參考鏈接
- FFMPEG結構體分析:AVIOContext_雷霄驊的博客-CSDN博客_aviocontext
AVIOContext
- AVIOContext是FFMPEG管理輸入輸出數據的結構體
- 結構體的定義位于位于avio.h

關鍵的變量如下所示
- unsigned char *buffer:緩存開始位置
- int buffer_size:緩存大小(默認32768)
- unsigned char *buf_ptr:當前指針讀取到的位置
- unsigned char *buf_end:緩存結束的位置
- void *opaque:URLContext結構體?
- 在解碼的情況下,buffer用于存儲ffmpeg讀入的數據。
- 例如打開一個視頻文件的時候,先把數據從硬盤讀入buffer,然后在送給解碼器用于解碼。
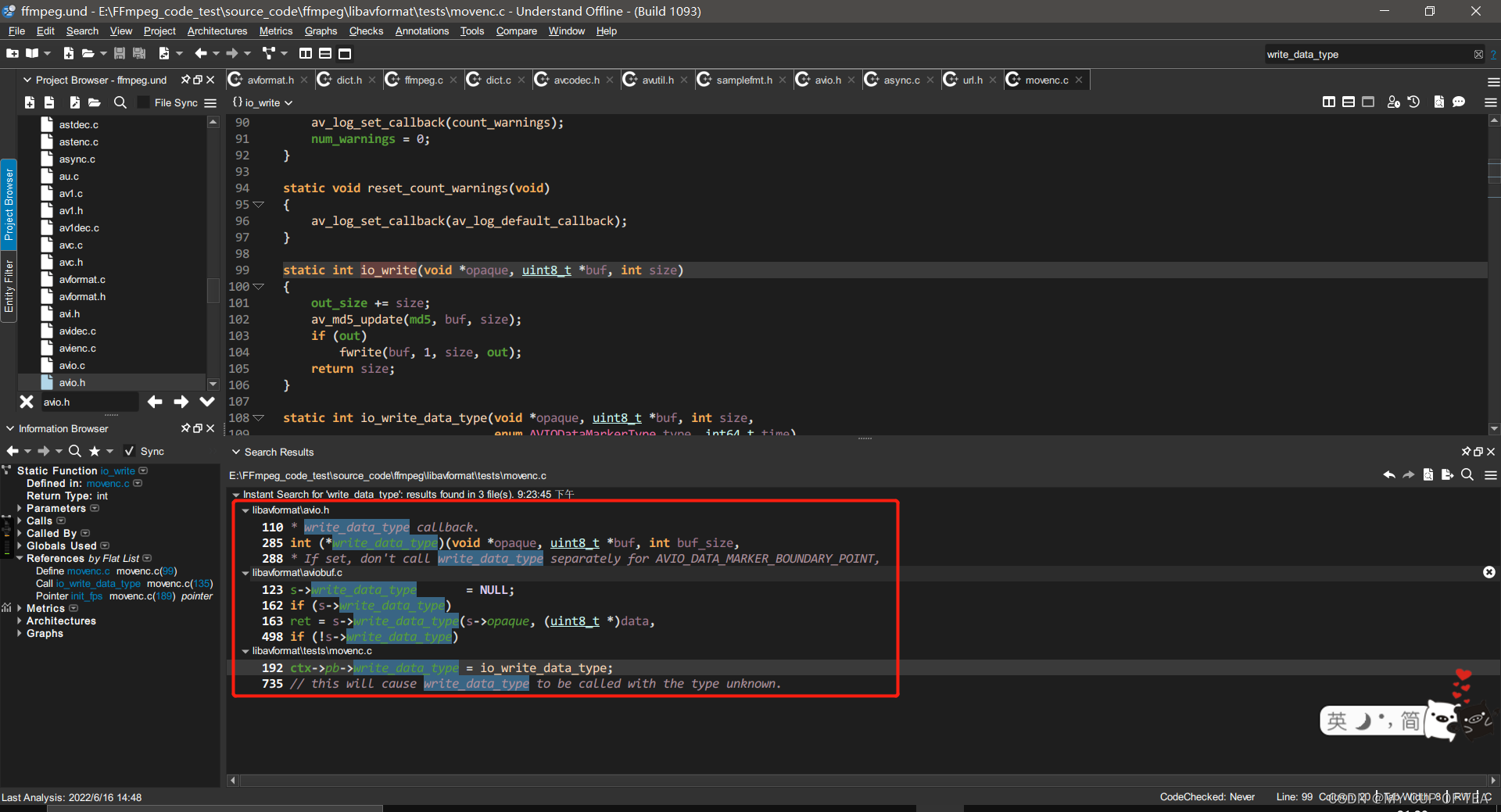
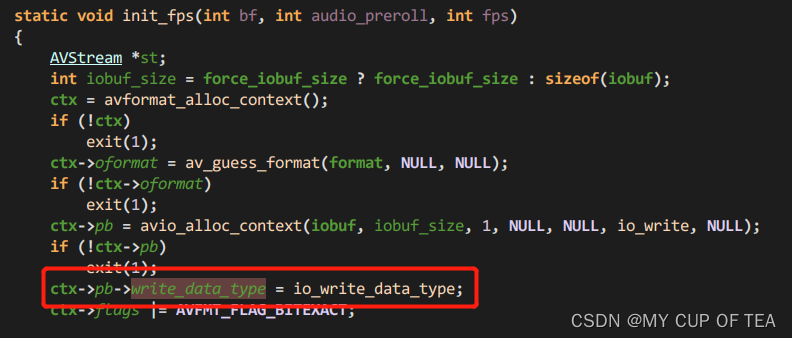
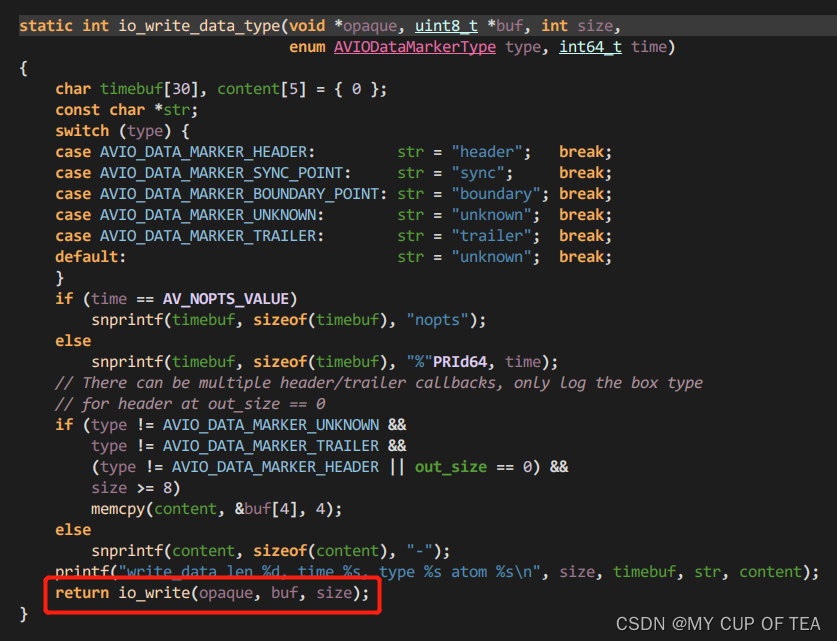
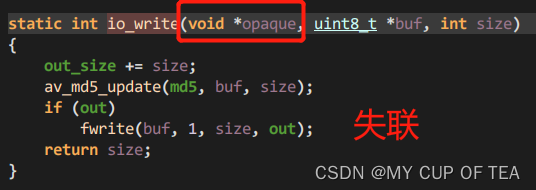
/*** A callback that is used instead of write_packet.*/int (*write_data_type)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size,enum AVIODataMarkerType type, int64_t time);- 其中opaque指向了URLContext。不是很理解這句話的含義
- 涉及到write_data_type的一共僅有三處
- 第一部分:函數的定義
- 第二部分:if判斷
- 第三部分:函數的調用?
?
- 注意,這個結構體并不在FFMPEG提供的頭文件中,而是在FFMPEG的源代碼中。修正:目前在url.h文件中
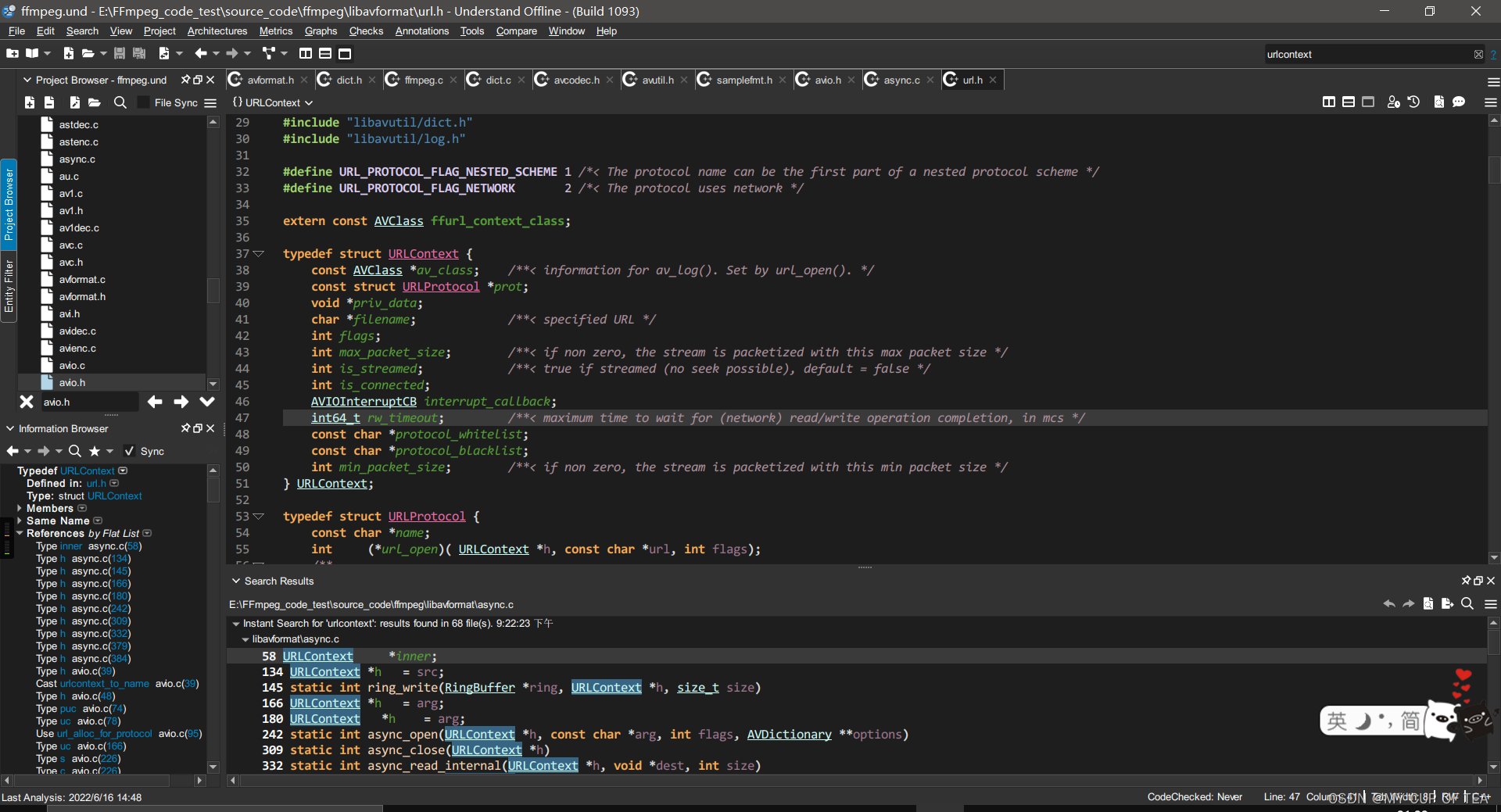
- URLContext結構體中還有一個結構體URLProtocol
- 注:每種協議(rtp,rtmp,file等)對應一個URLProtocol
typedef struct URLProtocol {const char *name;int (*url_open)( URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags);/*** This callback is to be used by protocols which open further nested* protocols. options are then to be passed to ffurl_open_whitelist()* or ffurl_connect() for those nested protocols.*/int (*url_open2)(URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);int (*url_accept)(URLContext *s, URLContext **c);int (*url_handshake)(URLContext *c);/*** Read data from the protocol.* If data is immediately available (even less than size), EOF is* reached or an error occurs (including EINTR), return immediately.* Otherwise:* In non-blocking mode, return AVERROR(EAGAIN) immediately.* In blocking mode, wait for data/EOF/error with a short timeout (0.1s),* and return AVERROR(EAGAIN) on timeout.