鏈表結構
- 單鏈表的節點結構? 由以下結構的節點依次連接起來所形成的鏈叫單鏈表結構
Clas Node<V>{ V value; Node next;
} - 雙鏈表的節點結構 由以下結構的節點依次連接起來所形成的鏈叫雙鏈表結構
Clas Node<V>{ V value; Node next; Node last;
} - ?單鏈表和雙鏈表結構只需要給定一個頭部節點head,就可以找到剩下的所有的節點
反轉單向和雙向鏈表
- [題目]?分別實現反轉單向鏈表和反轉雙向鏈表的函數
- [要求]?如果鏈表長度為N,時間復雜度要求為O(N),額外空間復雜度要求為 O(1)
package com.example.algorithm.demo.class04;public class Code02_ReverseList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}public static Node reverseList(Node head) {Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static class DoubleNode {public int value;public DoubleNode last;public DoubleNode next;public DoubleNode(int data) {this.value = data;}}public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode pre = null;DoubleNode next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;head.last = next;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static void printLinkedList(Node head) {System.out.print("Linked List: ");while (head != null) {System.out.print(head.value + " ");head = head.next;}System.out.println();}public static void printDoubleLinkedList(DoubleNode head) {System.out.print("Double Linked List: ");DoubleNode end = null;while (head != null) {System.out.print(head.value + " ");end = head;head = head.next;}System.out.print("| ");while (end != null) {System.out.print(end.value + " ");end = end.last;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head1 = new Node(1);head1.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next = new Node(3);printLinkedList(head1);head1 = reverseList(head1);printLinkedList(head1);DoubleNode head2 = new DoubleNode(1);head2.next = new DoubleNode(2);head2.next.last = head2;head2.next.next = new DoubleNode(3);head2.next.next.last = head2.next;head2.next.next.next = new DoubleNode(4);head2.next.next.next.last = head2.next.next;printDoubleLinkedList(head2);printDoubleLinkedList(reverseList(head2));}}
打印兩個有序鏈表的公共部分
- [題目]?給定兩個有序鏈表的頭指針head1和head2,打印兩個鏈表的公共部分。
- [要求]?如果兩個鏈表的長度之和為N,時間復雜度要求為O(N),額外空間復雜度要求為O(1)
- [思路] head1指向第一個有序鏈表,head2指向第二個有序鏈表,比較元素的大小,如果相等打印元素的數值。否則,指針指向的元素的數值小的率先移動,比較大小,元素數值小的移動
package com.example.algorithm.demo.class04;public class Code03_PrintCommonPart {public static class Node{public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data){this.value = data;}}public static void printCommonPart(Node head1,Node head2){System.out.println("Common Part: ");while (head1 != null && head2 != null){if (head1.value < head2.value){head1 = head1.next;} else if(head2.value < head1.value){head2 = head2.next;} else{System.out.print(head1.value+" ");head1 = head1.next;head2 = head2.next;}}System.out.println();}public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {System.out.print("Linked List: ");while (node != null) {System.out.print(node.value + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {Node node1 = new Node(2);node1.next = new Node(3);node1.next.next = new Node(5);node1.next.next.next = new Node(6);Node node2 = new Node(1);node2.next = new Node(2);node2.next.next = new Node(5);node2.next.next.next = new Node(7);node2.next.next.next.next = new Node(8);printLinkedList(node1);printLinkedList(node2);printCommonPart(node1, node2);}
}
面試時鏈表解題的方法論
- 1)對于筆試,不用太在乎空間復雜度,一切為了時間復雜度
- 2)對于面試,時間復雜度依然放在第一位,但是一定要找到空間最省的方法
重要技巧:
- 1)額外數據結構記錄(哈希表等)
- 2)快慢指針
快速找到鏈表的中點
- 快慢指針的方式,慢指針每次移動一個長度,快指針每次移動二個長度。當快指針到達鏈表的末尾,慢指針到達鏈表的中點。
- 問題:奇數偶數判定不一樣的,需要細節定制
回文結構
- 將鏈表的后半部分放到棧里邊,存儲的是后半部分數據的逆序
