參考鏈接
- Linux加密框架中的主要數據結構(四)_家有一希的博客-CSDN博客
- algapi.h - include/crypto/algapi.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
struct crypto_instance {struct crypto_alg alg;struct crypto_template *tmpl;union {/* Node in list of instances after registration. */struct hlist_node list;/* List of attached spawns before registration. */struct crypto_spawn *spawns;};void *__ctx[] CRYPTO_MINALIGN_ATTR;
};
算法模板實例數據結構 crypto_instance各成員變量含義如下所示:
- 1)alg:算法模板實例對應的算法說明
- Linux加密框架crypto crypto_alg|cipher_alg數據結構|AES例子_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
- 2)tmpl:算法模板實例使用的算法模板
- algapi.h - include/crypto/algapi.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
- 3)list:算法模板實例在算法模板的實例哈希鏈表中對應的節點。
- 注冊后實例列表中的節點。
- spawns:注冊前的附加生成列表。
- algapi.h - include/crypto/algapi.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
- 4)__ctx:算法模板實例的上下文。
例子
- 由算法模板實例數據結構定義,算法模板實例也是一種算法,如分組算法根據算法模板(如CBC模式)創建的塊加密算法。
- CBC算法模板的創建實例接口為crypto_cbc_alloc,輸入參數為創建CBC算法模板實例的參數tb,返回值為新創建的算法模板實例。
- crypto_cbc_alloc函數創建CBC算法模板流程如下所示
- 上面參考鏈接的內容,如下,但是在目前較為新的版本中 v5.15.11已經不再使用了

- ?根據上述流程進行推導
- 無論是通過alloc接口還是create接口創建算法模板實例,輸入參數tb為創建算法模板實例的相關參數,至少包括算法類型及屏蔽位(tb[0])和基礎算法的算法名(tb[1])。每個參數都是TLV格式,類型T有CRYPTOA_TYPE(算法類型)、CRYPTOA_ALG(基礎算法名)、CRYPTOA_U32等多種類型,而每種類型的參數值不同,因此接口輸入參數tb的數據類型struct rtattr只包括rta_len和rta_type兩個成員變量,分別對應著TLV結構的L和T,參數值數據結構根據參數類型定義。
- ?參數類型為CRYPTOA_TYPE時,算法類型TLV結構(即tb[0])如下所示,通過函數crypto_get_attr_type可以獲取算法類型和屏蔽位。
/* Generic structure for encapsulation of optional route information.It is reminiscent of sockaddr, but with sa_family replacedwith attribute type.*/struct rtattr {unsigned short rta_len;unsigned short rta_type;
};- Linux加密框架 crypto 算法模板_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
- 首先調用 crypto_attr_type

- ?其中? crypto_attr_type 顯示如下,包含type和mask
- crypto_attr_type返回的類型是 RTA_DATA(rta),
- 其中RTA_DATA 定義如下,返回的是void*指向一塊內存區域,這個內存區域使用的時候可以轉型為crypto_attr_type的結構
- #define RTA_DATA(rta) ? ((void*)(((char*)(rta)) + RTA_LENGTH(0)))
- #define RTA_LENGTH(len)?? ?(RTA_ALIGN(sizeof(struct rtattr)) + (len))
struct crypto_attr_type {u32 type;u32 mask;
};- Linux加密框架 crypto 算法模板_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客

- ?參數類型為CRYPTOA_ALG時,基礎算法名TLV結構(即tb[1])如下所示,通過函數crypto_attr_alg_name獲取基礎算法名

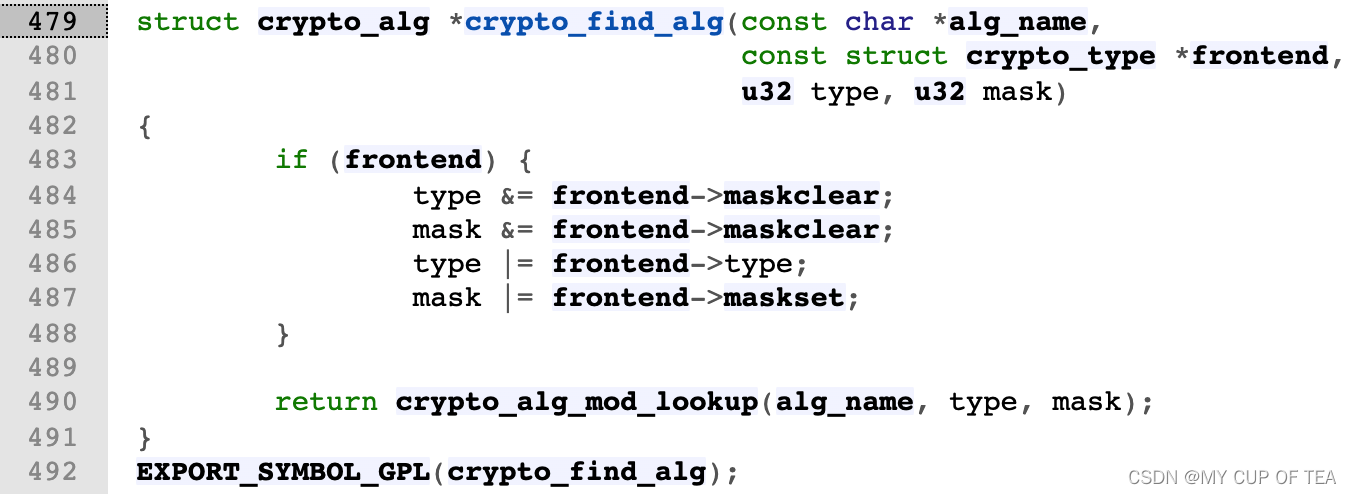

- crypto_template結構體內部的 create函數,需要輸入?crypto_template模板名字和rtattr類型(rta_len 和 rta_type )進行創建
- crypto_spawn
- list: 在基礎算法的用戶鏈表users中的鏈表節點
- alg: 關聯的基礎算法
- frontend: 關聯的算法實例前端,即算法類型常量
- mask: 算法的類型屏蔽位
- crypto_type

