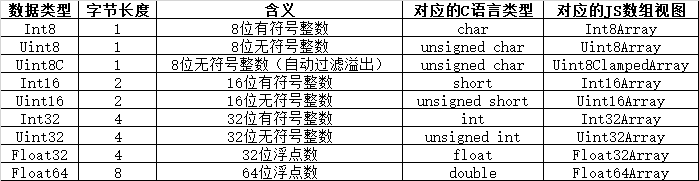
這些視圖實現了數組接口,均有length屬性,都可以使用方括號運算符來獲取單個元素,所有數組方法都可以在其上面使用。普通數組和TypedArray數組的差異主要在以下方面:
1、TypedArray數組的所有成員都是同一種類型。
2、TypedArray數組的成員是連續的,不會有空位,不存在稀疏數組的情況。
3、TypedArray數組成員的默認值是0。
TypedArray數組只是一個視圖,本身不存儲數據,它的數據都存儲在底層的ArrayBuffer對象中,要獲取底層對象必須使用buffer屬性。
TypedArray構造函數
TypedArray有四種形式的構造函數,分別是:
1、TypedArray(buffer, byteOffset, length)
參數buffer代表了視圖底層的ArrayBuffer對象,byteOffset表示視圖開始的字節序號,默認從0開始,length代表視圖包含的數據個數,默認直到本段內存區域結束。
其中,byteOffset必須是與所要建立的數據類型的字節長度的整數倍,否則會出錯。
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(32);
var i16 = new Uint16Array(buffer, 1); // RangeError, Uint16的每個數據的長度為2個字節,故byteOffset必須是
2、TypedArray(length)
視圖可以不通過ArrayBuffer對象,直接指定長度,分配相應的內存。構造函數的參數代表要分配的成員個數。
var i16 = new Int16Array(3); // 分配了3*2=6個字節的內存
i16.buffer.byteLength; // 6
3、TypedArray(typedArray)
可以通過一個TypedArray實例來構建另一個TypedArray實例,兩個實例的類型可以不一樣,此時新實例只是復制了源實例的值,底層的內存是不一樣的。
var source = new Uint16Array(16);
var target = new Int16Array(source);
4、TypedArray(arrayLikeObject)
可以通過一個類數組對象來創建TypedArray實例,數組對象的每一個值就是新實例數組的每一項對應的值。
var a = new Uint32Array([1,2,3,4]);
a[2]; // 3TypedArray的屬性
1、TypedArray有一個name屬性,是用于描述類型數組的字符串值。九個類型數組的name屬性分別是:
Int8Array.name; // "Int8Array"
Uint8Array.name; // "Uint8Array"
Uint8ClampedArray.name; // "Uint8ClampedArray"
Int16Array.name; // "Int16Array"
Uint16Array.name; // "Uint16Array"
Int32Array.name; // "Int32Array"
Uint32Array.name; // "Uint32Array"
Float32Array.name; // "Float32Array"
Float64Array.name; // "Float64Array"
2、BYTES_PER_ELEMENT屬性表示這種數據類型的每個元素所占用的字節數。
Int8Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 1
Uint8Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 1
Uint8ClampedArray.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 1
Int16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 2
Uint16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 2
Int32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 4
Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 4
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 4
Float64Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT; // 8
3、TypedArray實例的buffer屬性返回整段內存區域對于的ArrayBuffer對象。該屬性為只讀屬性。
var ab = new ArrayBuffer(32);
var ui16 = new Uint16Array(ab);
ui16.buffer === ab; // true
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Uint16Array.prototype.__proto__, 'buffer');
// {get: ?, set: undefined, enumerable: false, configurable: true}
4、TypedArray實例的byteLength屬性返回TypedArray數組占據的內存長度,單位為字節。
var ab = new ArrayBuffer(32);
var ui16 = new Uint16Array(ab, 2);
ui16.byteLength; // 30
5、TypedArray實例的byteOffset屬性表示TypedArray數組從底層ArrayBuffer對象的哪個字節開始。
var ab = new ArrayBuffer(32);
var ui16 = new Uint16Array(ab, 2);
ui16.byteOffset; // 2
6、TypedArray實例的length屬性表示實例有多少個成員。
var ab = new ArrayBuffer(32);
var ui16 = new Uint16Array(ab, 2);
ui16.length; // 15
TypedArray構造函數的靜態方法
TypedArray數組的所有構造函數上都有一個靜態方法of,用于將參數轉為一個TypedArray實例。
Float32Array.of(12.213, -8, 83.1); // [12.213, -8, 83.1]
// 也可以用下面的方法新建同樣的數組
var a = new Float32Array([12.213, -8, 83.1]);
var b = new Float32Array(3);
b[0] = 12.213;
b[1] = -8;
b[2] = 83.1
