概述
- SGI STL的list是一個雙向鏈表,單向鏈表是slist,其不在標準規格之內
- 單向和雙向鏈表的區別在于,單向鏈表的迭代器是單向的 Forward Iterator,雙向鏈表的迭代器屬于雙向的Bidirectional Iterator。因此很多功能都被受限
- 但是單向鏈表的耗用的空間更小,某些操作更快
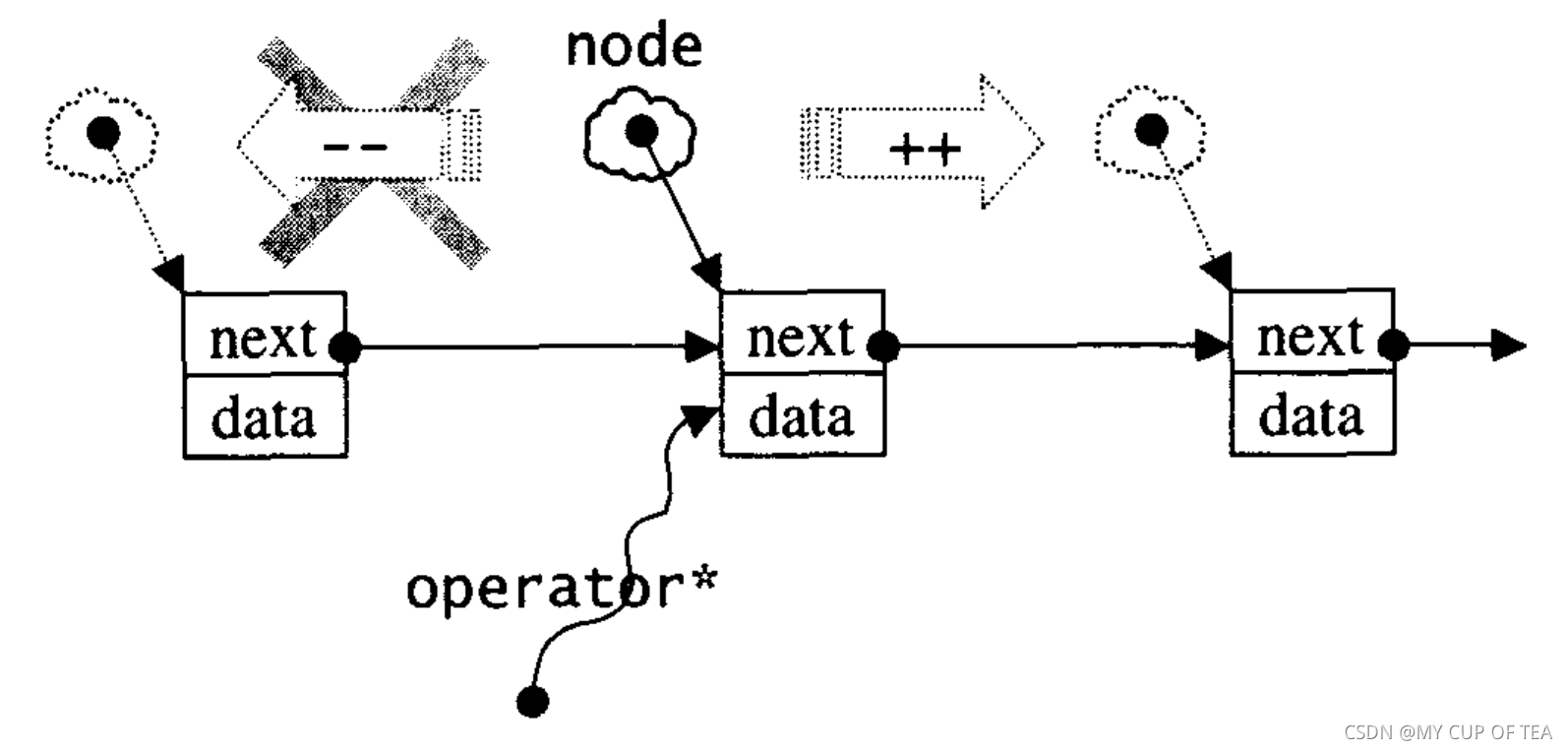
- 注意事項:插入操作會將新的元素插入到指定的位置之前,而不是之后的位置。但是單向鏈表無法回頭確定前一個位置,因此需要從頭部開始重新找起,即 除了在單向鏈表的起始處附近其余的地方進行insert 或者 erase都是不合適的操作。這也是單向和雙向鏈表之間最大的差異,因此 單向鏈表提供了 insert_after() 和 erase_after() 供靈活使用
- 基于上述的考慮,slist 也不提供push_back() 只提供push_front(),因此一定要注意單向鏈表元素的順序和 元素的插入進來的順序 相反
slist的節點
- 單向鏈表的迭代器比雙向鏈表更為復雜一些,運用了繼承關系,因此在型別轉換層面上有著復雜的表現

#include <iostream>//單向鏈表的節點的基本結構
struct __slist_node_base{__slist_node_base* next;
};//單向鏈表的節點結構
template <class T>
struct __slist_node : public __slist_node_base{T data;
};//全局函數 已知某一個節點,插入新的節點于其后
inline __slist_node_base* __slist_make_link(__slist_node_base* prev_node,__slist_node_base* new_node){//令new_node節點的下一個節點為prev節點的下一節點new_node->next = prev_node->next->next;prev_node->next = new_node; //令prev節點的next指針指向new節點return new_node;
}//全局函數 單向鏈表的大小(元素的個數)
inline std::size_t __slist_size(__slist_node_base* node){std::size_t result = 0;for( ; node != 0;node = node->next){++result; //一個一個累計}return result;
}
slist的迭代器
//單向鏈表的迭代器的基本結構
struct __slist_iterator_base{typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef std::ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef std::forward_iterator_tag iterator_category; //注意 單向__slist_node_base* node; //指向節點的基本結構 next指針__slist_iterator_base(__slist_node_base* x): node(x){}void incr(){node = node->next; } //前進一個節點bool operator==(const __slist_iterator_base& x)const{return node == x.node;}bool operator!=(const __slist_iterator_base& x)const{return node != x.node;}
};//單向鏈表的迭代器結構
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __slist_iterator : public __slist_iterator_base{typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __slist_iterator<T,const T&,const T*>const_iterator;typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> self;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __slist_node<T> list_node;//調用slist<T>::end()會造成__slist_iterator(0) 于是調用如下函數__slist_iterator(list_node* x) : __slist_iterator_base(x){}__slist_iterator(): __slist_iterator_base(0){}__slist_iterator(const iterator& x): __slist_iterator_base(x.node){}reference operator*() const {return ((list_node*)node)->data;}reference operator->() const {return &(operator*());}self& operator++(){incr(); //前進一個節點return *this;}self& operator++(int){self tmp = *this;incr(); //前進一個節點return tmp;}//沒有實現operator-- 因為這是一個單向鏈表,使用的是forward iterator
};
- 注意比較兩個slist迭代器是否等同時,比如常規循環下需要判斷 迭代器是否等同于 slist.end()?
- 但是__slist_iterator并沒有對operator==進行重載,所以會調用 __slist_iterator_base::operator== ,__slist_iterator_base::operator==內部通過判定?__slist_iterator_base* node來判定兩個迭代器是否等同
slist的數據結構
#include <iostream>//單向鏈表的節點的基本結構
struct __slist_node_base{__slist_node_base* next;
