1、Set基本數據類型
a、set集合,是一個無序且不重復的元素集合
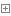

class set(object):"""set() -> new empty set objectset(iterable) -> new set objectBuild an unordered collection of unique elements."""def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Add an element to a set,添加元素This has no effect if the element is already present."""passdef clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Remove all elements from this set. 清楚內容"""passdef copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Return a shallow copy of a set. 淺拷貝 """passdef difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在(i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)"""passdef difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Remove all elements of another set from this set. 從當前集合中刪除和B中相同的元素"""passdef discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Remove an element from a set if it is a member.If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保錯"""passdef intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集(i.e. all elements that are in both sets.)"""passdef intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """passdef isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果沒有交集,返回True,否則返回False"""passdef issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列"""passdef issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列"""passdef pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Remove and return an arbitrary set element.Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素"""passdef remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Remove an element from a set; it must be a member.If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保錯"""passdef symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 對稱交集(i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)"""passdef symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 對稱交集,并更新到a中 """passdef union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown"""Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集(i.e. all elements that are in either set.)"""passdef update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """pass
set
b、數據類型模塊舉例
se = {11,22,33,44,55}
be = {44,55,66,77,88}# se.add(66)
# print(se) #添加元素,不能直接打印!
#
#
#
# se.clear()
# print(se) #清除se集合里面所有的值,不能清除單個
#
#
#
# ce=be.difference(se) #se中存在,be中不存在的值,必須賦值給一個新的變量
# print(ce)
#
#
# se.difference_update(be)
# print(se) #在se中刪除和be相同的值,不能賦值給一個新的變量,先輸入轉換,然后打印,也不能直接打印!# se.discard(11)
# print(se) #移除指定元素,移除不存在的時候,不會報錯# se.remove(11)
# print(se) #移除指定的元素,移除不存在的會報錯# se.pop()
# print(se) #移除隨機的元素
#
#
# ret=se.pop()
# print(ret) #移除元素,并且可以把移除的元素賦值給另一個變量# ce = se.intersection(be)
# print(ce) #取出兩個集合的交集(相同的元素)# se.intersection_update(be)
# print(se) #取出兩個集合的交集,并更新到se集合中# ret = se.isdisjoint(be)
# print(ret) #判斷兩個集合之間又沒有交集,如果有交集返回False,沒有返回True# ret=se.issubset(be)
# print(ret) #判斷se是否是be集合的子序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase# ret = se.issuperset(be)
# print(ret) #判斷se是不是be集合的父序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase# ret=se.symmetric_difference(be)
# print(ret) #對稱交集,取出除了不相同的元素# se.symmetric_difference_update(be)
# print(se) #對稱交集,取出不相同的元素并更新到se集合中# ret = se.union(be)
# print(ret) #并集,把兩個元素集合并在一個新的變量中
2、深淺拷貝
a、數字和字符串
對于 數字 和 字符串 而言,賦值、淺拷貝和深拷貝無意義,因為其永遠指向同一個內存地址。
import copy
# ######### 數字、字符串 #########
n1 = 123
# n1 = "i am alex age 10"
print(id(n1))
# ## 賦值 ##
n2 = n1
print(id(n2))
# ## 淺拷貝 ##
n2 = copy.copy(n1)
print(id(n2))# ## 深拷貝 ##
n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1)
print(id(n3))

b、其他基本數據類型
對于字典、元祖、列表 而言,進行賦值、淺拷貝和深拷貝時,其內存地址的變化是不同的。
1、賦值
賦值 ,只是創建一個變量,該變量指向原來內存地址,如:
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["Aylin", 456]}n2 = n1

2、淺拷貝
淺拷貝 ,在內存中只額外創建第一層數據
import copyn1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["aylin", 456]}n3 = copy.copy(n1)
3、深拷貝
深拷貝 ,在內存中將所有的數據重新創建一份(排除最后一層,即:python內部對字符串和數字的優化)

3、函數
- 函數式:將某功能代碼封裝到函數中,日后便無需重復編寫,僅調用函數即可
- 面向對象:對函數進行分類和封裝,讓開發“更快更好更強…
- 函數傳參數傳的是引用
.函數的定義主要有如下要點:
- def:表示函數的關鍵字
- 函數名:函數的名稱,日后根據函數名調用函數
- 函數體:函數中進行一系列的邏輯計算,如:發送郵件、計算出 [11,22,38,888,2]中的最大數等…
- 參數:為函數體提供數據
- 返回值:當函數執行完畢后,可以給調用者返回數據。
1、返回值
函數是一個功能塊,該功能到底執行成功與否,需要通過返回值來告知調用者。
以上要點中,比較重要有參數和返回值:
def 發送短信():發送短信的代碼...if 發送成功:return Trueelse:return Falsewhile True:# 每次執行發送短信函數,都會將返回值自動賦值給result# 之后,可以根據result來寫日志,或重發等操作result = 發送短信()if result == False:短信發送失敗...
