本章代碼:https://github.com/zhangxiann/PyTorch_Practice/blob/master/lesson1/linear_regression.py
張量的操作
拼接
torch.cat()
torch.cat(tensors,?dim=0,?out=None)
功能:將張量按照 dim 維度進行拼接
- tensors: 張量序列
- dim: 要拼接的維度
代碼示例:
t?=?torch.ones((2,?3))
t_0?=?torch.cat([t,?t],?dim=0)
t_1?=?torch.cat([t,?t],?dim=1)
print("t_0:{}?shape:{}\nt_1:{}?shape:{}".format(t_0,?t_0.shape,?t_1,?t_1.shape))
輸出是:
t_0:tensor([[1.,?1.,?1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.]])?shape:torch.Size([4,?3])
t_1:tensor([[1.,?1.,?1.,?1.,?1.,?1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.,?1.,?1.,?1.]])?shape:torch.Size([2,?6])
torch.stack()
torch.stack(tensors,?dim=0,?out=None)
功能:將張量在新創建的 dim 維度上進行拼接
- tensors: 張量序列
- dim: 要拼接的維度
代碼示例:
t?=?torch.ones((2,?3))
#?dim?=2
t_stack?=?torch.stack([t,?t,?t],?dim=2)
print("\nt_stack.shape:{}".format(t_stack.shape))
#?dim?=0
t_stack?=?torch.stack([t,?t,?t],?dim=0)
print("\nt_stack.shape:{}".format(t_stack.shape))
輸出為:
t_stack.shape:torch.Size([2,?3,?3])
t_stack.shape:torch.Size([3,?2,?3])
第一次指定拼接的維度 dim =2,結果的維度是 [2, 3, 3]。后面指定拼接的維度 dim =0,由于原來的 tensor 已經有了維度 0,因此會把 tensor 往后移動一個維度變為 [1,2,3],再拼接變為 [3,2,3]。
切分
torch.chunk()
torch.chunk(input,?chunks,?dim=0)
功能:將張量按照維度 dim 進行平均切分。若不能整除,則最后一份張量小于其他張量。
- input: 要切分的張量
- chunks: 要切分的份數
- dim: 要切分的維度
代碼示例:
a?=?torch.ones((2,?7))??#?7
list_of_tensors?=?torch.chunk(a,?dim=1,?chunks=3)???#?3
for?idx,?t?in?enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}個張量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1,?t,?t.shape))
輸出為:
第1個張量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?3])
第2個張量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
????????[1.,?1.,?1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?3])
第3個張量:tensor([[1.],
????????[1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?1])
由于 7 不能整除 3,7/3 再向上取整是 3,因此前兩個維度是 [2, 3],所以最后一個切分的張量維度是 [2,1]。
torch.split()
torch.split(tensor,?split_size_or_sections,?dim=0)
功能:將張量按照維度 dim 進行平均切分。可以指定每一個分量的切分長度。
- tensor: 要切分的張量
