- testmgr.c - crypto/testmgr.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
- 上述代碼是內核內部即crypto子系統對外提供密碼服務的測試程序
- 調用流程:crypto API <—> crypto core <—> crypto_register_alg
- 處于用戶態的程序想要調用處于內核態的密碼算法,需要使用crypto_register_alg函數提交對應的相關信息,進行注冊,將一個內核支持的算法注冊到crypto系統里。
- crypto_alg參考鏈接如下
- Linux加密框架crypto crypto_alg|cipher_alg數據結構|AES例子_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
- crypto_alg 結構
struct crypto_alg {struct list_head cra_list;struct list_head cra_users;u32 cra_flags;unsigned int cra_blocksize;unsigned int cra_ctxsize;unsigned int cra_alignmask;int cra_priority;refcount_t cra_refcnt;char cra_name[CRYPTO_MAX_ALG_NAME];char cra_driver_name[CRYPTO_MAX_ALG_NAME];const struct crypto_type *cra_type;union {struct cipher_alg cipher;struct compress_alg compress;} cra_u;int (*cra_init)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm);void (*cra_exit)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm);void (*cra_destroy)(struct crypto_alg *alg);struct module *cra_module;#ifdef CONFIG_CRYPTO_STATSunion {struct crypto_istat_aead aead;struct crypto_istat_akcipher akcipher;struct crypto_istat_cipher cipher;struct crypto_istat_compress compress;struct crypto_istat_hash hash;struct crypto_istat_rng rng;struct crypto_istat_kpp kpp;} stats;
#endif /* CONFIG_CRYPTO_STATS */} CRYPTO_MINALIGN_ATTR;- 執行一個請求的時候,還有維護一組上下文的信息, 這些信息記錄在結構體: struct crypto_tfm
- crypto_tfm類型指針tfm可以理解為指代了一個算法對象
- 參考鏈接?Linux內核 crypto文件夾 密碼學知識學習_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
- cra_init是準備上下文的函數,比如,你用一個硬件設備壓縮數據,實際的物理操作發生在這個硬件的一個隊列上,那么就需要準備這個隊列,準備必要的緩存等等。
- cra_exit 是退出上下文。
- cra_u里是具體執行算法的函數,比如可以壓縮和解壓縮的函數。
struct crypto_tfm {u32 crt_flags;int node;void (*exit)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm);struct crypto_alg *__crt_alg;void *__crt_ctx[] CRYPTO_MINALIGN_ATTR;
};
- crypto_tfm中最后一個元素__crt_ctx是這個上下文的私有數據。
- 上面的crypto_alg中cra_ctxsize參數就是這個私有數據的__crt_ctx的大小
例子? ?同步接口
/* 分配一個壓縮解壓縮的上下文, 可以看到這里的壓縮解壓縮的上下文完全就是crypto_tfm */
struct crypto_comp = crypto_alloc_comp(driver, type, mask);--> crypto_alloc_base(alg_name, type, mask)/* find algrithm: use alg_name, driver name */--> alg = crypto_alg_mod_lookup(alg_name, type, mask);/* 上下文是依據具體的算法去分配的 */--> tfm = __crypto_alloc_tfm(alg, type, mask);/* 上下文中指定相關的算法 */--> tfm->__crt_alg = alg;--> crypto_init_ops/* 把相應的算法中的壓縮解壓縮函數傳遞給上下文 */--> crypto_init_compress_ops(tfm)/* ops is struct compress_tfm */--> ops->cot_compress = crypto_compress;--> tfm->__crt_alg->cra_compress.coa_compress--> ops->cot_decompress = crypto_decompress;/** 在創建上下文的最后調用下,算法里的初始化函數,如果是和一個硬件* 的驅動適配,那么這里就可以執行相應硬件初始化的內容。*/--> if (!tfm->exit && alg->cra_init && (err = alg->cra_init(tfm)))第二,就是執行壓縮的操作:
crypto_comp_compress(tfm, input, ilen, result, &dlen)crypto_comp_decompress(crypto_comp, src, slen, dst, dlen)/* so hardware can do compress here! */--> compress_tfm->cot_compress;第三,就是釋放這個壓縮的上下文
crypto_free_comp(comp)-
從設備驅動的角度講, 設備驅動只是看到了crypto_alg這個結構。
-
這個結構里的crypt_tfm 即一個操作執行的上下文是從哪里知道的呢?畢竟crypto_alg這個結構里的.cra_init, .cra_exit, .cra_u里的.coa_compress都需要這個執行上下文。
-
知道這些內部的數據結構對我們理解外部的API有幫助。現在假設crypto的設備驅動已經有了,那么,其他的內核模塊怎么用呢? 其實一開頭我們已經講到crypto/testmgr.c測試程序。
-
測試的代碼里有異步的測試和同步的測試流程,我們這里先看同步的測試:
-
主要的邏輯就三個函數, 首先需要分配一個壓縮的上下文(本文用壓縮的例子), 其實它就是crypto_tfm的包裝,和cryto_tfm是一樣的:? ? 紫色的刪去 ,我沒找到這個壓縮的例子?
struct crypto_comp {struct crypto_tfm base;
};
- 使用testmgr.c文件中的函數進行分析?
第一步 創建對象? 進行準備操作

