文章目錄
- 嫌啰嗦直接看代碼
- Q2 Image Captioning with Vanilla RNNs
- 一個給的工具代碼里的bug
- 問題展示
- 問題解決思路
- 解決辦法
- rnn_step_forward
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- rnn_step_backward
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- rnn_forward
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- rnn_backward
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- word_embedding_forward
- word embedding 技術解釋
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
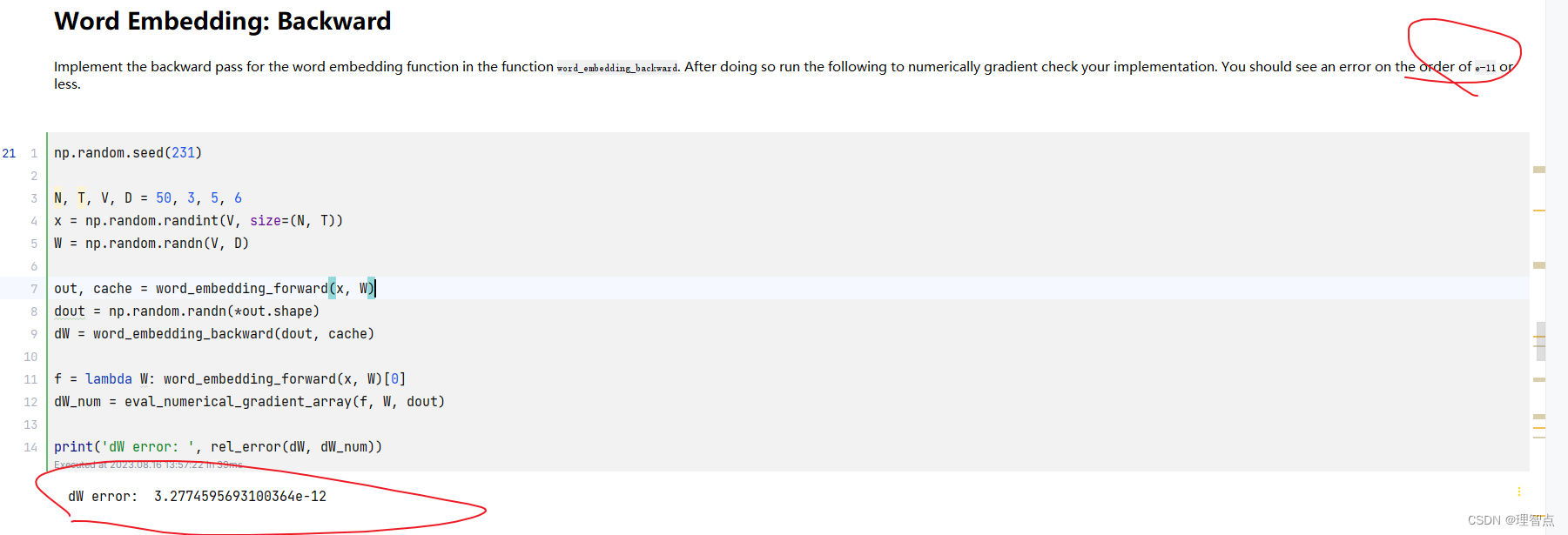
- word_embedding_backward
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- CaptioningRNN .loss
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- CaptioningRNN.sample
- 題面
- 解析
- 代碼
- 輸出
- 結語
嫌啰嗦直接看代碼
Q2 Image Captioning with Vanilla RNNs
一個給的工具代碼里的bug
image_from_url 里的報錯
[WinError 32] 另一個程序正在使用此文件,進程無法訪問。: 'C:\\Users\\Leezed\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\tmp7r3fjusu'
問題展示
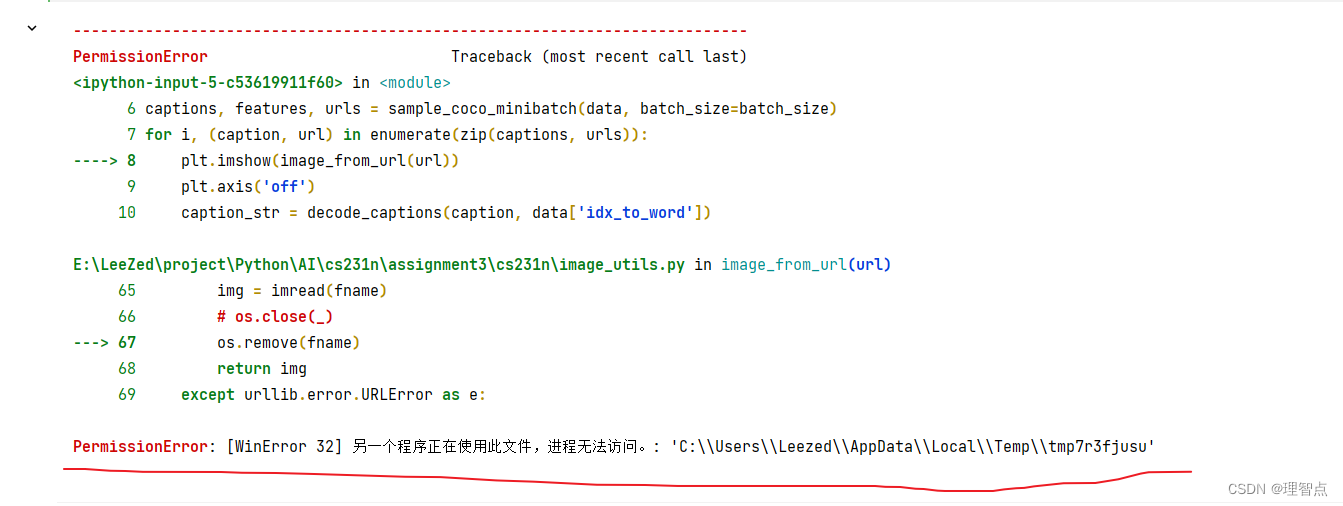
我在運行這段代碼的時候就報錯了 另一個進程正在使用此文件,文件無法訪問
問題解決思路
- 我一開始以為是img = imread(fname) 里的問題導致文件還在被占用,所以無法釋放文件的所有權,導致os.remove(fname)無法刪除。 就是我以為img = imread(fname) 是另開了一個線程去讀取圖片,然后直接運行了os.remove,但是圖片還沒有讀取完,導致占用沒有被釋放,所以刪除失敗
- 所以我一開始加了延時函數,time.sleep(5),但是還是同樣的問題,正常情況下一張圖片5秒肯定能讀完了,我不死心再檢查了一下,我直接吧img = imread(fname) 改成了 img =None ,結果還是報了同樣的錯,我就知道肯定不是它的問題了
- 我后來甚至開始懷疑是ff沒有close的問題了,但是with as 語句會自動關閉ff,這就很奇怪了
- 最后我一步步排查覺得是tempfile.mkstemp的問題
- 查閱相關文檔,這個函數返回的是兩個參數,一個是fd,一個是fname,fd是文件描述符,fname是指生成的文件的絕對路徑。
那么文件描述符是啥呢
內核(kernel)利用文件描述符(file descriptor)來訪問文件。文件描述符是非負整數。打開現存文件或新建文件時,內核會返回一個文件描述符。讀寫文件也需要使用文件描述符來指定待讀寫的文件。
文件描述符在同一進程下與文件是對應的,一個描述符只指向一個文件,但是一個文件可以被多個文件描述符關聯。
同一進程下,文件描述符是不可重復的。但是不同進程可以有一樣的文件描述符。它們也可以指向不同的文件。
因此如果直接使用os.remove(fname)刪除文件的話,文件描述符還在我們的內存里,而文件描述符還在內存里說明文件還被占用著,所以無法刪除
那我們應該怎么刪除臨時文件呢
首先需要使用os.close(fd) 方法用于關閉指定的文件描述符 fd,
然后再使用os.remove(fname)刪除臨時文件。
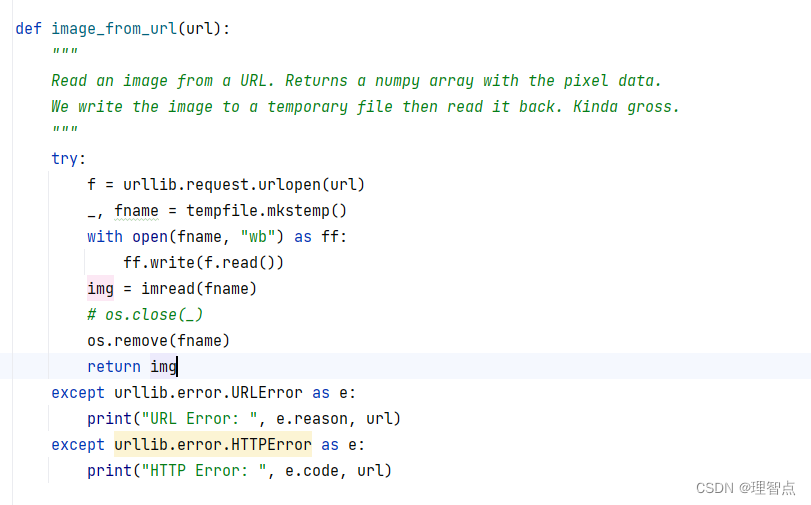
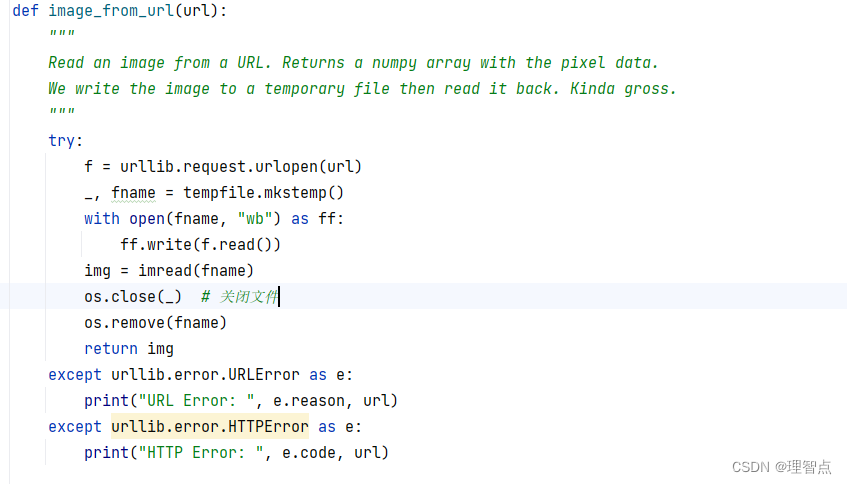
解決辦法
在os.remove(fname)之前加一句代碼 os.close(_)就好了,如下圖所示
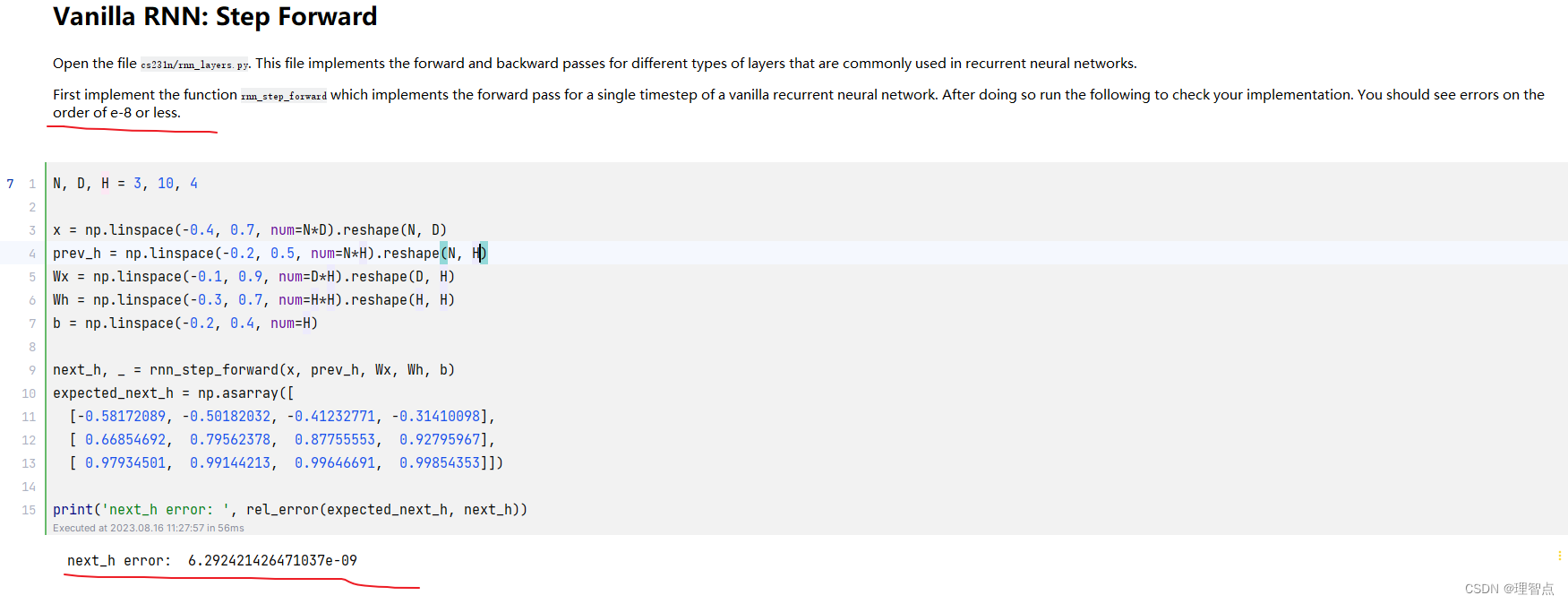
rnn_step_forward
題面
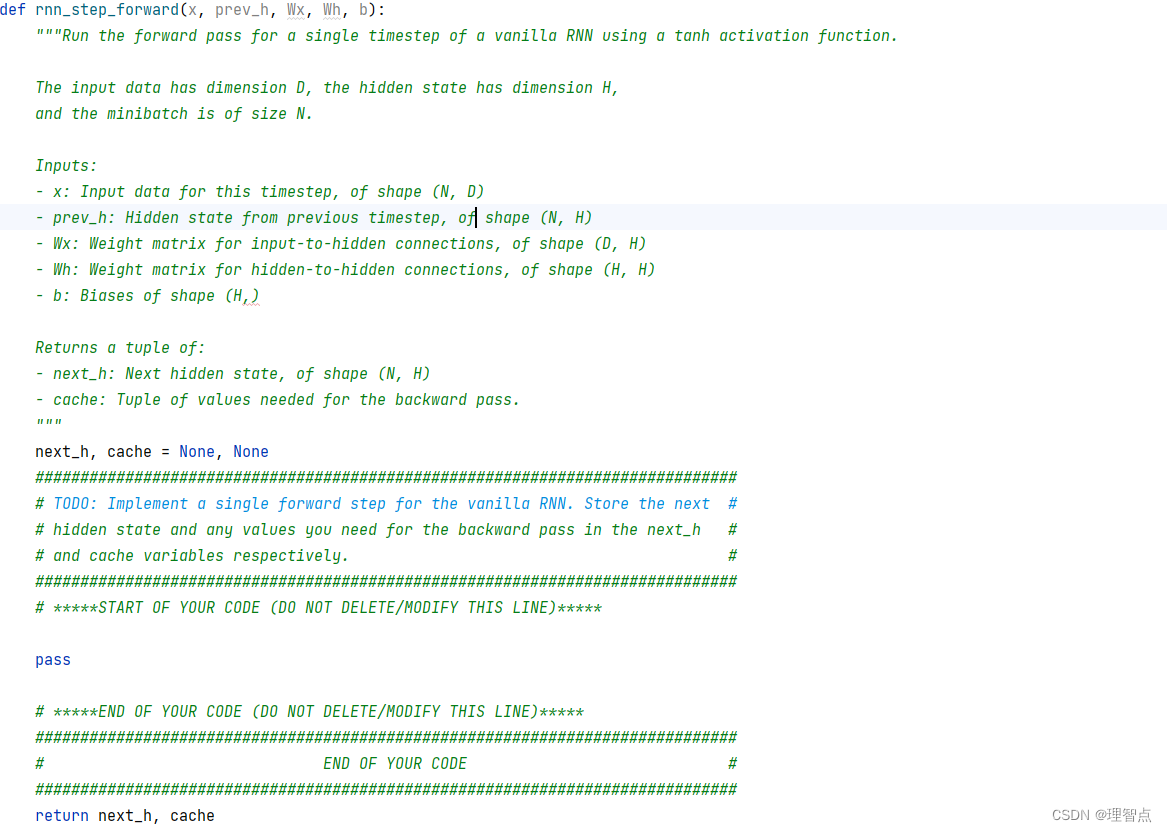
讓我們完成循環神經網絡的前向一步
解析
看課吧,我覺得課程里講的很詳細了,或者看代碼注釋
代碼