* Checking interrupt_callback, looping on EINTR and EAGAIN and until* enough data has been read is left to the calling function; see* retry_transfer_wrapper in avio.c.*/int (*url_read)( URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size);int (*url_write)(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size);int64_t (*url_seek)( URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence);int (*url_close)(URLContext *h);int (*url_read_pause)(URLContext *h, int pause);int64_t (*url_read_seek)(URLContext *h, int stream_index,int64_t timestamp, int flags);int (*url_get_file_handle)(URLContext *h);int (*url_get_multi_file_handle)(URLContext *h, int **handles,int *numhandles);int (*url_get_short_seek)(URLContext *h);int (*url_shutdown)(URLContext *h, int flags);const AVClass *priv_data_class;int priv_data_size;int flags;int (*url_check)(URLContext *h, int mask);int (*url_open_dir)(URLContext *h);int (*url_read_dir)(URLContext *h, AVIODirEntry **next);int (*url_close_dir)(URLContext *h);int (*url_delete)(URLContext *h);int (*url_move)(URLContext *h_src, URLContext *h_dst);const char *default_whitelist;
} URLProtocol;
- 在這個結構體中,除了一些回調函數接口之外,有一個變量const char *name,該變量存儲了協議的名稱。
- 每一種輸入協議都對應這樣一個結構體。
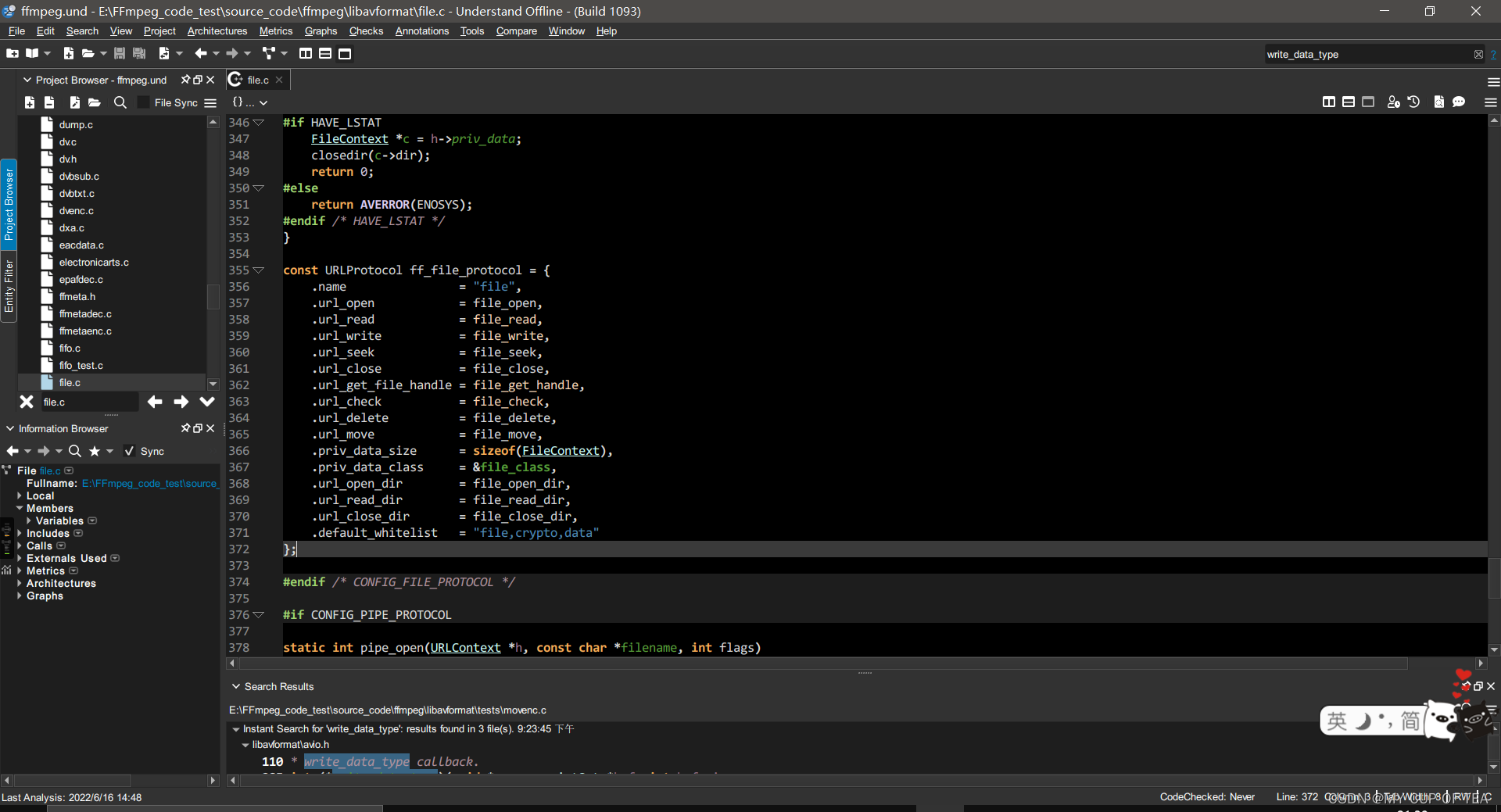
文件協議? 數據結構ff_file_protocol
- 位于file.c
- 函數指針 指向具體的執行函數
- 等號右邊的函數是完成具體讀寫功能的函數。可以看一下file協議的幾個函數(其實就是讀文件,寫文件這樣的操作)
const URLProtocol ff_file_protocol = {.name = "file",.url_open = file_open,.url_read = file_read,.url_write = file_write,.url_seek = file_seek,.url_close = file_close,.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,.url_check = file_check,.url_delete = file_delete,.url_move = file_move,.priv_data_size = sizeof(FileContext),.priv_data_class = &file_class,.url_open_dir = file_open_dir,.url_read_dir = file_read_dir,.url_close_dir = file_close_dir,.default_whitelist = "file,crypto,data"