函數的有三中不同的參數:
-
普通參數
######### 定義函數
name 叫做函數func的形式參數,簡稱:形參
def func(name):
print name######### 執行函數
‘zhangyanlin’ 叫做函數func的實際參數,簡稱:實參
func(‘zhangyanlin’)
-
默認參數
def func(name, age = 18):
print "%s:%s" %(name,age)指定參數
func(‘zhangyanlin’, 19)
使用默認參數
func(‘nick’)
注:默認參數需要放在參數列表最后
-
動態參數
def func(*args):
print args執行方式一
func(11,33,4,4454,5)
執行方式二
li = [11,2,2,3,3,4,54]
func(*li)def func(**kwargs):
print args執行方式一
func(name=’wupeiqi’,age=18)
執行方式二
li = {‘name’:‘wupeiqi’, age:18, ‘gender’:‘male’}
func(**li)def func(*args, **kwargs):
print args print kwargs
郵件實例:
def email(p,j,k):import smtplibfrom email.mime.text import MIMETextfrom email.utils import formataddrset = Truetry:msg = MIMEText('j', 'plain', 'utf-8') #j 郵件內容msg['From'] = formataddr(["武沛齊",'wptawy@126.com'])msg['To'] = formataddr(["走人",'424662508@qq.com'])msg['Subject'] = "k" #k主題server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.126.com", 25)server.login("wptawy@126.com", "WW.3945.59")server.sendmail('wptawy@126.com', [p], msg.as_string())server.quit()except:set = Falsereturn Trueformmail = input("請你輸入收件人郵箱:")
zhuti = input("請您輸入郵件主題:")
neirong = input("請您輸入郵件內容:")
aa=email(formmail,neirong,zhuti)
if aa:print("郵件發送成功!")
else:print("郵件發送失敗!")
2、 內置函數

# abs絕對值
# i = abs(-123)
# print(i) #返回123,絕對值# #all,循環參數,如果每個元素為真,那么all返回的為真,有一個為假返回的就是假的
# a = all((None,123,456,False))
# print(a) #返回的為假的,證明中間有False值
#
# #所有的假值有
# #0,None,空值
## #any 只要之前有一個是真的,返回的就是真
# b = any([11,False])
# print(b)#ascii,去指定對象的類中找__repr__,獲取返回值
# #ascii函數
# class Foo:
# def __repr__(self):
# return "zhangyanlin"
# obj =Foo()
# r = ascii(obj)
# print(r)# 布爾值返回真或假
# print(bool(1))
# print(bool(0))# #bin二進制
# r = bin(123)
# print(r)# #oct八進制
# r = oct(123)
# print(r)# #int十進制
# r = int(123)
# print(r)# #hex十六進制
# r = hex(123)
# print(r)# #二進制轉十進制
# i= int("0b11",base=2)
# print(i)# #八進制轉十進制
# i= int("11",base=8)
# print(i)# #十六進制轉十進制
# i = int("0xe",base=16)
# print(i)# #數字代表字母
# c = chr(66)
# print(c)# #字母代表數字
# c = ord("a")
# print(c)#bytes, 字節
#字節和字符串的轉換
# a = bytes("zhangyanlin",encoding="utf-8")
# print(a)
#bytearray 字節列表#chr(),把數字轉換成字母,只適用于ascii碼
# a = chr(65)
# print(a)#ord(),把字母轉換成數字,只適用于ascii碼
# a = ord("a")
# print(a)#callable表示一個對象是否可執行
# def f1(): #看這個函數能不能執行,能發揮True
# return 123
# f1()
# r = callable(f1)
# print(r)#dir,查看一個類里面存在的功能
# li = []
# print(dir(li))
# help(list)#divmod(),#分頁的時候使用
# a = 10/3
# r = divmod(10,3)
# print(r)#compile編譯, 把字符串轉移成python可執行的代碼,知道就行#eval(),簡單的表達式,可以給算出來
# b = eval("a + 69" , {"a":99}) #a可以通過字典聲明變量去寫入
# print(b)#exec,不會返回值,直接輸出結果
# exec("for i in range(10):print(i)")# filter對于序列中的元素進行篩選,最終獲取符合條件的序列(需要循環)
# def f1(x):
# if x >22:
# return True
# else:
# return False
#
# ret = filter(f1,[11,22,33,44,55])
# for i in ret:
# print(i)# ret = filter(lambda x: x > 22, [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77])
# for i in ret:
# print(i)#map(函數,可以迭代的對象,讓元素統一操作)
# def f1(x):
# return x+123
#
# # li = [11,22,33,44,55,66]
# # ret = map(f1,li)
# print(ret)
# for i in ret:
# print(i)
#
# ret = map(lambda x: x + 100 if x%2==1 else x, [11, 22, 33, 44])
# print(ret)
# for i in ret:
# print(i)#globals()獲取當前所有的全局變量#locals()獲取當前所有的局部變量
# ret = "kaszhfiusdhf"
# def fu1():
