參考鏈接
- FFmpeg源代碼簡單分析:內存的分配和釋放(av_malloc()、av_free()等)_雷霄驊的博客-CSDN博客_av_malloc
內容介紹
- 內存操作的常見函數位于libavutil\mem.c中
- 本文記錄最常使用的幾個函數:
- av_malloc()
- av_realloc()
- av_mallocz()
- av_calloc()
- av_free()
- av_freep()
代碼
av_malloc()
void *av_malloc(size_t size)
{void *ptr = NULL;if (size > atomic_load_explicit(&max_alloc_size, memory_order_relaxed))return NULL;#if HAVE_POSIX_MEMALIGNif (size) //OS X on SDK 10.6 has a broken posix_memalign implementationif (posix_memalign(&ptr, ALIGN, size))ptr = NULL;
#elif HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOCptr = _aligned_malloc(size, ALIGN);
#elif HAVE_MEMALIGN
#ifndef __DJGPP__ptr = memalign(ALIGN, size);
#elseptr = memalign(size, ALIGN);
#endif/* Why 64?* Indeed, we should align it:* on 4 for 386* on 16 for 486* on 32 for 586, PPro - K6-III* on 64 for K7 (maybe for P3 too).* Because L1 and L2 caches are aligned on those values.* But I don't want to code such logic here!*//* Why 32?* For AVX ASM. SSE / NEON needs only 16.* Why not larger? Because I did not see a difference in benchmarks ...*//* benchmarks with P3* memalign(64) + 1 3071, 3051, 3032* memalign(64) + 2 3051, 3032, 3041* memalign(64) + 4 2911, 2896, 2915* memalign(64) + 8 2545, 2554, 2550* memalign(64) + 16 2543, 2572, 2563* memalign(64) + 32 2546, 2545, 2571* memalign(64) + 64 2570, 2533, 2558** BTW, malloc seems to do 8-byte alignment by default here.*/
#elseptr = malloc(size);
#endifif(!ptr && !size) {size = 1;ptr= av_malloc(1);}
#if CONFIG_MEMORY_POISONINGif (ptr)memset(ptr, FF_MEMORY_POISON, size);
#endifreturn ptr;
}
- 如果不考慮上述代碼中的一大堆宏定義
- av_malloc()的代碼可以簡化成如下形式
- 可以看出,此時的av_malloc()就是簡單的封裝了系統函數malloc(),并做了一些錯誤檢查工作
void *av_malloc(size_t size)
{void *ptr = NULL;/* let's disallow possibly ambiguous cases */if (size > (max_alloc_size - 32))return NULL;ptr = malloc(size);if(!ptr && !size) {size = 1;ptr= av_malloc(1);}return ptr;
}
av_realloc()
void *av_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
{void *ret;if (size > atomic_load_explicit(&max_alloc_size, memory_order_relaxed))return NULL;#if HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOCret = _aligned_realloc(ptr, size + !size, ALIGN);
#elseret = realloc(ptr, size + !size);
#endif
#if CONFIG_MEMORY_POISONINGif (ret && !ptr)memset(ret, FF_MEMORY_POISON, size);
#endifreturn ret;
}
- 默認情況下的代碼:
- 可以看出av_realloc()簡單封裝了系統的realloc()函數。
- C 庫函數 – realloc() | 菜鳥教程
void *av_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
{/* let's disallow possibly ambiguous cases */if (size > (max_alloc_size - 32))return NULL;return realloc(ptr, size + !size);
}
av_mallocz()
void *av_mallocz(size_t size)
{void *ptr = av_malloc(size);if (ptr)memset(ptr, 0, size);return ptr;
}
- av_mallocz()可以理解為av_malloc()+zeromemory
- av_mallocz()中調用了av_malloc()之后,又調用memset()將分配的內存設置為0
av_calloc()
void *av_calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size)
{size_t result;if (size_mult(nmemb, size, &result) < 0)return NULL;return av_mallocz(result);
}
static int size_mult(size_t a, size_t b, size_t *r)
{size_t t;#if (!defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(5,1)) || AV_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_mul_overflow)if (__builtin_mul_overflow(a, b, &t))return AVERROR(EINVAL);
#elset = a * b;/* Hack inspired from glibc: don't try the division if nelem and elsize* are both less than sqrt(SIZE_MAX). */if ((a | b) >= ((size_t)1 << (sizeof(size_t) * 4)) && a && t / a != b)return AVERROR(EINVAL);
#endif*r = t;return 0;
}
- av_calloc()則是簡單封裝了av_mallocz()?
- 從代碼中可以看出,它調用av_mallocz()分配了nmemb*size個字節的內存。
av_free()
void av_free(void *ptr)
{
#if HAVE_ALIGNED_MALLOC_aligned_free(ptr);
#elsefree(ptr);
#endif
}
- 可以看出av_free()簡單的封裝了free()?
av_freep()
void av_freep(void *arg)
{void *val;memcpy(&val, arg, sizeof(val));memcpy(arg, &(void *){ NULL }, sizeof(val));av_free(val);
}
- av_freep()簡單封裝了av_free()。并且在釋放內存之后將目標指針設置為NULL。
- C 庫函數 – memcpy() | 菜鳥教程?
補充知識
內存對齊
- 參考鏈接:計算機中的內存對齊與大小端 | MuYi's Blog
- 程序員通常認為內存就是一個字節數組,每次可以一個一個字節存取內存。例如在C語言中使用char *指代“一塊內存”,Java中使用byte[]指代一塊內存。如下所示。

- 但那實際上計算機處理器卻不是這樣認為的。處理器相對比較“懶惰”,它以塊為單位進行數據的讀取,塊的大小可以是2字節,4字節,8字節,16字節甚至32字節來存取內存。例如下圖顯示了以4字節為單位讀寫內存的處理器“看待”上述內存的方式。

- 上述的存取單位的大小稱之為內存存取粒度。
- 下面看一個實例,分別從地址0,和地址1讀取4個字節到寄存器。
- 從程序員的角度來看,讀取方式如下圖所示。
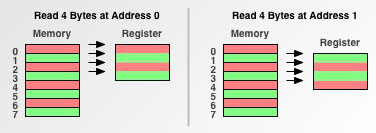

- 可以看出2字節存取粒度的處理器從地址0讀取4個字節一共讀取2次;從地址1讀取4個字節一共讀取了3次。
- 存儲的時候也是將2個字節作為數據塊的大小進行存儲
- 由于每次讀取的開銷是固定的,因此從地址1讀取4字節的效率有所下降。
- 4字節存取粒度的處理器的讀取方式如下圖所示。
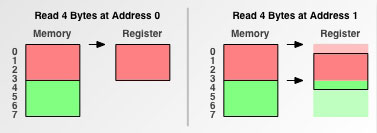
- 可以看出4字節存取粒度的處理器從地址0讀取4個字節一共讀取1次;從地址1讀取4個字節一共讀取了2次。從地址1讀取的開銷比從地址0讀取多了一倍。
- 由此可見內存不對齊對CPU的性能是有影響的。















)








KMP算法(求子串的位置)______字符串的匹配)