- 目錄
- 1、簡單算子說明
- 2、復雜算子說明
目錄
SparkRDD算子分為兩類:Transformation與Action.
Transformation:即延遲加載數據,Transformation會記錄元數據信息,當計算任務觸發Action時,才會真正開始計算。
Action:即立即加載數據,開始計算。
創建RDD的方式有兩種:
1、通過sc.textFile(“/root/words.txt”)從文件系統中創建 RDD。
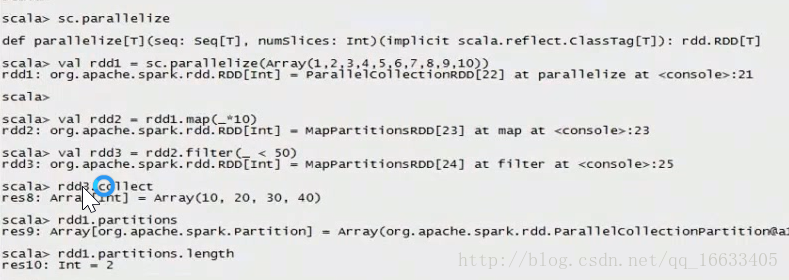
2、#通過并行化scala集合創建RDD:val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8))
1、簡單算子說明
這里先說下簡單的Transformation算子
//通過并行化scala集合創建RDD
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8))
//查看該rdd的分區數量
rdd1.partitions.length
//map方法同scala中的一樣,將List中的每個數據拿出來做函數運算。
//sortBy:將數據進行排序
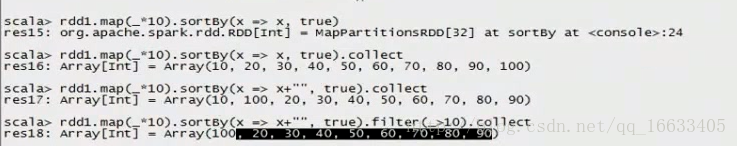
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7,3,8,2,9,1,10)).map(_*2).sortBy(x=>x,true)
//filter:將List中的每個數據進行函數造作,挑選出大于10的值。
val rdd3 = rdd2.filter(_>10)
//collect:將最終結果顯示出來
//flatMap:對數據先進行map操作,再進行flat(碾壓)操作。
rdd4.flatMap(_.split(’ ‘)).collect
運行效果圖
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7,3,8,2,9,1,10))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7,3,8,2,9,1,10)).map(_*2).sortBy(x=>x,true)
val rdd3 = rdd2.filter(_>10)
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7,3,8,2,9,1,10)).map(_*2).sortBy(x=>x+”“,true)
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7,3,8,2,9,1,10)).map(_*2).sortBy(x=>x.toString,true)
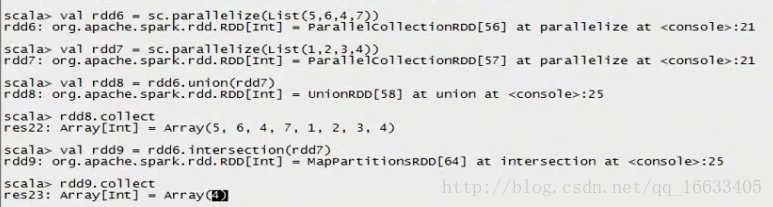
//intersection求交集
val rdd9 = rdd6.intersection(rdd7)
