文章目錄
- 一、實驗目的:
- 二、實驗要求
- 三、實驗內容
- 1、編寫一段C語言程序使其完成:父進程創建兩個子進程,每個進程都在屏幕上顯示自己的進程ID號。
- 2、上機調試下面的程序,觀察運行結果,分析原因。
- 3、利用兩個管道進行雙向通信,實現父子進程協作把整數x從1加到10。
- 4、利用消息隊列實現父子進程的通信。父進程創建消息隊列,并向消息隊列發送消息;子進程接受消息;父進程等待子進程接收消息后刪除消息隊列。
一、實驗目的:
1、學會用系統調用和庫函數進行編程
2、加深對進程概念的理解,明確進程和程序的區別。
3、進一步認識并發執行的實質。
4、分析進程競爭資源現象,學習解決進程互斥的方法。
5、了解Linux系統中進程通信的基本原理。
二、實驗要求
1、用fork( )創建進程,觀察進程的并發執行
2、使用管道、消息隊列機制進行進程間通信
三、實驗內容
1、編寫一段C語言程序使其完成:父進程創建兩個子進程,每個進程都在屏幕上顯示自己的進程ID號。
運行結果示例:
# ./forktest
this is child1:16602
this is child2:16603
this is parent:16601


2、上機調試下面的程序,觀察運行結果,分析原因。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int glob=3;
int main()
{pid_t pid;int loc=3;printf("befor fork():glob=%d,loc=%d\n", glob, loc);if ((pid=fork()) < 0){printf("fork() error\n");exit(0);}else if (pid == 0){glob++;loc--;printf("child:glob=%d, loc=%d\n", glob, loc);else{printf("parent:glob=%d, loc=%d\n", glob, loc);exit(0);}return 0;
}


fork()后會有兩個并發進程執行,子進程賦值了父進程的數據段,包括全局變量。父進程執行進入pid>0的情況,子進程進入pid==0的情況,分別做glob和loc的運算以及輸出。
3、利用兩個管道進行雙向通信,實現父子進程協作把整數x從1加到10。
運行結果示例:
# ./pipetest
child 5938 read: 1
parent 5937 read: 2
child 5938 read: 3
parent 5937 read: 4
child 5938 read: 5
parent 5937 read: 6
child 5938 read: 7
parent 5937 read: 8
child 5938 read: 9
parent 5937 read: 10
·說明:5938和5937分別是子進程和父進程的pid


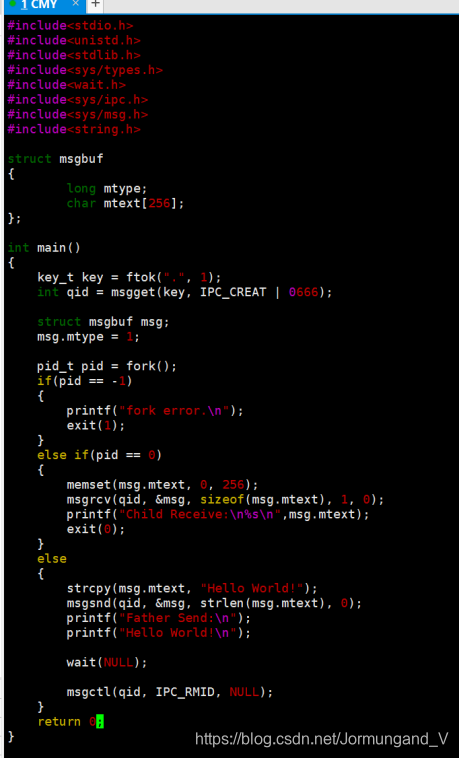
4、利用消息隊列實現父子進程的通信。父進程創建消息隊列,并向消息隊列發送消息;子進程接受消息;父進程等待子進程接收消息后刪除消息隊列。
運行結果示例:
# ./msgtest
Parent:Send to the message queue successfully!
The message sent is :This is the input!
Child:Receiving from the message queue:This is the input!

)

)

)

)

)
【fork函數、pipe函數、write/read操作、wait函數】)
)
)
)
)
、where()、cumsum()、argmax()的用法詳解】)
)

)

方法)