- crypto.h - include/linux/crypto.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin? ?crypto_alloc_comp
- 創建對象

- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin?crypto_alloc_base
- 調用 crypto_alg_mod_lookup尋找 用戶輸入的函數的名字是否是內核支持的算法類型

- ?crypto_alloc_base通過crypro_alg_mod_lookup判斷這個算法類型是存在的
- 才會使用函數__crypto_alloc_tfm為其創建對象

- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin?
- 使用上層輸入的 參數 初始化對象

- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin? crypto_init_ops

- 調用crypto_type的init?
- algapi.h - include/crypto/algapi.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin

第二步 執行具體的函數操作
- ?本例子具體執行的函數操作是crypto_comp_compress和crypto_comp_decompress
- testmgr.c - crypto/testmgr.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin


 ?第三步 釋放壓縮的上下文
?第三步 釋放壓縮的上下文

例子 異步接口?
- testmgr.c - crypto/testmgr.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
- ?異步接口和同步接口不一樣的是,這里又創建一個acomp_req的上下文, 后續的操作都圍繞著這個req結構展開。
- 可以看到req里面包含了異步接口需要的回調函數
static int test_acomp(struct crypto_acomp *tfm,const struct comp_testvec *ctemplate,const struct comp_testvec *dtemplate,int ctcount, int dtcount)
{const char *algo = crypto_tfm_alg_driver_name(crypto_acomp_tfm(tfm));unsigned int i;char *output, *decomp_out;int ret;struct scatterlist src, dst;struct acomp_req *req;struct crypto_wait wait;output = kmalloc(COMP_BUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);if (!output)return -ENOMEM;decomp_out = kmalloc(COMP_BUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);if (!decomp_out) {kfree(output);return -ENOMEM;}for (i = 0; i < ctcount; i++) {unsigned int dlen = COMP_BUF_SIZE;int ilen = ctemplate[i].inlen;void *input_vec;input_vec = kmemdup(ctemplate[i].input, ilen, GFP_KERNEL);if (!input_vec) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}memset(output, 0, dlen);crypto_init_wait(&wait);sg_init_one(&src, input_vec, ilen);sg_init_one(&dst, output, dlen);req = acomp_request_alloc(tfm);if (!req) {pr_err("alg: acomp: request alloc failed for %s\n",algo);kfree(input_vec);ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}acomp_request_set_params(req, &src, &dst, ilen, dlen);acomp_request_set_callback(req, CRYPTO_TFM_REQ_MAY_BACKLOG,crypto_req_done, &wait);ret = crypto_wait_req(crypto_acomp_compress(req), &wait);if (ret) {pr_err("alg: acomp: compression failed on test %d for %s: ret=%d\n",i + 1, algo, -ret);kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}ilen = req->dlen;dlen = COMP_BUF_SIZE;sg_init_one(&src, output, ilen);sg_init_one(&dst, decomp_out, dlen);crypto_init_wait(&wait);acomp_request_set_params(req, &src, &dst, ilen, dlen);ret = crypto_wait_req(crypto_acomp_decompress(req), &wait);if (ret) {pr_err("alg: acomp: compression failed on test %d for %s: ret=%d\n",i + 1, algo, -ret);kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}if (req->dlen != ctemplate[i].inlen) {pr_err("alg: acomp: Compression test %d failed for %s: output len = %d\n",i + 1, algo, req->dlen);ret = -EINVAL;kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}if (memcmp(input_vec, decomp_out, req->dlen)) {pr_err("alg: acomp: Compression test %d failed for %s\n",i + 1, algo);hexdump(output, req->dlen);ret = -EINVAL;kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);}for (i = 0; i < dtcount; i++) {unsigned int dlen = COMP_BUF_SIZE;int ilen = dtemplate[i].inlen;void *input_vec;input_vec = kmemdup(dtemplate[i].input, ilen, GFP_KERNEL);if (!input_vec) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}memset(output, 