};//單向鏈表的節點結構
template <class T>
struct __slist_node : public __slist_node_base{T data;
};//全局函數 已知某一個節點,插入新的節點于其后
inline __slist_node_base* __slist_make_link(__slist_node_base* prev_node,__slist_node_base* new_node){//令new_node節點的下一個節點為prev節點的下一節點new_node->next = prev_node->next->next;prev_node->next = new_node; //令prev節點的next指針指向new節點return new_node;
}//全局函數 單向鏈表的大小(元素的個數)
inline std::size_t __slist_size(__slist_node_base* node){std::size_t result = 0;for( ; node != 0;node = node->next){++result; //一個一個累計}return result;
}//單向鏈表的迭代器的基本結構
struct __slist_iterator_base{typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef std::ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef std::forward_iterator_tag iterator_category; //注意 單向__slist_node_base* node; //指向節點的基本結構 next指針__slist_iterator_base(__slist_node_base* x): node(x){}void incr(){node = node->next; } //前進一個節點bool operator==(const __slist_iterator_base& x)const{return node == x.node;}bool operator!=(const __slist_iterator_base& x)const{return node != x.node;}
};//單向鏈表的迭代器結構
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __slist_iterator : public __slist_iterator_base{typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __slist_iterator<T,const T&,const T*>const_iterator;typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> self;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __slist_node<T> list_node;//調用slist<T>::end()會造成__slist_iterator(0) 于是調用如下函數__slist_iterator(list_node* x) : __slist_iterator_base(x){}__slist_iterator(): __slist_iterator_base(0){}__slist_iterator(const iterator& x): __slist_iterator_base(x.node){}reference operator*() const {return ((list_node*)node)->data;}reference operator->() const {return &(operator*());}self& operator++(){incr(); //前進一個節點return *this;}self& operator++(int){self tmp = *this;incr(); //前進一個節點return tmp;}//沒有實現operator-- 因為這是一個單向鏈表,使用的是forward iterator
};template<class T,class Alloc>
class simple_alloc{
public:static T* allocate(std::size_t n){return 0==n?0:(T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof (T));}static void deallocate(T* p,size_t n){if (n!=0){Alloc::deallocate(p,n * sizeof(T));}}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p,sizeof(T));}
};#ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
#define __STL_TRY try
#define __STL_UNWIND(action) catch(...) { action; throw; }
#else
#define __STL_TRY
#define __STL_UNWIND(action)