- 面試考慮內存空間,進一步優化。找到鏈表的中點之后,將中點的下一個指針指向nullptr,然后將中點之后的節點的下一個指針進行逆向排序,如下圖所示,主要目的是為了節省空間。然后兩個指針一個從頭 一個從尾進行依次讀取數據進行比較,如果一致滿足回文結構。但是最后需要將鏈表進行還原,恢復成 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 ->1 的結構
- 1 -> 2 -> 3 <- 2 <- 1
- 第二種方式 初始化的時候,將right初始化為head->next;將cur初始化為head節點;主要目的是為了將慢指針移動到中心節點的右邊,然后將中心節點開始的位置到null這段區間的節點都拷貝到棧空間
package class04;import java.util.Stack;public class Code04_IsPalindromeList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}// need n extra spacepublic static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) {Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.next;}while (head != null) {if (head.value != stack.pop().value) {return false;}head = head.next;}return true;}// need n/2 extra spacepublic static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}Node right = head.next;Node cur = head;while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {right = right.next;cur = cur.next.next;}Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();while (right != null) {stack.push(right);right = right.next;}while (!stack.isEmpty()) {if (head.value != stack.pop().value) {return false;}head = head.next;}return true;}// need O(1) extra spacepublic static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}Node n1 = head;Node n2 = head;while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) { // find mid noden1 = n1.next; // n1 -> midn2 = n2.next.next; // n2 -> end}n2 = n1.next; // n2 -> right part first noden1.next = null; // mid.next -> nullNode n3 = null;while (n2 != null) { // right part convertn3 = n2.next; // n3 -> save next noden2.next = n1; // next of right node convertn1 = n2; // n1 moven2 = n3; // n2 move}n3 = n1; // n3 -> save last noden2 = head;// n2 -> left first nodeboolean res = true;while (n1 != null && n2 != null) { // check palindromeif (n1.value != n2.value) {res = false;break;}n1 = n1.next; // left to midn2 = n2.next; // right to mid}n1 = n3.next;n3.next = null;while (n1 != null) { // recover listn2 = n1.next;n1.next = n3;n3 = n1;n1 = n2;}return res;}public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {System.out.print("Linked List: ");while (node != null) {System.out.print(node.value + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = null;printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(3);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(3);head.next.next.next = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(3);head.next.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);printLinkedList(head);System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");printLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");}}將單鏈表按照給定的數值,劃分成左邊小、中間相等、右邊大的形式 (荷蘭國旗)
思路 方法一
- 1,申請一個鏈表長度大小一致的數組,然后遍歷鏈表的過程中,將每一個點放到數組容器中,在數組里面進行荷蘭國旗問題,再把數組容器中的元素都串聯起來,形成一個鏈表返回
- 第一種方法使用的排序 方式思路以及代碼如下:
- 設置 small 從左邊開始移動,只要small對應位置的元素的數值小于pivot(用戶輸入的數值),small就進行移動,同時移動index,使small和index同時向后移動;注意++small index-- ;和初始賦值有關系
- big從右邊開始移動;只有index對應位置上的元素的數值 大于 用戶輸入的數值,就需要交換 index上的數值? 和? big指向的數值;將大的數移動到右邊,--big,index不要動,接下來檢查index的數值
- 如果index 指向的數值? 和? 用戶輸入的數值相等,只需要移動index
public static void arrPartition(Node[] nodeArr,int pivot){int small = -1;int big = nodeArr.length;int index = 0;while (index != big){if (nodeArr[index].value < pivot){swap(nodeArr,++small,index++);} else if (nodeArr[index].value == pivot){++index;} else{swap(nodeArr,--big,index);}}}思路 方法二?
