特性關系
- C語言面向過程
- C++面向過程 + 面向對象(封裝 繼承 多態)
- C++具備C語言的全部特性的基礎上,并且支持更多新的特性
內存泄露
- 申請內存,沒有釋放
- 申請 malloc new
- 釋放 free delete
- ProcessExplorer查看內存是否釋放
代碼移植
- 將生成的exe運行在別的平臺,不因為缺乏環境而出錯
- 使用軟件 ProcessExplorer軟件查找exe程序執行需要的dll等配置文件
- 或者在程序編譯的時候整合對應的庫文件,(屬性->C/C++ -> 代碼生成 ->運行庫)
- 多線程 MT? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??靜態編譯 -> 鏈接庫文件
- 多線程調試 MTH? ? ? ? ? 靜態編譯 -> 鏈接庫文件
- 多線程 DLL MD
- 多線程調試DLL MDT
pragma once
- 確保.h文件減少包含,減少編譯錯誤
C++輸入輸出方式
- 輸入? 輸入設備-> 輸入流->scanf/cin -> 變量? ? cin>>a>>b;
- 輸出? 變量 ->? printf/cout -> 輸出流 -> 輸出設備? cout<< a << endl;(endl輸出換行)
- 不需要關注 數據類型 和 占位符號
命名空間
- std?
- 關鍵字 namespace ,不同的命名空間使用相同的變量名字和函數
- 使用? 命名空間:: 函數名? 進行函數的調用

數據類型
- 布爾類型 bool?
- 真 true
- 假 false
- bool flag = false;
- std::cout << boolalpha << flag << endl;//輸出false
- 特性:C++隨用隨定義
引用
- 一般作為函數的參數,這樣就不需要返回數據,直接取元素的數值?
- 引用,避免了申請多個變量,大家對引用的使用都是針對同一個元素進行

函數默認值
- 缺省值 default value
- 函數使用默認值?
- void fun(int i,int j = 7,int k = 8)??
- 有默認值的參數必須在參數表的最右端
- 聲明和定義同時給出默認值,有些編譯器會報錯。最好在函數的聲明時給出默認值
void fun(int i,int j = 7,int k = 8){std::cout << "i = " << i << std::endl;std::cout << "j = " << j << std::endl;std::cout << "k = " << k << std::endl;
}int main(void)
{int i = 7;fun(i);return 0;
}函數的重載
- 重載函數的參數的個數、參數的類型、參數的順序三者中必須至少有一種不同,返回值不同不作為重載依據
- 重載函數的功能應該相近,不可以為了重載而重載
- main函數不可以重載
內存管理
- 棧區:由編譯器自動分配釋放? ?char型指針p
- 全局區(靜態區)(static):存放全局變量、靜態數據、常量? int x = 0;x屬于全局變量
- 文字常量區:常量字符串就是存放在這里,程序結束之后,由系統釋放? ? 文字常量 Hello
- 程序代碼區:存放函數體的二進制代碼? ?整個代碼的二進制數據
- 堆區:程序員申請/釋放內存? ?由程序員申請釋放
int x = 0;
int main(void)
{char *p = "Hello";x = 10;return 0;
}- 申請內存 new? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?釋放內存 delete
- int *p = new int;? ? ? ? ? ? ? delete p;
- int *p = new int(10);? ? ? ?delete p;
- int *p = new int[5];? ? ? ? ??delete []p;
- 內存申請有可能失敗?
- if (p == null) return False; p = null;最后讓指針指向null
- 內存忘記釋放會產生內存的泄露
- 如果需要大的內存 啟用大地址
- 輸入和輸出都是相對于內存來說的
- 內存的特點是 有電則生,斷電則往