};static int file_read(URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;int ret;size = FFMIN(size, c->blocksize);ret = read(c->fd, buf, size);if (ret == 0 && c->follow)return AVERROR(EAGAIN);if (ret == 0)return AVERROR_EOF;return (ret == -1) ? AVERROR(errno) : ret;
}static int file_write(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;int ret;size = FFMIN(size, c->blocksize);ret = write(c->fd, buf, size);return (ret == -1) ? AVERROR(errno) : ret;
}static int file_get_handle(URLContext *h)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;return c->fd;
}static int file_check(URLContext *h, int mask)
{int ret = 0;const char *filename = h->filename;av_strstart(filename, "file:", &filename);{
#if HAVE_ACCESS && defined(R_OK)if (access(filename, F_OK) < 0)return AVERROR(errno);if (mask&AVIO_FLAG_READ)if (access(filename, R_OK) >= 0)ret |= AVIO_FLAG_READ;if (mask&AVIO_FLAG_WRITE)if (access(filename, W_OK) >= 0)ret |= AVIO_FLAG_WRITE;
#elsestruct stat st;ret = stat(filename, &st);if (ret < 0)return AVERROR(errno);ret |= st.st_mode&S_IRUSR ? mask&AVIO_FLAG_READ : 0;ret |= st.st_mode&S_IWUSR ? mask&AVIO_FLAG_WRITE : 0;
#endif}return ret;
}#if CONFIG_FILE_PROTOCOLstatic int file_delete(URLContext *h)
{
#if HAVE_UNISTD_Hint ret;const char *filename = h->filename;av_strstart(filename, "file:", &filename);ret = rmdir(filename);if (ret < 0 && (errno == ENOTDIR
# ifdef _WIN32|| errno == EINVAL
# endif))ret = unlink(filename);if (ret < 0)return AVERROR(errno);return ret;
#elsereturn AVERROR(ENOSYS);
#endif /* HAVE_UNISTD_H */
}static int file_move(URLContext *h_src, URLContext *h_dst)