def rnn_step_forward(x, prev_h, Wx, Wh, b):"""Run the forward pass for a single timestep of a vanilla RNN using a tanh activation function.The input data has dimension D, the hidden state has dimension H,and the minibatch is of size N.Inputs:- x: Input data for this timestep, of shape (N, D)- prev_h: Hidden state from previous timestep, of shape (N, H)- Wx: Weight matrix for input-to-hidden connections, of shape (D, H)- Wh: Weight matrix for hidden-to-hidden connections, of shape (H, H)- b: Biases of shape (H,)Returns a tuple of:- next_h: Next hidden state, of shape (N, H)- cache: Tuple of values needed for the backward pass."""next_h, cache = None, None############################################################################### TODO: Implement a single forward step for the vanilla RNN. Store the next ## hidden state and any values you need for the backward pass in the next_h ## and cache variables respectively. ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****next_h = x @ Wx + prev_h @ Wh + bnext_h = np.tanh(next_h)cache = (x, prev_h, Wx, Wh, b, next_h)# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return next_h, cache
輸出
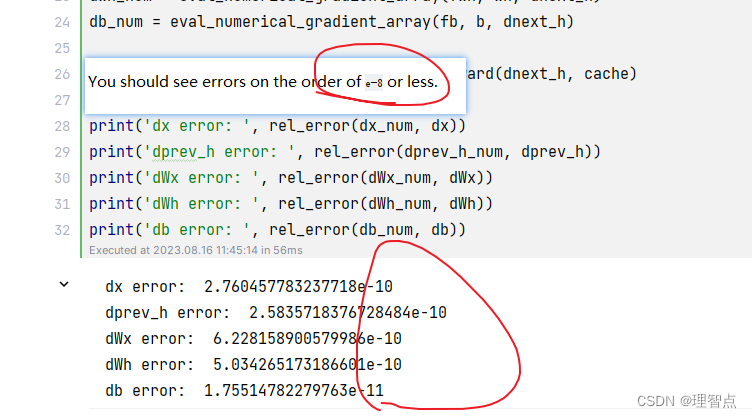
rnn_step_backward
題面
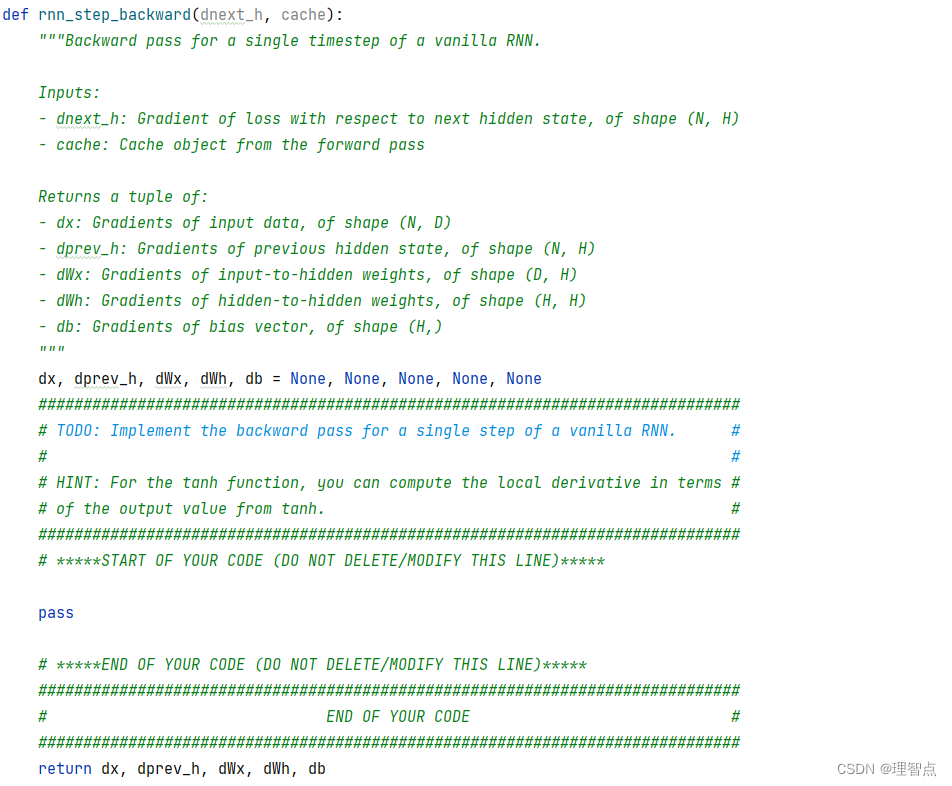
讓我們完成循環神經網絡的后向一步
解析
不贅述了,看代碼吧
tanh函數求導公式可以看下面這個連接的文章
激活函數tanh(x)求導
代碼
def rnn_step_backward(dnext_h, cache):"""Backward pass for a single timestep of a vanilla RNN.Inputs:- dnext_h: Gradient of loss with respect to next hidden state, of shape (N, H)- cache: Cache object from the forward passReturns a tuple of:- dx: Gradients of input data, of shape (N, D)- dprev_h: Gradients of previous hidden state, of shape (N, H)- dWx: Gradients of input-to-hidden weights, of shape (D, H)- dWh: Gradients of hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (H, H)- db: Gradients of bias vector, of shape (H,)"""dx, dprev_h, dWx, dWh, db = None, None, None, None, None############################################################################### TODO: Implement the backward pass for a single step of a vanilla RNN. ## ## HINT: For the tanh function, you can compute the local derivative in terms ## of the output value from tanh. ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****x, prev_h, Wx, Wh, b, next_h = cache# 求導 tanh(x) = (1 - tanh(x)^2) * dxdnext_h = dnext_h * (1 - next_h ** 2)dx = dnext_h @ Wx.Tdprev_h = dnext_h @ Wh.TdWx = x.T @ dnext_hdWh = prev_h.T @ dnext_hdb = np.sum(dnext_h, axis=0)# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return dx, dprev_h, dWx, dWh, db
輸出
