創建并顯示原始內容
其中的lxml第三方解釋器加快解析速度
import bs4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2"><!-- Lacie --></a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
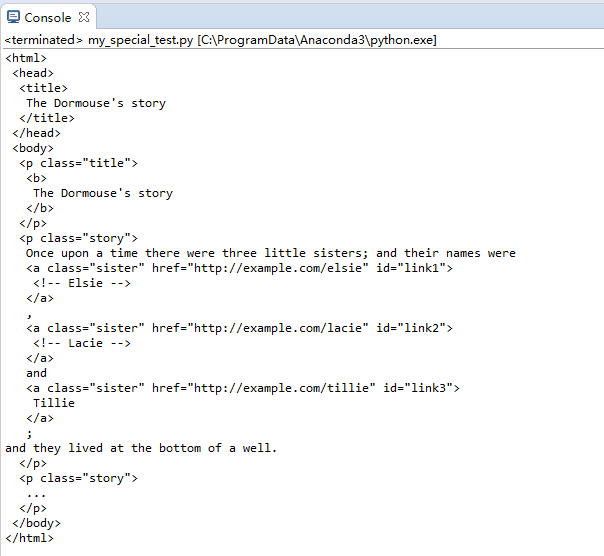
print(soup.prettify())
控制臺顯示出soup需要處理的內容:
?
提取對象內容和屬性
搜索包括了所有的標簽。默認提取第一個符合條件的標簽。
提取Tag對象
其中,name用于顯示標簽名,去掉name則內容直接顯示。
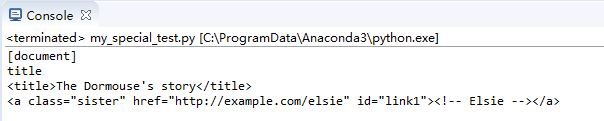
print(soup.name)
print(soup.title.name)
print(soup.title)
print(soup.a)
控制臺輸出效果如下:
顯示屬性
attrs用于顯示屬性。class用于顯示選中的標簽Tag中的類名。
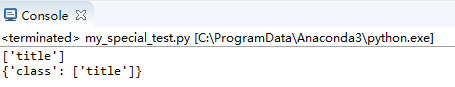
print(soup.p['class'])
print(soup.p.attrs)
輸出結果:
內容文字
顯示標記中的文字,NavigableString類型
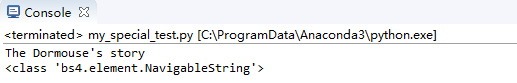
print(soup.p.string)
print(type(soup.p.string))
效果:
顯示注釋
顯示注釋內容,注意與普通string的區別在于最后的類,用于數據分類
print(soup.a.string)
print(type(soup.a.string))
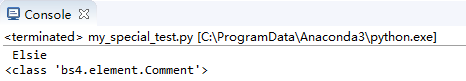
?
文檔相關結點
直接子節點數組
結點中的contents輸出直接子節點數組,可以通過for逐個輸出,通過string屬性直接輸出內容
print(soup.body.contents)
輸出body標簽下的直接子節點:
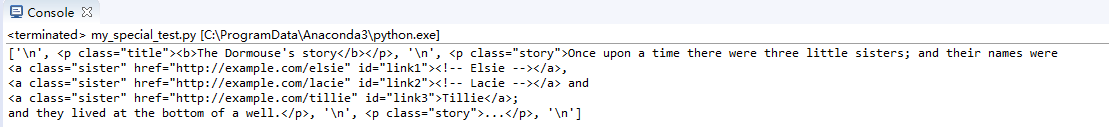
結點children輸出直接子節點,和contents類似。不一樣的是返回了生成器,一點參考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wj-1314/p/8490822.html
for i in soup.body.children:print(i,end='')
添加了end=''用于去掉print的自動換行
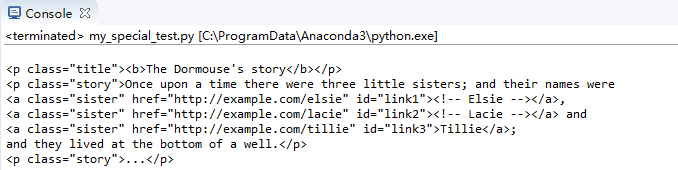
子、孫節點
結點descendants可以輸出子節點和孫節點
for i in soup.body.descendants:print(i)
效果:
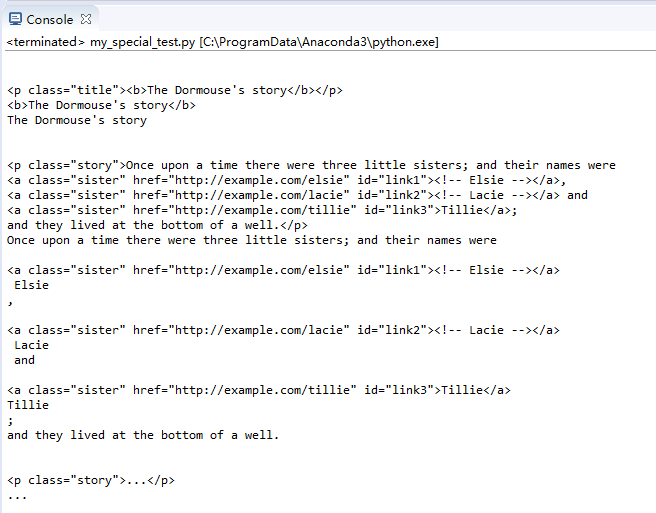
節點strings輸出全部子節點內容值
print(soup.strings)
print('------------------------')
for text in soup.strings:print(text,end='')
效果:
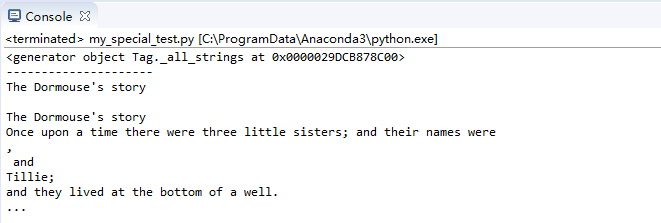
節點stripped_strings輸出全部內容并去掉回車和空格
for text in soup.stripped_strings:print(text)
print每次輸出加上換行后,效果:
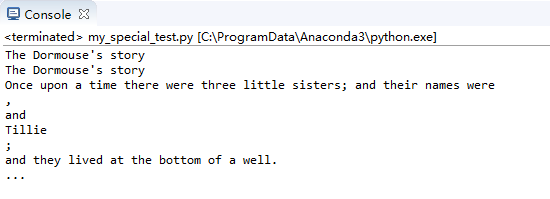
父節點相關
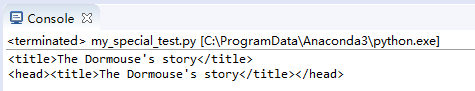
父節點parent
print(soup.title)
print(soup.title.parent)
效果:
父輩節點parents,這里只輸出名字就好了,否則內容過多
for i in soup.a.parents:print(i.name)
效果:
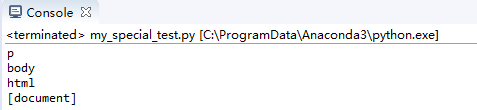
兄弟節點等
兄弟節點next_sibling,previous_sibling,另有 :next_siblings,previous_siblings
print(soup.p.next_sibling.next_sibling)
print(soup.p.previous_sibling)
效果:
前后節點:next_element,next_elements等......
?
BeautifulSoup的搜索方法
包括了find_all,find,find_parents等等,這里只舉例find_all。
find_all中參數name查找名稱標記
查找所有b標簽
print(soup.find_all('b'))
輸出:
查找所有b開頭的標簽
配合正則表達式使用
import re
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")):print(tag.name)
輸出:
查找a開頭和b開頭的標簽
print(soup.find_all(["a", "b"]))
輸出:(一個數組,過長)
查找所有標簽,True可以匹配任何值
for tag in soup.find_all(True):print(tag.name)
輸出:

自定義過濾
查找含有class和id屬性的Tag標簽
def hasClass_Id(tag):return tag.has_attr('class') and tag.has_attr('id')
print(soup.find_all(hasClass_Id))
效果:
查找關鍵詞參數kwargs并輸出
查找id參數為link2的標簽
print(soup.find_all(id='link2'))
輸出:
查找鏈接中含有elsie的標簽
配合正則表達式
print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie")))
輸出:
查找所有有id屬性的標簽
print(soup.find_all(id=True))
輸出:
查找所有a標簽且class內容為sister
print(soup.find_all("a", class_="sister"))
輸出:
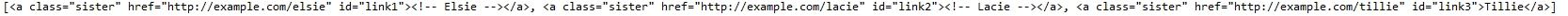
查找所有鏈接含有elsie的標簽,id為link1
print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"), id='link1'))
輸出:
不能表達的屬性的解決方案
在html5中有些屬性不被支持,查找時,通過定義字典實現輸出
data_soup = BeautifulSoup('<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>','lxml')
print(data_soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"}))
輸出: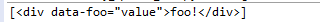
通過text參數查找文本內容并過濾
?輸入:
print(soup.find_all(text=["Tillie", "Elsie", "Lacie"]))
print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse")))
輸出:
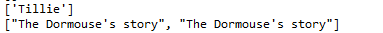
通過limit參數限制查找數量
輸入:
print(soup.find_all("a", limit=2))
輸出只有兩個:

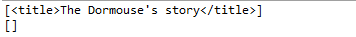
通過recursive參數只查找直接子節點
soup位于根處
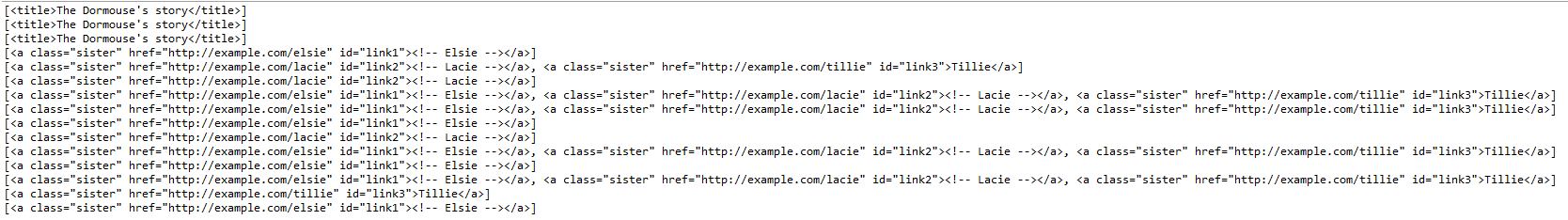
print(soup.find_all("title"))
print(soup.find_all("title", recursive=False))
輸出:
使用CSS選擇器查找
#直接查找title標簽
print soup.select("title")
#逐層查找title標簽
print soup.select("html head title")
#查找直接子節點
#查找head下的title標簽
print soup.select("head > title")
#查找p下的id="link1"的標簽
print soup.select("p > #link1")
#查找兄弟節點
#查找id="link1"之后class=sisiter的所有兄弟標簽
print soup.select("#link1 ~ .sister")
#查找緊跟著id="link1"之后class=sisiter的子標簽
print soup.select("#link1 + .sister")print soup.select(".sister")
print soup.select("[class~=sister]")print soup.select("#link1")
print soup.select("a#link2")print soup.select('a[href]')print soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')
print soup.select('a[href^="http://example.com/"]')
print soup.select('a[href$="tillie"]')
print soup.select('a[href*=".com/el"]')
?輸出:
?



)





)





(快速冪))
)