TypedArray數組的另一個靜態方法from()接受一個可遍歷的數據結構(比如數組)作為參數,返回一個基于此結構的TypedArray實例。同時還可以接受第二個函數參數,在新建實例時,對每一個元素向映射到函數中,將函數的結果作為新實例的值。
Uint16Array.from([1,2,3]); // [1,2,3]
Uint16Array.from([1,2,3], value => value * 2); // [2,4,6]
TypedArray原型對象上的方法
由于TypedArray實現了數組接口,故可以在TypedArray上使用數組的方法來進行操作。
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Uint16Array.prototype.__proto__);
/* [
"constructor",
"buffer",
"byteLength",
"byteOffset",
"length",
"entries",
"keys",
"values",
"copyWithin",
"subarray",
"set",
"every",
"fill",
"filter",
"find",
"findIndex",
"includes",
"indexOf",
"join",
"lastIndexOf",
"forEach",
"map",
"reduce",
"reduceRight",
"reverse",
"slice", "some",
"sort",
"toLocaleString",
"toString"] */
1、TypedArray.prototype.copyWithin(target, start[, end = this.length])
從原數組的start位置開始復制數據到end(不含),填充到target及以后的位置上,并返回修改后的數組。
var array = new Int16Array(10);
array.set([1,2,3]);
array; // [1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
array.copyWithin(3, 0, 3);
array; // [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0]
2、TypedArray.prototype.entries()
返回TypedArray的鍵值對遍歷器
var array = new Int16Array(3);
array.set([1,2,3]);
var iter = array.entries();
for (let element of iter) {console.log(element);
}
/*
[0,1]
[1,2]
[2,3]
*/
3、TypedArray.prototype.every(callback[, thisArg])
對數組的每一個元素都指向一次函數操作,如果每個元素都能通過測試,則返回true,否則返回false。
var array = new Int16Array(3);
array.set([1,2,3]);
array.every(function (value) { return value % 2 == 1; }); // false 2不是奇數
4、TypedArray.prototype.fill(value[, start = 0[, end = this.length]])
使用指定值填充TypedArray從start到end(不含)的全部元素。
new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]).fill(4); // Uint8Array [4, 4, 4]
new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]).fill(4, 1); // Uint8Array [1, 4, 4]
new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]).fill(4, 1, 2); // Uint8Array [1, 4, 3]
new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]).fill(4, 1, 1); // Uint8Array [1, 2, 3]
new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]).fill(4, -3, -2); // Uint8Array [4, 2, 3]
5、TypedArray.prototype.filter(callback[, thisArg])
對每個數組元素進行測試,保留通過測試函數的值。
function isBigEnough(element, index, array) {return element >= 10;
}
new Uint8Array([12, 5, 8, 130, 44]).filter(isBigEnough);
// Uint8Array [ 12, 130, 44 ]
6、TypedArray.prototype.find(callback[, thisArg])
返回第一個通過測試函數的值。如果沒有一個元素通過測試,則返回undefined。
function isPrime(element, index, array) {var start = 2;while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {if (element % start++ < 1) {return false;}}return element > 1;
}var uint8 = new Uint8Array([4, 5, 8, 12]);
console.log(uint8.find(isPrime)); // 5
7、TypedArray.prototype.findIndex(callback[, thisArg])
返回第一個通過測試函數的值的下標。如果沒有一個元素通過測試,則返回undefined。
function isPrime(element, index, array) {var start = 2;while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {if (element % start++ < 1) {return false;}}return element > 1;
}var uint16 = new Uint16Array([4, 5, 8, 12]);
console.log(uint16.findIndex(isPrime)); // 1
8、TypedArray.prototype.forEach(callback[, thisArg])
為每一個數組元素執行指定的函數。