文件的輸出

常量const
- 關鍵字 修飾一個變量使其成為常量
- const int x = 0; 等價于? int const x = 0;
- const int * p = 0; 等價于 int const * p = 0;
- int * const p = 0;
- const int * const p = 0; 等價于 int const * const p = 0;
- const 修飾普通數據類型?const int x = 0; x=10;錯誤
- const修飾指針類型?? ?
- int const *p = &x; const修飾*,因此p可以變化,但是*p 不可以
- int * const p = &x;const 修飾p,因此*p可以變化 但是p不可以
//const 修飾指針類型int x=0,y=0;int const *p = &x;*p = 4;//錯誤p = &y;//正確 //const 修飾指針類型int x=0,y=0;int *const p = &x;*p = 4;//錯誤p = &y;//正確- const修飾函數參數
- int max(const int x,const int y)? 代碼內部無法對其修改
- int max(int const *p,int *const q)
- #define 和const定義常量的區別?#define是預編譯器,只進行字符串替換,const在編譯的時候進行參數的檢查
類和對象之間的關系
- 類 抽象
- 對象 具體
- class類關鍵字 類名 數據成員? 成員函數
- 訪問限定符號? public private protected?
- 訪問限定符號 可以多次使用
class Student{
public:char name[20];int gender;int age;void study(){std::cout << "learning!" << std::endl;}private:};屬性的封裝
- 通過set和get的方式對成員變量進行封裝
- 通過函數將private私有屬性 進行返回
類的實例化
- 棧中定義 Car car;? ? ?操作系統會回收資源
- 堆中定義? Car *p = new Car();? ? ?資源需要由程序員進行釋放
類成員的訪問
- 棧中定義 Car car;? ?car.getWheelCount();? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?.? ? ? ? ?操作系統釋放資源
- 堆中定義?Car *p = new Car();? p->getWheelCount();? ? ? ? ->? ? ? ?delete p; p = nullptr;
- 相似于結構體(struct)
- 類的默認訪問權限是private? 結構體的默認訪問權限是public
- struct結構體的使用和函數類似,也可以使用上述 堆和棧的方式進行定義
- Student *p = new Student[20];//定義20個學生變量,p[0].age = 10;控制第一個學生的age變量? 使用delete[] p刪除內存空間
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>struct Student{
public:char name[20];int age;void study(){std::cout << "learning!" << std::endl;}private:int gender;int money;
};
int main(void)
{Student student{};student.study();Student *p = new Student[20];p[0].study();delete []p;p = nullptr;return 0;
}類內定義和類外定義
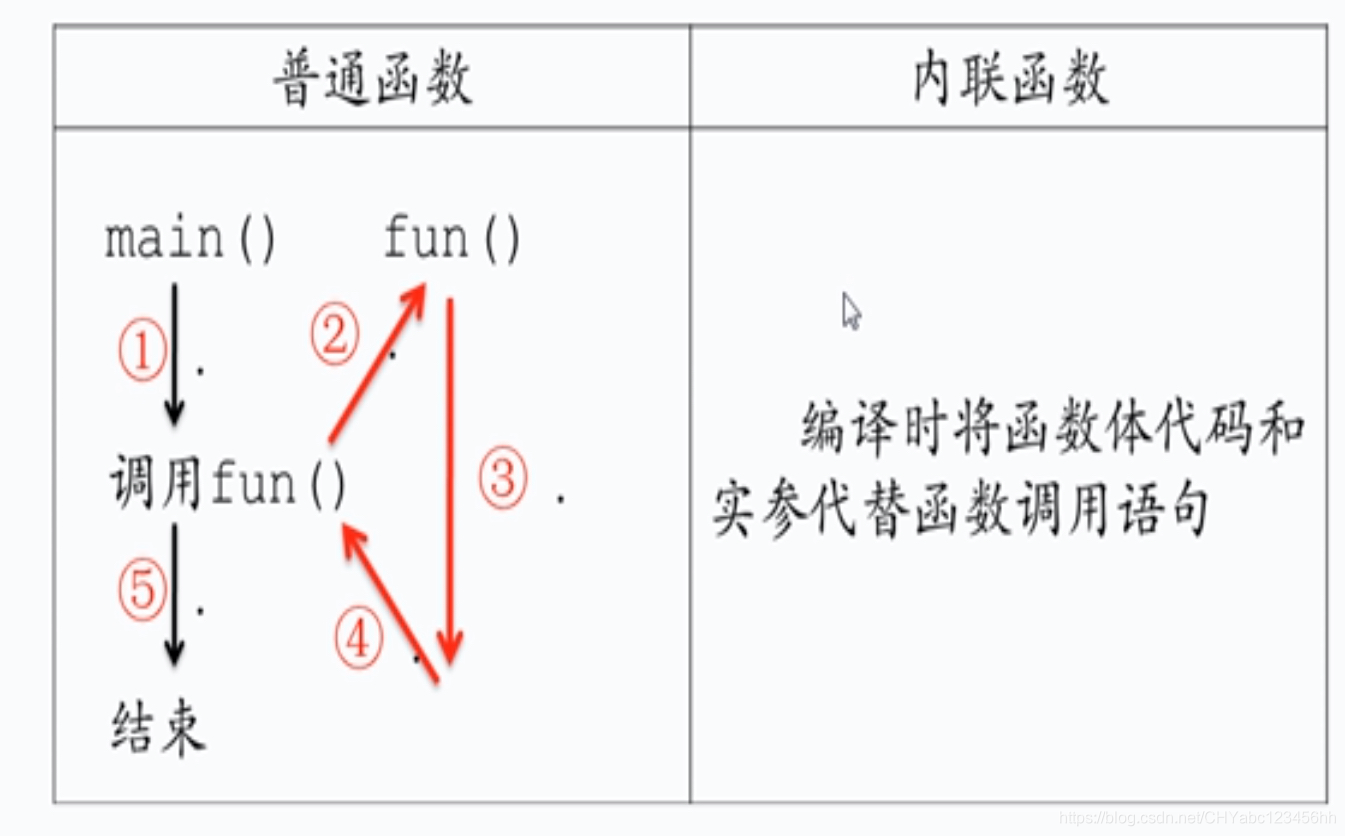
- 類內定義 建議編譯器使用內聯方式進行編譯
- 如圖所示,普通函數需要進行函數的跳轉;而內聯函數將需要跳轉的函數拷貝到指定的位置,避免了函數的拷貝,即避免了2和4的步驟,只剩下3的步驟,并且使用實參進行參數的替代
- 邏輯簡單的函數才會使用內聯的方式,如果函數很復雜,就按照普通函數處理


內聯函數和宏函數
- 宏函數走預編譯器 內聯函數走編譯器
- 宏函數沒有參數類型的要求,不會進行參數檢查
類內定義和類外定義

命名規范
- 類名單詞首字母大寫
- 文件名字 和 類名 相同
- 函數名第二個單詞首字母大寫,由單詞或動賓短語構成
- 數據成員以(m_類型)作為前綴? int m_i? ?m作為類內成員變量
對象的存儲結構
- 類申明多個對象,每個對象占據不同的地址
- 類內的函數 只有一份,共同調用
構造函數
- 實例化對象的時候 自動調用
- 構造函數名字 和 類名相同,并且沒有返回值
- 如果沒有自定義構造函數,系統提供默認構造函數
- 構造函數可以使用 帶參數的進行初始化

- 構造函數 可以重載
- 系統構造函數 Student(){} 也叫默認構造函數
- 有了自定義的構造函數,系統的構造函數還可以使用嗎?不可以。如果自定義了帶參數構造函數,使用的時候使用不帶參數的默認構造函數會造成錯誤。因為,用戶定義了構造函數,系統就不會再產生默認構造函數
初始化列表

- 使用Car():m_iWheelCount(4);進行初始化
- 初始化列表 伴隨著構造函數,在構造函數的后面使用 : 進行對變量的賦值
- 即使是const修飾的變量? 也可以使用初始化列表進行 賦值
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>class Car{
public:Car():m_iWheelCount(4),m_iSpeed(0){};void getWheelCount(){std::cout << m_iWheelCount << std::endl;std::cout << m_iSpeed << std::endl;}
private:const int m_iWheelCount;int m_iSpeed;
};
int main(void)
{Car car;car.getWheelCount();return 0;
}拷貝構造函數
- 對象初始化的兩種方式?
- 直接初始化? int x = 1024;
- 復制初始化? Student stu(stu1);