- split_size_or_sections: 為 int 時,表示每一份的長度,如果不能被整除,則最后一份張量小于其他張量;為 list 時,按照 list 元素作為每一個分量的長度切分。如果 list 元素之和不等于切分維度 (dim) 的值,就會報錯。
- dim: 要切分的維度
代碼示例:
t?=?torch.ones((2,?5))
list_of_tensors?=?torch.split(t,?[2,?1,?2],?dim=1)
for?idx,?t?in?enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}個張量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1,?t,?t.shape))
結果為:
第1個張量:tensor([[1., 1.],
????????[1.,?1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?2])
第2個張量:tensor([[1.],
????????[1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?1])
第3個張量:tensor([[1., 1.],
????????[1.,?1.]]),?shape?is?torch.Size([2,?2])
索引
torch.index_select()
torch.index_select(input,?dim,?index,?out=None)
功能:在維度 dim 上,按照 index 索引取出數據拼接為張量返回。
- input: 要索引的張量
- dim: 要索引的維度
- index: 要索引數據的序號
代碼示例:
#?創建均勻分布
t?=?torch.randint(0,?9,?size=(3,?3))
#?注意?idx?的?dtype?不能指定為?torch.float
idx?=?torch.tensor([0,?2],?dtype=torch.long)
#?取出第?0?行和第?2?行
t_select?=?torch.index_select(t,?dim=0,?index=idx)
print("t:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}".format(t,?t_select))
輸出為:
t:
tensor([[4,?5,?0],
????????[5,?7,?1],
????????[2,?5,?8]])
t_select:
tensor([[4,?5,?0],
????????[2,?5,?8]])
torch.mask_select()
torch.masked_select(input,?mask,?out=None)
功能:按照 mask 中的 True 進行索引拼接得到一維張量返回。
- 要索引的張量
- mask: 與 input 同形狀的布爾類型張量
代碼示例:
t?=?torch.randint(0,?9,?size=(3,?3))
mask?=?t.le(5)??#?ge?is?mean?greater?than?or?equal/???gt:?greater?than??le??lt
#?取出大于?5?的數
t_select?=?torch.masked_select(t,?mask)
print("t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}?".format(t,?mask,?t_select))
結果為:
t:
tensor([[4,?5,?0],
????????[5,?7,?1],
????????[2,?5,?8]])
mask:
tensor([[?True,??True,??True],
????????[?True,?False,??True],
????????[?True,??True,?False]])
t_select:
tensor([4,?5,?0,?5,?1,?2,?5])
最后返回的是一維張量。
變換
torch.reshape()
torch.reshape(input,?shape)
功能:變換張量的形狀。當張量在內存中是連續時,返回的張量和原來的張量共享數據內存,改變一個變量時,另一個變量也會被改變。
- input: 要變換的張量
- shape: 新張量的形狀
代碼示例:
#?生成?0?到?8?的隨機排列
t?=?torch.randperm(8)
#?-1?表示這個維度是根據其他維度計算得出的
t_reshape?=?torch.reshape(t,?(-1,?2,?2))
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t,?t_reshape))