{const char *filename_src = h_src->filename;const char *filename_dst = h_dst->filename;av_strstart(filename_src, "file:", &filename_src);av_strstart(filename_dst, "file:", &filename_dst);if (rename(filename_src, filename_dst) < 0)return AVERROR(errno);return 0;
}static int file_open(URLContext *h, const char *filename, int flags)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;int access;int fd;struct stat st;av_strstart(filename, "file:", &filename);if (flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE && flags & AVIO_FLAG_READ) {access = O_CREAT | O_RDWR;if (c->trunc)access |= O_TRUNC;} else if (flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) {access = O_CREAT | O_WRONLY;if (c->trunc)access |= O_TRUNC;} else {access = O_RDONLY;}
#ifdef O_BINARYaccess |= O_BINARY;
#endiffd = avpriv_open(filename, access, 0666);if (fd == -1)return AVERROR(errno);c->fd = fd;h->is_streamed = !fstat(fd, &st) && S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode);/* Buffer writes more than the default 32k to improve throughput especially* with networked file systems */if (!h->is_streamed && flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE)h->min_packet_size = h->max_packet_size = 262144;if (c->seekable >= 0)h->is_streamed = !c->seekable;return 0;
}/* XXX: use llseek */
static int64_t file_seek(URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;int64_t ret;if (whence == AVSEEK_SIZE) {struct stat st;ret = fstat(c->fd, &st);return ret < 0 ? AVERROR(errno) : (S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode) ? 0 : st.st_size);}ret = lseek(c->fd, pos, whence);return ret < 0 ? AVERROR(errno) : ret;
}static int file_close(URLContext *h)
{FileContext *c = h->priv_data;int ret = close(c->fd);return (ret == -1) ? AVERROR(errno) : 0;
}static int file_open_dir(URLContext *h)
{
#if HAVE_LSTATFileContext *c = h->priv_data;c->dir = opendir(h->filename);if (!c->dir)return AVERROR(errno);return 0;
