一、chown 命令
下面以實例簡單講解下 chown 的使用方法。當前登錄的賬號是 sunbin
- 創建測試文件

當前 test.txt 文件所有者是sunbin,所屬組也是sunbin。
- 利用 chown 命令修改 test.txt 的所有者和所屬組
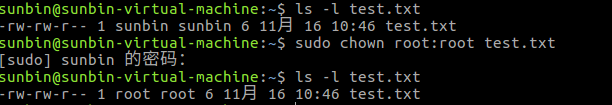
.可以看到,test.txt 的擁有者變成了 root,所屬組變為了root。
?
二、chown函數
1. chown函數原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int chown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);若成功,返回0;若出錯,返回-1參數:
- pathname:要更改的文件名
- owner:擁有者 uid
- gropu:所屬組 gid
?
需要注意的是,這個函數接受的是 uid 和 gid,而不是以字符串表示的用戶名和用戶組。所以需要另一個函數getpwnam根據字符串名稱來獲取 uid 和 gid. 它的原型如下:
?
1. 測試代碼:
struct passwd
{char *pw_name; // usernamechar *pw_passwd; // user passworduid_t pw_uid; // user IDgid_t pw_gid; // group IDchar *pw_gecos; // user informationchar *pw_dir; // home directorychar *pw_shell; // shell program
}struct passwd *getpwnam(const char *name);
?
1. 測試代碼:
#include <pwd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{uid_t uid;struct passwd *pwd;char *endptr;if (argc != 3 || argv[1][0] == '\0') {fprintf(stderr, "%s <owner> <file>\n", argv[0]);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}uid = strtol(argv[1], &endptr, 10); /* Allow a numeric string */if (*endptr != '\0') { /* Was not pure numeric string */pwd = getpwnam(argv[1]); /* Try getting UID for username */if (pwd == NULL) {perror("getpwnam");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}uid = pwd->pw_uid;}if (chown(argv[2], uid, -1) == -1) {perror("chown");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}輸出結果:
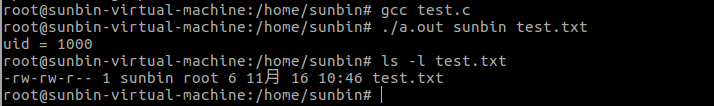
?
strtol用法:鏈接
#include <stdlib.h>
long int strtol(const char *nptr, char **endptr, int base);測試代碼:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{char buffer[20] = "10379cend$3";char *stop;printf("%d\n", strtol(buffer, &stop, 2)); //2printf("%s\n", stop);char a[] = "100";char b[] = "100";char c[] = "ffff";printf("a = %d\n", strtol(a, NULL, 10)); //100printf("b = %d\n", strtol(b, NULL, 2)); //4printf("c = %d\n", strtol(c, NULL, 16)); //65535
}輸出結果:
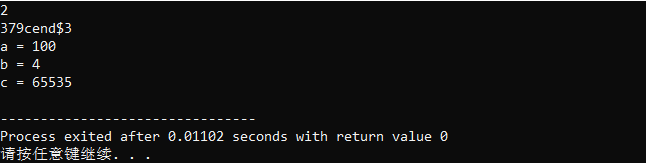
?
參考資料
1.?17-chown 函數



)











)



)