結果為:
t:tensor([5,?4,?2,?6,?7,?3,?1,?0])
t_reshape:
tensor([[[5,?4],
?????????[2,?6]],
????????[[7,?3],
?????????[1,?0]]])
在上面代碼的基礎上,修改原來的張量的一個元素,新張量也會被改變。
代碼示例:
#?修改張量?t?的第?0?個元素,張量?t_reshape?也會被改變
t[0]?=?1024
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t,?t_reshape))
print("t.data?內存地址:{}".format(id(t.data)))
print("t_reshape.data?內存地址:{}".format(id(t_reshape.data)))
結果為:
t:tensor([1024,????4,????2,????6,????7,????3,????1,????0])
t_reshape:
tensor([[[1024,????4],
?????????[???2,????6]],
????????[[???7,????3],
?????????[???1,????0]]])
t.data?內存地址:2636803119936
t_reshape.data?內存地址:2636803119792
torch.transpose()
torch.transpose(input,?dim0,?dim1)
功能:交換張量的兩個維度。常用于圖像的變換,比如把c*h*w變換為h*w*c。
- input: 要交換的變量
- dim0: 要交換的第一個維度
- dim1: 要交換的第二個維度
代碼示例:
#把?c?*?h?*?w?變換為?h?*?w?*?c
t?=?torch.rand((2,?3,?4))
t_transpose?=?torch.transpose(t,?dim0=1,?dim1=2)????#?c*h*w?????h*w*c
print("t?shape:{}\nt_transpose?shape:?{}".format(t.shape,?t_transpose.shape))
結果為:
t?shape:torch.Size([2,?3,?4])
t_transpose?shape:?torch.Size([2,?4,?3])
torch.t()
功能:2 維張量轉置,對于 2 維矩陣而言,等價于torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)。
torch.squeeze()
torch.squeeze(input,?dim=None,?out=None)
功能:壓縮長度為 1 的維度。
- dim: 若為 None,則移除所有長度為 1 的維度;若指定維度,則當且僅當該維度長度為 1 時可以移除。
代碼示例:
????#?維度?0?和?3?的長度是?1
????t?=?torch.rand((1,?2,?3,?1))
????#?可以移除維度?0?和?3
????t_sq?=?torch.squeeze(t)
????#?可以移除維度?0
????t_0?=?torch.squeeze(t,?dim=0)
????#?不能移除?1
????t_1?=?torch.squeeze(t,?dim=1)
????print("t.shape:?{}".format(t.shape))
????print("t_sq.shape:?{}".format(t_sq.shape))
????print("t_0.shape:?{}".format(t_0.shape))
????print("t_1.shape:?{}".format(t_1.shape))
結果為:
t.shape:?torch.Size([1,?2,?3,?1])
t_sq.shape:?torch.Size([2,?3])
t_0.shape:?torch.Size([2,?3,?1])
t_1.shape:?torch.Size([1,?2,?3,?1])
torch.unsqueeze()
torch.unsqueeze(input,?dim)
功能:根據 dim 擴展維度,長度為 1。
張量的數學運算
主要分為 3 類:加減乘除,對數,指數,冪函數 和三角函數。
這里介紹一下常用的幾種方法。
torch.add()
torch.add(input,?other,?out=None)
torch.add(input,?other,?*,?alpha=1,?out=None)