#elsereturn AVERROR(ENOSYS);
#endif /* HAVE_LSTAT */
}static int file_read_dir(URLContext *h, AVIODirEntry **next)
{
#if HAVE_LSTATFileContext *c = h->priv_data;struct dirent *dir;char *fullpath = NULL;*next = ff_alloc_dir_entry();if (!*next)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);do {errno = 0;dir = readdir(c->dir);if (!dir) {av_freep(next);return AVERROR(errno);}} while (!strcmp(dir->d_name, ".") || !strcmp(dir->d_name, ".."));fullpath = av_append_path_component(h->filename, dir->d_name);if (fullpath) {struct stat st;if (!lstat(fullpath, &st)) {if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_DIRECTORY;else if (S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_NAMED_PIPE;else if (S_ISCHR(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_CHARACTER_DEVICE;else if (S_ISBLK(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_BLOCK_DEVICE;else if (S_ISLNK(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_SYMBOLIC_LINK;else if (S_ISSOCK(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_SOCKET;else if (S_ISREG(st.st_mode))(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_FILE;else(*next)->type = AVIO_ENTRY_UNKNOWN;(*next)->group_id = st.st_gid;(*next)->user_id = st.st_uid;(*next)->size = st.st_size;(*next)->filemode = st.st_mode & 0777;(*next)->modification_timestamp = INT64_C(1000000) * st.st_mtime;(*next)->access_timestamp = INT64_C(1000000) * st.st_atime;(*next)->status_change_timestamp = INT64_C(1000000) * st.st_ctime;}av_free(fullpath);}(*next)->name = av_strdup(dir->d_name);return 0;
#elsereturn AVERROR(ENOSYS);
#endif /* HAVE_LSTAT */
}static int file_close_dir(URLContext *h)
{
#if HAVE_LSTATFileContext *c = h->priv_data;closedir(c->dir);return 0;
#elsereturn AVERROR(ENOSYS);
#endif /* HAVE_LSTAT */
}?