# name = 123
# print(locals())
# print(globals())
#
# fu1()#hash 對key的優化,相當于給輸出一種哈希值
# li = "sdglgmdgongoaerngonaeorgnienrg"
# print(hash(li))#isinstance()判斷是不是一個類型
# li = [11,22]
# ret = isinstance(li,list)
# print(ret)#iter創建一個可以被迭代的元素
# obj = iter([11,22,33,44])
# print(obj)
# #next,取下一個值,一個變量里的值可以一直往下取,直到沒有就報錯
# ret = next(obj)#max()取最大的值
# li = [11,22,33,44]
# ret = max(li)
# print(ret)#min()取最小值
# li = [11,22,33,44]
# ret = min(li)
# print(ret)#求一個數字的多少次方
# ret = pow(2,10)
# print(ret)#reversed反轉
# a = [11,22,33,44]
# b = reversed(a)
# for i in b:
# print(i)#round 四舍五入
# ret = round(4.8)
# print(ret)#sum求和
# ret = sum((11,22,33,44))
# print(ret)#zip,1 1對應
# li1 = [11,22,33,44,55]
# li2 = [99,88,77,66,89]
# dic = dict(zip(li1,li2))
# print(dic)#sorted 排序
# li = ["1","2sdg;l","57","a","b","A","中國人"]
# lis = sorted(li)
# print(lis)
# for i in lis:
# print(bytes(i,encoding="utf-8"))# #隨機生成6位驗證碼
# import random
# temp = ''
# for i in range(6):
# num = random.randrange(0,4)
# if num ==3 or num ==1:
# rad1 = random.randrange(0,10)
# temp+=str(rad1)
# else:
# rad2 = random.randrange(65,91)
# c1 = chr(rad2)
# temp+=c1
# print(temp)
4、文件處理
a、打開文件
name = open('文件路徑', '模式')
打開文件時,需要指定文件路徑和以何等方式打開文件,打開后,即可獲取該文件句柄,日后通過此文件句柄對該文件操作。
打開文件的模式有:
- r ,只讀模式【默認】
- w,只寫模式【不可讀;不存在則創建;存在則清空內容;】
- x, 只寫模式【不可讀;不存在則創建,存在則報錯】
- a, 追加模式【不可讀; 不存在則創建;存在則只追加內容;】
“+” 表示可以同時讀寫某個文件
- r+, 讀寫【可讀,可寫】
- w+,寫讀【可讀,可寫】
- x+ ,寫讀【可讀,可寫】
- a+, 寫讀【可讀,可寫】
"b"表示以字節的方式操作
- rb 或 r+b
- wb 或 w+b
- xb 或 w+b
- ab 或 a+b
注:以b方式打開時,讀取到的內容是字節類型,寫入時也需要提供字節類型
例:
#普通方式打開
# ====pythobnn內部將二進制轉換成字符串,通過字符串操作#二進制打開方式
#用戶自己操作把字符串轉成二進制,然后讓電腦識別# 1. 只讀模式,r
# a = open("1.log","r") #打開1.log,賦予只讀的權限
# ret = a.read() #讀取文件
# a.close() #退出文件
# print(ret) #打印文件內容#2.只寫模式,w, 如果不存在會創建文件,存在則清空內容
# a = open("3.log","w")
# a.write("sdfhsuigfhuisg")
# a.close()#3.只寫模式,x, 如果不存在會創建文件,存在則報錯
# a = open("4.log","x")
# a.write("12345678")
# a.close()#4.追加模式,a,不可讀,不存在則創建文件,存在則會追加內容
# a = open("4.log","a")
# a.write("asjfioshf")
# a.close()# "b"表示處理二進制文件(如:FTP發送上傳ISO鏡像文件,linux可忽略,windows處理二進制文件時需標注)#5.只讀模式,rb,以字節方式打開,默認打開是字節的方式
# a = open("2.log","rb") #二進制方式讀取2.log文件
# date = a.read() #定義變量,讀文件
# a.close() #關閉文件
# print(date) #打印文件
# str_data = str(date, encoding="utf-8") #字節轉換成utf-8
# print(str_data) # 打印文件#6.只寫模式,wb,
# a = open("2.log","wb") #打開文件2.log,可寫的模式
# date = "中國人" #定義字符串
# a.write(bytes(date , encoding="utf-8")) #轉換成字節,方便計算機識別
# a.close() #關閉文件
# print(date) #打印出來#7.只寫模式,xb,
# a = open("6.log","xb")
# date = "張巖林非常帥"
# # a.write("sakfdhisf") #字符串形式會報錯,計算機不識別,得轉換成字節
# a.write(bytes(date,encoding="utf-8"))
# a.close()
# print(date)#8.追加模式,ab,
# a = open("5.log","ab")
# date = "!張巖林是個帥小伙子"
# a.write(bytes(date,encoding="utf-8"))
# a.close()
# print(date)# #"+"表示具有讀寫的功能# #9.r+,讀寫(可讀,可寫)
# a = open("5.log","r+",encoding="utf-8")
# print(a.tell()) #打開文件后觀看指針位置在第幾位,默認在起始位置
#
# date = a.read() #第一次讀取,指針讀取到最后了,(可以加讀取的索引位置,3表示只看前三位)
# print(date)
#
# a.write("太帥了") #寫的時候會把指針調到最后去寫
#
# a.seek(0) #把指針放在第一位進行第二次讀取
#
# date = a.read() #第二次讀取
# print(date)
# a.close()#10.w+,寫讀,(可寫,可讀),先清空內容,在寫之后需要把指針放在第一位才能讀
# a = open("5.log","w+",encoding="utf-8")
# a.write("張巖林") #清空內容寫入“張巖林”
# a.seek(0) #把指針放在第一位
# date = a.read() #進行讀取
# a.close() #退出文件
# print(date)#11.x+,寫讀,(可寫,可讀),需要創建一個新文件,文件存在會報錯,在寫之后需要把指針放在第一位才能讀
# a = open("7.log","x+",encoding="utf-8")
# a.write("張巖林") #清空內容寫入“張巖林”
# a.seek(0) #把指針放在第一位
# date = a.read() #進行讀取
# a.close() #退出文件
# print(date)#12.a+,寫讀,(可寫,可讀),打開文件的同時,指針已經在最后了
# a = open("5.log","a+",encoding="utf-8")
# date = a.read() #第一次讀,沒數據,因為指針在最后
# print(date)
#
# a.write("張張") #往最后寫入 張
#
# a.seek(0) #把指針放在第一位,讓他進行曲讀
# date = a.read()
# print(date)
#
# a.close()
b、操作操作


