目錄
一、標準庫中的string類
1、簡單介紹string類
2、string類的常用接口注意事項
2.1、string類對象的常用構造
2.2、string類對象的容量操作
2.3、string類對象的訪問及遍歷操作
2.4、string類對象的修改操作
二、string類的模擬實現
一、標準庫中的string類
1、簡單介紹string類
? ? ? ? (1)string是表示字符串的字符串類;
? ? ? ? (2)string類的接口與常規容器的接口基本相同,在添加了一些專門用來操作string的常規操作;
? ? ? ? (3)string的底層實際是:basic_string模板類的別名,typedef basic_string<char,char_traits,allocator> string;
? ? ? ? (4)不能操作多字節或者變長字符的序列。
2、string類的常用接口注意事項
2.1、string類對象的常用構造
? ? ? ? 標準庫給出的string類對象常用的構造函數有很多,我們經常用到的主流構造方式有三種:用模板提供的默認構造函數構造空的string類對象、用常量字符串構造string類對象以及用現有的string類對象進行拷貝構造string類對象。

2.2、string類對象的容量操作

? ? ? ? (1)size()與length()方法的底層實現原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是為了與其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情況先都是用size()。
? ? ? ? (2)clear()只是將string類對象中的有效字符清空,不改變底層空間大小。
? ? ? ? (3)resize(size_t n)與resize(size_t n,char c)都是將字符串中的有效字符個數改變成n個,不同的是當字符個數增多時:resize(n)用0來填充多出來的元素空間,resize(size_t n,char c)是用字符c來填充多出來的元素空間。注意:resize()在改變元素個數時,如果是將元素個數增多,可能會改變底層容量的大小,如果是將元素個數減少,底層空間的總大小保持不變,并不會隨著元素個數的減少而縮小容量空間。
? ? ? ? (4)reserve(size_t res_arg=0):為string預留空間,不改變有效元素個數,當reserve的參數小于string的底層空間總大小時,reserve不會改變容量的大小。
2.3、string類對象的訪問及遍歷操作
? ? ? ? string類對象的訪問方式有三種:下標訪問、迭代器訪問、范圍for訪問。這里主要討論迭代器訪問方式。
? ? ? ? 迭代器是一個類,現階段可以把迭代器當成一個指針來使用(實際上不一定是指針),迭代器是在類的里邊定義的,即內部類,使用方式如:string::iterator。string類中與迭代器搭配使用的成員函數包括begin()、end()、rbegin()、rend()。

