文章目錄
- 目錄
- 第 21題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第22 題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第23 題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第24 題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- 非遞歸實現
- 遞歸實現
- python
- 第25題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第26 題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第27 題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第28題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第29題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
- 第30題:
- 解題思路:
- 代碼實現:
- c++
- python
目錄
第 21題:
從上往下打印出二叉樹的每個節點,同層節點從左至右打印。
解題思路:
其實這就是一個二叉樹層序遍歷的問題,我們可以有以下兩種方法來實現
- 使用輔助隊列完成對二叉樹的層序遍歷
- 使用數組輔助來完成對二叉樹的輔助遍歷
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:vector<int> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> printArray; //用于保存輸出的節點queue<TreeNode*> tempQueue; //輔助隊列if(root != NULL){tempQueue.push(root);}while(!tempQueue.empty()){ //只要隊列不空就可以數據if(tempQueue.front()->left != NULL){ //遍歷左子樹tempQueue.push(tempQueue.front()->left);}if(tempQueue.front()->right != NULL){ //遍歷右子樹tempQueue.push(tempQueue.front()->right);}printArray.push_back(tempQueue.front()->val); //將要打印的東西輸出tempQueue.pop();}return printArray; }
};
運行時間:3ms
占用內存:604k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:# 返回從上到下每個節點值列表,例:[1,2,3]def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root):# write code hereif not root:return []currentStack = [root] #用于保存雙親節點的列表res = []while currentStack:nextStack = [] #用于記錄當前雙親節點下的孩子節點for i in currentStack:if i.left: nextStack.append(i.left) #左孩子存在,則將左孩子保存下來if i.right: nextStack.append(i.right) #右孩子存在,則將右孩子保存下來res.append(i.val)currentStack = nextStack #更新雙親節點return res
運行時間:30ms
占用內存:5700k
第22 題:
輸入一個整數數組,判斷該數組是不是某二叉搜索樹的后序遍歷的結果。如果是則輸出Yes,否則輸出No。假設輸入的數組的任意兩個數字都互不相同。
解題思路:
BST的后序序列的合法序列是,對于一個序列S,最后一個元素是x (也就是根),如果去掉最后一個元素的序列為T,那么T滿足:T可以分成兩段,前一段(左子樹)小于x,后一段(右子樹)大于x,且這兩段(子樹)都是合法的后序序列。完美的遞歸定義 : ) 。
代碼實現:
c++
鏈接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/a861533d45854474ac791d90e447bafd
來源:牛客網public class Solution {public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {if(sequence.length == 0){return false;}if(sequence.length == 1){return true;}return judge(sequence,0,sequence.length-1);}//判斷是否為二叉搜索樹,采用分治思想public boolean judge(int[] a,int start,int end){if(start >= end){//當二叉樹的左子樹為空時,肯定是一個二叉搜索樹return true;}int i = start; //找到第一個比root節點大的元素的位置,便是右子樹的起始位置while(a[i] < a[end]){++i;}//判斷右子樹是否都比root節點大for(int j=i;j<end;j++){if(a[j] < a[end]){return false; //存在不大的情況則為false}}return judge(a,start,i-1) && judge(a,i,end-1); //沒看懂這部分}
};
運行時間:4ms
占用內存:480k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-第23 題:
輸入一顆二叉樹的跟節點和一個整數,打印出二叉樹中結點值的和為輸入整數的所有路徑。路徑定義為從樹的根結點開始往下一直到葉結點所經過的結點形成一條路徑。(注意: 在返回值的list中,數組長度大的數組靠前)
解題思路:
- 這其實是一道樹的深度優先遍歷的算法題,我們可以通過帶有記憶的深度優先算法來做。