function logArrayElements(element, index, array) {console.log('a[' + index + '] = ' + element);
}new Uint8Array([0, 1, 2, 3]).forEach(logArrayElements);
/*
a[0] = 0
a[1] = 1
a[2] = 2
a[3] = 3
*/
9、TypedArray.prototype.includes(searchElement[, fromIndex])
返回一個布爾值,表明數組中從下標fromIndex開始到結尾,是否包含了指定的搜索元素。
var uint8 = new Uint8Array([1,2,3]);
uint8.includes(2); // true
uint8.includes(4); // false
uint8.includes(3, 3); // false// NaN 的處理 (僅僅對 Float32 和 Float64 為 true)
new Uint8Array([NaN]).includes(NaN); // false, 因為 NaN 傳遞給構造器時轉換為 0
new Float32Array([NaN]).includes(NaN); // true;
new Float64Array([NaN]).includes(NaN); // true;
10、TypedArray.prototype.indexOf(searchElement[, fromIndex = 0])
在TypedArray中搜索元素,返回第一次出現的位置下標,如果找不到對應的元素,則返回-1。
let uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9]);
uint8.indexOf(2); // 0
uint8.indexOf(7); // -1
uint8.indexOf(9, 2); // 2
uint8.indexOf(2, -1); // -1
uint8.indexOf(2, -3); // 0
11、TypedArray.prototype.join([separator = ','])
將數值各個元素轉為字符串,再使用separator將其各個字符串連接后返回。
var array = new Int16Array([1,2,3,4]);
var str = array.join('-');
str; // "1-2-3-4"
12、TypedArray.prototype.keys()
返回一個數組下標的遍歷器。
var array = new Int16Array(3);
array.set([1,2,3]);
var iter = array.keys();
for (let index of iter) {console.log(index);
}
/*
0
1
2
*/
13、TypedArray.prototype.lastIndexOf(searchElement[, fromIndex = typedarray.length])
在TypedArray中搜索元素,返回最后一次出現的位置下標,如果找不到對應的元素,則返回-1。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.lastIndexOf(5); // 4
14、TypedArray.prototype.map(callback[, thisArg])
map方法對類型化數組中的元素調用提供的 callback函數,按照順序,并且會從結果構造新的類型化數組。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
const new_ui8 = uint8.map(function (value) {return value * 2;
});
new_ui8; // [4,10,18,8,10,6]
15、TypedArray.prototype.reduce(callback[, initialValue])
reduce() 方法接受一個函數作為參數,這個函數作為一個累加器,從左到右遍歷整個類型數組,最后返回一個單一的值。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.reduce(function (a, b) {return a + b;
}, 0); // 28
16、TypedArray.prototype.reduceRight(callback[, initialValue])
reduceRight()在累加器和類型化數組的每個元素上(從右到左)調用函數,使其歸約為單一的值。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.reduceRight(function (a, b) {return a + b;
}); // 28
17、TypedArray.prototype.reverse()
原地逆序TypedArray數組。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.reverse(); // [3,5,4,9,5,2]
18、TypedArray.prototype.set(array [,offset])
set()方法用于從指定數組中讀取值,并將其存儲在類型化數組中。
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(8);
var uint8 = new Uint8Array(buffer);
uint8.set([1,2,3], 3);
console.log(uint8); // Uint8Array [ 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0 ]
19、TypedArray.prototype.slice([begin[, end]])
返回一個指定位置的新的TypedArray實例。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.slice(2,5); // [9,4,5]
20、TypedArray.prototype.some(callback[, thisArg])
提供一個測試函數,當TypedArray中的某一個元素通過測試函數,則返回true。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
uint8.some(function (value) { return value > 5; }); // true21、TypedArray.prototype.sort([compareFunction])
sort()方法原地排序類型化數組的元素,并且返回類型化數組。這個方法的算法和Array.prototype.sort()相同。
var numbers = new Uint8Array([40, 1, 5, 200]);
numbers.sort();