- 如上圖所示 stu1 使用默認構造函數
- stu2 和 stu3 使用? 拷貝構造函數
- 拷貝構造函數的特點
- 1,如果沒有自定義的拷貝構造函數 則系統自動生成
- 2,當對象直接初始化 或者? 復制初始化? 時候 自動調用拷貝構造函數
- 3,當自定義了拷貝構造函數則系統 不再生成 默認的拷貝構造函數
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>class Car{
public:Car(){};Car(const Car &car){ //拷貝構造初始化std::cout << "Car(const Car &car)" << std::endl;}
private:};
int main(void)
{Car car1; //直接初始化Car car2(car1); //拷貝構造初始化Car car3 = car1; //拷貝構造初始化return 0;
}類的析構函數
- 析構函數名字 如 ~類名(){}
- 析構函數沒有參數
- 析構函數沒有返回數值
- 析構函數不可以重載
- 析構函數 銷毀時候 自動執行
- 堆 和 棧 使用一致
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>class Car{
public:Car(){std::cout << " 對象創建" << std::endl;};~Car(){std::cout << " 對象銷毀 " << std::endl;}
private:};
int main(void)
{Car *car = new Car();delete car;car = nullptr;return 0;
}- 什么時候需要自定義析構函數?比如在堆上申請了一大段內存空間,使用delete []p,進行資源的釋放
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>class Car{
public:Car(){m_pName = new char [20];std::cout << " 對象創建" << std::endl;};~Car(){delete[] m_pName;std::cout << " 對象銷毀 " << std::endl;}
private:char *m_pName;
};
int main(void)
{Car *car = new Car();delete car;car = nullptr;return 0;
}- 當函數參數是一個對象的時候,使用拷貝構造函數
對象成員
- 多個類之間互相使用調用,使用&得到對象
對象數組
#include <iostream>class Coordinate{
public:int m_iX;int m_iY;
};
int main(void)
{Coordinate coord[3]; //棧上申請內存coord[1].m_iX = 4;Coordinate *p = new Coordinate[3]; //堆上申請內存p[0].m_iX = 20;delete []p;//刪除對象數組p = nullptr;return 0;
}- 應該使用delete []p方式刪除對象數組,不加上[] 只會清除一個對象
靜態數據成員
- 靜態數據成員 放在全局區
- 靜態數據成員 沒有對象仍然可以使用
- 靜態數據成員 與 類? 同生共死
- 靜態成員函數 只可以使用 靜態數據成員??
- 非靜態成員函數 可以使用 靜態數據成員
#include <iostream>class Tank{
public:Tank(std::string code);~Tank();void attack();static int getCount();
private:std::string m_strCode;static int g_iCount;
};
int Tank::g_iCount = 0;Tank::Tank(std::string code) {m_strCode = code;g_iCount++;
}Tank::~Tank() {g_iCount--;
}
void Tank::attack() {if (g_iCount > 3){std::cout << "" << std::endl;} else{std::cout << "" << std::endl;}
}int Tank::getCount() {return g_iCount;
}int main(void)
{std::cout << Tank::getCount << std::endl;return 0;
}對象指針成員
- 對象成員? ? 如圖左邊所示,對象A的構造函數,需要先等對象B構造完成之后,才執行對象A的構造函數
- 對象成員指針??如圖右邊所示,對象B的指針不會提前執行對象B的構造函數,直接進行對象A的構造函數,對象B的構造函數 伴隨其過程而產生

this指針
- this進行同名變量之間,使用this標記當前對象
- this指向這個類
- 每個對象都有自己的this指針,每個this指針都指向該對象的首地址