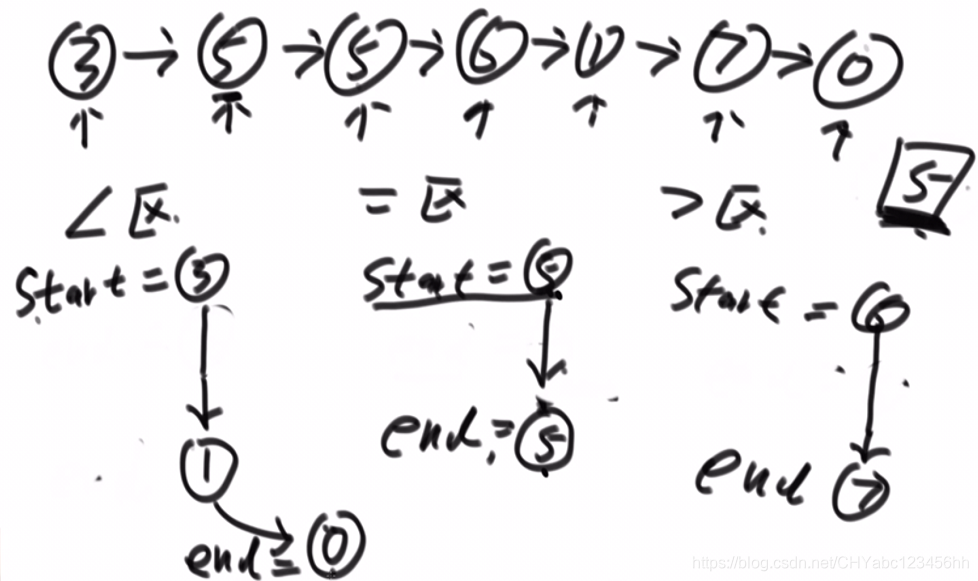
- 2,保證穩定性:根據題目要求設置三個區,小于區、等于區和大于區,每個區間包含兩個變量,開始節點和結尾節點,一共設置6個變量,6個變量都指向null;當遇到第一個元素3的時候,它是小于指定元素5的,將小于區域的開始和結束指針都指向3;第二個元素是5,屬于等于區,讓等于區的start和end都指向第二個元素5;第3個元素也是5,讓等于區的end只想第三個元素。以此類推,得到上面的結果。最后將小于區域的end指針鏈接等于區域的start指針,等于區域的end指針鏈接大于區域的start指針。
- 需要注意的是,有可能上面6個變量有不存在的情形,需要仔細判別。
- 鏈表天然具有穩定性? 保持元素的前后位置的一致性;相較于方法一,避免了數據的交換
package com.example.algorithm.demo.class04;import org.w3c.dom.Node;public class Code05_SmallerEqualBigger {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data){this.value = data;}}public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr,int a,int b){Node tmp = nodeArr[a];nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b];nodeArr[b] = tmp;}public static void arrPartition(Node[] nodeArr,int pivot){int small = -1;int big = nodeArr.length;int index = 0;while (index != big){if (nodeArr[index].value < pivot){swap(nodeArr,++small,index++);} else if (nodeArr[index].value == pivot){++index;} else{swap(nodeArr,--big,index);}}}public static Node listPartition1(Node head,int pivot){if (head == null){return head;}Node cur = head;int i = 0;while (cur != null){i++;cur = cur.next;}Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i];i = 0;cur = head;for (i = 0; i != nodeArr.length;i++){nodeArr[i] = cur;cur = cur.next;}arrPartition(nodeArr,pivot);for (i = 1;i != nodeArr.length;i++){nodeArr[i-1].next = nodeArr[i];}nodeArr[i-1].next = null;return nodeArr[0];}public static Node listPartition2(Node head,int pivot){Node sH = null;Node sT = null;Node eH = null;Node eT = null;Node bH = null;Node bT = null;Node next = null;while (head != null){next = head.next;head.next = null;if (head.value < pivot){if (sH == null){sH = head;sT = head;} else {sT.next = head;sT = head;}} else if(head.value == pivot){if (eH == null){eH = head;eT = head;} else {eT.next = head;eT = head;}} else {if (bH == null){bH = head;bT = head;} else {bT.next = head;bT = head;}}}head = next;if (sT != null){sT.next = eH;eT = eT == null ? sT : eT;}if (eT != null){eT.next = bH;}return sH != null ? sH : eH != null ? eH : bH;}public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {System.out.print("Linked List: ");while (node != null) {System.out.print(node.value + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head1 = new Node(7);head1.next = new Node(9);head1.next.next = new Node(1);head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);printLinkedList(head1);head1 = listPartition1(head1, 4);
// head1 = listPartition2(head1, 5);printLinkedList(head1);}
}
復制含有隨機指針節點的鏈表
-
【題目】一種特殊的單鏈表節點類描述如下
public static class Node{public int value;public Node next;public Node rand;public Node(int data){this.value = data;}}- rand指針是單鏈表節點結構中新增的指針,rand可能指向鏈表中的任意一個節點,也可能指向null。
- 給定一個由Node節點類型組成的無環單鏈表的頭節點 head,請實現一個函數完成這個鏈表的復制,并返回復制的新鏈表的頭節點。
- 【要求】時間復雜度O(N),額外空間復雜度O(1)