功能:逐元素計算 input + alpha * other。因為在深度學習中經常用到先乘后加的操作。
- input: 第一個張量
- alpha: 乘項因子
- other: 第二個張量
torch.addcdiv()
torch.addcdiv(input,?tensor1,?tensor2,?*,?value=1,?out=None)
計算公式為:out value
torch.addcmul()
torch.addcmul(input,?tensor1,?tensor2,?*,?value=1,?out=None)
計算公式為:out input value tensor tensor
線性回歸
線性回歸是分析一個變量 () 與另外一 (多) 個變量 () 之間的關系的方法。一般可以寫成 。線性回歸的目的就是求解參數 。
線性回歸的求解可以分為 3 步:
- 確定模型:
- 選擇損失函數,一般使用均方誤差 MSE:。其中 是預測值, 是真實值。
- 使用梯度下降法求解梯度 (其中 是學習率),并更新參數:
代碼如下:
import?torch
import?matplotlib.pyplot?as?plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
lr?=?0.05??#?學習率
#?創建訓練數據
x?=?torch.rand(20,?1)?*?10??#?x?data?(tensor),?shape=(20,?1)
#?torch.randn(20,?1)?用于添加噪聲
y?=?2*x?+?(5?+?torch.randn(20,?1))??#?y?data?(tensor),?shape=(20,?1)
#?構建線性回歸參數
w?=?torch.randn((1),?requires_grad=True)?#?設置梯度求解為?true
b?=?torch.zeros((1),?requires_grad=True)?#?設置梯度求解為?true
#?迭代訓練?1000?次
for?iteration?in?range(1000):
????#?前向傳播,計算預測值
????wx?=?torch.mul(w,?x)
????y_pred?=?torch.add(wx,?b)
????#?計算?MSE?loss
????loss?=?(0.5?*?(y?-?y_pred)?**?2).mean()
????#?反向傳播
????loss.backward()
????#?更新參數
????b.data.sub_(lr?*?b.grad)
????w.data.sub_(lr?*?w.grad)
????#?每次更新參數之后,都要清零張量的梯度
????w.grad.zero_()
????b.grad.zero_()
????#?繪圖,每隔?20?次重新繪制直線
????if?iteration?%?20?==?0:
????????plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(),?y.data.numpy())
????????plt.plot(x.data.numpy(),?y_pred.data.numpy(),?'r-',?lw=5)
????????plt.text(2,?20,?'Loss=%.4f'?%?loss.data.numpy(),?fontdict={'size':?20,?'color':??'red'})
????????plt.xlim(1.5,?10)
????????plt.ylim(8,?28)
????????plt.title("Iteration:?{}\nw:?{}?b:?{}".format(iteration,?w.data.numpy(),?b.data.numpy()))
????????plt.pause(0.5)
????????#?如果?MSE?小于?1,則停止訓練
????????if?loss.data.numpy()?????????????break
訓練的直線的可視化如下:
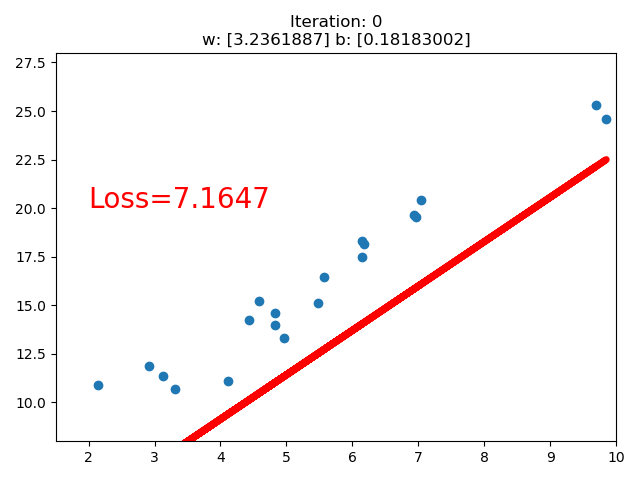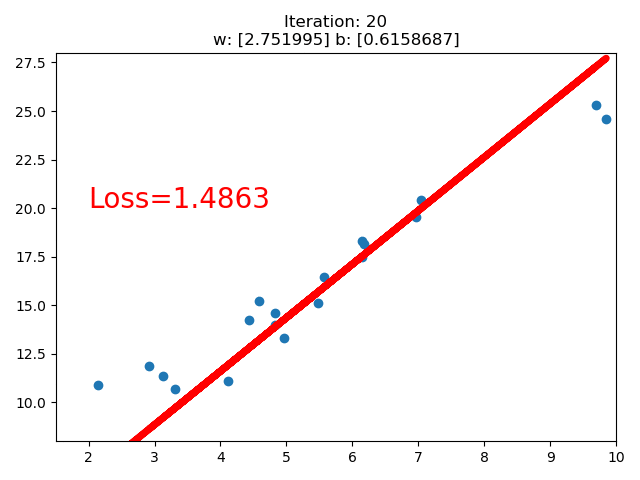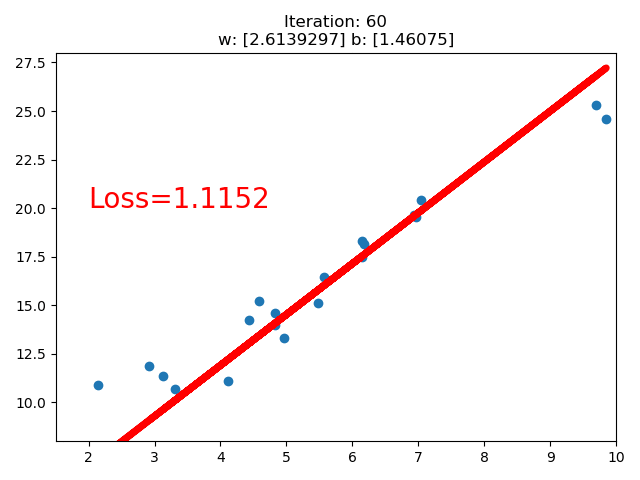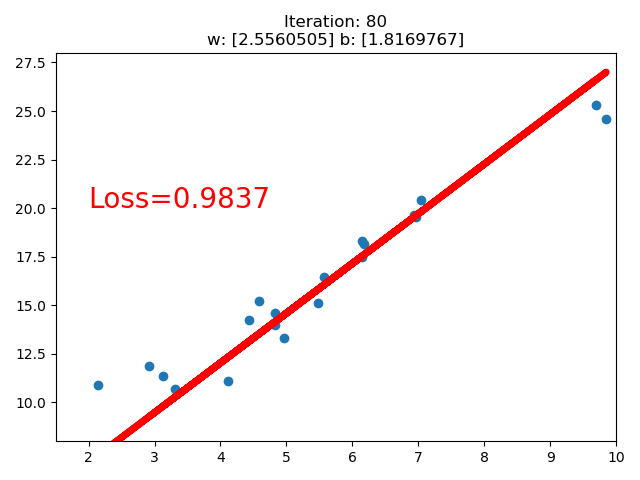
在 80 次的時候,Loss 已經小于 1 了,因此停止了訓練。
參考資料
- 深度之眼 PyTorch 框架班
如果你覺得這篇文章對你有幫助,不妨點個贊,讓我有更多動力寫出好文章。?



)

)













方法的使用)