#endifnamespace Chy{template <class T>inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size,T*){std::set_new_handler(0);T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((std::size_t)(size * sizeof (T))));if (tmp == 0){std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl;exit(1);}return tmp;}template<class T>inline void _deallocate(T* buffer){::operator delete (buffer);}template<class T1,class T2>inline void _construct(T1 *p,const T2& value){new(p) T1 (value); //沒看懂}template <class T>inline void _destroy(T* ptr){ptr->~T();}template <class T>class allocator{public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef const T* const_pointer;typedef T& reference;typedef const T& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;template<class U>struct rebind{typedef allocator<U>other;};pointer allocate(size_type n,const void * hint = 0){return _allocate((difference_type)n,(pointer)0);}void deallocate(pointer p,size_type n){_deallocate(p);}void construct(pointer p,const T& value){_construct(p,value);}void destroy(pointer p){_destroy(p);}pointer address(reference x){return (pointer)&x;}const_pointer const_address(const_reference x){return (const_pointer)&x;}size_type max_size()const{return size_type(UINT_MAX/sizeof (T));}};
}template <class T,class Alloc>
class slist{
public:typedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef std::ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __slist_iterator<T,const T&,const T*>const_iterator;
private:typedef __slist_node<T> list_node;typedef __slist_node_base list_node_base;typedef __slist_iterator_base iterator_base;typedef simple_alloc<list_node,Alloc>list_node_allocator;static list_node* create_node(const value_type& x){list_node* node = list_node_allocator::allocate(); //配置空間__STL_TRY{Chy::allocator<T>::construct(&node->data,x);node->next = 0;};__STL_UNWIND(list_node_allocator::deallocate(node);) //釋放空間}static void destroy_node(list_node* node){Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(&node->data);//將元素析構list_node_allocator::deallocate(node); //釋放空間}
private:list_node_base head; //頭部 注意head不是指針,是事物
public:slist(){head.next = 0;}~slist(){clear();}
public:void clear(){erase_after(&head,0);}//全局函數 傳遞鏈表的頭部和尾部inline list_node_base* erase_after(list_node_base* before_first,list_node_base* last_node){list_node * cur = (list_node*)(before_first->next);while (cur != last_node){list_node * tmp = cur;cur = (list_node *)cur->next;destroy_node(tmp);}before_first->next = last_node;return last_node;}
public:iterator begin(){return iterator((list_node*)head.next);}iterator end(){return iterator(0);}size_type size() const{return __slist_size(head.next);}bool empty() const {return head.next == 0;}//兩個slist之間互換,只需要交換head頭結點即可void swap(slist& L){list_node_base* tmp = head.next;head.next = L.head.next;L.head.next = tmp;}//獲取頭部元素reference front(){return ((list_node*)head.next)->data;}//從頭部插入元素 新的元素成為slist的第一個元素void push_front(const value_type& x){__slist_make_link(&head, create_node(x));}//注意 沒有push_back()//從頭部取出元素,將其刪除之 修改headvoid pop_front(){list_node * node = (list_node*)head.next;head.next = node->next;destroy_node(node);}};
元素操作



參考鏈接
- STL源碼剖析(十二)序列式容器之slist_JT同學的博客-CSDN博客







:40+個依賴子模塊之ActionBarShadow)
