- 方法1 利用map,key和value都是Node類型;使用新建的類型為Node的Value節點存儲節點的下一個和隨機指針,然后拋棄先前的鏈表,使用map存儲的記錄實現鏈表的拼接;map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);分別指定節點的下一個和隨機指針 - 方法2 遍歷鏈表,在每個節點的后面創建對應的副本;然后將每一個新建的節點進行串聯,形成拷貝;
//創建節點 填入元素Node cur = head;Node next = null;while (cur != null){next = cur.next; //指向新創建的節點的下一個cur.next = new Node(cur.value); //新建節點cur.next.next = next; //銜接新創建的節點和先前節點,相當于在指定位置插入節點cur = next; //指向舊的節點}//分離節點Node res = head.next;cur = head;while (cur != null){next = cur.next.next;curCopy = cur.next;cur.next = next;curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null;cur = next;}Codepackage class04;import java.util.HashMap;public class Code06_CopyListWithRandom {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node rand;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head) {HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value));cur = cur.next;}cur = head;while (cur != null) {map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);cur = cur.next;}return map.get(head);}public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}Node cur = head;Node next = null;// copy node and link to every nodewhile (cur != null) {next = cur.next;cur.next = new Node(cur.value);cur.next.next = next;cur = next;}cur = head;Node curCopy = null;// set copy node randwhile (cur != null) {next = cur.next.next;curCopy = cur.next;curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;cur = next;}Node res = head.next;cur = head;// splitwhile (cur != null) {next = cur.next.next;curCopy = cur.next;cur.next = next;curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null;cur = next;}return res;}public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) {Node cur = head;System.out.print("order: ");while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.value + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();cur = head;System.out.print("rand: ");while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = null;Node res1 = null;Node res2 = null;printRandLinkedList(head);res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);printRandLinkedList(res1);res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);printRandLinkedList(res2);printRandLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(3);head.next.next.next = new Node(4);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> nullhead.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4printRandLinkedList(head);res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);printRandLinkedList(res1);res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);printRandLinkedList(res2);printRandLinkedList(head);System.out.println("=========================");}}
兩個單鏈表相交的一系列問題
- 【題目】給定兩個可能有環也可能無環的單鏈表,頭節點head1和head2。請實現一個函數,如果兩個鏈表相交,請返回相交的 第一個節點。如果不相交,返 回null
- 【要求】如果兩個鏈表長度之和為N,時間復雜度請達到O(N),額外空間復雜度 請達到O(1)。
- 兩個單鏈表相交的一系列問題
- 相交:共用內存地址??