#include <iostream>class Student{
public:Student(std::string name);Student* getIt1(); //獲取當前對象的指針Student& getIt2(); //獲取當前對象void getIt3(Student **it); //獲取當前對象指針void getIt4(Student &it); //通過傳入引用 獲取當前對象void printName();//打印名字void setName(std::string name);//設置名字
private:std::string m_strName;
};Student::Student(std::string name) {this->m_strName = name;
}Student * Student::getIt1() {return this;
}Student &Student::getIt2() {return *this;//返回this指針指向的對象
}void Student::getIt3(Student **it) {*it = this;
}void Student::getIt4(Student &it) {it = *this;
}void Student::printName() {std::cout << m_strName << std::endl;
}void Student::setName(std::string name) {m_strName = name;
}
int main() {//測試 getIt1
// Student stu("zhangsan");
// Student *p = stu.getIt1();
// p->printName();
// Student stu1("lisi");
// p = stu1.getIt1();
// p->printName();//測試 getIt2
// Student stu("zhangsan");
// stu.printName();
// Student &stu1 = stu.getIt2();
// stu1.setName("lisi");
// stu1.printName();//測試 getIt3 *無法拿到指針指向的數據 需要使用**
// Student stu("zhangsan");
// Student *p = nullptr;
// stu.printName();
// stu.getIt3(&p); //注意
// p->printName();//測試 getIt4Student stu("zhangsan");Student stu1("liis");stu.getIt4(stu1);stu1.printName();return 0;
}
常成員函數
- 在函數的名字后面添加 const,表示這個函數是常成員函數
- 在常成員函數中不能改變數據成員的數值
- const 也是函數重載的一個特性
- 只有常對象 才可以使用? 常成員函數
- 常對象指針
- 常對象引用
#include <iostream>class Student{
public:Student(std::string name);void printInfo();//常成員函數//重載函數void printInfo() const;
private:std::string m_strName;
};void Student::printInfo() {std::cout << m_strName << std::endl;
}void Student::printInfo() const {//在常成員函數中不能改變數據成員的數值std::cout << m_strName << std::endl;
}int main() {Student s1("zhangsan");s1.printInfo();const Student s2("lisi");//1,常對象//修飾的時候 const 可以放在Student的前面 或者 后面s2.printInfo();Student *s3 = new Student("Merry");s3->printInfo();//2,常對象指針Student const *s4 = new Student("Jim");s4->printInfo();Student s5("Merry");Student &s6 = s5;Student const &s7 = s5;//常對象引用s6.printInfo();s7.printInfo();return 0;
}
深拷貝和淺拷貝
- 深拷貝和淺拷貝最根本的區別在于是否真正獲取一個對象的復制實體,而不是引用。
- 假設B復制了A,修改A的時候,看B是否發生變化:
- 如果B跟著也變了,說明是淺拷貝(修改堆內存中的同一個值)
- 如果B沒有改變,說明是深拷貝(修改堆內存中的不同的值)
- 深拷貝和淺拷貝的區別
友元函數
- friend? 友元全局函數
- friend 類型 函數名字 (形參列表);
- 友元成員函數? friend 類型 類名::函數名字(形參表);
- 友元? 不可以傳遞
- 友元? 是單向的
- 私有private變量? 通過申明為友元函數訪問 私有變量
- friend友元函數 放在private public 都可以,不影響使用,但是一般放在類的最前邊
友元全局函數 Time.h
#pragma onceclass Time{friend void printTime(Time &t);// 友元全局函數(當前類 + 引用)
// friend void Student::setTime(Time &t);//友元成員函數(類名 + 函數名字)
public:Time(int year,int month,int day){m_iYear = year;m_iMonth = month;m_iDay = day;};
private:int m_iYear;int m_iMonth;int m_iDay;
};
主函數
#include <iostream>
#include "lib/Time.h"void printTime(Time &t);int main() {Time t1(2015,8,7);printTime(t1);return 0;
}void printTime(Time &t){std::cout << t.m_iYear <<"-" << t.m_iMonth << "-" << t.m_iDay << std::endl;
}
友元成員函數??
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date;//對Date類的提前引用聲明
class Time
{
public:Time(int, int, int);//聲明構造函數void display(Date &);
private:int hour;int sec;int minute;
};class Date
{
public:Date(int, int, int);//聲明構造函數friend void Time::display(Date &);
private:int mouth;int day;int year;
};Time::Time(int h, int m, int s)
{hour = h;minute = m;sec = s;
}void Time::display(Date &d)//display的作用是輸出年月日,時分秒
{cout << d.mouth << "/" << d.day << "/" << d.year << endl;cout << hour << ":" << minute << ":" << sec << endl;
}Date::Date(int m, int d, int y)
{mouth = m;day = d;year = y;
}int main(void)
{Time t1(10, 13, 56);Date d1(4, 15, 2019);t1.display(d1);return 0;
}
- 友元 一般是在先前代碼上進行使用,準確說是一種設計缺陷的彌補措施,盡量不要使用
繼承
- 父類 叫做 基類
- 子類 叫做 派生類
- 父類是抽象,子類是在父類抽象的基礎上進一步的細化;比如父類是人;子類是工人;子類的子類是 電工,逐步細化
三種派生方式
- 公有派生? 公有繼承? public
- 保護派生? 保護繼承? protected
- 私有派生? 私有繼承? private
?多繼承
- 一個類繼承了多個類。比如童工類? 繼承? 兒童類 的同時? 也繼承了 工人類
多重繼承
- 類和類之間逐級繼承。比如 技術工人類? 繼承? 工人類;電焊工人類? 繼承? 技術工人類;
菱形繼承
- 類和類之間的繼承關系構成了一個菱形
- 比如 工人類 和 農民類都繼承自? 人類;而農民工類? 繼承了工人類 和? 農民類。四者之間構成了一個菱形
- 為了解決這個問題,需要使用虛繼承 或者在? 頭文件引用?#pragma once
公有繼承
- 如果未定義 默認使用??私有派生? 私有繼承? private
- 子類 派生自 父類。所以先執行 父類的構造函數 再 執行 子類的構造函數;銷毀的時候,先執行 子類的析構函數 再執行 父類的析構函數
- 通過在父類 添加字段和方法,影響子類。而且派生自不同的父類,子類之間的影響是最低的
- 父類 的 private成員,子類無法訪問
#include <iostream>class Worker{
public:Worker(std::string name,std::string code);~Worker();std::string getName() const;
protected:std::string m_strName;std::string m_strCode;
};Worker::Worker(std::string name,std::string code) {m_strName = name;m_strCode = code;
}Worker::~Worker() {}std::string Worker::getName() const {return m_strName;
}class Electrician : public Worker{