 ?
?
libRTMP
- 位于librtmp.c
RTMP_CLASS(rtmp)
const URLProtocol ff_librtmp_protocol = {.name = "rtmp",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmp_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};RTMP_CLASS(rtmpt)
const URLProtocol ff_librtmpt_protocol = {.name = "rtmpt",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmpt_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};RTMP_CLASS(rtmpe)
const URLProtocol ff_librtmpe_protocol = {.name = "rtmpe",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmpe_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};RTMP_CLASS(rtmpte)
const URLProtocol ff_librtmpte_protocol = {.name = "rtmpte",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmpte_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};RTMP_CLASS(rtmps)
const URLProtocol ff_librtmps_protocol = {.name = "rtmps",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmps_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};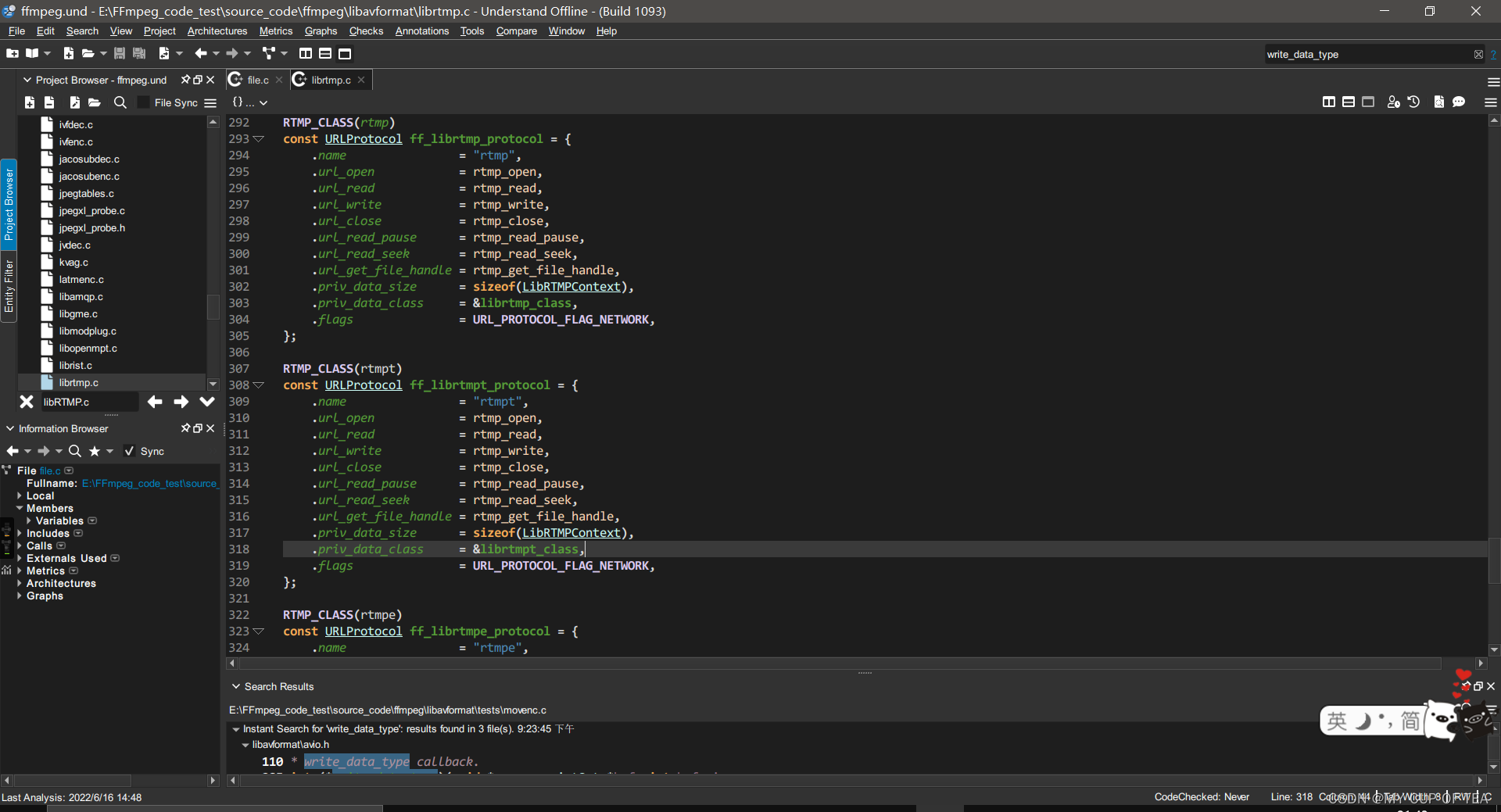 ?
?