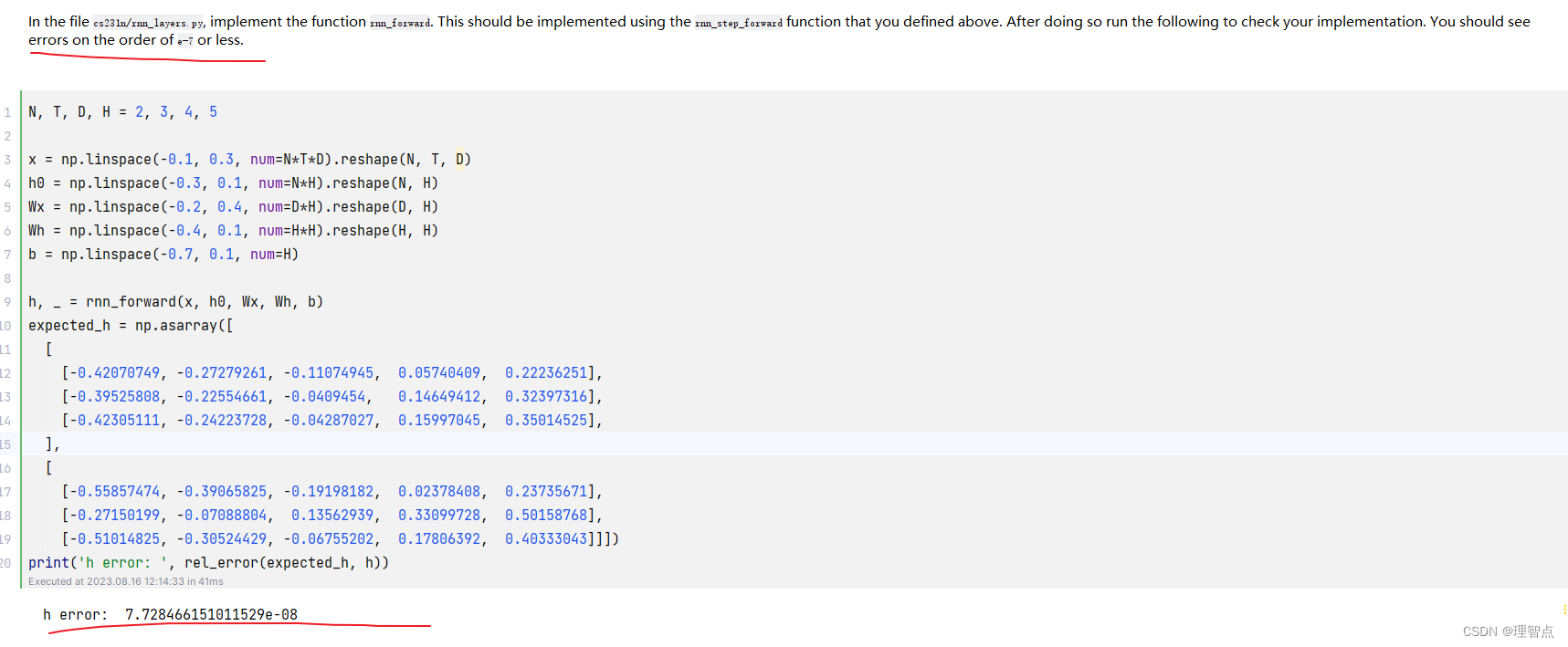
rnn_forward
題面
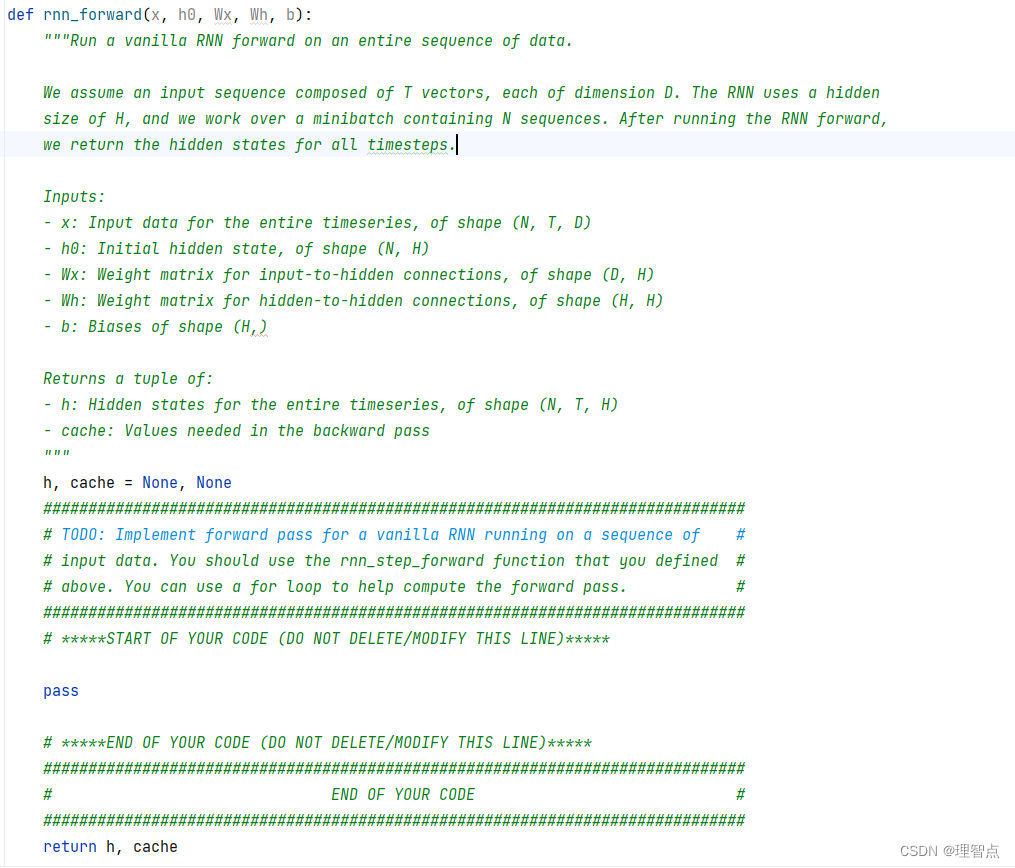
解析
看代碼吧
代碼
def rnn_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b):"""Run a vanilla RNN forward on an entire sequence of data.We assume an input sequence composed of T vectors, each of dimension D. The RNN uses a hiddensize of H, and we work over a minibatch containing N sequences. After running the RNN forward,we return the hidden states for all timesteps.Inputs:- x: Input data for the entire timeseries, of shape (N, T, D)- h0: Initial hidden state, of shape (N, H)- Wx: Weight matrix for input-to-hidden connections, of shape (D, H)- Wh: Weight matrix for hidden-to-hidden connections, of shape (H, H)- b: Biases of shape (H,)Returns a tuple of:- h: Hidden states for the entire timeseries, of shape (N, T, H)- cache: Values needed in the backward pass"""h, cache = None, None############################################################################### TODO: Implement forward pass for a vanilla RNN running on a sequence of ## input data. You should use the rnn_step_forward function that you defined ## above. You can use a for loop to help compute the forward pass. ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****# 獲取維度N, T, _ = x.shape_, H = h0.shape# 初始化h = np.zeros((N, T, H))cache = []# 前向傳播for i in range(T):if i == 0:h[:, i, :], cache_i = rnn_step_forward(x[:, i, :], h0, Wx, Wh, b)else:h[:, i, :], cache_i = rnn_step_forward(x[:, i, :], h[:, i - 1, :], Wx, Wh, b)cache.append(cache_i)cache = tuple(cache)# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return h, cache
輸出
rnn_backward
題面
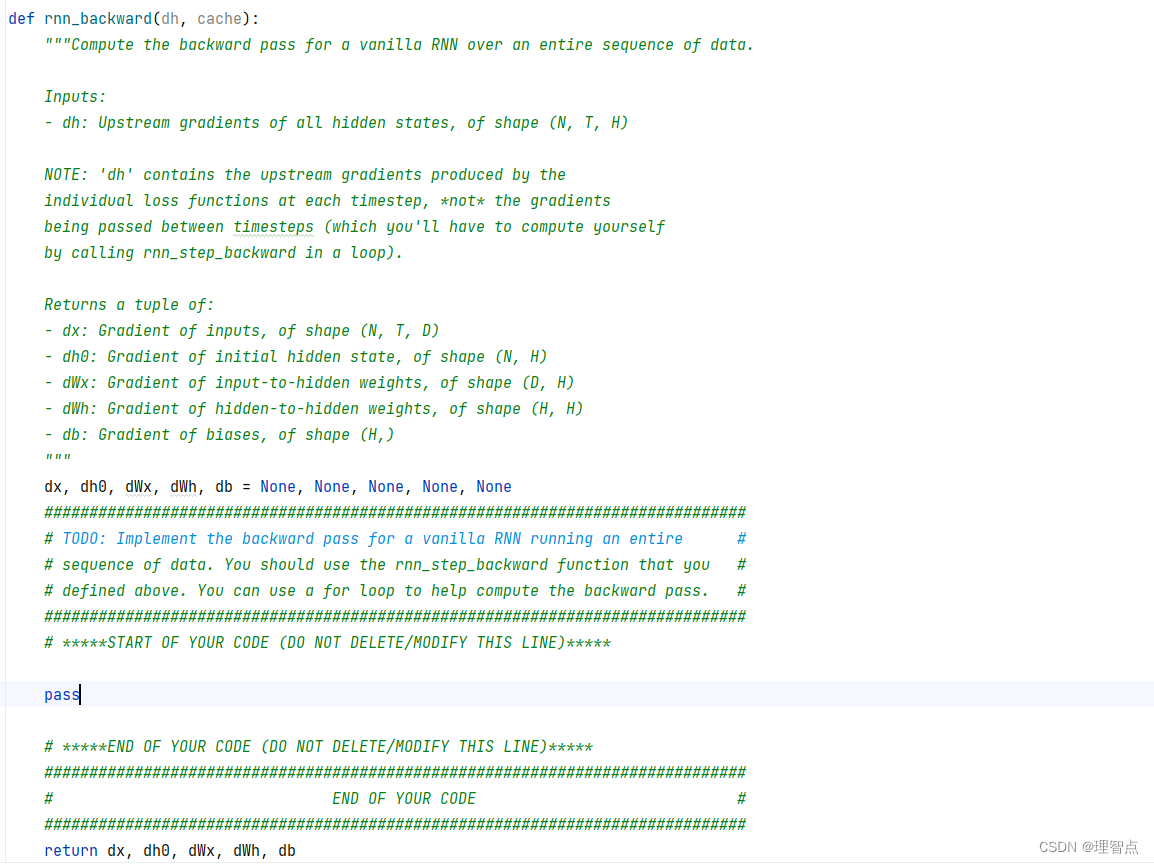
解析
看代碼吧,認真聽課的話肯定能理解的
代碼
def rnn_backward(dh, cache):"""Compute the backward pass for a vanilla RNN over an entire sequence of data.Inputs:- dh: Upstream gradients of all hidden states, of shape (N, T, H)NOTE: 'dh' contains the upstream gradients produced by the individual loss functions at each timestep, *not* the gradientsbeing passed between timesteps (which you'll have to compute yourselfby calling rnn_step_backward in a loop).Returns a tuple of:- dx: Gradient of inputs, of shape (N, T, D)- dh0: Gradient of initial hidden state, of shape (N, H)- dWx: Gradient of input-to-hidden weights, of shape (D, H)- dWh: Gradient of hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (H, H)- db: Gradient of biases, of shape (H,)"""dx, dh0, dWx, dWh, db = None, None, None, None, None############################################################################### TODO: Implement the backward pass for a vanilla RNN running an entire ## sequence of data. You should use the rnn_step_backward function that you ## defined above. You can use a for loop to help compute the backward pass. ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****# 獲取維度N, T, H = dh.shapeD, _ = cache[0][2].shape# 初始化dx = np.zeros((N, T, D))dh0 = np.zeros((N, H))dWx = np.zeros((D, H))dWh = np.zeros((H, H))db = np.zeros((H,))# 反向傳播for i in range(T - 1, -1, -1):dx[:, i, :], dh0, dWx_i, dWh_i, db_i = rnn_step_backward(dh[:, i, :] + dh0, cache[i])dWx += dWx_idWh += dWh_idb += db_i# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return dx, dh0, dWx, dWh, db
輸出
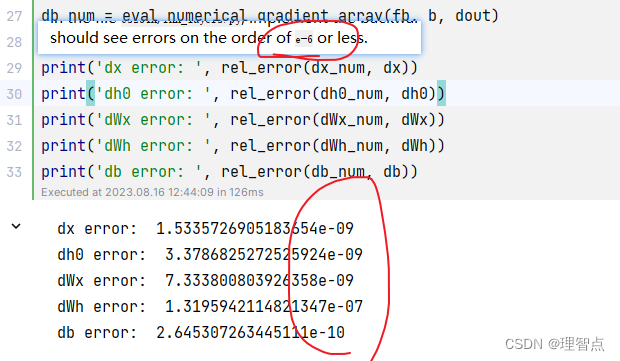
word_embedding_forward
word embedding 技術解釋
word embedding 技術解釋

題面
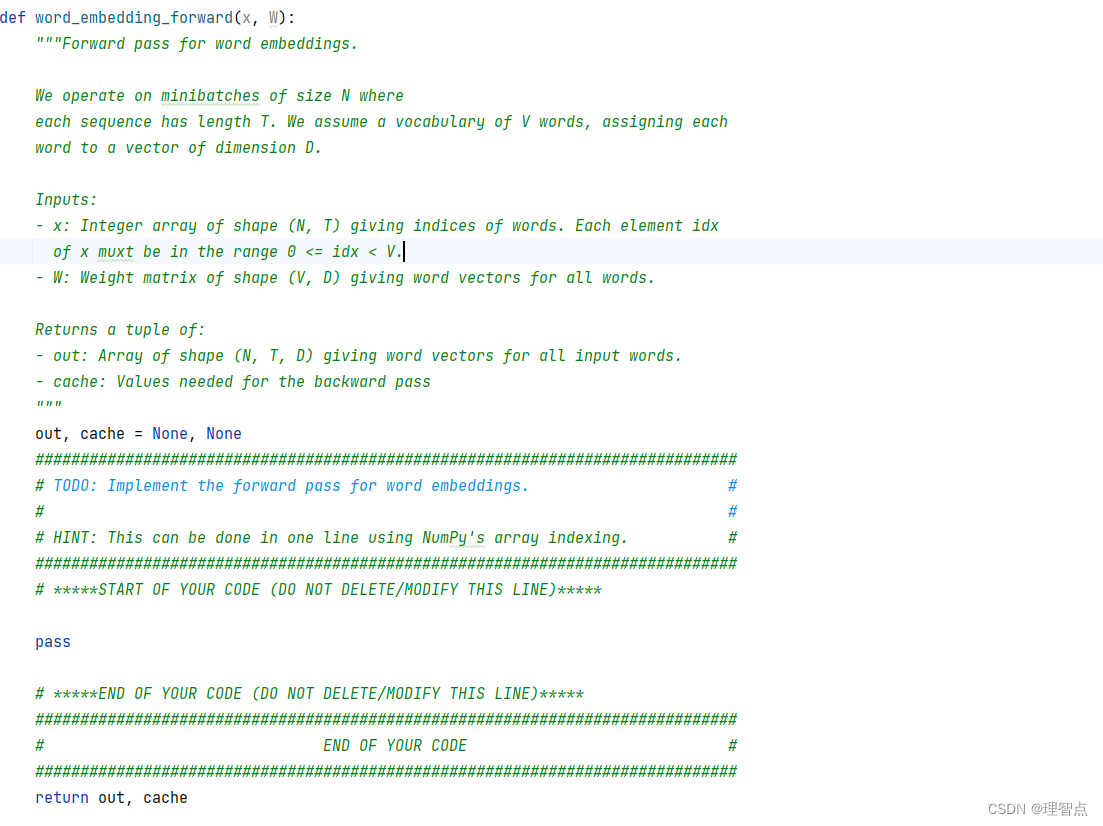
解析
看代碼吧
代碼
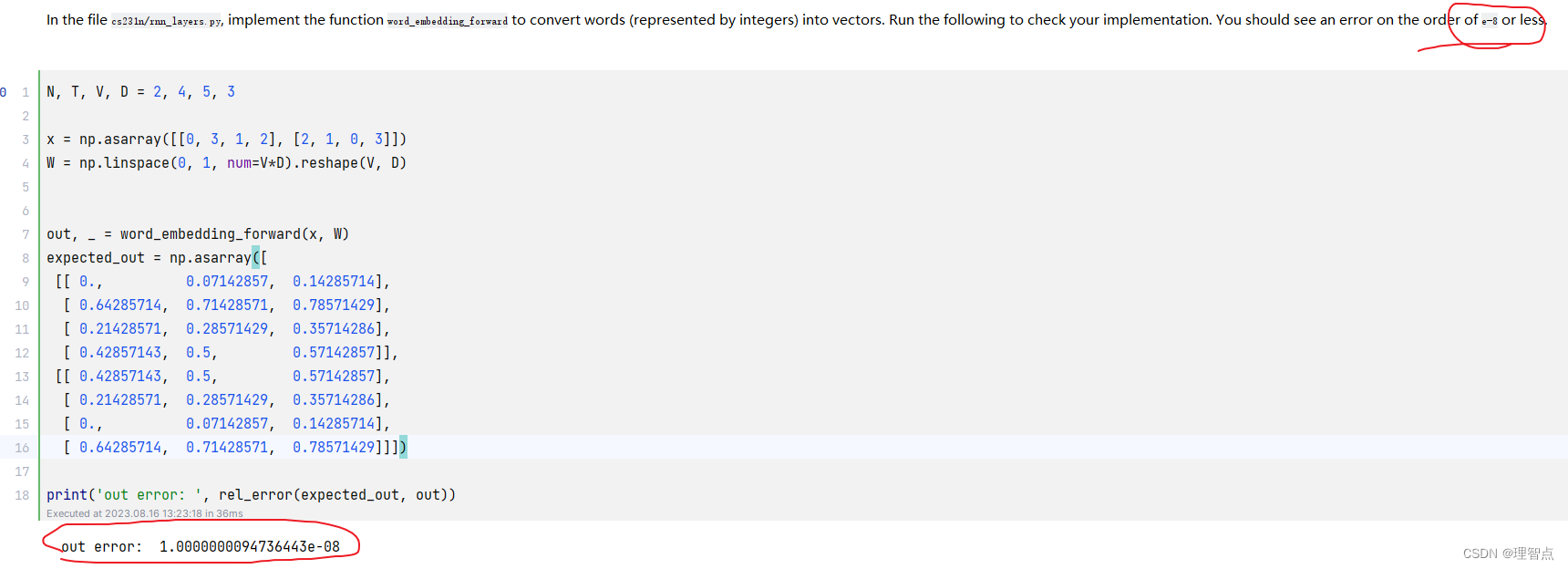
def word_embedding_forward(x, W):"""Forward pass for word embeddings.We operate on minibatches of size N whereeach sequence has length T. We assume a vocabulary of V words, assigning eachword to a vector of dimension D.Inputs:- x: Integer array of shape (N, T) giving indices of words. Each element idxof x muxt be in the range 0 <= idx < V.- W: Weight matrix of shape (V, D) giving word vectors for all words.Returns a tuple of:- out: Array of shape (N, T, D) giving word vectors for all input words.- cache: Values needed for the backward pass"""out, cache = None, None############################################################################### TODO: Implement the forward pass for word embeddings. ## ## HINT: This can be done in one line using NumPy's array indexing. ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****out = W[x]cache = (x, W)# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return out, cache
輸出
word_embedding_backward
題面
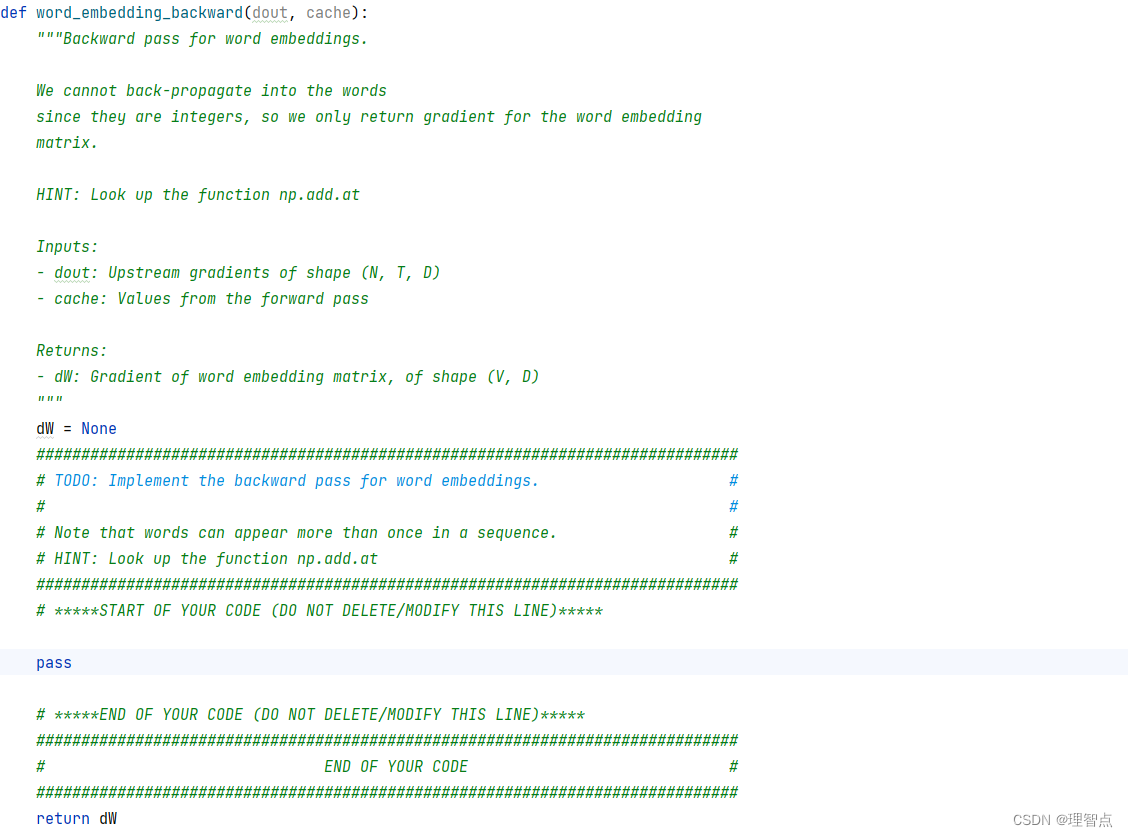
解析
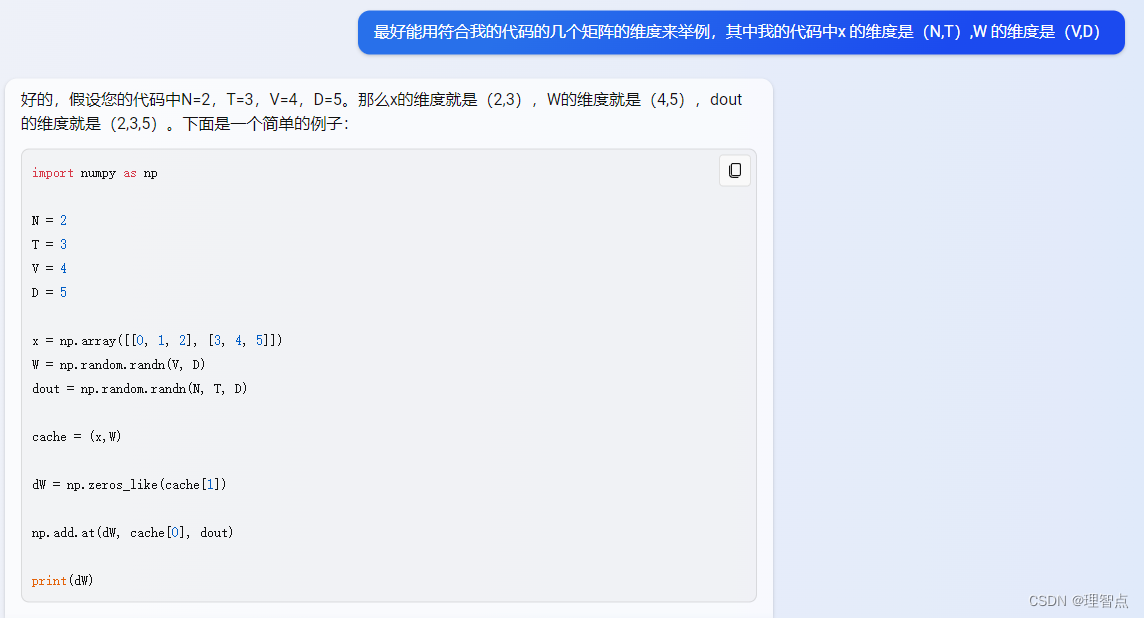
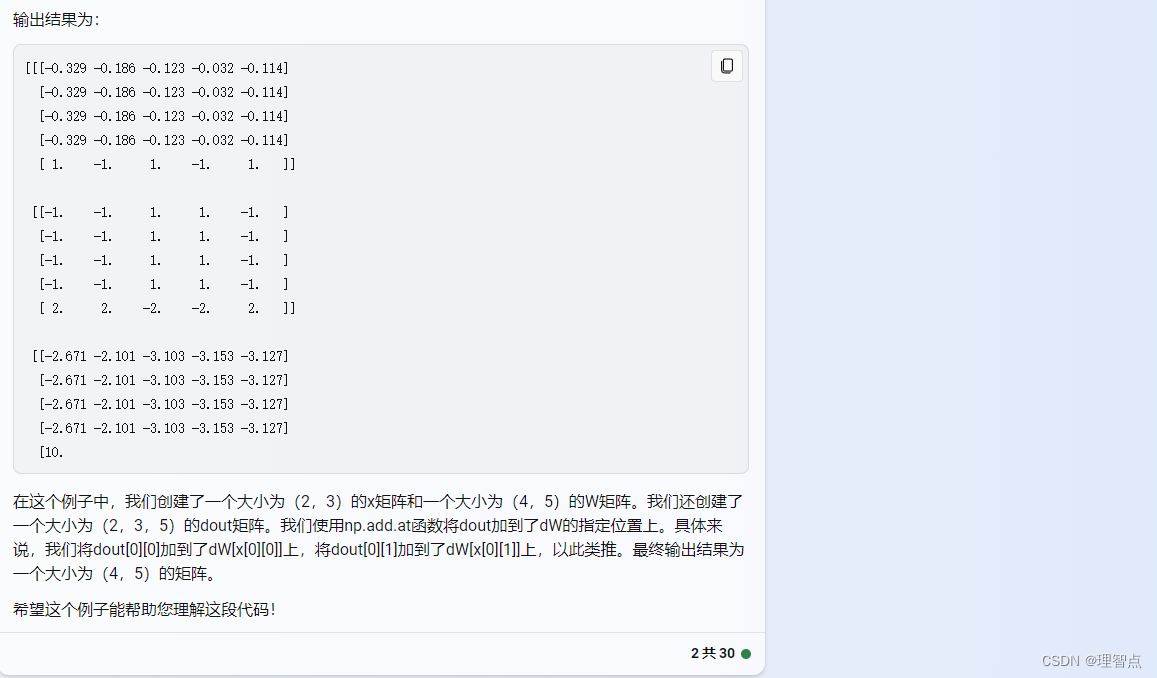
代碼
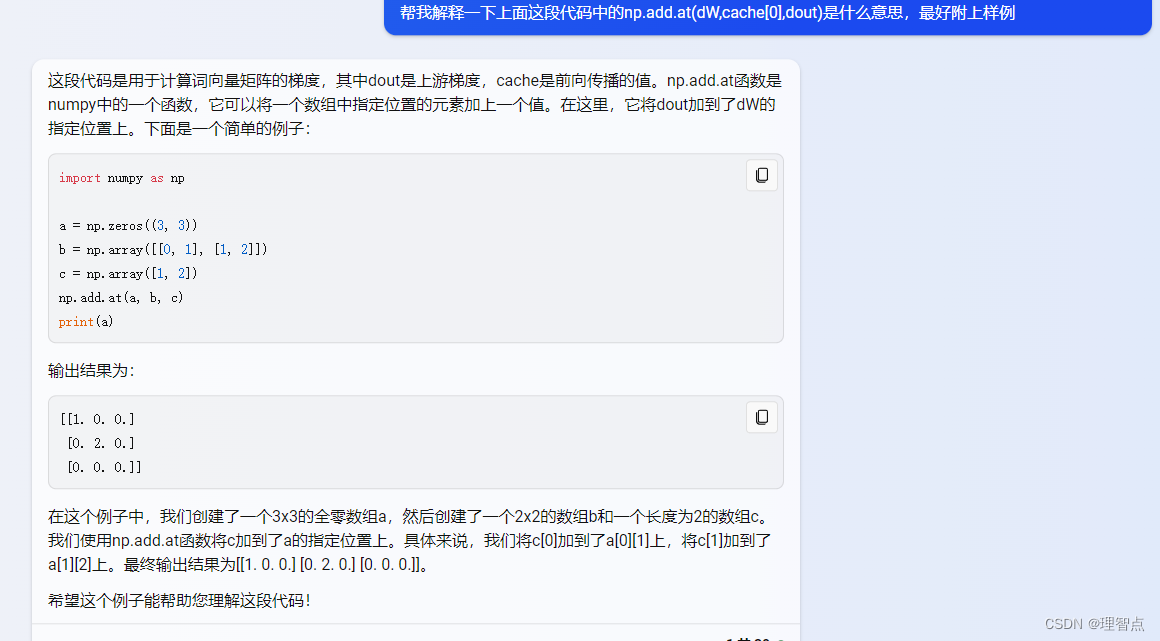