public:Electrician(std::string name,std::string code,size_t salary):Worker(name,code){m_iSalary = salary;};void printInfo() const{std::cout << m_strName <<" " << m_strCode <<" " << m_iSalary << std::endl;}protected:size_t m_iSalary;
};int main(void)
{Electrician *electrician = new Electrician("Jim","1234",1200000);std::cout << electrician->getName() << std::endl;electrician->printInfo();return 0;
}三種繼承方式
- public? ? ? ? 公有繼承方式? ?父類的public 派生到 子類的public;父類的protected 派生到 子類的protected;父類的private 對于子類不可見
- protected? 保護繼承方式? ?父類的public 派生到 子類的protected;父類的protected 派生到 子類的protected;父類的private 對于子類不可見
- private? ? ? 私有繼承方式? ?父類的public 派生到 子類的private;父類的protected 派生到 子類的privat;父類的private 對于子類不可見
同名隱藏
- 父類 和 子類 的成員函數的名字一致,參數無限制
- 成員函數的名字一樣,但是所處的作用域不一樣,比如處于protected public等
- 同名的時候? ?子類的函數名字? 會? 隱藏父類的名字,但是父類的名字也是可以使用的。比如 使用子類定義的對象.父類的名字::同名的函數的名字();
#include <iostream>class Worker{
public:Worker(std::string name,std::string code);~Worker();std::string getName() const;void printInfo(){std::cout << " 父類 " << std::endl;};
protected:std::string m_strName;std::string m_strCode;
};Worker::Worker(std::string name,std::string code) {m_strName = name;m_strCode = code;
}Worker::~Worker() {}std::string Worker::getName() const {return m_strName;
}class Electrician : public Worker{
public:Electrician(std::string name,std::string code,size_t salary):Worker(name,code){m_iSalary = salary;};void printInfo() const{std::cout << m_strName <<" " << m_strCode <<" " << m_iSalary << std::endl;std::cout << " 子類 " << std::endl;}protected:size_t m_iSalary;
};int main(void)
{Electrician *electrician = new Electrician("Jim","1234",1200000);std::cout << electrician->getName() << std::endl;electrician->printInfo();//子類electrician->Worker::printInfo();//父類return 0;
}多重繼承
- 電工類 繼承自 技術工人類;技術工人類 繼承自 工人類;
- 逐級繼承,超過量層就是 多重繼承
- 例子:m_strName來自Worker、m_strSkill 來自SkillWorker? m_iSalary來自子類獨有變量
#include <iostream>class Person{
public:Person(int age);~Person();int getAge();protected:int m_iAge;
};Person::Person(int age) {std::cout << "Person" << std::endl;m_iAge = age;
}Person::~Person() {std::cout << "~Person" << std::endl;
}int Person::getAge() {return m_iAge;
}
class Worker : public Person{
public:Worker(std::string name,int age);~Worker();std::string getName()const;
protected:std::string m_strName;
};
Worker::Worker(std::string name, int age):Person(age) {m_strName = name;std::cout << "Worker" << std::endl;
}Worker::~Worker() {std::cout << "~Worker" << std::endl;
}
std::string Worker::getName() const {return m_strName;
}class Electrician : public Worker{
public:Electrician(std::string name, int age, int salary): Worker(name,age){m_iSalary = salary;std::cout << "Electrician" << std::endl;};~Electrician(){std::cout << "~Electrician" << std::endl;};void printInfo() const;protected:int m_iSalary;
};
int main(void)
{Electrician *electrician = new Electrician("jim",30,233333);delete electrician;electrician = nullptr;return 0;
}// _ooOoo_ //
// o8888888o //
// 88" . "88 //
// (| ^_^ |) //
// O\ = /O //
// ____/`---'\____ //
// .' \\| |// `. //
// / \\||| : |||// \ //
// / _||||| -:- |||||- \ //
// | | \\\ - /// | | //
// | \_| ''\---/'' | | //
// \ .-\__ `-` ___/-. / //
// ___`. .' /--.--\ `. . ___ //
// ."" '< `.___\_<|>_/___.' >'"". //
// | | : `- \`.;`\ _ /`;.`/ - ` : | | //
// \ \ `-. \_ __\ /__ _/ .-` / / //
// ========`-.____`-.___\_____/___.-`____.-'======== //
// `=---=' //
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ //
// 佛祖保佑 永不宕機 永無BUG //
多繼承
- 多繼承是橫向的,作為一個子類不僅僅擁有一個父類
- 例? 在職研究生繼承自研究生和職員兩個類? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?兩個類都是實體
- 例? 水路兩棲坦克繼承自坦克和? 能水中行駛? 兩個類? 其中一個類表示能力、屬性(多態)
- 繼承的多個類 需要聲明屬性,并且使用 逗號相隔
#include <iostream>class Farmer{
public:Farmer(int age);~Farmer();int getAge();protected:int m_iAge;
};Farmer::Farmer(int age) {std::cout << "Farmer" << std::endl;m_iAge = age;
}Farmer::~Farmer() {std::cout << "~Farmer" << std::endl;
}int Farmer::getAge() {return m_iAge;
}
class Worker {
public:Worker(std::string name);~Worker();std::string getName()const;
protected:std::string m_strName;
};
Worker::Worker(std::string name) {m_strName = name;std::cout << "Worker" << std::endl;
}Worker::~Worker() {std::cout << "~Worker" << std::endl;
}
std::string Worker::getName() const {return m_strName;
}class MigrantWorker : public Worker,public Farmer{
public:MigrantWorker(std::string name, int age, int salary):Worker(name),Farmer(age){m_iSalary = salary;std::cout << "MigrantWorker" << std::endl;};~MigrantWorker(){std::cout << "~MigrantWorker" << std::endl;};void printInfo() const;protected:int m_iSalary;
};
void MigrantWorker::printInfo() const {std::cout << m_strName << " " << m_iAge << " " << m_iSalary << std::endl;
}
int main(void)