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List((“tom”, 1), (“jerry”, 2), (“kitty”, 3)))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List((“jerry”, 9), (“tom”, 8), (“shuke”, 7)))
//join
val rdd3 = rdd1.join(rdd2)
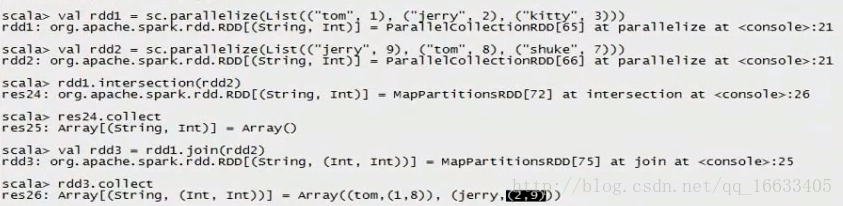
val rdd3 = rdd1.leftOuterJoin(rdd2)
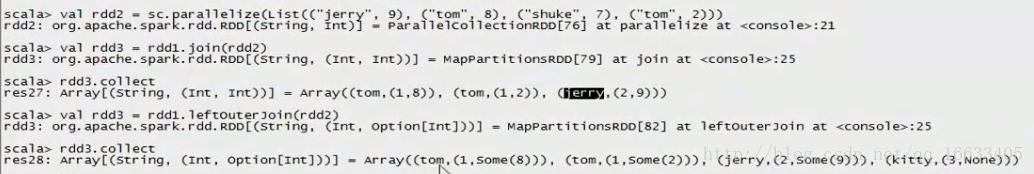
val rdd3 = rdd1.rightOuterJoin(rdd2)
//union:求并集,注意類型要一致
val rdd6 = sc.parallelize(List(5,6,4,7))
val rdd7 = sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3,4))
val rdd8 = rdd6.union(rdd7)
rdd8.distinct.sortBy(x=>x).collect
//groupByKey
val rdd3 = rdd1 union rdd2
rdd3.groupByKey
rdd3.groupByKey.map(x=>(x._1,x._2.sum))
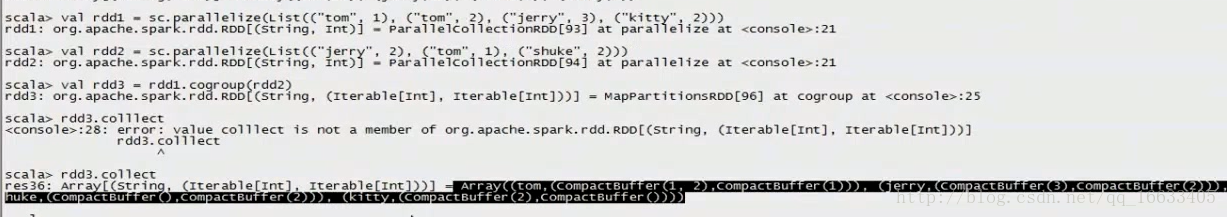
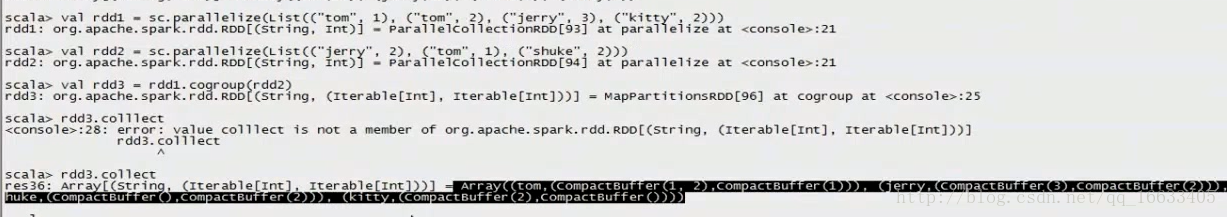
//cogroup
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List((“tom”, 1), (“tom”, 2), (“jerry”, 3), (“kitty”, 2)))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List((“jerry”, 2), (“tom”, 1), (“shuke”, 2)))
val rdd3 = rdd1.cogroup(rdd2)
val rdd4 = rdd3.map(t=>(t._1, t._2._1.sum + t._2._2.sum))
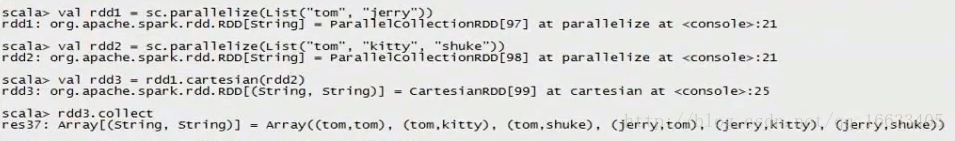
//cartesian笛卡爾積
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(“tom”, “jerry”))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(List(“tom”, “kitty”, “shuke”))
val rdd3 = rdd1.cartesian(rdd2)
接下來說下簡單的Action算子
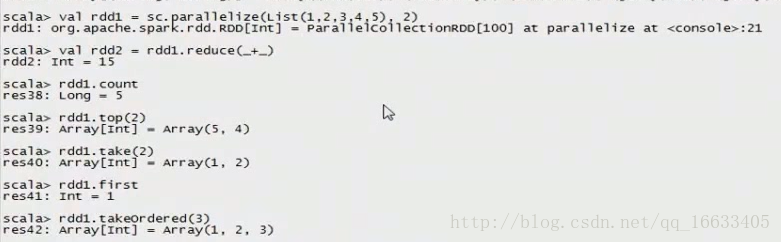
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3,4,5), 2)
#collect
rdd1.collect
#reduce
val rdd2 = rdd1.reduce(+)
#count
rdd1.count
#top
rdd1.top(2)
#take
rdd1.take(2)