?udp協議
- 位于udp.c
const URLProtocol ff_udp_protocol = {.name = "udp",.url_open = udp_open,.url_read = udp_read,.url_write = udp_write,.url_close = udp_close,.url_get_file_handle = udp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(UDPContext),.priv_data_class = &udp_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};const URLProtocol ff_udplite_protocol = {.name = "udplite",.url_open = udplite_open,.url_read = udp_read,.url_write = udp_write,.url_close = udp_close,.url_get_file_handle = udp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(UDPContext),.priv_data_class = &udplite_context_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};
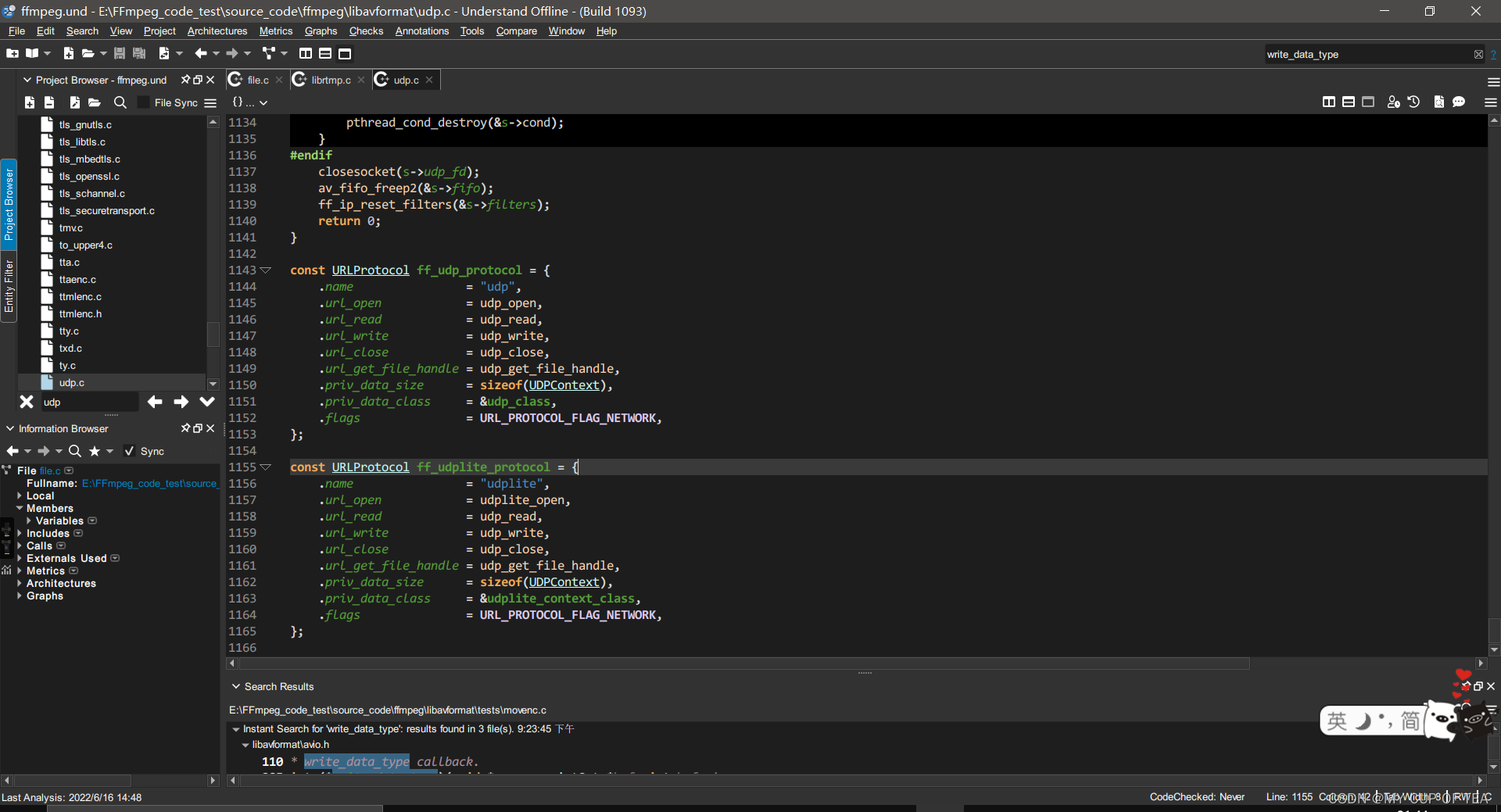 ?
?
?