{MigrantWorker *p = new MigrantWorker("001",20,222222);p->printInfo();delete p;p = nullptr;return 0;
}菱形繼承
- 類和類之間的繼承關系構成了一個菱形
- 比如 工人類 和 農民類都繼承自? 人類;而農民工類? 繼承了工人類 和? 農民類。四者之間構成了一個菱形
- 為了解決這個問題,需要使用虛繼承 或者在? 頭文件引用?#pragma once
- Person? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?人類
- Worker? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?工人
- Farmer? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?農民
- MigrantWorker? ?農民工
- 工人類 和 農民類? 在自己的頭文件中引用Person類,會多次引用 造成重定義 ,因此使用??#pragma once? 或者#ifndef XXXX 換行?define XXXX 在代碼的最末尾輸入 #endif
- 農民工 繼承的工人和農民都包含了 來自人類的冗余字段,即 人類類中的字段 擁有三份,分別來自? 人類? 工人? 和農民。因此需要指定 繼承的字段來自于哪個特定的類? 使用虛繼承
- class MigrantWorker : virtual public Worker? ?使用virtual,將相同的數據成員合并
- virtual 寫在public前后 都可以
注意事項
- 結構體 也可以使用 繼承機制
- 對于父類是基于屬性的,不是抽象的實體,需要對其進行重寫
- 面向對象的三大特征 封裝 -> 繼承?-> 多態
多態 虛函數理論
- 虛函數? virtual
- 如果不使用虛函數 virtual,子類都會使用父類的方法,不會使用自己重新定義的方法
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>class Shape{
public:Shape(){std::cout << "Shape" << std::endl;};double calcArea(){std::cout << "Shape calcArea" << std::endl;};
};class Rectangle : public Shape{
public:Rectangle(double width,double height){m_dHeight = height;m_dWidth = width;std::cout << "Rectangle" << std::endl;}double caleArea(){std::cout << "Rectangle calcArea" << std::endl;return m_dWidth * m_dHeight;};protected:double m_dWidth;double m_dHeight;
};class Circle : public Shape{
public:Circle(double r){std::cout << "Circle" << std::endl;m_iR = r;};double caleArea(){std::cout << "Circle calcArea" << std::endl;return 3.14 * pow(m_iR,2);}protected:double m_iR;
};int main(void)
{Shape *p1 = new Rectangle(2.0,3.0);Shape *p2 = new Circle(2.0);p1->calcArea();p2->calcArea();return 0;
}
Shape.h
- 基類中 使用virtual,調用的時候,將執行子類的方法,不再使用父類的方法
#pragma onceclass Shape{
public:Shape();virtual double calcArea();
};Shape::Shape() {std::cout << "Shape" << std::endl;
}
double Shape::calcArea() {std::cout << "Shape calcArea" << std::endl;return -1;
}Rectangle.h
#pragma once
#include "Shape.h"class Rectangle : public Shape{
public:Rectangle(double width,double height);virtual double calcArea();protected:double m_dWidth;double m_dHeight;
};Rectangle::Rectangle(double width, double height) {m_dHeight = height;m_dWidth = width;std::cout << "Rectangle" << std::endl;
}double Rectangle::calcArea() {std::cout << "Rectangle calcArea" << std::endl;return m_dWidth * m_dHeight;
}Circle.h
#pragma once
#include "Shape.h"
#include <cmath>class Circle : public Shape{
public:Circle(double r);double calcArea();protected:double m_iR;
};Circle::Circle(double r) {std::cout << "Circle" << std::endl;m_iR = r;
}double Circle::calcArea(){std::cout << "Circle calcArea" << std::endl;return 3.14 * pow(m_iR,2);
}main.c
#include <iostream>
#include "include/Shape.h"
#include "include/Rectangle.h"
#include "include/Circle.h"int main(void)
{Shape *p1 = new Rectangle(2.0,3.0);Shape *p2 = new Circle(2.0);p1->calcArea();p2->calcArea();return 0;
}虛析構函數
- 父類指針 指向子類對象的副作用
- 虛析構函數,Shape *p1 = new Rectangle(2.0,3.0);? Shape *p2 = new Circle(2.0);? ?delete p1或者p2,刪除他們指向的內存空間
- 但是 如果Rectangle或者CIrcle內部在堆上 申請的內存 無法通過父類指針 p1 p2 釋放內部的內存空間,造成內存的泄露
- 需要定義 虛析構函數,子類定義自己的析構函數,否則自己申請的內存釋放
- 定義析構函數之后? delete p1;就會執行子類的析構函數
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>class Shape{
public:Shape();virtual ~Shape();virtual double calcArea();
};Shape::Shape() {std::cout << "Shape" << std::endl;
}Shape::~Shape() {std::cout << "~Shape" << std::endl;
}double Shape::calcArea() {std::cout << "Shape calcArea" << std::endl;return -1;
}class Rectangle : public Shape{
public:Rectangle(double width,double height);virtual double calcArea();~Rectangle();
protected:double m_dWidth;double m_dHeight;int *m_pArr;
};Rectangle::Rectangle(double width, double height) {m_dHeight = height;m_dWidth = width;std::cout << "Rectangle" << std::endl;m_pArr = new int[20];
}double Rectangle::calcArea() {std::cout << "Rectangle calcArea" << std::endl;return m_dWidth * m_dHeight;
}Rectangle::~Rectangle() {delete []m_pArr;std::cout << "~Rectangle" << std::endl;
}class Circle : public Shape{
public:Circle(double r);double calcArea();~Circle();
protected:double m_iR;
};Circle::~Circle() {std::cout << "~Circle" << std::endl;
}
Circle::Circle(double r) {std::cout << "Circle" << std::endl;m_iR = r;
}double Circle::calcArea(){std::cout << "Circle calcArea" << std::endl;return 3.14 * pow(m_iR,2);
}int main(void)
{Shape *p1 = new Rectangle(2.0,3.0);Shape *p2 = new Circle(2.0);p1->calcArea();p2->calcArea();delete p1;delete p2;p1 = nullptr;p2 = nullptr;return 0;
}虛函數的實現原理
- 虛函數表只放? 虛函數指針
- 虛析構函數? 先調用子類的析構函數,如果父類的析構函數存在,再調用父類的析構函數。兩者之間使用鏈表結構銜接
- 任何類型的指針 都占據 4個字節 用于驗證虛函數 表指針的存在 (配合sizeof使用)