#first(similer to take(1))
rdd1.first
#takeOrdered
rdd1.takeOrdered(3)
2、復雜算子說明
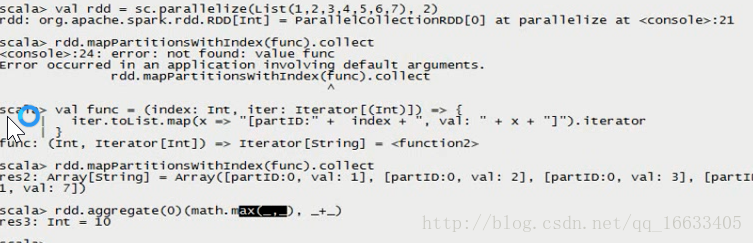
mapPartitionsWithIndex : 把每個partition中的分區號和對應的值拿出來, 看源碼
val func = (index: Int, iter: Iterator[(Int)]) => {
iter.toList.map(x => “[partID:” + index + “, val: ” + x + “]”).iterator
}
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9), 2)
rdd1.mapPartitionsWithIndex(func).collect
aggregate
def func1(index: Int, iter: Iterator[(Int)]) : Iterator[String] = {
iter.toList.map(x => “[partID:” + index + “, val: ” + x + “]”).iterator
}
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9), 2)
rdd1.mapPartitionsWithIndex(func1).collect
###是action操作, 第一個參數是初始值, 二:是2個函數(第一個函數:先對個個分區進行合并, 第二個函數:對個個分區合并后的結果再進行合并)
###0 + (0+1+2+3+4 + 0+5+6+7+8+9)
rdd1.aggregate(0)(_+_, _+_)rdd1.aggregate(0)(math.max(, ), _ + _)
###0分別與0和1分區的List元素對比得到每個分區中的最大值,在這里分別是3和7,然后將0+3+7=10
###5和1比, 得5再和234比得5 –> 5和6789比,得9 –> 5 + (5+9)
rdd1.aggregate(5)(math.max(, ), _ + _)
val rdd3 = sc.parallelize(List(“12”,”23”,”345”,”4567”),2)
rdd3.aggregate(“”)((x,y) => math.max(x.length, y.length).toString, (x,y) => x + y)
######### “”.length分別與兩個分區元素的length進行比較得到0分區為字符串”2”,1分區為字符串”4”,然而結果返回不分先后,所以結果是24或42
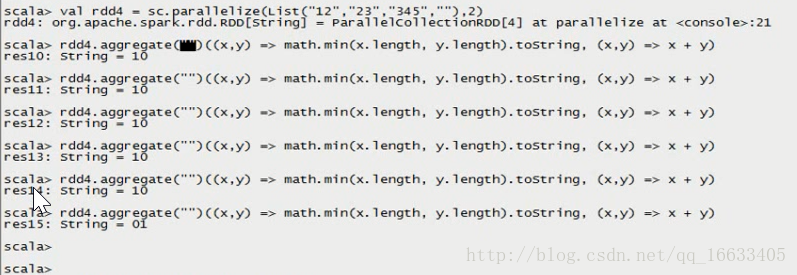
val rdd4 = sc.parallelize(List(“12”,”23”,”345”,”“),2)
rdd4.aggregate(“”)((x,y) => math.min(x.length, y.length).toString, (x,y) => x + y)
######## “”.length的為0,與“12”比較后得到字符串“0”,然后字符串“0”再與“23”比較得到最小值為1.