0, dlen);crypto_init_wait(&wait);sg_init_one(&src, input_vec, ilen);sg_init_one(&dst, output, dlen);req = acomp_request_alloc(tfm);if (!req) {pr_err("alg: acomp: request alloc failed for %s\n",algo);kfree(input_vec);ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}acomp_request_set_params(req, &src, &dst, ilen, dlen);acomp_request_set_callback(req, CRYPTO_TFM_REQ_MAY_BACKLOG,crypto_req_done, &wait);ret = crypto_wait_req(crypto_acomp_decompress(req), &wait);if (ret) {pr_err("alg: acomp: decompression failed on test %d for %s: ret=%d\n",i + 1, algo, -ret);kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}if (req->dlen != dtemplate[i].outlen) {pr_err("alg: acomp: Decompression test %d failed for %s: output len = %d\n",i + 1, algo, req->dlen);ret = -EINVAL;kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}if (memcmp(output, dtemplate[i].output, req->dlen)) {pr_err("alg: acomp: Decompression test %d failed for %s\n",i + 1, algo);hexdump(output, req->dlen);ret = -EINVAL;kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);goto out;}kfree(input_vec);acomp_request_free(req);}ret = 0;out:kfree(decomp_out);kfree(output);return ret;
}
- 這里需要說明的是,testmsg.c里的這個acomp的測試程序里加了wait的相關內容。這里應該是為了測試方便而加的,一般的異步接口里, 當硬件完成操作的時候,在中斷函數里直接調用異步接口的回調函數就可以了。
- request是為了異步而創建的,但是wait對象的存在的主要目的目前還不清楚
例外一個例子
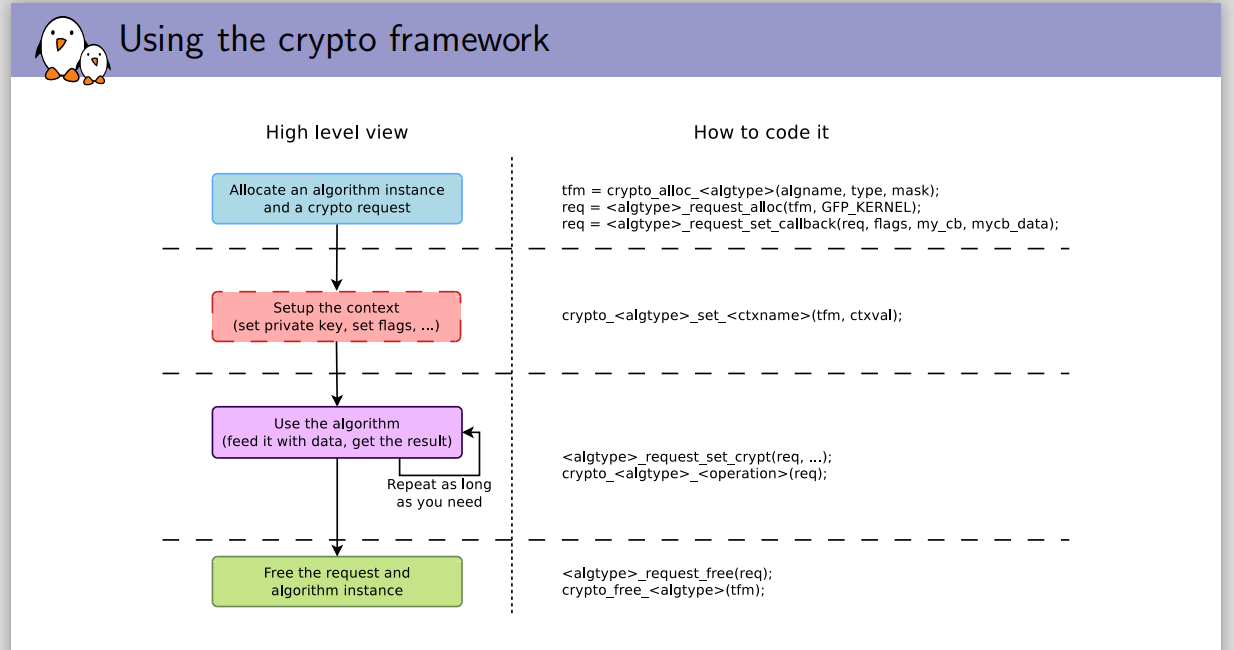
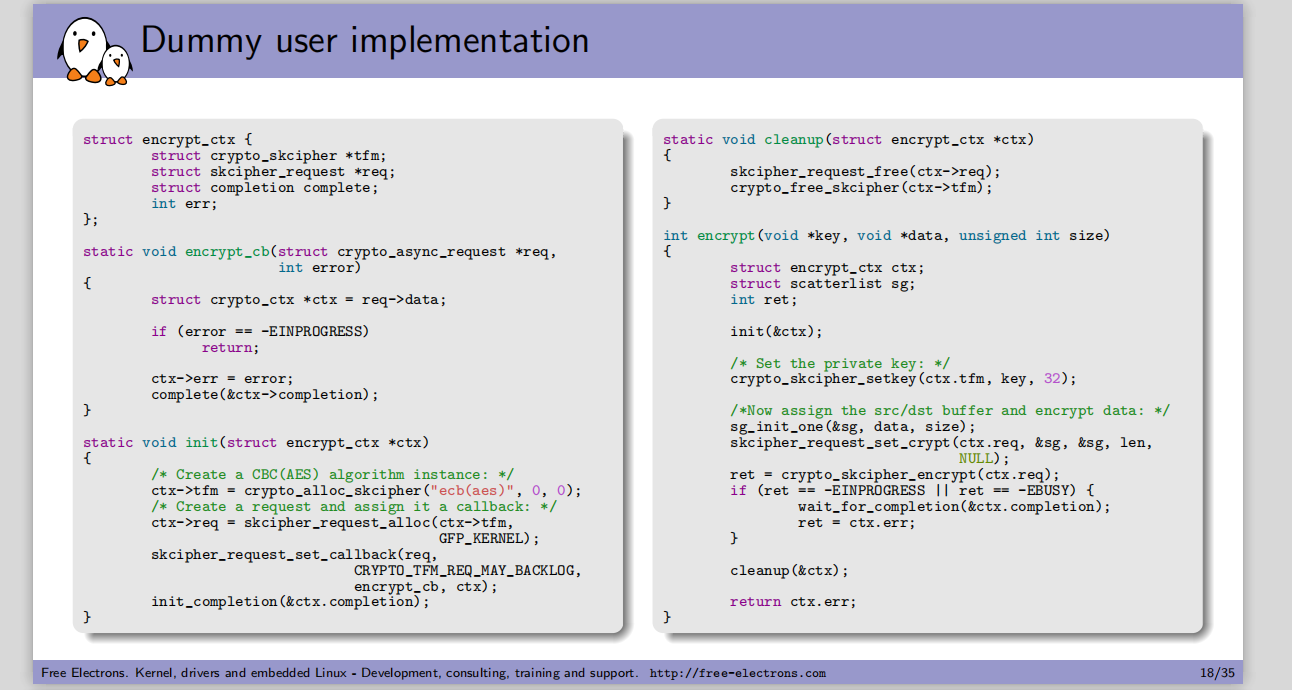 ?
?
總的來說,在內核態使用加密算法的過程分為以下幾步:
- 分配tranform對象 ? 也就是具體的算法
- 分配request對象 ?異步操作等待對象
- 設置上下文 如加密密鑰/驗簽公鑰,填充數據源,給scatterlist設置緩沖區,給異步請求對象設置回調函數/初始化向量等,給密碼算法對象設置密鑰
- 完成加密/解密/摘要/驗簽
- 釋放transform,request等對象
- 如果是同步調用的方式,不需要創建request對象
參考鏈接
- Linux內核crypto子系統深入理解_Linux教程_Linux公社-Linux系統門戶網站
- Linux內核 crypto文件夾 密碼學知識學習_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客

















)