// Uint8Array [ 1, 5, 40, 200 ]
// 在這里,按數值排序數值時,
// 不需要比較函數。
22、TypedArray.prototype.subarray([begin [,end]])
對TypedArray數組的一部分再建立一個新的視圖。第一個參數是起始的成員序號,第二個參數是結束的成員序號(不含該成員)如果省略則包含剩余的全部成員。新視圖和源視圖底層的ArrayBuffer是共用的。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
const new_uint8 = uint8.subarray(2, 5); // [9,4,5]
new_uint8[1] = 10;
new_uint8; // [9,10,5]
uint8; // [2,5,9,10,5,3]
23、TypedArray.prototype.toLocaleString()
toLocaleString()方法返回一個字符串,表明該類型化數組的元素。這些元素被轉化為字符串并由一個區域設置指定的分隔符(例如逗號 “,”)分隔。這個方法與Array.prototype.toLocaleString()擁有相同的算法。同時,由于類型化數組的元素都是數,將每個元素轉化為字符串的算法與Number.prototype.toLocaleString()是相同的。
var uint = new Uint32Array([2000, 500, 8123, 12, 4212]);
uint.toLocaleString('ja-JP', { style: 'currency', currency: 'JPY' });
// "¥2,000,¥500,¥8,123,¥12,¥4,212"
24、TypedArray.prototype.toString()
TypedArray 對象重寫了Object的 toString方法。對 TypedArray 對象來說,toString 方法聯結了數組,并返回一個字符串,它包含由逗號分隔的數組元素。
var numbers = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 8, 1, 4])
numbers.toString(); // "2,5,8,1,4"
25、TypedArray.prototype.values()
返回TypedArray的鍵值遍歷器。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
var iter = uint8.values();
for (let ele of iter) {console.log(ele);
}
/*
2
5
9
4
5
3
*/
26、TypedArray.prototype[@@iterator]()
返回TypedArray鍵值對的遍歷器,效果和values()方法一樣。
const uint8 = new Uint8Array([2, 5, 9, 4, 5, 3]);
var iter = uint8[Symbol.iterator]();
for (let ele of iter) {console.log(ele);
}
/*
2
5
9
4
5
3
*/
TypedArray的字節序
字節序是指數值在內存中的表示方式。
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(16);
var int32View = new Int32Array(buffer);
for (let i = 0; i < int32View.length; i++) {int32View[i] = i * 2;
}
int32View; // [0,2,4,6]
上述代碼新建了一個16字節的內存區域,并在其上建了一個32位(4字節)的視圖,該視圖有4個元素,對元素分別賦值為0,2,4,6。如果對該內存區域上新建一個16位(2字節)的視圖,我們可以看出數據的存儲方式。
var int16View = new Int16Array(buffer);
for (let value of int16View) {console.log(value);
}
/*
0
0
2
0
4
0
6
0
*/
用圖來說明如下:

由于x86體系的計算機都采用小端字節序,相對重要的字節排在后面的內存地址,相對不重要的字節排在前面的內存地址。
比如,一個占據4字節的十六進制數0x12345678,決定其大小的最重要的字節是“12”,最不重要的是“78”,故在內存中,存儲順序是“78563412”。TypedArray數組內部也采用的是本機操作系統設定的字節序讀寫數據。
TypedArray對溢出的處理
不同的視圖類型所能容納的數值范圍是確定的,超出這個范圍就會出現溢出。
TypedArray數組對于溢出采用的處理方法是求余值。正向溢出的含義是指輸入值大于可容納的當前數據類型的最大值,最后得到的值等于當前數據類型的最小值加上余值,再減去1。負向溢出等于當前數據類型的最大值減去余值,再加上1。
// 無符號單字節整型可容納的最大數值是255,最小數值是0
var uint8 = new Uint8Array(1);
uint8[0] = 256; // 正向溢出,超出最大值范圍,余值是1
uint8[0]; // 0 最小值+余值-1=0uint8[0] = -12; // 負向溢出,超出最小值范圍,余值是12
uint8[0]; // 最大值-余值+1=255-12+1=244
UInt8ClampedArray視圖的溢出與其他8種類型的規則有所不同。負向溢出的值都是0,正向溢出的值都是255。
var a = new Uint8ClampedArray(1);
a[0] = 2112;
a[0]; // 255
a[0] = -123
a[0]; // 0
利用TypedArray構建復合視圖
由于視圖的構造函數可以指定起始位置和長度,所以在同一段內存中可以依次存放不同類型的數據,這就叫復合視圖。
var ab = new ArrayBuffer(24);
var idView = new Uint32Array(buffer, 0, 1);
var userNameView = new Uint8Array(buffer, 4, 16);
var amountView = new Float32Array(buffer, 20, 1);
上面的代碼將一個24字節的內存分成3個部分:
字節0到字節3,1個32位無符號整數,用于存放ID。
字節4到字節19存放16個8位無符號整數。
剩下4個字節存放1個32位浮點數。
這樣數據接口用C語言描述如下:
struct User {unsigned int id;char[16] username;float amount;
};同系列文章:
《JavaScript二進制數組(1)ArrayBuffer》
《JavaScript二進制數組(2)TypedArray視圖》
《JavaScript二進制數組(3)DataView視圖》

)







-34)
)






)