class TextIOWrapper(_TextIOBase):"""Character and line based layer over a BufferedIOBase object, buffer.encoding gives the name of the encoding that the stream will bedecoded or encoded with. It defaults to locale.getpreferredencoding(False).errors determines the strictness of encoding and decoding (seehelp(codecs.Codec) or the documentation for codecs.register) anddefaults to "strict".newline controls how line endings are handled. It can be None, '','\n', '\r', and '\r\n'. It works as follows:* On input, if newline is None, universal newlines mode isenabled. Lines in the input can end in '\n', '\r', or '\r\n', andthese are translated into '\n' before being returned to thecaller. If it is '', universal newline mode is enabled, but lineendings are returned to the caller untranslated. If it has any ofthe other legal values, input lines are only terminated by the givenstring, and the line ending is returned to the caller untranslated.* On output, if newline is None, any '\n' characters written aretranslated to the system default line separator, os.linesep. Ifnewline is '' or '\n', no translation takes place. If newline is anyof the other legal values, any '\n' characters written are translatedto the given string.If line_buffering is True, a call to flush is implied when a call towrite contains a newline character."""def close(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown關閉文件passdef fileno(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown文件描述符 passdef flush(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown刷新文件內部緩沖區passdef isatty(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown判斷文件是否是同意tty設備passdef read(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown讀取指定字節數據passdef readable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown是否可讀passdef readline(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown僅讀取一行數據passdef seek(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown指定文件中指針位置passdef seekable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown指針是否可操作passdef tell(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown獲取指針位置passdef truncate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown截斷數據,僅保留指定之前數據passdef writable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown是否可寫passdef write(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown寫內容passdef __getstate__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknownpassdef __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknownpass@staticmethod # known case of __new__def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """passdef __next__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Implement next(self). """passdef __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown""" Return