代碼
/*** Bytestream IO Context. //字節流 IO 上下文* New public fields can be added with minor version bumps. //新的公共字段可以添加小版本顛簸* Removal, reordering and changes to existing public fields require * a major version bump. 移除、重新排序和更改現有公共字段需要一個主要版本的凹凸* sizeof(AVIOContext) must not be used outside libav*. //sizeof(AVIOContext) 不得在 libav* 之外使用** @note None of the function pointers in AVIOContext should be called* directly, they should only be set by the client application* when implementing custom I/O. Normally these are set to the* function pointers specified in avio_alloc_context()* AVIOContext 中的任何函數指針都不應直接調用,它們只能由客戶端應用程序* 在實現自定義 I/O 時設置。 通常這些設置為 avio_alloc_context() 中指定的函數指針*/
typedef struct AVIOContext {/*** A class for private options. //一個私人選項類** If this AVIOContext is created by avio_open2(), av_class is set and* passes the options down to protocols.* 如果此 AVIOContext 由 avio_open2() 創建,則設置 av_class 并將選項傳遞給協議** If this AVIOContext is manually allocated, then av_class may be set by* the caller.* 如果這個 AVIOContext 是手動分配的,那么 av_class 可能由調用者設置* * warning -- this field can be NULL, be sure to not pass this AVIOContext * to any av_opt_* functions in that case.* 警告——該字段可以為 NULL,在這種情況下,請確保不要將此 AVIOContext 傳遞給任何 av_opt_* 函數*/const AVClass *av_class;/** The following shows the relationship between buffer, buf_ptr,* buf_ptr_max, buf_end, buf_size, and pos, when reading and when writing* (since AVIOContext is used for both):************************************************************************************ READING************************************************************************************ | buffer_size |* |---------------------------------------|* | |** buffer buf_ptr buf_end* +---------------+-----------------------+* |/ / / / / / / /|/ / / / / / /| |* read buffer: |/ / consumed / | to be read /| |* |/ / / / / / / /|/ / / / / / /| |* +---------------+-----------------------+** pos* +-------------------------------------------+-----------------+* input file: | | |* +-------------------------------------------+-----------------+************************************************************************************* WRITING************************************************************************************ | buffer_size |* |--------------------------------------|* | |** buf_ptr_max* buffer (buf_ptr) buf_end* +-----------------------+--------------+* |/ / / / / / / / / / / /| |* write buffer: | / / to be flushed / / | |* |/ / / / / / / / / / / /| |* +-----------------------+--------------+* buf_ptr can be in this* due to a backward seek** pos* +-------------+----------------------------------------------+* output file: | | |* +-------------+----------------------------------------------+**/unsigned char *buffer; /**< Start of the buffer. */int buffer_size; /**< Maximum buffer size */unsigned char *buf_ptr; /**< Current position in the buffer */unsigned char *buf_end; /**< End of the data, may be less thanbuffer+buffer_size if the read function returnedless data than requested, e.g. for streams whereno more data has been received yet. */void *opaque; /**< A private pointer, passed to the read/write/seek/...functions. */int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size);int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size);int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence);int64_t pos; /**< position in the file of the current buffer */int eof_reached; /**< true if was unable to read due to error or eof */int error; /**< contains the error code or 0 if no error happened */int write_flag; /**< true if open for writing */int max_packet_size;int min_packet_size; /**< Try to buffer at least this amount of databefore flushing it. */unsigned long checksum;unsigned char *checksum_ptr;unsigned long (*update_checksum)(unsigned long checksum, const uint8_t *buf, unsigned int size);/*** Pause or resume playback for network streaming protocols - e.g. MMS.*/int (*read_pause)(void *opaque, int pause);/*** Seek to a given timestamp in stream with the specified stream_index.* Needed for some network streaming protocols which don't support seeking* to byte position.*/int64_t (*read_seek)(void *opaque, int stream_index,int64_t timestamp, int flags);/*** A combination of AVIO_SEEKABLE_ flags or 0 when the stream is not seekable.*/int seekable;/*** avio_read and avio_write should if possible be satisfied directly* instead of going through a buffer, and avio_seek will always* call the underlying seek function directly.*/int direct;/*** ',' separated list of allowed protocols.*/const char *protocol_whitelist;/*** ',' separated list of disallowed protocols.*/const char *protocol_blacklist;/*** A callback that is used instead of write_packet.*/int (*write_data_type)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size,enum AVIODataMarkerType type, int64_t time);/*** If set, don't call write_data_type separately for AVIO_DATA_MARKER_BOUNDARY_POINT,* but ignore them and treat them as AVIO_DATA_MARKER_UNKNOWN (to avoid needlessly* small chunks of data returned from the callback).*/int ignore_boundary_point;#if FF_API_AVIOCONTEXT_WRITTEN/*** @deprecated field utilized privately by libavformat. For a public* statistic of how many bytes were written out, see* AVIOContext::bytes_written.*/attribute_deprecatedint64_t written;
#endif/*** Maximum reached position before a backward seek in the write buffer,* used keeping track of already written data for a later flush.*/unsigned char *buf_ptr_max;/*** Read-only statistic of bytes read for this AVIOContext.*/int64_t bytes_read;/*** Read-only statistic of bytes written for this AVIOContext.*/int64_t bytes_written;
} AVIOContext;

)








KMP算法(求子串的位置)______字符串的匹配)




)

)