aggregateByKey
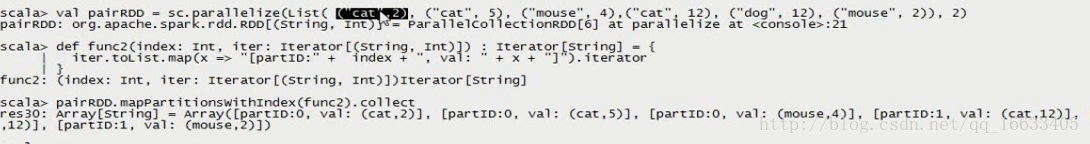
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize(List( (“cat”,2), (“cat”, 5), (“mouse”, 4),(“cat”, 12), (“dog”, 12), (“mouse”, 2)), 2)
def func2(index: Int, iter: Iterator[(String, Int)]) : Iterator[String] = {
iter.toList.map(x => “[partID:” + index + “, val: ” + x + “]”).iterator
}
pairRDD.mapPartitionsWithIndex(func2).collect
pairRDD.aggregateByKey(0)(math.max(, ), _ + _).collect
########## 先對0號分區中的各個數據進行操作(拿初始值和各個數據進行比較)得到(cat,5)(mouse,4).然后再對1號分區中的數據進行操作得到(cat,12)(dog,12)(mouse,2)。然后再對兩個分區的數據進行相加得到最終結果
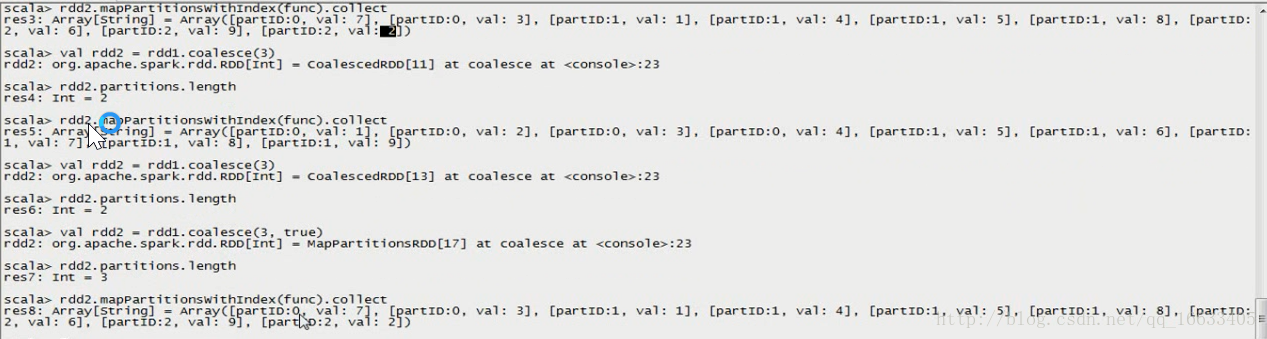
coalesce
#coalesce(2, false)代表將數據重新分成2個區,不進行shuffle(將數據重新進行隨機分配,數據通過網絡可分配在不同的機器上)
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(1 to 10, 10)
val rdd2 = rdd1.coalesce(2, false)
rdd2.partitions.length
repartition
repartition效果等同于coalesce(x, true)
collectAsMap : Map(b -> 2, a -> 1)
val rdd = sc.parallelize(List((“a”, 1), (“b”, 2)))
rdd.collectAsMap
combineByKey : 和reduceByKey是相同的效果
###第一個參數x:原封不動取出來, 第二個參數:是函數, 局部運算, 第三個:是函數, 對局部運算后的結果再做運算
###每個分區中每個key中value中的第一個值, (hello,1)(hello,1)(good,1)–>(hello(1,1),good(1))–>x就相當于hello的第一個1, good中的1
val rdd1 = sc.textFile(“hdfs://master:9000/wordcount/input/”).flatMap(.split(” “)).map((, 1))
val rdd2 = rdd1.combineByKey(x => x, (a: Int, b: Int) => a + b, (m: Int, n: Int) => m + n)
rdd1.collect
###當input下有3個文件時(有3個block塊分三個區, 不是有3個文件就有3個block, ), 每個會多加3個10
val rdd3 = rdd1.combineByKey(x => x + 10, (a: Int, b: Int) => a + b, (m: Int, n: Int) => m + n)
rdd3.collect
val rdd4 = sc.parallelize(List(“dog”,”cat”,”gnu”,”salmon”,”rabbit”,”turkey”,”wolf”,”bear”,”bee”), 3)
val rdd5 = sc.parallelize(List(1,1,2,2,2,1,2,2,2), 3)
val rdd6 = rdd5.zip(rdd4)
//第一個參數List(_)代表的是將第一個元素轉換為一個List,第 二個參數x: List[String], y: String) => x :+ y,代表將元素y加入到這個list中。第三個參數:(m: List[String], n: List[String]) => m ++ n),代表將兩個分區的各個list合并成新的List。
val rdd7 = rdd6.combineByKey(List(_), (x: List[String], y: String) => x :+ y, (m: List[String], n: List[String]) => m ++ n)
countByKey
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List((“a”, 1), (“b”, 2), (“b”, 2), (“c”, 2), (“c”, 1)))
rdd1.countByKey
rdd1.countByValue
filterByRange
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List((“e”, 5), (“c”, 3), (“d”, 4), (“c”, 2), (“a”, 1)))
val rdd2 = rdd1.filterByRange(“b”, “d”)
rdd2.collect
flatMapValues : Array((a,1), (a,2), (b,3), (b,4))
val rdd3 = sc.parallelize(List((“a”, “1 2”), (“b”, “3 4”)))
val rdd4 = rdd3.flatMapValues(_.split(” “))
rdd4.collect
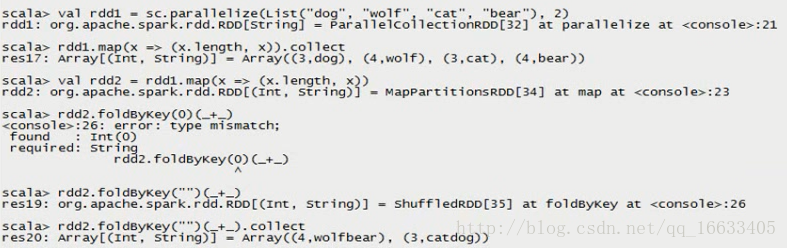
foldByKey
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(“dog”, “wolf”, “cat”, “bear”), 2)
val rdd2 = rdd1.map(x => (x.length, x))
val rdd3 = rdd2.foldByKey(“”)(+)
keyBy : 以傳入的參數做key
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(“dog”, “salmon”, “salmon”, “rat”, “elephant”), 3)
val rdd2 = rdd1.keyBy(_.length)
rdd2.collect
keys values
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(“dog”, “tiger”, “lion”, “cat”, “panther”, “eagle”), 2)
val rdd2 = rdd1.map(x => (x.length, x))
rdd2.keys.collect
rdd2.values.collect
以下是一些方法的英文解釋
#
map(func)
Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func.
filter(func)
Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which func returns true.