純虛函數
- 基類 virtual double calcArea() = 0; 純虛函數,沒有函數體
- 當子類繼承 基類的純虛函數 需要對純虛函數的內容進行 填寫
- 含有純虛函數的類叫做 抽象類
- Shape *p = new Shape();? //抽象類不可以實例化,抽象類不可以new出對象,因為對象無法表達內部的函數行為
- 純虛函數本質,基于純虛函數的子類也可以是子類,性質一致,直到可以形成對象
- 抽象類中只有純虛函數呢?接口類
純虛函數 抽象類
- 純虛函數的改正? virtual double calcArea() = 0;
- 刪除先前的基類對其 的定義
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>class Shape{
public:Shape();virtual ~Shape();virtual double calcArea() = 0;
};Shape::Shape() {std::cout << "Shape" << std::endl;
}Shape::~Shape() {std::cout << "~Shape" << std::endl;
}class Rectangle : public Shape{
public:Rectangle(double width,double height);virtual double calcArea();~Rectangle();
protected:double m_dWidth;double m_dHeight;int *m_pArr;
};Rectangle::Rectangle(double width, double height) {m_dHeight = height;m_dWidth = width;std::cout << "Rectangle" << std::endl;m_pArr = new int[20];
}double Rectangle::calcArea() {std::cout << "Rectangle calcArea" << std::endl;return m_dWidth * m_dHeight;
}Rectangle::~Rectangle() {delete []m_pArr;std::cout << "~Rectangle" << std::endl;
}class Circle : public Shape{
public:Circle(double r);double calcArea();~Circle();
protected:double m_iR;
};Circle::~Circle() {std::cout << "~Circle" << std::endl;
}
Circle::Circle(double r) {std::cout << "Circle" << std::endl;m_iR = r;
}double Circle::calcArea(){std::cout << "Circle calcArea" << std::endl;return 3.14 * pow(m_iR,2);
}int main(void)
{Shape *p1 = new Rectangle(2.0,3.0);Shape *p2 = new Circle(2.0);p1->calcArea();p2->calcArea();delete p1;delete p2;p1 = nullptr;p2 = nullptr;return 0;
}- 僅僅含有純虛函數的類 叫做接口類
- 在接口類的基礎上 實現部分純虛函數,叫做抽象類? 但是沒有實現全部? 不可以定義對象
- 只有全部實現父類 之路上所有的虛函數,才可以定義對象
- 抽象類 和 接口類的用途:??
- 抽象類用于表達不完全的實體概念
- 接口類用于表達一種強制協議或者能力
C++ 數據類型裝換
- reinterpret_cast<new_type>(expression)? ? 將指針和引用的數據類型進行轉換
- dynamic_cast<type>(expression)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 父類和子類數據之間的轉換? ?只有多態才可以采用
- static_cast<type>(expression)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?普通數據類型的轉換
- const_cast<type>(expression)? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?const 和 非const之間的轉換
#include <iostream>class Shape{
public:Shape();virtual ~Shape();virtual double calcArea();protected:double i_mNumber;
};class Circle : public Shape{
public:Circle(double r);~Circle();
protected:double m_iR;
};
int main(){double x = 2.5;//static_castint y = (int)x;//C語言int z = static_cast<int>(x);//C++//dynamic_castShape *p = new Circle(2.0);Circle *q = dynamic_cast<Circle *>(p);//reinterpret_castint r = 1000;int *w = reinterpret_cast<int *>(r);//將數值轉化為地址 很危險//const int c = 0;
// int *o = &x;//Errorint *g = const_cast<int *>(&c);
}
RTTI?
- C++中的RTTI機制
- RTTI的主要表現形式是 type_id
- RTTI的前提是 父類具有虛函數
異常處理
- 異常 程序運行期間出現的問題或者錯誤
- 異常處理:處理異常的方法在有可能發生異常的地方做出預見性的安排。異常處理提供了處理程序運行時出現的任何意外或者異常情況的方法
- C++ 處理異常基本思想:異常 的檢測和處理進行分離
- 遇到異常?
- 1,遇到錯誤,立即終止程序
- 2,返回一個表示錯誤的數值,同時保留錯誤的信息
- 3,針對錯誤情況再次分析處理
- throw
- try catch
- catch(...) 捕捉所有的異常
#include <iostream>void fun1(){std::cout << "fun1" << std::endl;throw "wer";
}void fun2(){try {fun1();} catch (int &e1){std::cout << "exception int:"<< e1 << std::endl;} catch (double &e2) {std::cout << "exception double:"<< e2 << std::endl;} catch (...) {std::cout << "全部捕捉!"<< std::endl;}std::cout << "fun2" << std::endl;
}
int main(){fun2();
}
- 異常的組織形式??
- 平行機構:通過枚舉來組織異常;
- 1,優點:語義相關的錯誤放在一起,條理清晰,適合一些簡單的帶有初始值的錯誤信息
- 2,缺點:無法詳細的描述異常的類型
- 樹形結構:通過異常的層次關系來組織異常
- 1,優點:可以在類的內部詳細的描述錯誤的類型
- 2,缺點:容易造成類層次的無限擴充,反而不容易理解
#include <iostream>#define ERR_OK 0x0000
#define ERR_OK_MSG "OK"#define ERR_CARD 0x8101
#define ERR_CARD_MSG "No Card"#define ERR_UNKnown 0x8000
#define ERR_UNK_MSG "unknown error"enum MathException{ZeroException = 10,NegativeException = 20,NoSolutionException = 30
};class MyException{
public:MyException(int code,std::string msg);virtual int getErrorInfo(std::string &msg);protected:int m_iCode;std::string m_strMsg;
};
MyException::MyException(int code, std::string msg) {std::cout << "MyException" << std::endl;m_iCode = code;m_strMsg = msg;
}int MyException::getErrorInfo(std::string &msg) {std::cout << "getErrorInfo" << std::endl;msg = m_strMsg;return m_iCode;
}
class HardwareMyException : public MyException{
public:HardwareMyException(int code,std::string msg);virtual int getErrorInfo(std::string &msg);
};
HardwareMyException::HardwareMyException(int code, std::string msg) :MyException(code,msg) {std::cout << "HardwareMyException" << std::endl;
}
int HardwareMyException::getErrorInfo(std::string &msg) {std::cout << "HardwareMyException getErrorInfo" << std::endl;msg = m_strMsg;return m_iCode;
}void fun1(int flag){switch (flag) {case 0:throw MyException(ERR_CARD,ERR_CARD_MSG);break;case 1:throw MyException(ERR_UNKnown,ERR_UNK_MSG);break;case 2:throw HardwareMyException(ERR_OK,ERR_OK_MSG);break;}
}
int main(){try {fun1(1);} catch (MyException &e) {std::string msg;std::cout << e.getErrorInfo(msg) << std::endl;std::cout << msg << std::endl;}
}
運算符號重載
- 運算符重載的方式
- 1,成員函數重載??
- 2,友元函數重載
- 一元運算符重載 負號(-)? 遞增運算符號(++)? 遞減運算符號(--)
- 二元運算符重載? 加減號(+-) 索引符號[]? 輸出流 <<
- 不可以重載運算符號 .? .*? ::? ?:? ?{}? ?sizeof
成員函數重載
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Binomial{
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator-();
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};
int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}
Binomial Binomial::operator-() {this->m_iA = -(this->m_iA);m_iB = -m_iB;return *this;//返回對象
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(0,0);bin2 = -bin1;std::cout << bin1.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin1.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getB() << std::endl;return 0;
}
友元函數重載? this指針失效
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}
//Binomial Binomial::operator-() {
// this->m_iA = -(this->m_iA);
// m_iB = -m_iB;
// return *this;//返回對象
//}
Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin){bin.m_iA = -bin.m_iA;bin.m_iB = -bin.m_iB;return bin;
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(0,0);bin2 = -bin1;std::cout << bin1.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin1.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getB() << std::endl;return 0;
}
遞增運算符重載
- ++J
- J++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}
//Binomial Binomial::operator-() {