repr(self). """passbuffer = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaultclosed = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaultencoding = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaulterrors = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaultline_buffering = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaultname = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # defaultnewlines = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default_CHUNK_SIZE = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default_finalizing = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
3.x
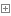

class file(object)def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__關閉文件"""close() -> None or (perhaps) an integer. Close the file.Sets data attribute .closed to True. A closed file cannot be used forfurther I/O operations. close() may be called more than once withouterror. Some kinds of file objects (for example, opened by popen())may return an exit status upon closing."""def fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__文件描述符 """fileno() -> integer "file descriptor".This is needed for lower-level file interfaces, such os.read()."""return 0 def flush(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__刷新文件內部緩沖區""" flush() -> None. Flush the internal I/O buffer. """passdef isatty(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__判斷文件是否是同意tty設備""" isatty() -> true or false. True if the file is connected to a tty device. """return Falsedef next(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__獲取下一行數據,不存在,則報錯""" x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration """passdef read(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__讀取指定字節數據"""read([size]) -> read at most size bytes, returned as a string.If the size argument is negative or omitted, read until EOF is reached.Notice that when in non-blocking mode, less data than what was requestedmay be returned, even if no size parameter was given."""passdef readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__讀取到緩沖區,不要用,將被遺棄""" readinto() -> Undocumented. Don't use this; it may go away. """passdef readline(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__僅讀取一行數據"""readline([size]) -> next line from the file, as a string.Retain newline. A non-negative size argument limits the maximumnumber of bytes to return (an incomplete line may be returned then).Return an empty string at EOF."""passdef readlines(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__讀取所有數據,并根據換行保存值列表"""readlines([size]) -> list of strings, each a line from the file.Call readline() repeatedly and return a list of the lines so read.The optional size argument, if given, is an approximate bound on thetotal number of bytes in the lines returned."""return []def seek(self, offset, whence=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__指定文件中指針位置"""seek(offset[, whence]) -> None. Move to new file position.Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to
(offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values are 1(move relative to current position, positive or negative), and 2 (moverelative to end of file, usually negative, although many platforms allowseeking beyond the end of a file). If the file is opened in text mode,only offsets returned by tell() are legal. Use of other offsets causesundefined behavior.Note that not all file objects are seekable."""passdef tell(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__獲取當前指針位置""" tell() -> current file position, an integer (may be a long integer). """passdef truncate(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__截斷數據,僅保留指定之前數據"""truncate([size]) -> None. Truncate the file to at most size bytes.Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell()."""passdef write(self, p_str): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__寫內容"""write(str) -> None. Write string str to file.Note that due to buffering, flush() or close() may be needed beforethe file on disk reflects the data written."""passdef writelines(self, sequence_of_strings): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__將一個字符串列表寫入文件"""writelines(sequence_of_strings) -> None. Write the strings to the file.Note that newlines are not added. The sequence can be any iterable objectproducing strings. This is equivalent to calling write() for each string."""passdef xreadlines(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__可用于逐行讀取文件,非全部"""xreadlines() -> returns self.For backward compatibility. File objects now include the performanceoptimizations previously implemented in the xreadlines module."""pass
2.x
a = open("5.log","r+",encoding="utf-8")
# a.truncate() #依賴于指針,截取數據,只剩下指針所在位置的前面的數據
# a.close() #關閉
# a.flush() #強行加入內存
# a.read() #讀
# a.readline() #只讀取第一行
# a.seek(0) #指針
# a.tell() #當前指針位置
# a.write() #寫
c、管理上下文
為了避免打開文件后忘記關閉,可以通過管理上下文,即:
with open('log','r') as f:...
如此方式,當with代碼塊執行完畢時,內部會自動關閉并釋放文件資源。
在Python 2.7 及以后,with又支持同時對多個文件的上下文進行管理,即:
with open('log1') as obj1, open('log2') as obj2:pass
例:
#關閉文件with
with open("5.log","r") as a:a.read()#同事打開兩個文件,把a復制到b中,讀一行寫一行,直到寫完
with open("5.log","r",encoding="utf-8") as a,open("6.log","w",encoding="utf-8") as b:for line in a:b.write(line)
lambda表達式
學習條件運算時,對于簡單的 if else 語句,可以使用三元運算來表示,即:
# 普通條件語句
if 1 == 1:name = 'wupeiqi'
else:name = 'alex'# 三元運算
name = 'wupeiqi' if 1 == 1 else 'alex'
對于簡單的函數,也存在一種簡便的表示方式,即:lambda表達式
# ###################### 普通函數 ######################
# 定義函數(普通方式)
def func(arg):return arg + 1# 執行函數
result = func(123)# ###################### lambda ####################### 定義函數(lambda表達式)
my_lambda = lambda arg : arg + 1# 執行函數
result = my_lambda(123)
遞歸
利用函數編寫如下數列:
斐波那契數列指的是這樣一個數列 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233,377,610,987,1597,2584,4181,6765,10946,17711,28657,46368…
def func(arg1,arg2):if arg1 == 0:print arg1, arg2arg3 = arg1 + arg2print arg3func(arg2, arg3)func(0,1)def func(n,a,b):if n == 10:return ac = a + breturn func(n+1,b,c)ret = func(1,0,1)
print(ret)# 列出一組數據
a,b = 0,1
while b <1000:print(a)a, b = b, a+ b
冒泡排序
# li = [11,2,35,14,22,35235,1232141,345,321423,123,123234]
# for j in range(1,len(li)):
# for i in range(len(li)-j):
# if li[i]<li[i+1]:
# temp = li[i]
# li[i]=li[i+1]
# li[i+1]=temp
# print(li)





)




:Mysql一致性視圖是啥時候建立的)







數據類型(基礎類型和任意類型))
及其在網絡安全與爬蟲中的應用)