def word_embedding_backward(dout, cache):"""Backward pass for word embeddings.We cannot back-propagate into the wordssince they are integers, so we only return gradient for the word embeddingmatrix.HINT: Look up the function np.add.atInputs:- dout: Upstream gradients of shape (N, T, D)- cache: Values from the forward passReturns:- dW: Gradient of word embedding matrix, of shape (V, D)"""dW = None############################################################################### TODO: Implement the backward pass for word embeddings. ## ## Note that words can appear more than once in a sequence. ## HINT: Look up the function np.add.at ################################################################################ *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****dW = np.zeros_like(cache[1])np.add.at(dW, cache[0], dout)# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################### END OF YOUR CODE ###############################################################################return dW
輸出
CaptioningRNN .loss
題面
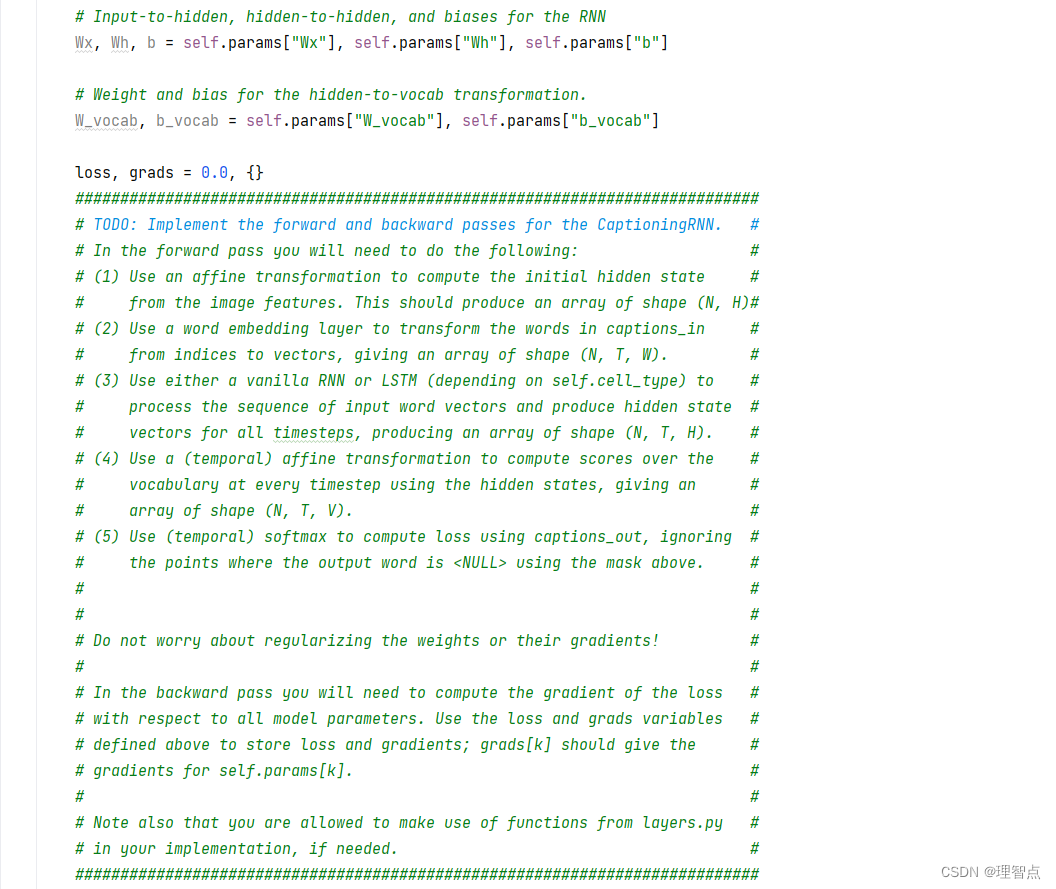
解析
就按照題面給的意思一步一步來就好了
代碼
def loss(self, features, captions):"""Compute training-time loss for the RNN. We input image features andground-truth captions for those images, and use an RNN (or LSTM) to computeloss and gradients on all parameters.Inputs:- features: Input image features, of shape (N, D)- captions: Ground-truth captions; an integer array of shape (N, T + 1) whereeach element is in the range 0 <= y[i, t] < VReturns a tuple of:- loss: Scalar loss- grads: Dictionary of gradients parallel to self.params"""# Cut captions into two pieces: captions_in has everything but the last word# and will be input to the RNN; captions_out has everything but the first# word and this is what we will expect the RNN to generate. These are offset# by one relative to each other because the RNN should produce word (t+1)# after receiving word t. The first element of captions_in will be the START# token, and the first element of captions_out will be the first word.captions_in = captions[:, :-1]captions_out = captions[:, 1:]# You'll need thismask = captions_out != self._null# Weight and bias for the affine transform from image features to initial# hidden stateW_proj, b_proj = self.params["W_proj"], self.params["b_proj"]# Word embedding matrixW_embed = self.params["W_embed"]# Input-to-hidden, hidden-to-hidden, and biases for the RNNWx, Wh, b = self.params["Wx"], self.params["Wh"], self.params["b"]# Weight