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {vector<vector<int> > res; //用于保存最終的路徑結果if (root == NULL)return res;stack<TreeNode *> s; // 輔助深度優先遍歷二叉樹的棧s.push(root); int sum = 0; //當前和vector<int> curPath; //當前路徑TreeNode *cur = root; //當前節點TreeNode *last = NULL; //保存上一個節點while (!s.empty()){if (cur == NULL){TreeNode *temp = s.top();if (temp->right != NULL && temp->right != last){cur = temp->right; //轉向未遍歷過的右子樹}else{last = temp; //保存上一個已遍歷的節點s.pop();curPath.pop_back(); //從當前路徑刪除sum -= temp->val;} }else{s.push(cur);sum += cur->val;curPath.push_back(cur->val);if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL && sum == expectNumber){res.push_back(curPath); //保存正確的路徑}cur = cur->left; //先序遍歷,左子樹先于右子樹}}return res;}
};
運行時間:3ms
占用內存:376k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-第24 題:
輸入一個復雜鏈表(每個節點中有節點值,以及兩個指針,一個指向下一個節點,另一個特殊指針指向任意一個節點),返回結果為復制后復雜鏈表的head。(注意,輸出結果中請不要返回參數中的節點引用,否則判題程序會直接返回空)
解題思路:
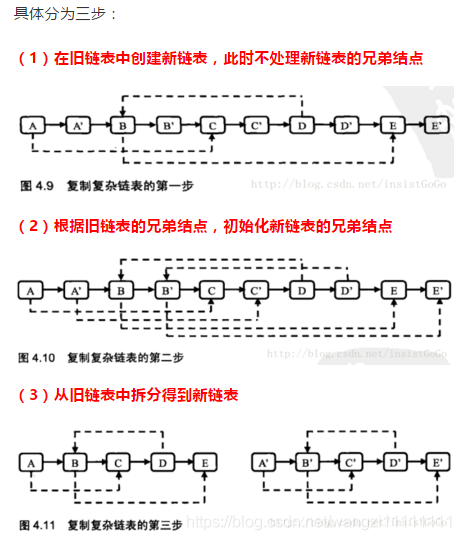
代碼實現:
c++
非遞歸實現
class Solution {
public://復制原始鏈表的任一節點N并創建新節點N',再把N'鏈接到N的后邊void CloneNodes(RandomListNode* pHead){RandomListNode* pNode=pHead;while(pNode!=NULL){RandomListNode* pCloned=new RandomListNode(0);pCloned->label=pNode->label;pCloned->next=pNode->next;pCloned->random=NULL;pNode->next=pCloned;pNode=pCloned->next;}}//如果原始鏈表上的節點N的random指向S,則對應的復制節點N'的random指向S的下一個節點S'void ConnectRandomNodes(RandomListNode* pHead){RandomListNode* pNode=pHead;while(pNode!=NULL){RandomListNode* pCloned=pNode->next;if(pNode->random!=NULL)pCloned->random=pNode->random->next;pNode=pCloned->next;}}//把得到的鏈表拆成兩個鏈表,奇數位置上的結點組成原始鏈表,偶數位置上的結點組成復制出來的鏈表RandomListNode* ReConnectNodes(RandomListNode* pHead){RandomListNode* pNode=pHead;RandomListNode* pClonedHead=NULL;RandomListNode* pClonedNode=NULL;//初始化if(pNode!=NULL){pClonedHead=pClonedNode=pNode->next;pNode->next=pClonedNode->next;pNode=pNode->next;}//循環while(pNode!=NULL){pClonedNode->next=pNode->next;pClonedNode=pClonedNode->next;pNode->next=pClonedNode->next;pNode=pNode->next;}return pClonedHead;}//三步合一RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead){CloneNodes(pHead);ConnectRandomNodes(pHead);return ReConnectNodes(pHead);}
};
運行時間:4ms
占用內存:484k
遞歸實現
鏈接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/f836b2c43afc4b35ad6adc41ec941dba
來源:牛客網/*遞歸思想:把大問題轉化若干子問題此題轉化為一個頭結點和除去頭結點剩余部分,剩余部分操作和原問題一致
*/
class Solution {
public:RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead){if(pHead==NULL)return NULL;//開辟一個新節點RandomListNode* pClonedHead=new RandomListNode(pHead->label);pClonedHead->next = pHead->next;pClonedHead->random = pHead->random;//遞歸其他節點pClonedHead->next=Clone(pHead->next);return pClonedHead;}
};
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-第25題:
輸入一棵二叉搜索樹,將該二叉搜索樹轉換成一個排序的雙向鏈表。要求不能創建任何新的結點,只能調整樹中結點指針的指向。
解題思路:
- 初步的想法:使用一個隊列輔助進行中序遍歷,然后讓節點出隊的時候進行節點的調整;具體的做法是:使用隊列保存該二叉搜索樹的中序遍歷結果,然后在將隊列中的節點一個一個進行出隊,出隊的同時將節點的指針進行調整,使得左節點指向后繼,右節點指向前驅。
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree){if(pRootOfTree == nullptr) return nullptr;TreeNode* pre = nullptr;convertHelper(pRootOfTree, pre);TreeNode* res = pRootOfTree;while(res ->left)res = res ->left;return res;}//中序遍歷即可。只需要記錄一個pre指針即可。void convertHelper(TreeNode* cur, TreeNode*& pre){if(cur == nullptr) return;convertHelper(cur ->left, pre);cur ->left = pre;if(pre) pre ->right = cur;pre = cur;convertHelper(cur ->right, pre); }
};
運行時間:3ms