// this->m_iA = -(this->m_iA);
// m_iB = -m_iB;
// return *this;//返回對象
//}
Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin){bin.m_iA = -bin.m_iA;bin.m_iB = -bin.m_iB;return bin;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++() {m_iA++;m_iB++;return *this;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++(int) {Binomial old(*this);m_iA++;m_iB++;return old;
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(0,0);
// bin2 = -bin1;++bin1;std::cout << bin1.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin1.getB() << std::endl;// std::cout << bin2.getA() << std::endl;
// std::cout << bin2.getB() << std::endl;return 0;
}
?二元運算符重載
- +??
- 成員函數重載??
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin);
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}
//Binomial Binomial::operator-() {
// this->m_iA = -(this->m_iA);
// m_iB = -m_iB;
// return *this;//返回對象
//}
Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin){bin.m_iA = -bin.m_iA;bin.m_iB = -bin.m_iB;return bin;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++() {m_iA++;m_iB++;return *this;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++(int) {Binomial old(*this);m_iA++;m_iB++;return old;
}Binomial Binomial::operator+(Binomial &bin) {Binomial temp(0,0);temp.m_iA += m_iA + bin.m_iA;temp.m_iB += m_iB + bin.m_iB;return temp;
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(8,-5);Binomial bin3(0,0);bin3 = bin1 + bin2;std::cout << bin1.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin1.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin3.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin3.getB() << std::endl;return 0;
}
//5
//3
//8
//-5
//13
//-2
友元類型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);friend Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++
// Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin);
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}
//Binomial Binomial::operator-() {
// this->m_iA = -(this->m_iA);
// m_iB = -m_iB;
// return *this;//返回對象
//}
Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin){bin.m_iA = -bin.m_iA;bin.m_iB = -bin.m_iB;return bin;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++() {m_iA++;m_iB++;return *this;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++(int) {Binomial old(*this);m_iA++;m_iB++;return old;
}Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2){Binomial temp(0,0);temp.m_iA += bin1.m_iA+ bin2.m_iA;temp.m_iB += bin1.m_iB + bin2.m_iB;return temp;
}
//Binomial Binomial::operator+(Binomial &bin) {
// Binomial temp(0,0);
// temp.m_iA += m_iA + bin.m_iA;
// temp.m_iB += m_iB + bin.m_iB;
// return temp;
//}int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(8,-5);Binomial bin3(0,0);bin3 = bin1 + bin2;std::cout << bin1.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin1.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin2.getB() << std::endl;std::cout << bin3.getA() << std::endl;std::cout << bin3.getB() << std::endl;return 0;
}
//5
//3
//8
//-5
//13
//-2
重載 <<?
- 只可以使用友元函數重載? ,不可以使用成員函數,因為第一個必須是cout類型
#include<ostream>
#include <iostream>class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);friend Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2);friend std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &out,Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++
// Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin);
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::getA() {return m_iA;
}
int Binomial::getB() {return m_iB;
}
Binomial::Binomial(int a, int b) {m_iA = a;m_iB = b;
}
Binomial::~Binomial() {}Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin){bin.m_iA = -bin.m_iA;bin.m_iB = -bin.m_iB;return bin;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++() {m_iA++;m_iB++;return *this;
}
Binomial Binomial::operator++(int) {Binomial old(*this);m_iA++;m_iB++;return old;
}Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2){Binomial temp(0,0);temp.m_iA += bin1.m_iA+ bin2.m_iA;temp.m_iB += bin1.m_iB + bin2.m_iB;return temp;
}std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &out,Binomial &bin){out << bin.m_iA << "x + (" << bin .m_iB << ")";return out;
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(8,-5);Binomial bin3(0,0);bin3 = bin1 + bin2;std::cout << bin1 << std::endl;//operator(cout , bin)std::cout << bin2 << std::endl;//operator(cout , bin2)std::cout << bin3 << std::endl;//operator(cout , bin3)return 0;
}索引運算符重載
- 一元函數運算 5x + 3;5為a 3為b
- 預期通過 bin[0] 得到a,通過bin[1] 得到b
#include<ostream>
#include <iostream>class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);friend Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2);friend std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &out,Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++int operator[](unsigned int i);
// Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin);
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};int Binomial::operator[](unsigned int i) {if (i == 0){return m_iA;} else if (i == 1){return m_iB;} else{throw 1;}
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);std::cout << bin1[0] << std::endl; //bin.operator[](0)std::cout << bin1[1] << std::endl; //bin.operator[](1)return 0;
}==等于重載
#include<ostream>
#include <iostream>class Binomial{friend Binomial operator-(Binomial &bin);friend Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin1,Binomial &bin2);friend std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &out,Binomial &bin);
public:Binomial(int a,int b);~Binomial();int getA();int getB();Binomial operator++();//前置 ++jBinomial operator++(int);//后置 j++int operator[](unsigned int i);bool operator==(Binomial &bin);
// Binomial operator+(Binomial &bin);
private:int m_iA;int m_iB;
};bool Binomial::operator==(Binomial &bin) {if (this->m_iA == bin.m_iA && this->m_iB == bin.m_iB){return true;}else{return false;}
}
int main(void)
{Binomial bin1(5,3);Binomial bin2(4,5);if (bin1 == bin2){std::cout << "A" << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "B" << std::endl;}return 0;
}
=運算符重載
注意事項
- 若一個運算的操作需要修改對象的狀態,選擇重載為成員函數,也可以使用友元函數修改對象的狀態
- 當運算符號所需要的操作數(尤其是第一個操作數)希望有隱式類型轉換,則只能使用友元函數
- 當需要重載運算符號具有可交換性,選擇重載為友元函數





)


 第一個C++ STL Application)




容器之分類與測試)


OOP(面向對象編程) Vs. GP(泛型編程))