and bias for the hidden-to-vocab transformation.W_vocab, b_vocab = self.params["W_vocab"], self.params["b_vocab"]loss, grads = 0.0, {}############################################################################# TODO: Implement the forward and backward passes for the CaptioningRNN. ## In the forward pass you will need to do the following: ## (1) Use an affine transformation to compute the initial hidden state ## from the image features. This should produce an array of shape (N, H)## (2) Use a word embedding layer to transform the words in captions_in ## from indices to vectors, giving an array of shape (N, T, W). ## (3) Use either a vanilla RNN or LSTM (depending on self.cell_type) to ## process the sequence of input word vectors and produce hidden state ## vectors for all timesteps, producing an array of shape (N, T, H). ## (4) Use a (temporal) affine transformation to compute scores over the ## vocabulary at every timestep using the hidden states, giving an ## array of shape (N, T, V). ## (5) Use (temporal) softmax to compute loss using captions_out, ignoring ## the points where the output word is <NULL> using the mask above. ## ## ## Do not worry about regularizing the weights or their gradients! ## ## In the backward pass you will need to compute the gradient of the loss ## with respect to all model parameters. Use the loss and grads variables ## defined above to store loss and gradients; grads[k] should give the ## gradients for self.params[k]. ## ## Note also that you are allowed to make use of functions from layers.py ## in your implementation, if needed. ############################################################################## *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****# 第一步,使用全連接層,將圖像特征轉換為隱藏層的初始狀態h0, cache_h0 = affine_forward(features, W_proj, b_proj)# 第二步,使用詞嵌入層,將輸入的單詞轉換為詞向量word_vector, cache_word_vector = word_embedding_forward(captions_in, W_embed)# 第三步,使用RNN或者LSTM,將詞向量序列轉換為隱藏層狀態序列if self.cell_type == "rnn":h, cache_h = rnn_forward(word_vector, h0, Wx, Wh, b)elif self.cell_type == "lstm":h, cache_h = lstm_forward(word_vector, h0, Wx, Wh, b)# 第四步,使用全連接層,將隱藏層狀態序列轉換為詞匯表上的得分序列scores, cache_scores = temporal_affine_forward(h, W_vocab, b_vocab)# 第五步,使用softmax,計算損失loss, dscores = temporal_softmax_loss(scores, captions_out, mask)# 反向傳播# 第四步,全連接層的反向傳播dh, dW_vocab, db_vocab = temporal_affine_backward(dscores, cache_scores)# 第三步,RNN或者LSTM的反向傳播if self.cell_type == "rnn":dword_vector, dh0, dWx, dWh, db = rnn_backward(dh, cache_h)elif self.cell_type == "lstm":dword_vector, dh0, dWx, dWh, db = lstm_backward(dh, cache_h)# 第二步,詞嵌入層的反向傳播dW_embed = word_embedding_backward(dword_vector, cache_word_vector)# 第一步,全連接層的反向傳播dfeatures, dW_proj, db_proj = affine_backward(dh0, cache_h0)# 將梯度保存到grads中grads["W_proj"] = dW_projgrads["b_proj"] = db_projgrads["W_embed"] = dW_embedgrads["Wx"] = dWxgrads["Wh"] = dWhgrads["b"] = dbgrads["W_vocab"] = dW_vocabgrads["b_vocab"] = db_vocab# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################# END OF YOUR CODE #############################################################################return loss, grads
輸出
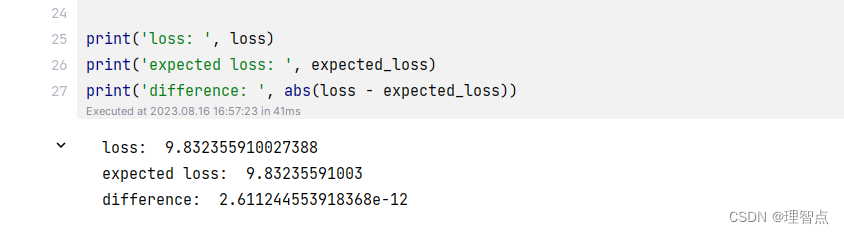
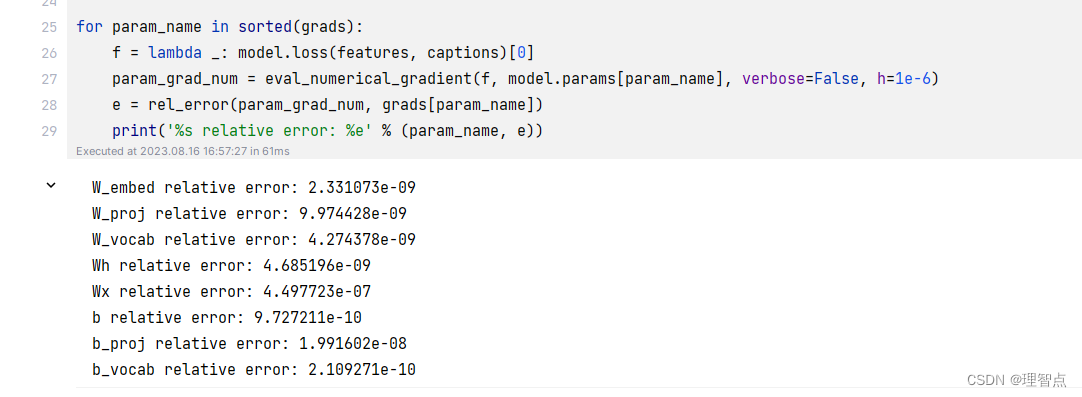
CaptioningRNN.sample
題面
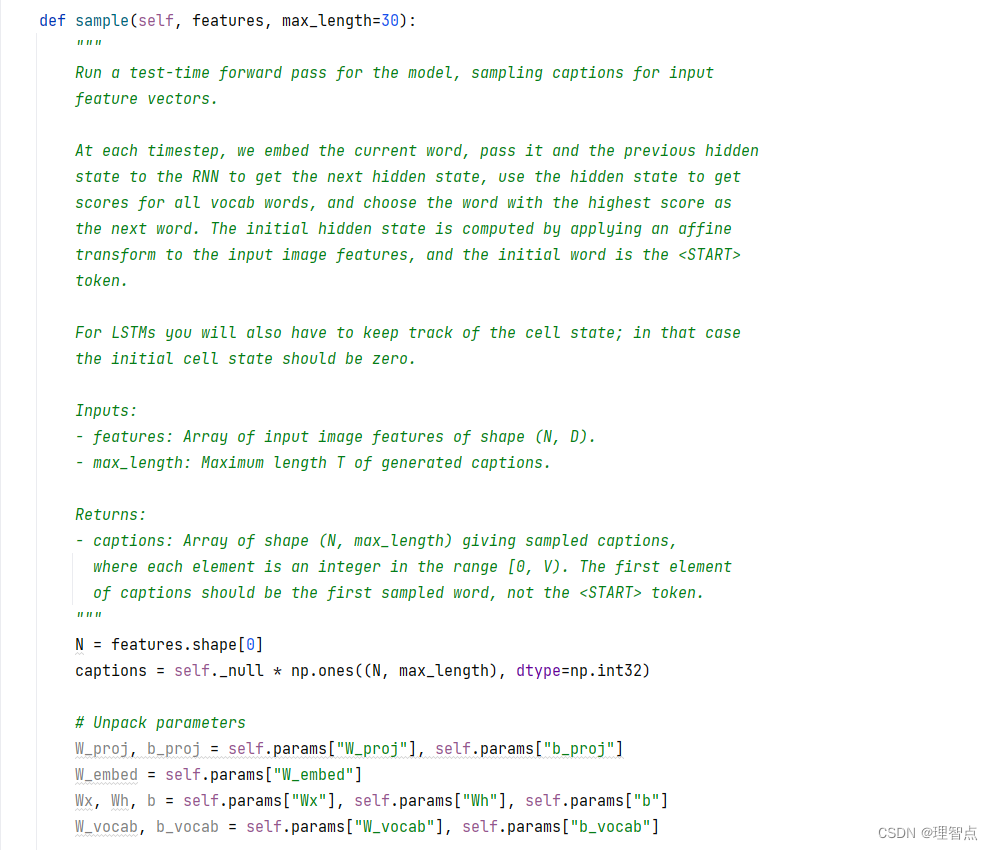
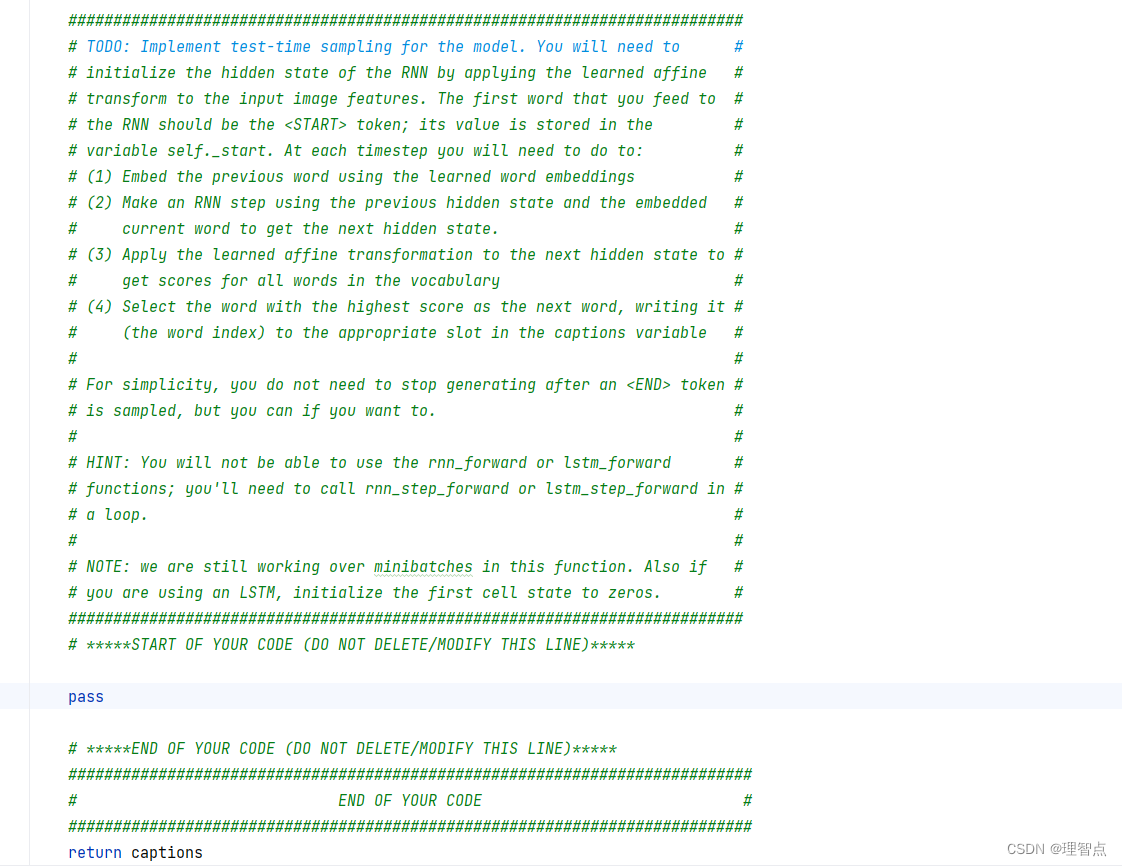
解析
看代碼注釋吧
代碼
def sample(self, features, max_length=30):"""Run a test-time forward pass for the model, sampling captions for inputfeature vectors.At each timestep, we embed the current word, pass it and the previous hiddenstate to the RNN to get the next hidden state, use the hidden state to getscores for all vocab words, and choose the word with the highest score asthe next word. The initial hidden state is computed by applying an affinetransform to the input image features, and the initial word is the <START>token.For LSTMs you will also have to keep track of the cell state; in that casethe initial cell state should be zero.Inputs:- features: Array of input image features of shape (N, D).- max_length: Maximum length T of generated captions.Returns:- captions: Array of shape (N, max_length) giving sampled captions,where each element is an integer in the range [0, V). The first elementof captions should be the first sampled word, not the <START> token."""N = features.shape[0]captions = self._null * np.ones((N, max_length), dtype=np.int32)# Unpack parametersW_proj, b_proj = self.params["W_proj"], self.params["b_proj"]W_embed = self.params["W_embed"]Wx, Wh, b = self.params["Wx"], self.params["Wh"], self.params["b"]W_vocab, b_vocab = self.params["W_vocab"], self.params["b_vocab"]############################################################################ TODO: Implement test-time sampling for the model. You will need to ## initialize the hidden state of the RNN by applying the learned affine ## transform to the input image features. The first word that you feed to ## the RNN should be the <START> token; its value is stored in the ## variable self._start. At each timestep you will need to do to: ## (1) Embed the previous word using the learned word embeddings ## (2) Make an RNN step using the previous hidden state and the embedded ## current word to get the next hidden state. ## (3) Apply the learned affine transformation to the next hidden state to ## get scores for all words in the vocabulary ## (4) Select the word with the highest score as the next word, writing it ## (the word index) to the appropriate slot in the captions variable ## ## For simplicity, you do not need to stop generating after an <END> token ## is sampled, but you can if you want to. ## ## HINT: You will not be able to use the rnn_forward or lstm_forward ## functions; you'll need to call rnn_step_forward or lstm_step_forward in ## a loop. ## ## NOTE: we are still working over minibatches in this function. Also if ## you are using an LSTM, initialize the first cell state to zeros. ############################################################################# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****# 第一步 初始化隱藏層狀態h, _ = affine_forward(features, W_proj, b_proj)# 第二步 初始化第一個單詞word = np.repeat(self._start, N)c = np.zeros_like(h)# 第三步 生成后面的單詞for i in range(max_length):# 第一步 生成第i個單詞的詞向量word, _ = word_embedding_forward(word, W_embed)# 第二步 生成第i個單詞的隱藏層狀態if self.cell_type == "rnn":h, _ = rnn_step_forward(word, h, Wx, Wh, b)elif self.cell_type == "lstm":h, c, _ = lstm_step_forward(word, h, c, Wx, Wh, b)# 第三步 生成第i個單詞的得分scores, _ = affine_forward(h, W_vocab, b_vocab)# 第四步 生成第i個單詞的預測值 并記錄到captions中,同時作為下一個單詞的輸入word = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)captions[:, i] = word# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****############################################################################# END OF YOUR CODE #############################################################################return captions
輸出
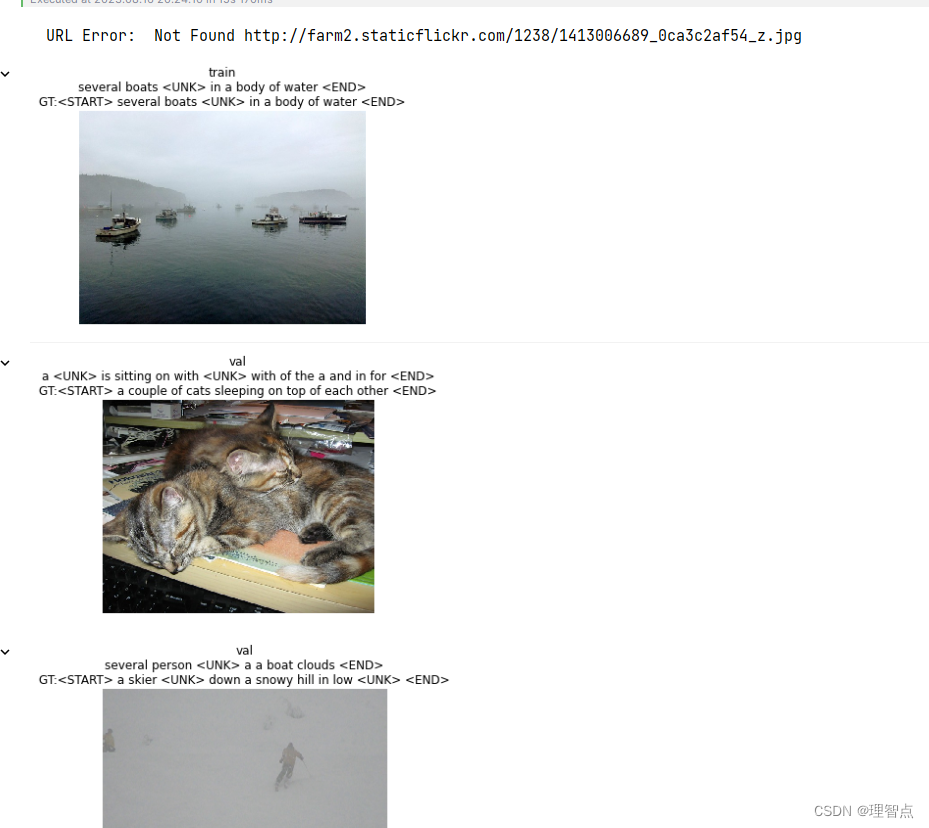
結語
對于循環神經網絡的理解,不僅需要課程的講解,也需要實驗的理解,然后在結合課程,會有一個更深的理解。
)

,一文讓你真正理解跨域)











)