2.4、string類對象的修改操作
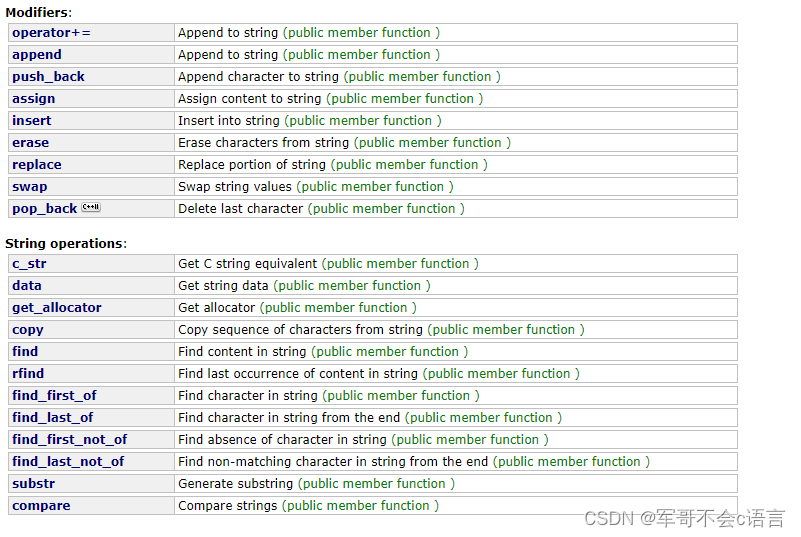
? ? ? ? string類提供了很多字符串修改接口,需要說的是:在string尾部追加自字符時,s.push_back(c)/s.append(1,c)/s+='c'三種實現方式幾乎一樣,一般情況下更多的選用+=操作,+=操作不僅可以連接單個字符,還可以連接字符串;對string操作時,如果能夠大概預估到待存儲字符串的長度,可以先通過reserve把空間預留好。
二、string類的模擬實現
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>namespace lbj
{class string{friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const string& s);friend istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, string& s);typedef char* iterator;public:string(const char* str = ""){_size = strlen(str);_capacity = _size;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}string(const string& s) : _str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){string tmp(s._str);this->swap(tmp);}string& operator=(const string& s){if (this != &s){string temp(s);this->swap(temp);}return *this;}~string(){if (_str){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}}//// iteratoriterator begin(){return _str;}iterator end(){return _str + _size;}/// modifyvoid push_back(char c){if (_size == _capacity)reserve(_capacity * 2);_str[_size++] = c;_str[_size] = '\0';}string& operator+=(char c){ push_back(c);return *this;}void append(const char* str){int len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity){reserve(_size + len);//_capacity = _size + len;}strcpy(_str + _size, str); //strcpy()會將‘\0’也拷貝過來,所以不需要手動添加'\0'_size += len;}string& operator+=(const char* str){append(str);return *this;}void clear(){_size = 0;_str[_size] = '\0';}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}const char* C_Str()const{return _str;}/// capacitysize_t size()const{return _size;}size_t capacity()const{return _capacity;}bool empty()const{return _size == 0;}void resize(size_t newSize, char c = '\0'){if (newSize > _size){// 如果newSize大于底層空間大小,則需要重新開辟空間if (newSize > _capacity){reserve(newSize);}memset(_str + _size, c, newSize - _size);}_size = newSize;_str[newSize] = '\0';}void reserve(size_t newCapacity){// 如果新容量大于舊容量,則開辟空間if (newCapacity > _capacity){char* str = new char[newCapacity + 1];strcpy(str, _str);// 釋放原來舊空間,然后使用新空間delete[] _str;_str = str;_capacity = newCapacity;}}/// accesschar& operator[](size_t index){assert(index < _size);return _str[index];}const char& operator[](size_t index)const{assert(index < _size);return _str[index];}///relational operatorsbool operator<(const string& s)const{int res = strcmp(_str, s._str);if (res < 0)return true;return false;}bool operator<=(const string& s)const{return !(*this > s);}bool operator>(const string& s)const{int res = strcmp(_str, s._str);if (res > 0)return true;return false;}bool operator>=(const string& s)const{return !(*this < s);}bool operator==(const string& s)const{int res = strcmp(_str, s._str);if (res == 0)return true;return false;}bool operator!=(const string& s)const{return !(*this == s);}// 返回c在string中第一次出現的位置size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const{for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; ++i){if (_str[i] == c)return i;//找到,返回下標}return -1;//未找到}// 返回子串s在string中第一次出現的位置size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const{assert(s);assert(pos < _size);const char* src = _str + pos;while (*src){const char* match = s;//如果不匹配,返回子串起始處重新查找const char* cur = src;while (*match && *match == *cur)//結束條件{++match;++cur;}if (*match == '\0')//找到子串{return src - _str;//返回下標}else{++src;}}return -1;//未找到}// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str,并返回該字符的位置string& insert(size_t pos, char c){assert(pos <= _size);if (_size > _capacity){//擴容char* newstr = new char[_capacity * 2 + 1];//開空間strcpy(newstr, _str);delete[] _str;_str = newstr;_capacity *= 2;//Expand(_capacity * 2);}//移數據for (int i = _size; i >= (int)pos; --i){_str[i + 1] = _str[i];}_str[pos] = c;_size++;return *this;}string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str){size_t len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity)//擴容{//擴容char* newstr = new char[_capacity * 2 + 1];//開空間strcpy(newstr, _str);delete[] _str;_str = newstr;_capacity *= 2;//Expand(_size + len);}//后移數據for (int i = _size; i >= (int)pos; --i){_str[len + i] = _str[i];}//拷貝字符串while (*str != '\0'){_str[pos++] = *str++;}_size += len;return *this;}// 刪除pos位置上的元素,并返回該元素的下一個位置string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len){assert(pos < _size);if (pos + len >= _size)//pos位置之后全為0{_str[pos] = '\0';_size = pos;}else{strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);_size -= len;}return *this;}private:char* _str;size_t _capacity;size_t _size;};//輸入流重載istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, string& s){//預分配100個空間char* str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);char* buf = str;int i = 1;//預處理:跳過流里面的所有空格和回車while ((*buf = getchar()) == ' ' || (*buf == '\n'));for (; ; ++i){if (*buf == '\n') //回車跳出{*buf = '\0';break;}else if (*buf == ' ') //空格跳出{*buf = '\0';break;}else if (i % 100 == 0) //空間不足{i += 100; //追加100個空間str = (char*)realloc(str, i);}else //每次getchar()一個值{buf = (str + i);//為了避免realloc返回首地址改變,不使用++buf,而是用str加上偏移.//每次讀取一個字符*buf = getchar();}}//輸入完成,更新ss._str = str;s._capacity = s._size = i;return _cin;}//輸出流重載ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const string& s){for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){_cout << s[i];}return _cout;}
};

 具體解釋)







)
配置)
)