占用內存:472k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:def Convert(self, pRootOfTree):# write code hereif not pRootOfTree:returnself.arr = []self.midTraversal(pRootOfTree)for i,v in enumerate(self.arr[:-1]):v.right = self.arr[i + 1]self.arr[i + 1].left = vreturn self.arr[0]def midTraversal(self, root):if not root: returnself.midTraversal(root.left)self.arr.append(root)self.midTraversal(root.right)
第26 題:
輸入一個字符串,按字典序打印出該字符串中字符的所有排列。例如輸入字符串abc,則打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出來的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
解題思路:
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:vector<string> Permutation(string str){vector<string> result;if(str.empty()) return result;Permutation(str,result,0);// 此時得到的result中排列并不是字典順序,可以單獨再排下序sort(result.begin(),result.end());return result;}void Permutation(string str,vector<string> &result,int begin){if(begin == str.size()-1) // 遞歸結束條件:索引已經指向str最后一個元素時{if(find(result.begin(),result.end(),str) == result.end()){// 如果result中不存在str,才添加;避免aa和aa重復添加的情況result.push_back(str);}}else{// 第一次循環i與begin相等,相當于第一個位置自身交換,關鍵在于之后的循環,// 之后i != begin,則會交換兩個不同位置上的字符,直到begin==str.size()-1,進行輸出;for(int i=begin;i<str.size();++i){swap(str[i],str[begin]);Permutation(str,result,begin+1);swap(str[i],str[begin]); // 復位,用以恢復之前字符串順序,達到第一位依次跟其他位交換的目的}}}void swap(char &fir,char &sec){char temp = fir;fir = sec;sec = temp;}
};
運行時間:5ms
占用內存:612k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-第27 題:
數組中有一個數字出現的次數超過數組長度的一半,請找出這個數字。例如輸入一個長度為9的數組{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于數字2在數組中出現了5次,超過數組長度的一半,因此輸出2。如果不存在則輸出0。
解題思路:
- 初步的想法:構建一個map映射表,key為數組中元素的值,value為出現的次數,運行的時間復雜度為O(N);
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) {if(numbers.size()<=0){return -1;}map<int,int> tempDataDict;for(int i = 0 ;i < numbers.size(); i++){if (tempDataDict.find(numbers[i]) == tempDataDict.end()){tempDataDict[numbers[i]] = 1;}else{tempDataDict[numbers[i]] += 1;}}for (map<int, int>::iterator iter = tempDataDict.begin(); iter != tempDataDict.end(); ++iter){if(iter->second > numbers.size() * 0.5){return iter->first;}}return 0; }
};
運行時間:4ms
占用內存:480k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:def MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(self, numbers):# write code heretempDict = {}for data in numbers:if data not in tempDict.keys():tempDict[data] = 1else:tempDict[data] += 1for key , value in tempDict.items():if value > len(numbers)/2:return keyreturn 0
運行時間:28ms
占用內存:5852k
第28題:
輸入n個整數,找出其中最小的K個數。例如輸入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8這8個數字,則最小的4個數字是1,2,3,4,。
解題思路:
- 先對這n個整數進行從小到大排序,然后取前K個數字就行。
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {vector<int> resultArray;if(input.size() < k){return resultArray;} sort(input.begin(),input.end());resultArray.assign(input.begin(), input.begin()+k);return resultArray; }
};
運行時間:5ms
占用內存:460k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:def GetLeastNumbers_Solution(self, tinput, k):# write code hereif len(tinput) < k:return []tinput.sort()return tinput[:k]
運行時間:20ms
占用內存:5856k
第29題:
HZ偶爾會拿些專業問題來忽悠那些非計算機專業的同學。今天測試組開完會后,他又發話了:在古老的一維模式識別中,常常需要計算連續子向量的最大和,當向量全為正數的時候,問題很好解決。但是,如果向量中包含負數,是否應該包含某個負數,并期望旁邊的正數會彌補它呢?例如:{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},連續子向量的最大和為8(從第0個開始,到第3個為止)。給一個數組,返回它的最大連續子序列的和,你會不會被他忽悠住?(子向量的長度至少是1)
解題思路:
使用動態規劃
F(i):以array[i]為末尾元素的子數組的和的最大值,子數組的元素的相對位置不變
F(i)=max(F(i-1)+array[i] , array[i])
res:所有子數組的和的最大值
res=max(res,F(i))
如數組[6, -3, -2, 7, -15, 1, 2, 2]
初始狀態:
F(0)=6
res=6
i=1:
F(1)=max(F(0)-3,-3)=max(6-3,3)=3
res=max(F(1),res)=max(3,6)=6
i=2:
F(2)=max(F(1)-2,-2)=max(3-2,-2)=1
res=max(F(2),res)=max(1,6)=6
i=3:
F(3)=max(F(2)+7,7)=max(1+7,7)=8
res=max(F(2),res)=max(8,6)=8
i=4:
F(4)=max(F(3)-15,-15)=max(8-15,-15)=-7
res=max(F(4),res)=max(-7,8)=8
以此類推
最終res的值為8
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public://找最大值函數int fMax(int a , int b){return a>b?a:b;}//找最大子序列的和int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector<int> array) {int res = array[0]; //記錄當前所有子數組的和的最大值int max=array[0]; //包含array[i]的連續數組最大值for (int i = 1; i < array.size(); i++) {max=fMax(max+array[i], array[i]); res=fMax(max, res);}return res;}
};
運行時間:3ms
占用內存:472k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:def fMax(self,a , b ):if a>b:return aelse:return bdef FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(self, array):# write code hereres = array[0]tempMaxValue = array[0]for i in range(1,len(array)):tempMaxValue = self.fMax(tempMaxValue + array[i] , array[i])res = self.fMax(tempMaxValue , res)return res
運行時間:29ms
占用內存:5664k
第30題:
求出113的整數中1出現的次數,并算出1001300的整數中1出現的次數?為此他特別數了一下1~13中包含1的數字有1、10、11、12、13因此共出現6次,但是對于后面問題他就沒轍了。ACMer希望你們幫幫他,并把問題更加普遍化,可以很快的求出任意非負整數區間中1出現的次數(從1 到 n 中1出現的次數)。
解題思路:
- 初步思想:對數字進行遍歷,然后將數字轉換為字符數組類型,然后統計字符數組中1的個數即可,時間復雜度0(n*m),使用Python非常容易實現。
- 參考:
注解:參考一位牛友提到的leetcode的鏈接網址(包括求1~n的所有整數中2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9出現的所有次數)
通過使用一個 位置乘子m 遍歷數字的位置, m 分別為1,10,100,1000…etc.(m<=n)
對于每個位置來說,把10進制數分成兩個部分,比如說 當m=100的時候, 把十進制數 n=3141592 分成 a=31415 和 b=92 ,以此來分析百位數為1時所有數的個數和。m=100時,百位數的前綴為3141,當百位數大于1時,為3142100,因為當百位數大于1時,前綴可以為0,即百位數可以從100到199,共100個數;當百位數不大于1時,為3141100;如何判斷百位數是否大于1?假設百位數為x,若(x+8)/10等于1,則大于1,若(x+8)/10等于0,則小于1。因此前綴可用(n/m + 8)/10 m來計算(若計算2的個數,可以改為(n/m + 7)/10m,若計算3的個數,改為(n/m + 6)/10*m,…以此類推)。
再例如m=1000時,n分為a=3141和 b=592;千位數的前綴為314,千位數不大于1,故前綴計算為3141000;因為千位數為1,再加b+1(0到592)。即千位數為1的所有書的個數和為3141000+592+1;公式(n/m + 8)/10*m + b +1。
注意:只有n的第m位為1時需要計算后綴,后綴計算為 (n/m%10==1)*(b+1),
即(n/m%101)判斷第m位是否為1,若為1,則加上(b+1),若不為1,則只計算前綴。(若計算2的個數,可以改為(n/m%102)(b+1),若計算3的個數,可以改為(n/m%10==3)(b+1)…以此類推)
代碼實現:
c++
class Solution {
public:int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n){int ones = 0;for (long long m = 1; m <= n; m *= 10) {int a = n/m, b = n%m;ones += (a + 8) / 10 * m + (a % 10 == 1) * (b + 1);}return ones;}
};
運行時間:3ms
占用內存:488k
python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:def NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(self, n):# write code hereif n == 0:return 0count = 0for i in range(n+1):tempList = list(str(i))for j in tempList:if j == "1":count += 1return count
運行時間:52ms
占用內存:5856k

--c++,Python版本)

--c++,Python版本)


--c++,Python版本)

--c++,Python版本)

)
)

)
)

)
)
-touch,mkdir,rm,mv,cp,ls,cd,cat)
)