- 例子
- Linux加密框架 crypto 算法模板 CBC模板舉例_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
/*** skcipher_alloc_instance_simple - allocate instance of simple block cipher mode** Allocate an skcipher_instance for a simple block cipher mode of operation,* e.g. cbc or ecb. The instance context will have just a single crypto_spawn,* that for the underlying cipher. The {min,max}_keysize, ivsize, blocksize,* alignmask, and priority are set from the underlying cipher but can be* overridden if needed. The tfm context defaults to skcipher_ctx_simple, and* default ->setkey(), ->init(), and ->exit() methods are installed.** @tmpl: the template being instantiated* @tb: the template parameters** Return: a pointer to the new instance, or an ERR_PTR(). The caller still* needs to register the instance.*/struct skcipher_instance *skcipher_alloc_instance_simple(struct crypto_template *tmpl, struct rtattr **tb)
{u32 mask;struct skcipher_instance *inst;struct crypto_cipher_spawn *spawn;struct crypto_alg *cipher_alg;int err;err = crypto_check_attr_type(tb, CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_SKCIPHER, &mask);if (err)return ERR_PTR(err);inst = kzalloc(sizeof(*inst) + sizeof(*spawn), GFP_KERNEL);if (!inst)return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);spawn = skcipher_instance_ctx(inst);err = crypto_grab_cipher(spawn, skcipher_crypto_instance(inst),crypto_attr_alg_name(tb[1]), 0, mask);if (err)goto err_free_inst;cipher_alg = crypto_spawn_cipher_alg(spawn);err = crypto_inst_setname(skcipher_crypto_instance(inst), tmpl->name,cipher_alg);if (err)goto err_free_inst;inst->free = skcipher_free_instance_simple;/* Default algorithm properties, can be overridden */inst->alg.base.cra_blocksize = cipher_alg->cra_blocksize;inst->alg.base.cra_alignmask = cipher_alg->cra_alignmask;inst->alg.base.cra_priority = cipher_alg->cra_priority;inst->alg.min_keysize = cipher_alg->cra_cipher.cia_min_keysize;inst->alg.max_keysize = cipher_alg->cra_cipher.cia_max_keysize;inst->alg.ivsize = cipher_alg->cra_blocksize;/* Use skcipher_ctx_simple by default, can be overridden */inst->alg.base.cra_ctxsize = sizeof(struct skcipher_ctx_simple);inst->alg.setkey = skcipher_setkey_simple;inst->alg.init = skcipher_init_tfm_simple;inst->alg.exit = skcipher_exit_tfm_simple;return inst;err_free_inst:skcipher_free_instance_simple(inst);return ERR_PTR(err);
} inst = kzalloc(sizeof(*inst) + sizeof(*spawn), GFP_KERNEL);
- 其中,*spawn的類型是crypto_cipher_spawn,參見代碼:crypto_cipher_spawn是在crypto_spawn的基礎上是進一步封裝
struct crypto_cipher_spawn {struct crypto_spawn base;
};- 回到參考鏈接中
- Linux加密框架中的主要數據結構(四)_家有一希的博客-CSDN博客
- head為0,表示算法模板實例前不預留空間
- spawn = skcipher_instance_ctx(inst)
- skcipher.h - include/crypto/internal/skcipher.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin

- algapi.h - include/crypto/algapi.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin?

- 通過上述兩個函數,實現了spawn和inst->_ctx 指向同一片區域,如圖所示

- ?? ?cipher_alg = crypto_spawn_cipher_alg(spawn);
- cipher.h - include/crypto/internal/cipher.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin?

- 也就是 spawn起到了一個銜接器的作用,銜接算法模板實例inst 和 基礎算法cipher_alg
- ?設置個性化算法屬性,繼承基礎算法的算法屬性 和? 設置算法通用屬性

- 參考鏈接里面中的 crypto_cbc_alloc函數接口好像不再使用了,目前與其相近是函數流程如下
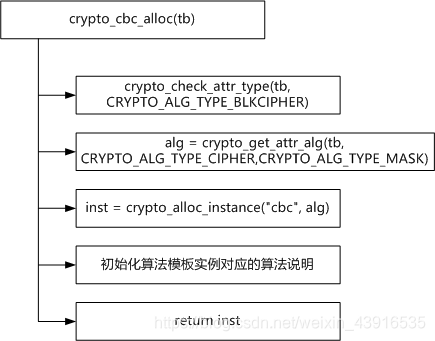
整體流程
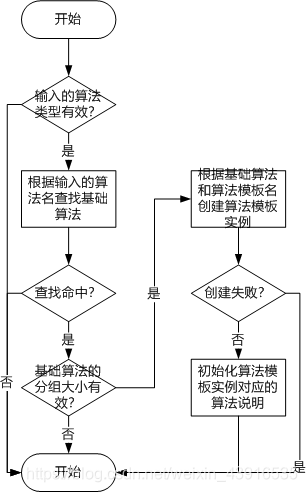 ?
?















)