flatMap(func)(內部執行順序是從右往左,先執行Map再執行Flat)
Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items (so func should return a Seq rather than a single item).
mapPartitions(func)
Similar to map, but runs separately on each partition (block) of the RDD, so func must be of type Iterator => Iterator when running on an RDD of type T.
mapPartitionsWithIndex(func)
Similar to mapPartitions, but also provides func with an integer value representing the index of the partition, so func must be of type (Int, Iterator) => Iterator when running on an RDD of type T.
sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed)
Sample a fraction fraction of the data, with or without replacement, using a given random number generator seed.
union(otherDataset)
Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument.
intersection(otherDataset)
Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument.
distinct([numTasks]))
Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset.
groupByKey([numTasks])
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable) pairs.
reduceByKey(func, [numTasks])
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function func, which must be of type (V,V) => V. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument.
aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numTasks])
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, U) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given combine functions and a neutral “zero” value. Allows an aggregated value type that is different than the input value type, while avoiding unnecessary allocations. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument.
sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks])
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument.
join(otherDataset, [numTasks])
When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. Outer joins are supported through leftOuterJoin, rightOuterJoin, and fullOuterJoin.
cogroup(otherDataset, [numTasks])
When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (Iterable, Iterable)) tuples. This operation is also called groupWith.
cartesian(otherDataset)
When called on datasets of types T and U, returns a dataset of (T, U) pairs (all pairs of elements).
pipe(command, [envVars])
Pipe each partition of the RDD through a shell command, e.g. a Perl or bash script. RDD elements are written to the process’s stdin and lines output to its stdout are returned as an RDD of strings.
coalesce(numPartitions)
Decrease the number of partitions in the RDD to numPartitions. Useful for running operations more efficiently after filtering down a large dataset.
repartition(numPartitions)
Reshuffle the data in the RDD randomly to create either more or fewer partitions and balance it across them. This always shuffles all data over the network.
repartitionAndSortWithinPartitions(partitioner)
Repartition the RDD according to the given partitioner and, within each resulting partition, sort records by their keys. This is more efficient than calling repartition and then sorting within each partition because it can push the sorting down into the shuffle machinery.
(K,(Iterable,Iterable))






















)











)