- 注意事項:每個節點只有next指針,不可以有兩個指出的指針
- 有環/無環:寫一個函數,輸入的類型是鏈表的頭節點,判斷是否有環,以及返回第一個入環的節點。
- 方法一:使用集合來做,遍歷鏈表,每遍歷一個元素,將其放入到集合中,判定是否存在此元素,如果將一個元素放入集合中,發現他已經存在,則是有環的,并且他就是第一個入環節點。
- 方法二:使用快慢指針來做,快指針每次移動倆個位置,慢指針每次移動一個位置,當快慢指針第一次相交之后,快指針回到鏈表的起始點,慢指針呆在原地不動。然后快指針和慢指針都每次移動一個位置,當他們再次相遇之后,相遇的元素就是入環的第一個元素,且能證明這個鏈表是有環的結構。上圖所示的是環外4個點,環內4個點,可以按照這個流程走一遍。
- 使用函數(返回第一個入環的節點)如果返回的是null 說明鏈表無環;如果兩個鏈表都無環,找到兩個鏈表最后的位置,如果最后的位置相等 ,說明鏈表相交;否則鏈表不想交;兩個無環鏈表相交問題,哪個鏈表長,先走比短鏈表多余的部分,然后一起走,只要有一點的內存地址相穩合,則代表兩者相交。

- 如果一個是有環的,一個是無環的,那么他倆一定不相交? 不可以出現兩個指出的指針

- 兩個都有環的 鏈表 ,可以出現三種情況
- 第一種情形,使用其中一個入環節點繞著環走一圈,如果可以找到另外的入環節點就是第三種情形;否則就是第一種情形
- 第二種情形,將第一個入環節點作為判斷終止的條件

package class04;public class Code07_FindFirstIntersectNode {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {return null;}Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {return noLoop(head1, head2);}if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);}return null;}public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {return null;}Node n1 = head.next; // n1 -> slowNode n2 = head.next.next; // n2 -> fastwhile (n1 != n2) {if (n2.next == null || n2.next.next == null) {return null;}n2 = n2.next.next;n1 = n1.next;}n2 = head; // n2 -> walk again from headwhile (n1 != n2) {n1 = n1.next;n2 = n2.next;}return n1;}public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {return null;}Node cur1 = head1;Node cur2 = head2;int n = 0;while (cur1.next != null) {n++;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur2.next != null) {n--;cur2 = cur2.next;}if (cur1 != cur2) {return null;}cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;n = Math.abs(n);while (n != 0) {n--;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur1 != cur2) {cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}return cur1;}public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {Node cur1 = null;Node cur2 = null;if (loop1 == loop2) {cur1 = head1;cur2 = head2;int n = 0;while (cur1 != loop1) {n++;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur2 != loop2) {n--;cur2 = cur2.next;}cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;n = Math.abs(n);while (n != 0) {n--;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur1 != cur2) {cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}return cur1;} else {cur1 = loop1.next;while (cur1 != loop1) {if (cur1 == loop2) {return loop1;}cur1 = cur1.next;}return null;}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->nullNode head1 = new Node(1);head1.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next = new Node(3);head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);// 0->9->8->6->7->nullNode head2 = new Node(0);head2.next = new Node(9);head2.next.next = new Node(8);head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...head1 = new Node(1);head1.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next = new Node(3);head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4// 0->9->8->2...head2 = new Node(0);head2.next = new Node(9);head2.next.next = new Node(8);head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..head2 = new Node(0);head2.next = new Node(9);head2.next.next = new Node(8);head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);}}
?
?
?
?


)










![C語言二維數組 int arr[2][3]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/C語言二維數組 int arr[2][3])




![C語言 指針數組-字符指針數組整型指針數組 char*s[3] int*a[5] 數組指針int(*p)[4]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/C語言 指針數組-字符指針數組整型指針數組 char*s[3] int*a[5] 數組指針int(*p)[4])
